Psych 3501 Exam 3: Radically Open Dialectical Behavior Therapy
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
We are at a crossroads: poor treatment response
Across mental disorders, meta-analytic evidence indicates for both psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy, response rates are ~50%
30% of patients with depression have “treatment resistant depression”
50% of patients with anorexia relapse within 2 months of discharge
Having a comorbid personality disorder is associated with treatment drop out and worsened outcomes in anorexia, depression and anxiety
High comorbidity between depression, anxiety, eating disorder, and personality disorder
Many evidence-based therapies:
- Have not been tested on comorbid or chronic populations
- Neglect the role (or don’t assess) personality and personality disorders
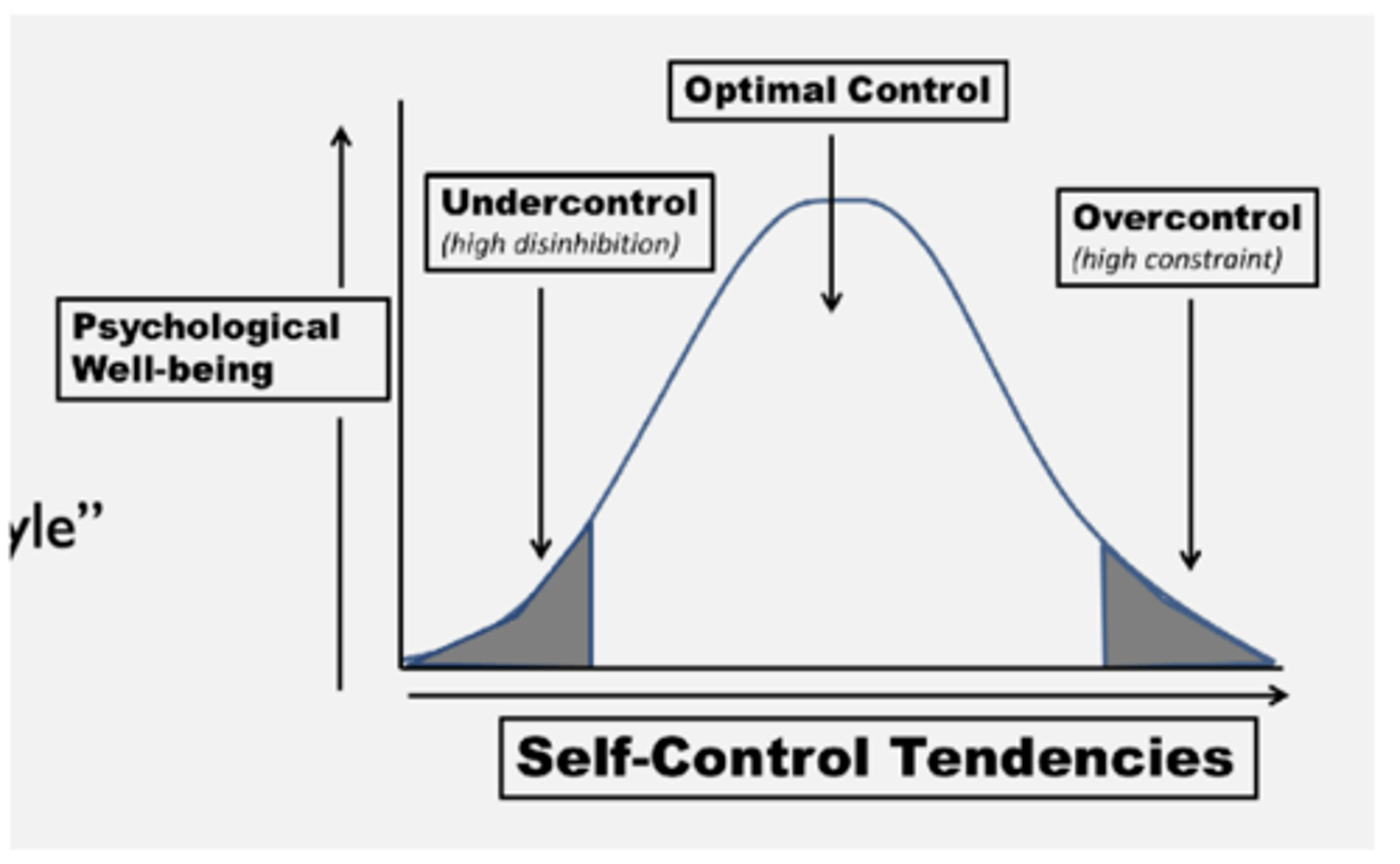
One factor of comorbidity: Overcontrol may be present across these disorders and is rooted in personality
Overcontrol
Behavior phenotype
Transdiagnostic
Rooted in personality: a "personality style"
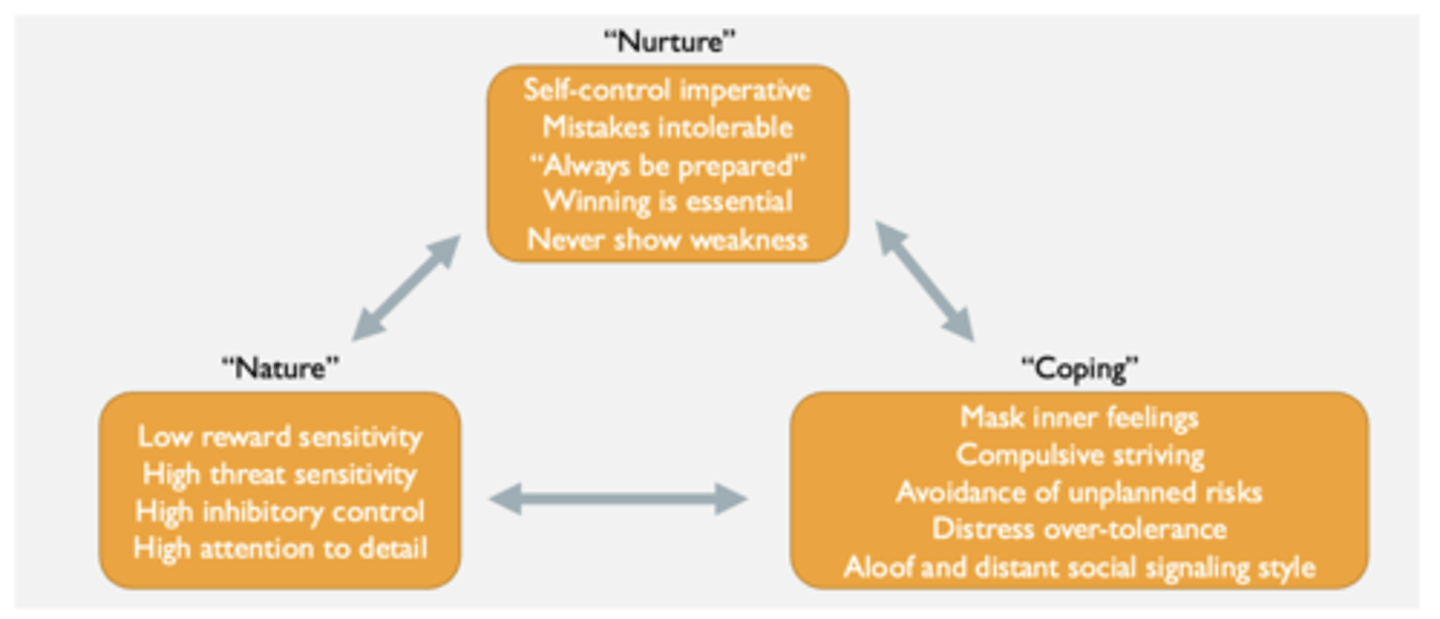
Biosocial model of overcontrol in RO DBT
Radically open dialectical behavior therapy (RO DBT): development
Some patients being treated with CBT, DBT, and exposure therapy were not getting better (treatment resistance)
These patients tend to be overcontrolled
