5..1 - Physical Fitness and Eating Disorders
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Define Physical Fitness
The ability to perform moderate to vigorous activity without excess fatigue.
What are the benefits from Physical Activity?
Increased cardiovascular function
Reduced Stress
Lower Blood Pressure
Weight Management
Improved Self Image
Better Sleep
Utilization of Fat
What was the government initiative for physical activity?
“Healthy People” a sponsored program to improve the nations healthy by increased physical activity in adults.
What are the current 2020 healthy people guidelines?
Find enjoyable varying activities
Exercise Partner for accountability
Start Slowly
Set Specific Goals
Reward Yourself ( not w/ food)
So where does someone begin? Studies suggest incorporating 30 minutes of activity into your daily routine is a good place to start. Those 30 minutes can be broken into shorter segments throughout the day.
List the three components to a fitness program.
Aerobic workout
Resistance Training
Stretching exercise.
What is the goal of an Aerobic workout
Should be performed for 20-60min 5 days a week in order to increase the heart rate to the target zone and build endurance.
How do I calculate Heart Rate
#of bpm = number of pusle beats in 10 seconds times 6
How to calculate the target zone for aerobic exercise?
The target zone is 60-90% of the maximum heart rate.
Max HR = 220 - age
Target zone = [Max HR x 0.6] : [ Max HR x 0.9]
Calculate the target zone using my age (22)
Max HR = 220 - 22 = 198
Target zone = 198 × 0.6 : 198 × 0.9
Final ans = [118.8 - 178.2]
What is the goal of Resistance Training and Strecthing?
Resistance Training → Helps maintain muscle as we age and increase basal metabolic rate.
Stretching→ Improve balance and flexibility
What is the role of digestion for ATP production?
Following digestion, energy is released from food and used to convert adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the addition of a phosphate group.
What is the immediate energy for the muscles? Describe & Classify.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is the first source of energy for cells.
Muscles store only 2-4 seconds worth of ATP
This energy use does not require oxygen → anareobic
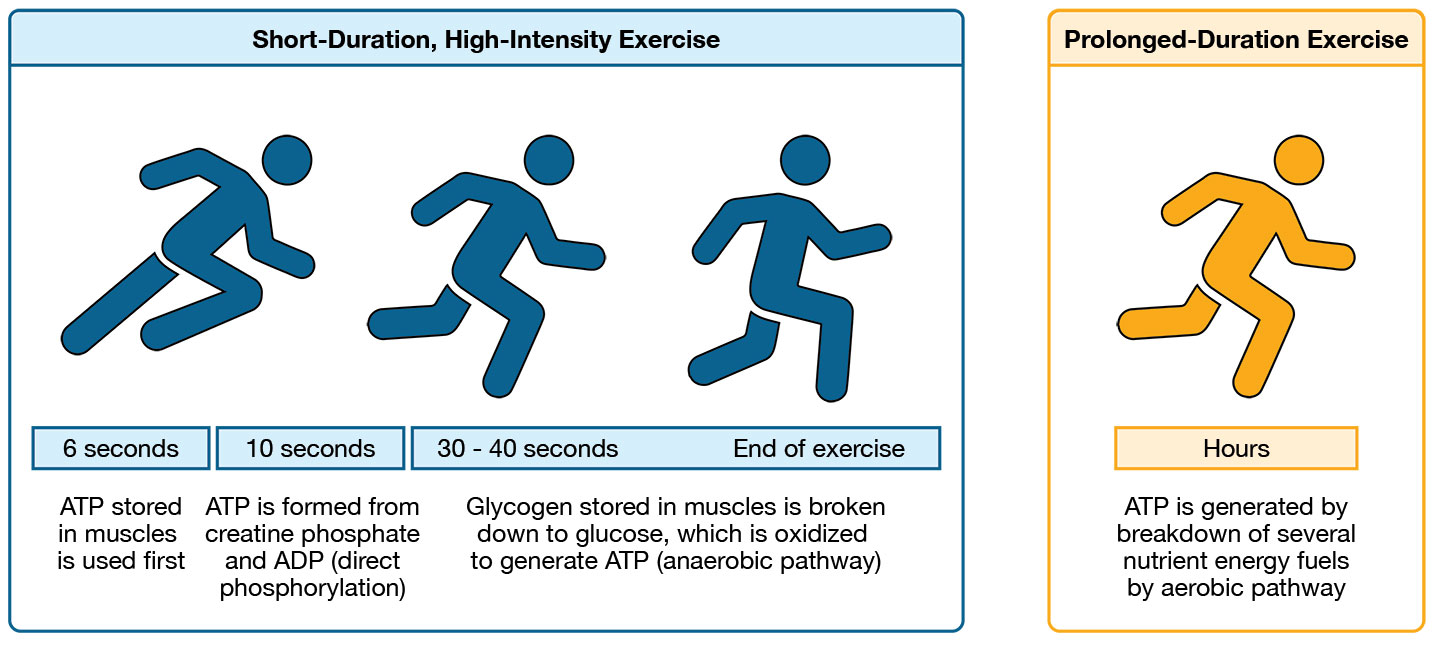
What is the short term backup energy source for muscles, Phosphocreatine?
