Introduction to Fungi
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Define fungi and mycology
Fungi : Eukaryotic microbes where some can cause superficial, cutaneous, subcutaneous, or systemic disease
Mycology: Study of fungi
Basic features of Fungi?
Saprophytic, parasitic, or commensal organism
All fungi are heterotrophs
Majority are obligate aerobes (limited anearobic capabilities)
Majority can grow in ordinary culture media.
Basic structure of Fungi?
Structure
Eukaryotic cell structure = Genetic material differentiated into chromosomes and cell contains ribosomes (80S rRNA) and mitochondria
Cell walls : Chitin, polysaccharide, polypeptide, B glucan
Cell (plasma) memb: contains sterols especially ergosterol = prevent antibiotics being effective against fungi
Microtubules composed of tubulin
Pathogenicity: Superficial vs Subcutaneous vs systemic mycosis vs Opportunistic vs Mycotoxicosis (examples)
Superficial mycosis = Affecting skin, hair or nails. Eg: pityriasis versicolor
Subcutaneous mycosis = aka Implantation mycosis. Eg: mycetoma
Systemic mycosis = aka Deep mycosis. Eg: histoplasmosis
Opportunistic mycosis. Eg: in HIV patient or other disease causing immunosuppression
Mycotoxicosis = Mycotoxins in mouldy food stored under damp humid condition. Eg Alfa toxins produced by Aspergillus flavus when growing in peanuts and grains
Define Hypha and Mycelium and Dimorphism
Hypha (pleural hyphae) : Microscopic branching filaments can be divided into cells by septum (septate) or non (non-septate)
