Chapter 11: Biosynthesis of Cell Components
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Photosynthetic electron transfer
energy derived from sunlight energizes electrons in the oigment chlorophyll
the transfer of energy to ATP and NADPH
what does the movement of electrons through an ETC result in during photosynthetic electron transfer?
Carbon fixation
the ATP and NADPH molecules produced during the light reactions serve as energy sources to drive the synthesis of glucose
chloroplasts
where do both light and dark reactions occur?
Photosynthesis
the conversion of sunlight energy into chemical energy by living organisms
generation of organic molecules from atomospheric CO2
end product of photosynthesis
Chloroplasts
organelles found in plant cells and eukaryotic algae that conduct photosynthesis
thylakoids
two membranes plus a 3rd membrane system in the chloroplasts
chlorophyll
photosynthetic pigment within chloroplasts
stroma
the space inside the chloroplast
thylakoid space
the space inside the thylakoids
electrons
during photosynthesis H2) is split into 1/2O2 and 2 H+ by a water-splitting enzyme releasing...
electrons are energized by sunlight and then move through an ETC in the thylakoid membrane
what happens to the electrons released from H2O in photosynthesis
H+ gradient forms across thylakoid membrane
what happens as the electrons move through the ETC in photosynthesis?
synthesize ATP
what is the energy in the H+ gradient used for in photosynthesis?
NADP+ which is reduced to NADPH
what is the final electron carrier in photosynthesis and what is it reduced to?
photosystems of the thylakoid membrane
where is chlorophyll found?
all but green
what visible wavelengths does chlorophyll absorb?
decentralized electron cloud
where is energy absorbed by electrons in chlorophyll?
jumps from chlorophyll to chlorophyll within the photosystem
where does the energy go once abosrbed in chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll Ila
the most abundant pigment in plants
central photosynthetic reaction center
central chlorophyll molecules
antenna
3 parts of the photosystem
contains the central chlorophyll molecules and antenna
structure of the photosystem
accept and donate electrons
what does the central chlorophyll molecules do?
harvest sunlgiht energy
what do the antenna chlorophyll molecules do?
sunlight
what excited the electrons in each antenna chlorophylls into an unstable high-energy state?
the two central chlorophylls in the reaction center
what finally traps the energy that is going from chlorophyll to chlorophyll?
energized electrons
the two central chlorophylls in the reaction center donate the energy in what form to the ETC?
electron carriers of the ETC
where do the special pair of chlorophylls in the reaction center of both photosystems I and II donate their energized electrons to?
plastocyanin
where does photosystem I accept electrons from?
water
where does photosystem II accept electrons from?
electrons in the special pair of chlorophylls in the reaction center
where is the energy absorbed by the antenna chlorophylls in photosystem II transfer it to?
ETC: first to plastoquinone and then the cytochrome bf complex
where do the pair of chlorophylls in the reaction center donate the energy?
water-splitting enzyme
extracts electrons from H2O to replace the electrons donated by photosystem II
cytochrome bf complex
an H+ pump that uses energy of the electrons to pump H+ into the thylakoid space
plastocyanin
what carries the electrons to photosystem I?
ATP and NADPH generated during light reactions
what is used to synthesize glucose in the dark reactions in the stroma
the calvin cycle
example of a dark reaction
carbon fixation
what is the first reaction of Calvin cycle?
CO2 is added to each of 3 molecules of Ribulose 1,5-biphosphate to yield 3 molecules of a 6-C unstable intermediate
what happens during the first reaction of Calvin cycle?
RuBP carboxylase
what is carbon fixation catalyzed by
2 3-C molecules
what do the intermediates of each split into during carbon fixation?
6 molecules of 3-Phosphoglycerate (3C) and carbon into the living world
what are the products of carbon fixation?
2 molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
what is the output of carbon fixation?
glucose
what are the 2 molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate used to synthesize?
CO2 and ribulose 1,5-biphosphate
the 2 substrates of Ribulose biphosphate carboxylase (rubisco)
Rubisco
the most abundant enzyme on earth
3 CO2
input of the Calvin Cycle
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
output of the calcin cycle
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
overall balanced equation of glucose
Gluconeogenesis
an anabolic pathway that synthesizes glucose from pyruvate
1,3,10
what steps of gluconeogenesis are irreversible?
enzymes
gluconeogenesis and glycolysis use different _______ for the irreversible steps
ATP is high
when does glycolysis occur?