Phosphocreatine (PCr) is broken down into creatine; phosphate→ which helps convert ADP into more ATP.
Provides energy to muscles for up 10 seconds
Used for short explosive movements ( bench, jumping, throwing, sprint)
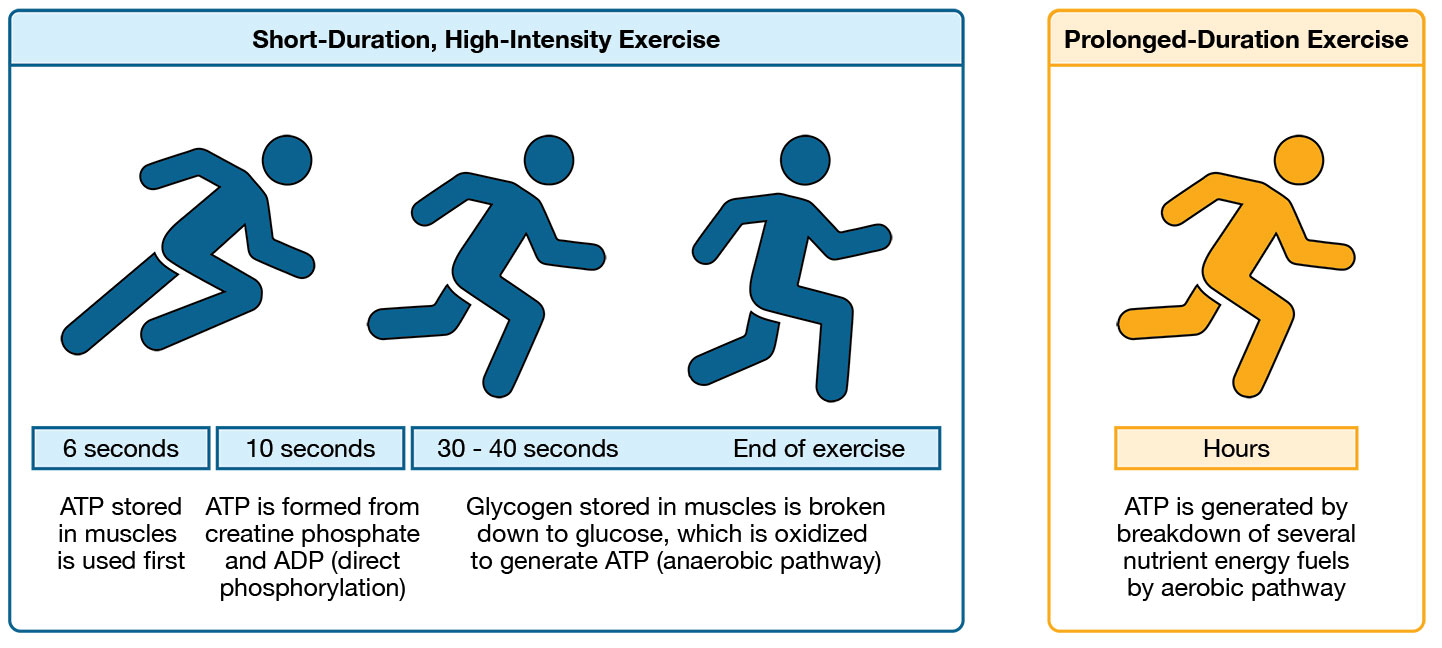
What is the energy source during short events for muscles, Carbohydrates? What is the con
For events lasting from 30 seconds to 3 minutes, the body uses carbohydrate under anaerobic conditions.