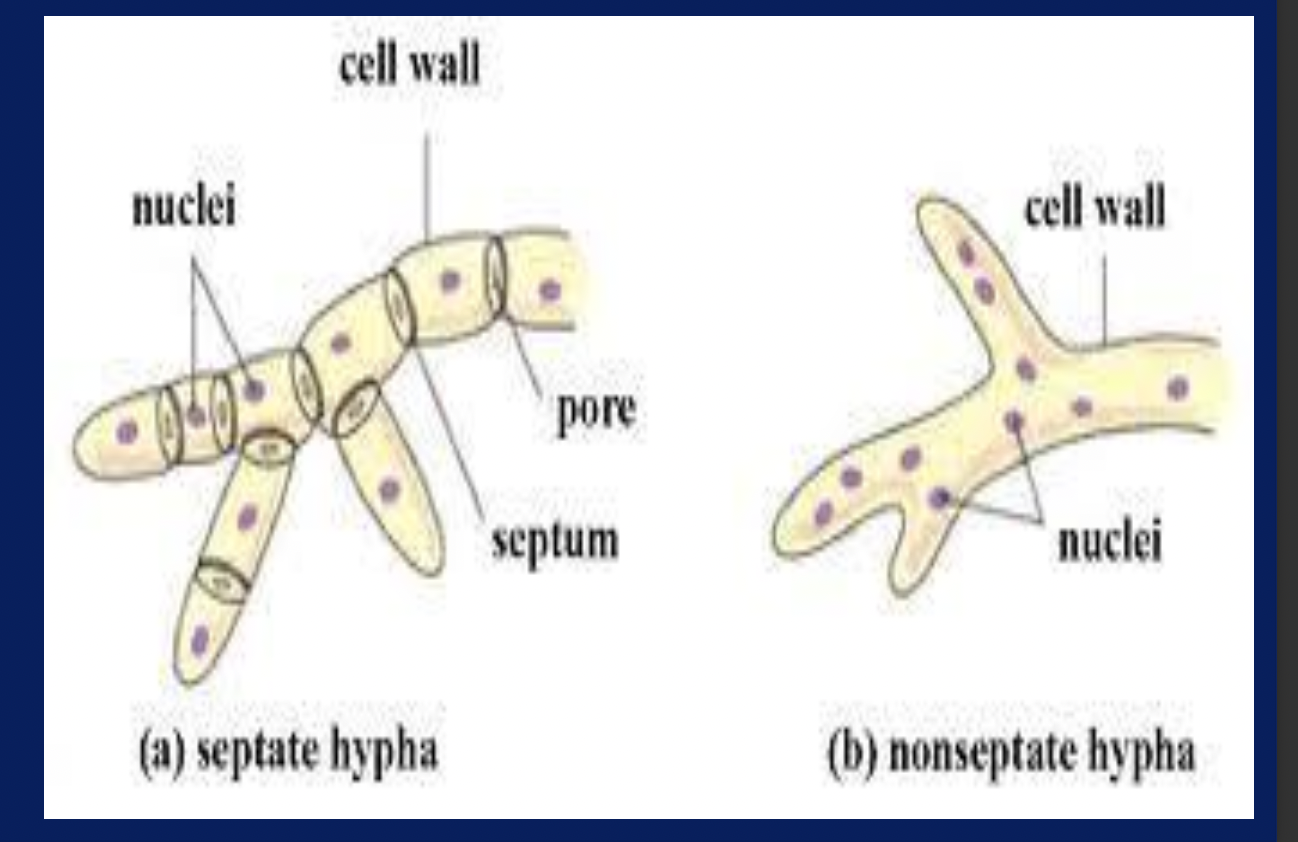
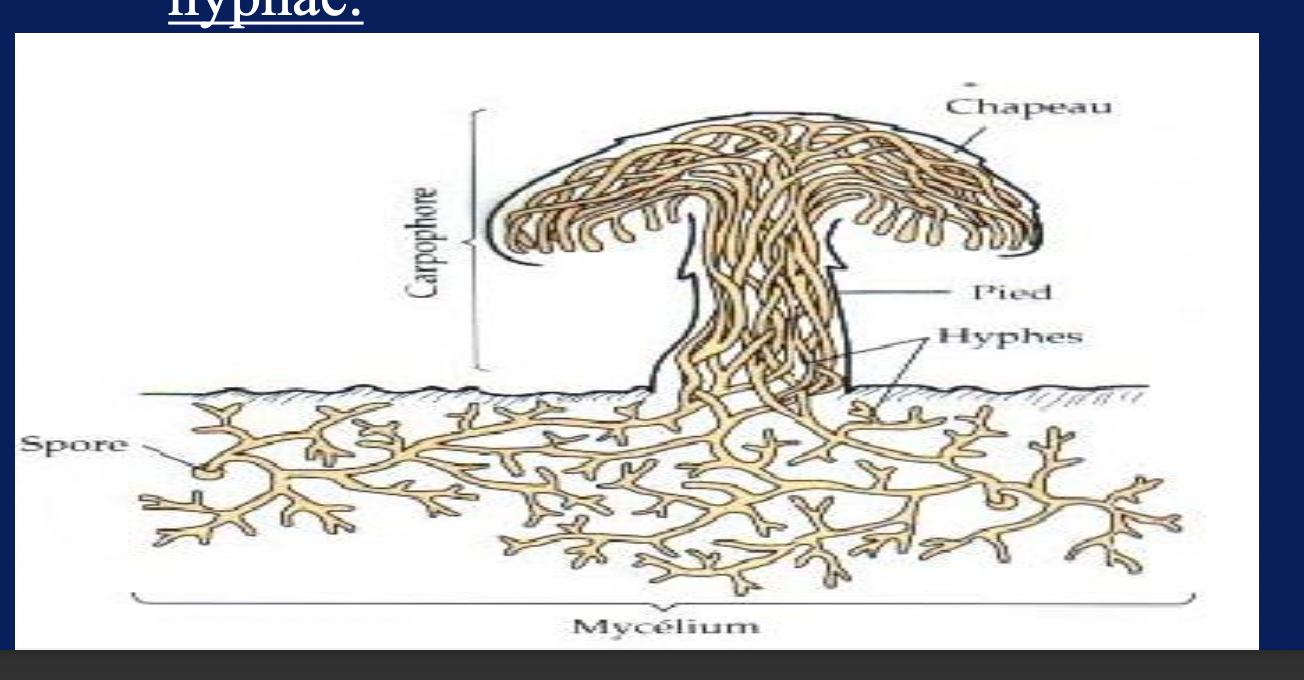
Mycelium : Visible mass of interwoven hyphae
Dimorphism : Fungus which occurs in 2 forms
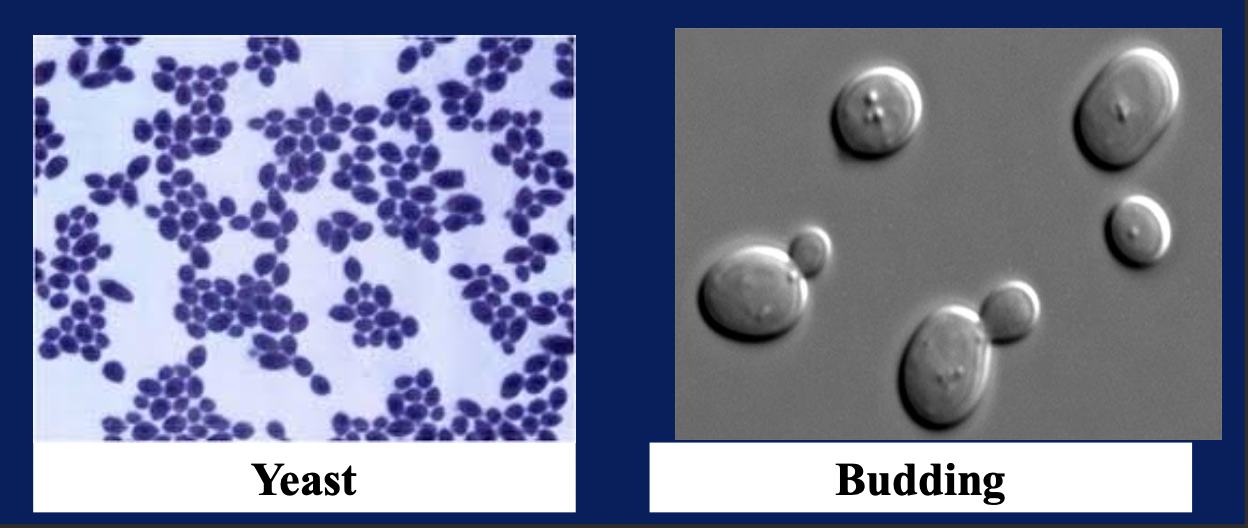
Define Mould and Yeast
Mould: Fungus which produces hyphae
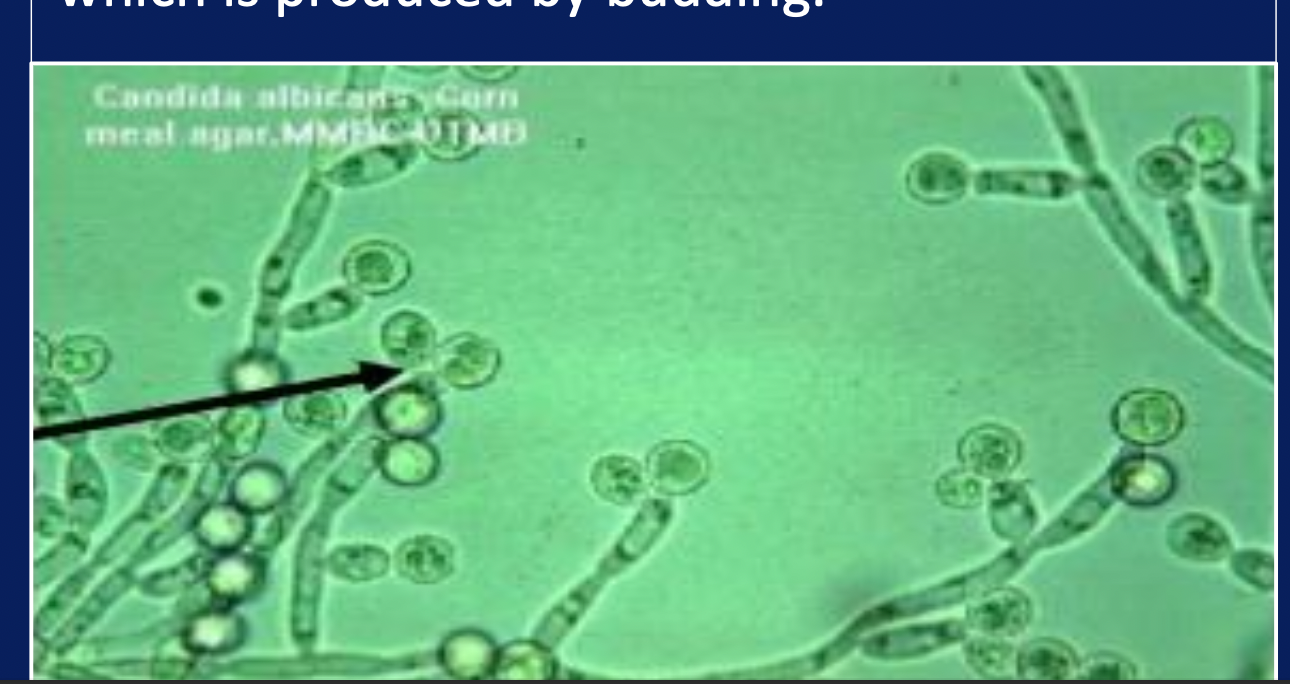
Yeast: Fungi which reproduce by budding
Fungal spores importance & 5 principal types
Importance:
Most fungi reproduce by forming spore
Spore size,shape ,colour and manner of production are important in identification
Principal types of spores:
Chlamydospore
Arhtrospore
Blastospore
Conidium
Sporangiospore
Define Chlamydospore