ATP low
when does gluconeogenesis occur?
free energy changed are very large
what makes steps 1,3,10 irreversible?
step 3
which step in glycolysis is the rate-limiting step?
energy is consumed
what happens during step 3 of glycolysis
phosphofructokinase
what catalyzes step 3 of glycolysis?
fructose biphosphate
what catalyzes the rate-limiting step of gluconeogenesis?
ATP acts as an allosteric inhibitor and ADP acts as an allosteric activator
during the regulation of phosphofructokinase (step 3 glycolysis), what do ATP and ADP serve as due to the enzyme used?
ADP acts as an allosteric inhibitor and ATP acts as an allosteric activator
during the regulation of ructose biphosphate in gluconeogenesis, what do ATP and ADP serve as due to the enzyme used?
de novo
salvage
what two ways are the subunits of nucleic acids synthesized as nucloside monophosphates?
de novo
long pathways that assemble the molecules from smaller components
salvage
recycling of nitrogenous bases; short pathways
gout
If HGPRT activity is deficient and hypoxanthine is instead converted to uric acid which precipitates as crystals in the joint of the big toe triggering...
accumulation of uric acid crystals in the mtatarsophalangeal joint due to HGPRT activity deficiency
what is gout caused by?
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
a severe HGPRT deficency
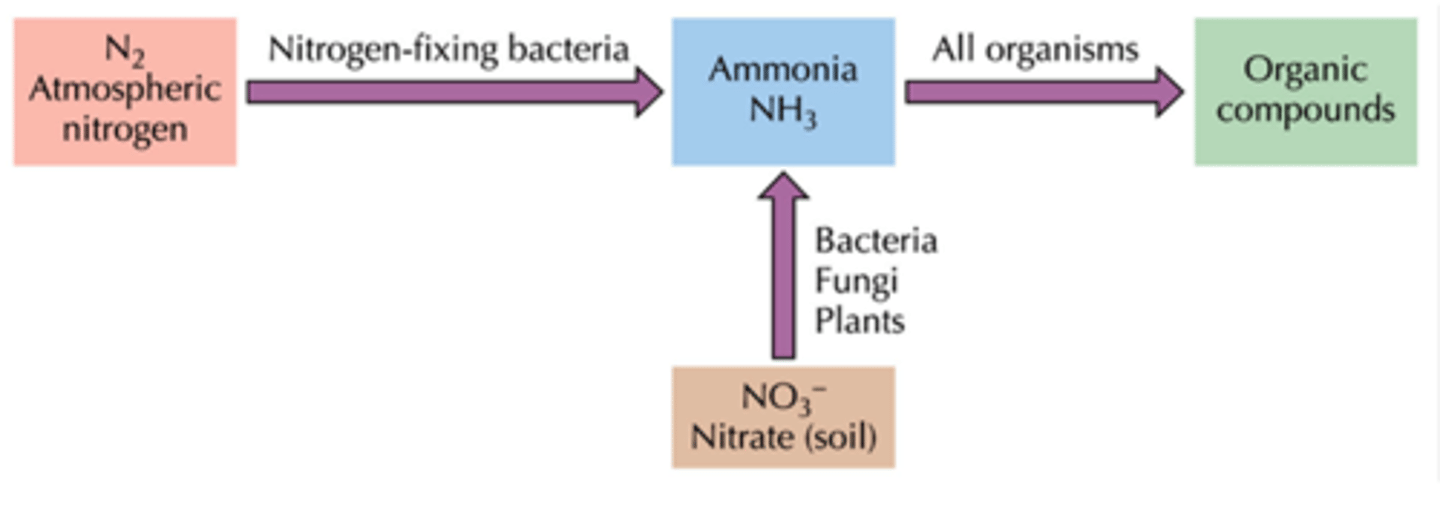
ATP is hydrolyzed and atomospheric N2 is reduced to NH3
what happens during nitrogen fixation during the assimilation of nitrogen?