Example Activity: 400m sprint
Con: Produces Latic acid as a byproduct which can lead to muscle fatigue.
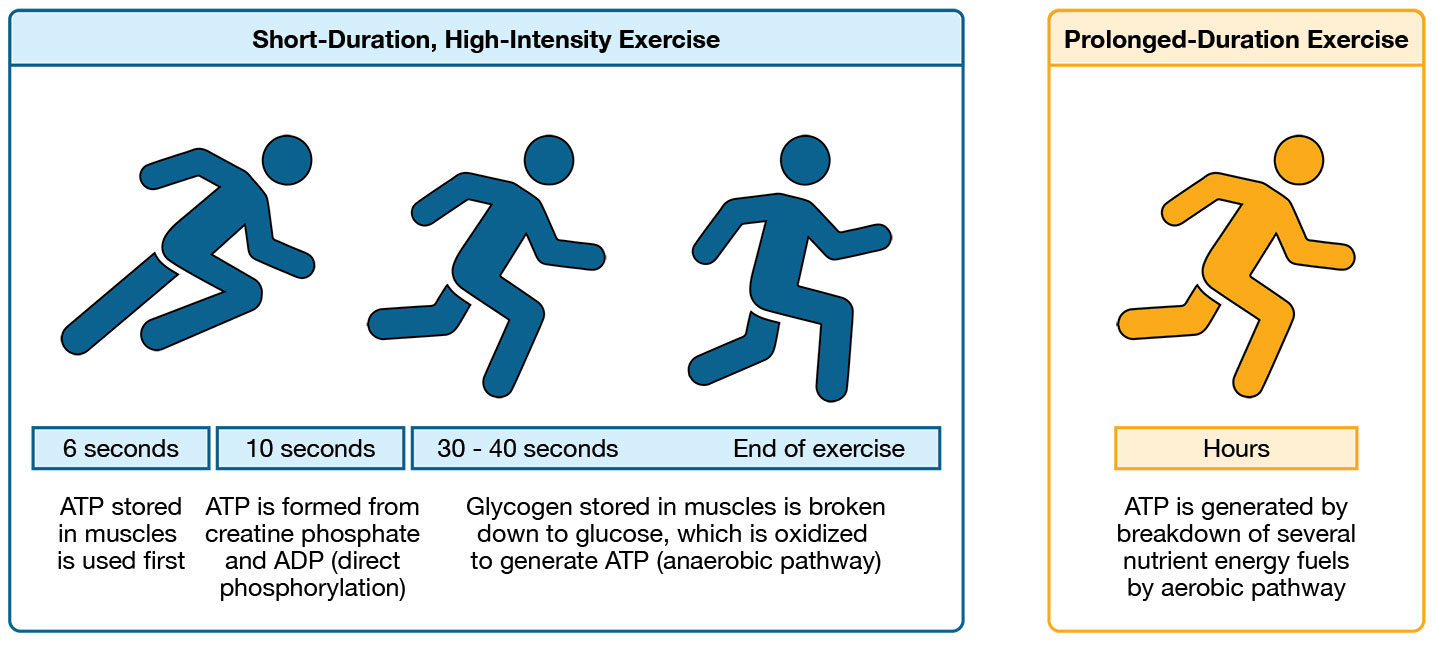
What is the energy source during aerobic activities for muscles? (Long Term)
Carbohydrates are the fuel for aerobic endurance activities (w/ Oxygen)
For events lasting 2 minutes to 3 hours
This produces 95% of the body’s ATP during sustained exercise.
Ex.) Cross country, long swimming.
