Biology: Key Concepts, Hierarchy, and Genetic Processes
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Biosphere
Is all life on earth and all places where life exist
Ecosystems
All living and non-living thing in a particular area and how they interact with each other
Community
All populations of organisms occupying a particular area
Population
All members of a specific species that occupy the same area
Organisms
individual living things
Organs
Groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or related functions
Tissues
Groups of specialised cells with a common function.
Cell
Lifes fundamental unit of structure and function (smallest unit of life)
Organelles
Specialised intracellular structures that carry out a specific function
Molecules
Groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
What are the 5 unifying themes
organization, information, energy and matter, interactions, evolution
Explain Organisation
The hierarchy of life is arranged in such a way that structure are related at each step in the hierarchy. Each new step is more complex, thus leading to the formation of emergent properties and the ability to carry out functions of life.
Explain Information
Lifes processes and functions involve the expressing of genetic material. Genetic information is stored in specific sequences of DNA molecules and is inheritable from parents to offspring.
Explain Energy and Matter
Energy is cycled through an ecosystem. This energy is used by organisms to do work and is eventually lost to the environment in the form of heat.
Explain Interactions
Organisms continuously interact with physical factors (both biotic and abiotic). Interactions amongst different organisms affect an ecosystem in many ways
Differentiate DNA, gene, chromosome, and genome.
DNA is a nucleic acid that stores genetic information
A gene is a specific sequence of nucleotides that codes for a polypeptide
A chromosome is a singular, condensed DNA molecule
A genome is the summation of all the genes in an organism
Describe transcription
Copying the gene in DNA into a complementary mRNA sequence
Describe translation
Process where the information carried by mRNA is used to produce proteins at the ribosome with the assistance of tRNA.
What are emergent properties?
New properties that arise with each step upward in the hierarchy of life, owing to the arrangement and interactions of parts as complexity increases.
What is the systems approach to biology?
It is the study of a biological system through the observation of the interactions of its various parts
What is gene expression?
the process of converting information from gene to cellular product
What are the pyrimidines?
cytosine, thymine, uracil
What are the purines?
Adenine and Guanine
What is a genome?
The entire set of genetic material in an organism (genetic library)
What is genomics?
the study of whole sets of genes in different organisms
What is proteomics?
the study of the full protein set encoded by a genome
What is a proteome?
The full range of proteins expressed by the genome
What is bioinformatics?
the application of computational methods to the storage and analysis of biological data
What are plants (in terms of energy)?
Producers (autotrophs)
Organisms that ingest plants and other organisms for energy are called?
Consumers (heterotrophs)
What does energy enter and leave the ecosystem as?
Enters as light, exits as heat
What happens to chemical elements/nutrients in an ecosystem?
They are recycled
How are certain biological processes regulated?
Through feedback mechanisms
Outline negative feedback with an example
Negative feedback is when a biological product downregulates its own production in order to maintain homeostasis - regulation of body temperature, regulation of blood glucose, regulation of blood pressure
Outline positive feedback with an example
Positive feedback is when a product upregulates its own production in order to maintain homeostasis - blood clotting, lactation, childbirth
What is climate change?
Directional change in global climate which lasts 3 decades or more
What is evolution?
Evolution is the concept that organisms are modified descendants of common ancestors
State the prokaryotic domains
Archaea and Bacteria
Outline the 4 classifications of the eukaryotic domain
Animal, Protist, Fungi, Plant
What were Darwins main 2 points?
- Species show evidence of descent with modification from common ancestors
- Natural selection causes descent with modification
Outline natural selection
Natural selection is the process by which organisms that are better adapted to the selective pressures of a given environment are more likely to survive and reproduce
Summarise the steps in the scientific method
- Observation
- Hypothesis
- Experimentation
- Results
- Conclusion
State the 3 subatomic particles, their charge, and where they are found
Proton - positively charged (nucleus)
Neutron - uncharged (nucleus)
Electron - negatively charged (arranged in orbitals)
Differentiate between atomic number and mass number
Atomic number is the number of protons in an atoms nucleus whereas mass number is the number of protons + neutrons in an atoms nucleus
What is meant by atomic mass?
The summation of the weight of all of the subatomic particles found in an atom
What is an isotope?
An isotope is a form of an element that differs in the number of neutrons it has (+ a neutron)
What are radioisotopes?
A radioisotope is a form of an element with an unstable nucleus (- a neutron usually through radioactive decay)
What is an electron orbital?
a restrictive three-dimensional space around the nucleus of an atom where an electron will be found
What is the formula for determining how many electrons will be found in an electron shell?
2n^2
What is the valence shell?
The outermost shell of an electron
How do you determine if an atom is stable?
If it has a full valence shell
How are atomic bonds formed?
When 2 atoms have incomplete valence shells they transfer or share electrons to achieve stability
How is an ionic bond formed?
Through the electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions. When a cation (metal) transfers an electron to an anion to achieve stability
How is a covalent bond formed?