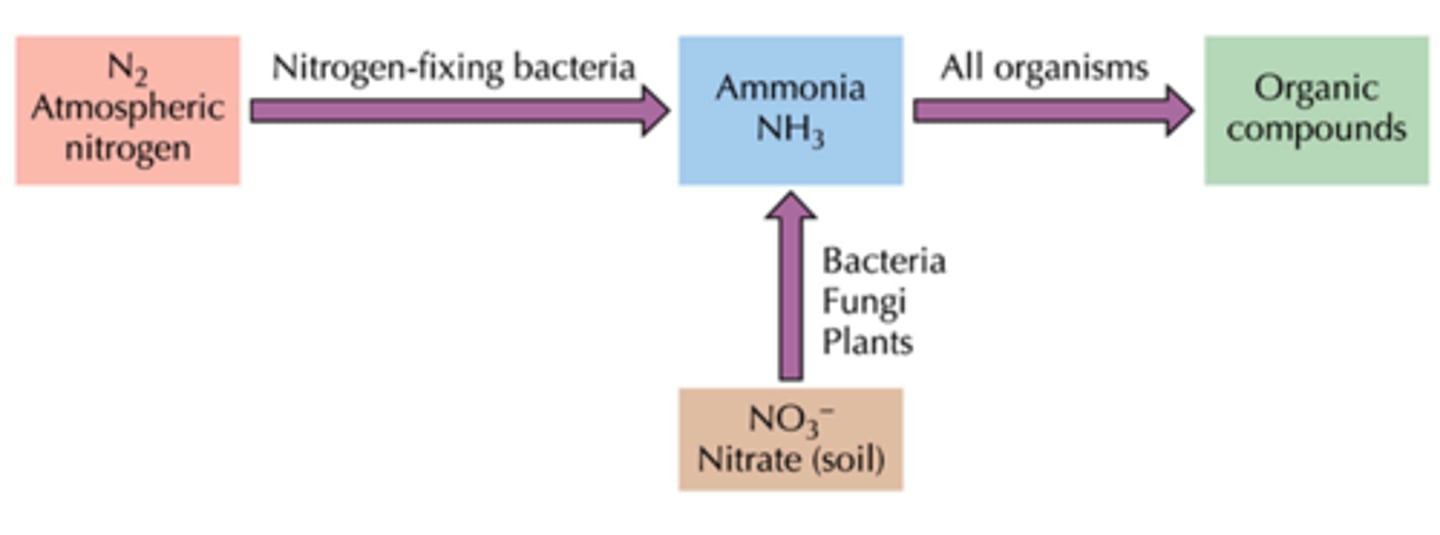
NADH or NADPH is oxidized and NO3- from soil is reduced to NH3
what happens during nitrate incorporation during the assimilation of nitrogen?
intermdiates of aerobic cellular respiration
Amino acids are reived from...
no
do all organisms have the enzymes necessary for the synthesis of all 20 amino acids?
dietary sources
where must essential AAs be obtained from?
humans
where are nonessential AAs be syntheisized from?
Phenylketonuria
a deficiency of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, which converts phenylalanine into tyrosine
phenyalanine is accumulated and is deaminated to phenylpyruvate
what occurs during phenylketonuria?
intellectual disability
what is caused in children due to phenylketonuria during their first yr of life?
screening og newborn children for elevated levels of phenylalanine and a low phenylalanine diet
prevention of phenylketonuria
nucleic acids
nucelotides form the macromolecule...
polysaccharides
simple sugars form the macromolecule...
polypeptides
amino acids for the macromolecule...
fats, lipids
fatty acids or other simple lipids form the macromolecule...
dehydration synthesis
macromolecules require the formation of bonds between the subunits by...
dehydration synthesis
condensation reactions that consume energy and yield water molecules
activated intermediate
in the synthesis of macromolecules, the porcesses requires what to be synthesized before the actual formation of the corresponding bond?
glycogen
example of polysaccharide in animals
starches and cellulose
example of polysaccahride in plants
formation of the glycosidic bond between simple sugars
what formation does the synthesis of polysaccharides involves?
nucleotide sugar intermediate
The synthesis of polysaccahrides is coupled with an energy yielding reaction causing the formation of what?
glucose
what is the starting molecule in the synthesis of polysaccharides?
phosphorylation of C6
step 1 of the synthesis of polysaccharides
glucose 6P
product of step 1 of synthesis of polysaccharides
isomerization
step 2 of the synthesis of polysaccharides
glucose 1P
product of step 2 of the synthesis of polysaccharides
condensation
step 3 of the synthesis of polysaccharides
UDP-glucose
product of step 3 of the synthesis of polysaccharides
reaction with UTP and release of pyrophosphate
what occurs during step 3 of the synthesis of polysaccharides?
formation of glycosidic bond
step 4 of the synthesis of polysaccharides
glucose is transferred from UDP to the growing polysaccharide chain
what occurs during step 4 of the synthesis of polysaccharides?
polysaccharide
product of step 4 of the synthesis of polysaccharides