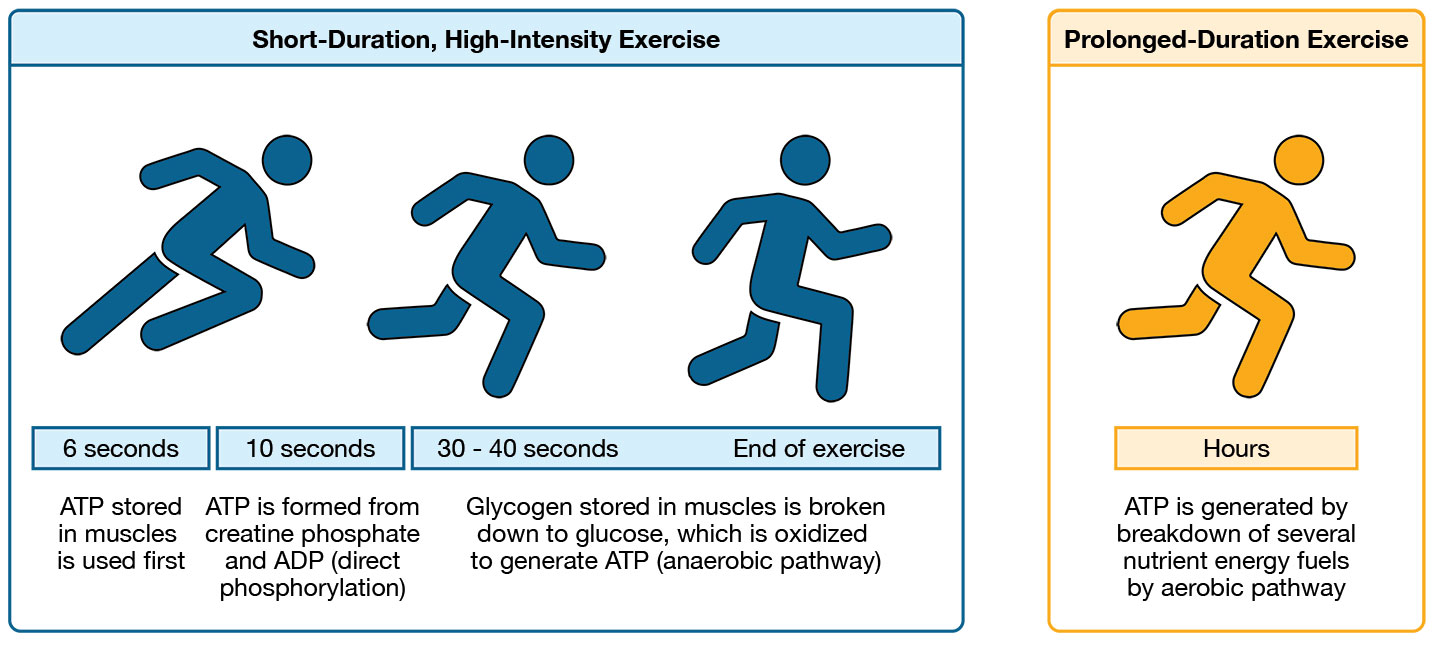
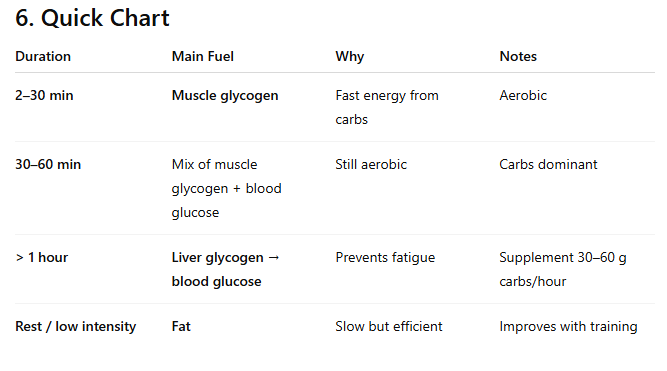
List the different time conditions for carbohydrates as an energy source.
Events < 30 minutes: Muscles use glycogen stores found in muscle.
Events > 1 Hour: Glucose comes from glycogen stores in the liver.
After stores finish, fatique and menal dysfucntion sets in.

Which Fuel source Is Dominant When?
Higher-intensity, longer-duration exercise: Carbohydrates (glucose).