When two atoms share pairs of valence electrons
Differentiate between a non polar covalent bond and a polar covalent bond
In a non-polar covalent bond, atoms share electrons equally amongst each other. In a polar covalent bond atoms are shared unequally amongst each other due to a significant difference in electronegativity.
Which are stronger in aqueous environments covalent bonds or ionic bonds?
Covalent bonds
Define electronegativity
Electronegativity refers to an atoms ability to attract and hold electrons in a covalent bond
What are the Pauling electronegativity values?
- > 1.7 - ionic
- < 0.4 - non-polar covalent
- 0.4 - 1.7 - polar covalent
What is the most electronegative element?
Fluorine
What characteristic of carbon allows it to be the backbone of all organic molecules?
It has 4 valence electrons, which allows it to form 4 stable covalent bonds
What is a hydrocarbon? Give examples
A hydrocarbon is a molecule composed entirely of hydrogen and carbon atoms. An example would be methane
What is a structural isomer?
Structural isomers are two or more compounds that have the same chemical formula but differ in their structural formula
What is a cis trans isomer?
Cis trans isomers are compounds that have the same covalent bonds but differ in their spatial arrangement. These structures are usually diastereomers arranged around a carbon-to-carbon double bond.
What is an enantiomer?
A pair of molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. These structures have a chiral carbon and can rotate polarised light (optically active). Usually, only one form of the enantiomer is biologically active
What is a functional group?
They are chemical groups that affect molecular function by being directly involved in chemical reactions
Name the 7 functional groups most important to life
- Hydroxyl
- Carboxyl
- Carbonyl
- Sulfhydryl
- Methyl
- Phosphate
- Amine(o)
How is ATP used for energy?
ATP stores potential to react with water. When it reacts, the energy released can be used by the cell to perform work