Chlamydospore: resting stage formed when cell swells up and develops thick wall
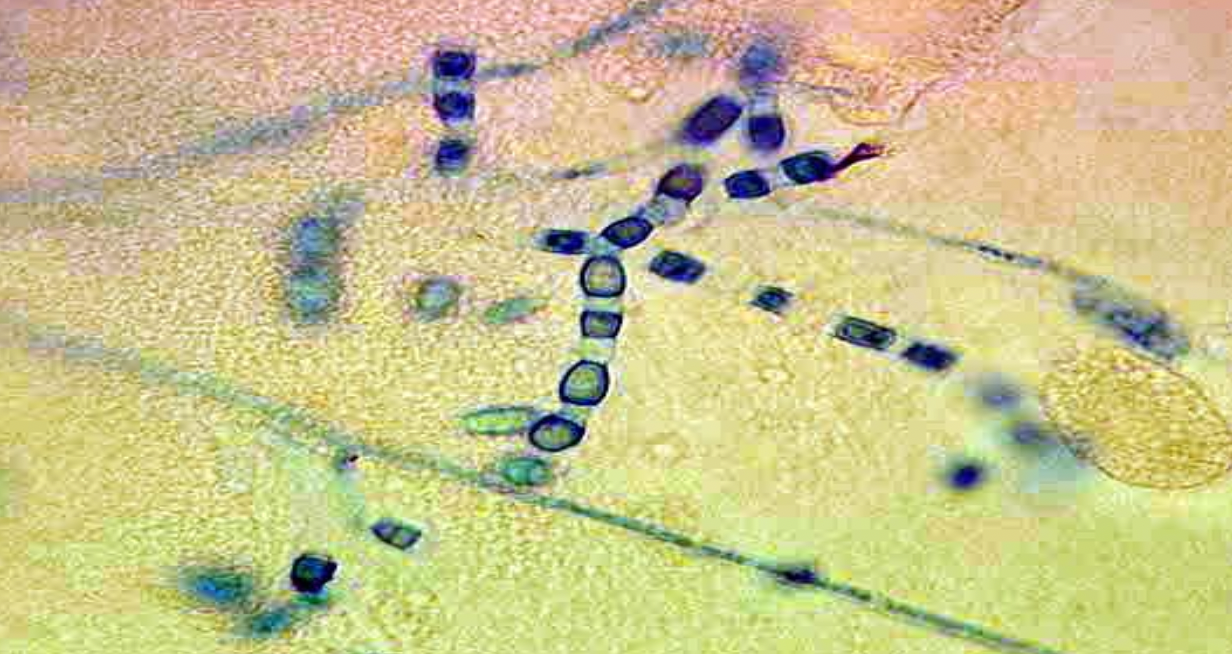
Define Arthrospore
Arthrospore: Spore formed by septation followed by fragmentation of a hypha
Define Blastospore
Blastospore: Single vegetative yeast cell produced by budding
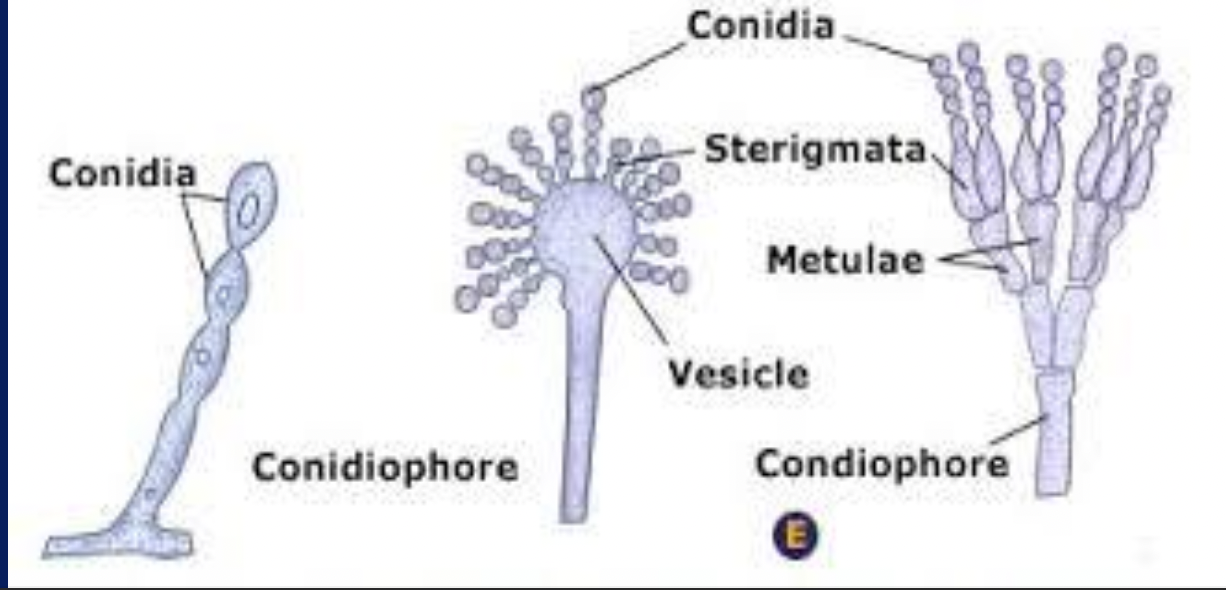
Define Conidium
Conidium (pleural conidia) : Spore produced externally on (specialised hypha) conidiophore → becomes detached when mature → important in identification
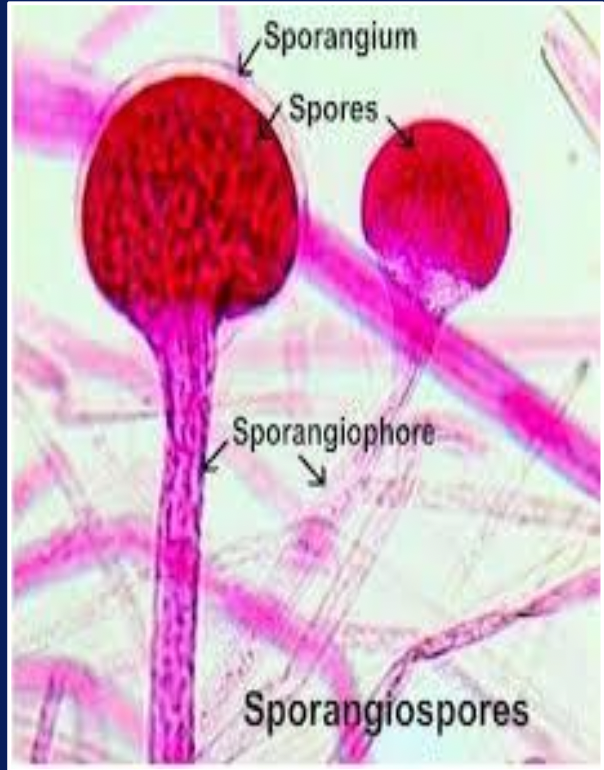
Define Sporangiospore
Sporangiospore: spore produced within swollen spherical cell (sporangium) at end of sporangiophore (specialised hypha)
Taxonomy of fungi Candida albicans (Kingdom, Phylum, subphylum, class, order,family, genus, species
Kingdom: Fungi
Phylum: mycota
Subphylum: mycotina
Class: mycetes
Order: ales
Family: acea
Genus: Candida
Species: Albicans
Classification of fungi
Classify fungi on what basis
Ascomycota, vs Basidomycota, vs Zygomycota vs Fungi imperfect (class, sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction)
Fungi classified on basis of ability to reproduce sexually, asexually or combo
All fungal genera of medical importance for human is 1 of 4…
Ascomycota
Class: Ascomycetes
Sexual: Ascospores
Asexual: Conidia
Basidomycota
Class: Basidomycetes
Sexual: Basidiospores
Asexual: Conidia
Zygomycota
Class: Zygomycetes
Sexual: Zygospores
Asexual: Conidia
Fungi Imperfecti
Class: X
Sexual: X
Asexual: Sporangiospores