Lower-intensity exercise or rest: Fat.
How and When is fat used to provide energy for fitness?
Fat is the primary fuel source during rest or low intensity activity greater than 20 minutes.
Fat is stored in a concreated form, then broken into fatty acids and glycerol for energy.
As fitness improves, the body becomes better at using fat for energy.
Ex.) Walking or Weight Lifting
Describe the importance of carbohydrates for fitness nutrition.
Carbohydrates are needed to prevent fatigue and fill glyogcen stores in muscles and liver
60% of total caloric intake are from carbohydrates. OR 5g of carbs per kg of bodyweight
activities > 60 minutes, 7-10 grams of CHO per kg

What is Carbohydrate Loading?
The process of consuming CHO prior to an event to maximize muscle glycogen load.
Describe the importance of Fats for fitness nutrition.
Monounsaturated fatty acids should be consumed for optimal performance.
Fats make up 35% of the total caloric intake
Avoid rich fatty foods with slow absorption before fitness events.
Describe the importance of Protein for fitness nutrition.
A minor fuel source that is utilized after glycogen stores in the muscles are depleted. (Endurance events)
During strength training, the extra protein is used for repair of muscle fibers.
The Daily Amount for protein in adults is 0.8g per kg of body weight. Athletes is 1.0-1.6g
Excess protein can increase urine output leading to dehydration and fatigue, negative effects on workout.
Describe the importance of Vitamin & Minerals for fitness nutrition.
Needs are met through a balanced diet w/o Supplements.
Certain athletes are at risk to develop deficiencies because of there low caloric intake.
Eating fewer than 1,400 calories per day makes it difficult to meet vitamin and mineral requirements. Especially B-Complex vit.
Describe the importance of Iron for fitness nutrition.
Important for the production of RBCs, transport of oxygen, and energy production.
Female athletes w/ low carloie intake are at higher risk of defincy due to menstrual cycle
Diet should include rich lean red meat or supplements.
Describe the importance of Calcium for fitness nutrition.
Needed for strong bones and normal muscle function.
Bones are in constant turnover, with calcium deposits and withdrawals being made until your mid twenties.
Bone mass after 20s relies on adequate daily calcium intake.
What is the Female Athlete Triad?
The combination of disordered eating leading to a low body mass index, osteoporosis, and loss of menstruation combined with excessive physical training
Define Ergogenic.
defined as a mechanical, nutritional, psychological, or physiological substance or treatment intended to improve performance.
Ex.) Good: Ensure Drink, sports drinks, drinks that include vitamins and minerals
BAD: steroid, growth hormones etc.
What is the importance of water for fitness nutrition.
Water is needed to regulate body temperature and stay cool. This prevents dehydrations and maintains performance.
List the three conditions that can occur due to WATER LOSS >3%.
Water loss > 3% of your body weight can not only affect your performance, but it also leads to several potentially fatal conditions:
heat exhaustion
heat cramps
heat stroke
dark yellow urine indicates a risk of dehydration
How much water should the average adult take per day?
The average adult needs 11-15 cups of fluid per day
How to determine fluid loss?
Weighing one’s self before, during, and after the activity can be used to determine fluid loss.
fluid requirements are based on body size, ability to sweat, level of activity, and duration of the exercise
Define Heat Exhaustion. What are the symptoms? Treatments?
Occurs when humidity levels are high, sweat becomes an inefficient way to keep the body cool. Symptoms:
profuse sweating, dizziness, nausea/vomiting
To treat: Move to a cool place, drink fluids, sponged w/ cool water.
Define Heat Cramps. What are the symptoms? Treatments?
occur when fluids are replaced but sodium levels in the body are low, Often when exercising over long periods in high temp. Symptoms: ]
painful contractions of the skeletal muscle
Prevention: moderation of activity and adequate salt and fluid intake
Define Heat Stroke. What are the symptoms? Treatments?
occurs when the body’s internal temperature reaches 104 degrees Fahrenheit and body’s cooling capacity fails. Symptoms:
hot and dry skin, fainting, confusion, poor coordination, and seizures, Death
Treatment: Replace lost fluids, limit training, monitor weight loss.