What are macromolecules?
Macromolecules are large organic molecules usually built from repeated smaller organic subunits
What is a polymer?
A large molecule composed of repeating subunits called monomers
What are monomers?
Smaller units which can be linked together to form larger molecules
What is the link between two monomers called?
Glycosidic linkage
Which macromolecule is not a polymer?
Lipids
What are the 4 classes of macromolecules?
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Nucleic acid
What are monosaccharides?
Simple sugars that can be linked together to form larger carbohydrates. Examples include glucose, fructose, and galactose
What are disaccharides?
2 monosaccharides joined together through a glycosidic linkage. Examples include sucrose, maltose, lactose
Draw the linear version of glucose
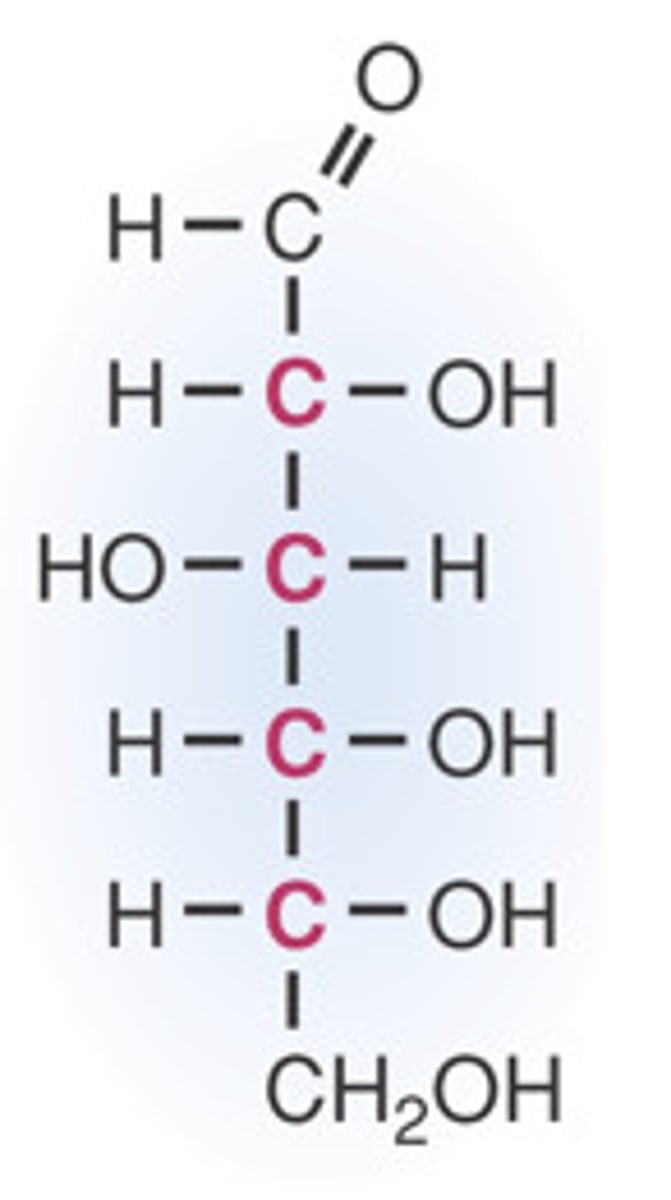
Draw the ring version of glucose
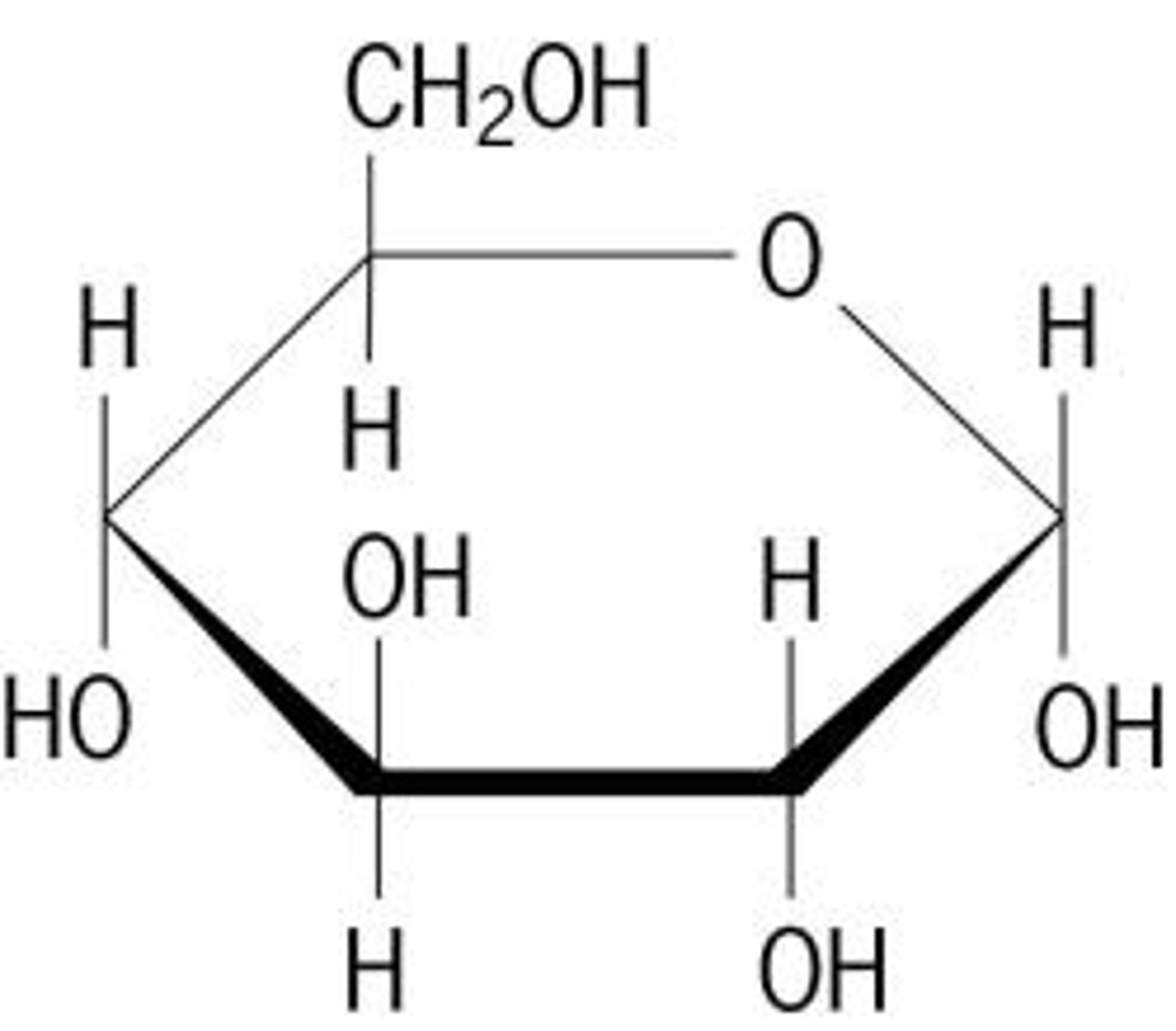
Differentiate between alpha and beta d-glucose
In alpha glucose, both the OH groups point downwards, whereas in beta glucose, one of them points upwards
What are the 4 structures of protein?
primary - specific sequence of amino acids
secondary - the type of folding a polypeptide chain undergoes
tertiary - the 3d structure of a protein
quaternary - the interactions between two or more polypeptide chains
What are some of the bonds that form the tertiary structure of a protein?
Disulphide bridge, ionic bond, hydrogen bond, and van der Waals forces
What is denaturation?
When a protein loses its native form and becomes biologically inactive due to a high temperatures or substantial fluctuation in pH
What are nucleic acids composed of?
A monomer called a nucleotide
What are the 3 components of a nucleotide?
Pentose sugar (Ribose or Deoxyribose), Phosphate group, and nitrogenous base
What are the differences between DNA and RNA
DNA: Double-stranded, Thymine, deoxyribose, and stores genetic information
RNA: Single-stranded, Uracil, Ribose, and copies genetic information