RO DBT emerged from DBT over 20 years of translational treatment development
RO DBT informed by:
- Dialectical philosophy
- Behavior therapy
- Mindfulness-based approaches
- Malamati Sufism: emphasize on we don't know what we don't know, we see things as we are not as they are, bring biases to our perceptions
Radically open dialectical behavior therapy (RO DBT)
Transdiagnostic treatment
Targets maladaptive overcontrol
Does not see depressive or anxiety symptoms, disordered eating etc… as the problem to be targeted
Overcontrol is a problem of emotional loneliness (not emotion dysregulation)
Not lack of social contact, but lack of social connectedness
Emotional loneliness stems from, or is secondary to (the result of), low openness and flexibility and social signaling deficits
Four core deficits of maladaptive overcontrol
1. Lack receptivity and openness
E.g., avoiding feedback and novel situations
2. Lack flexible responding
E.g., compulsive need for structure, rigid responding
3. Lack emotional expression and awareness
E.g., inhibited or disingenuous expressions
What’s showing outside vs. what’s experiencing
4. Lack social connectedness and intimacy
E.g., aloof and distant relationships
Lead to emotional loneliness
RO DBT primary treatment targets
Social signals are treatment targets
Decrease:
- Behavioral maladaptive overcontrol and rigidity
- Aloofness
- Emotional inhibition
Increase:
- Behavioral flexibility
- Openness
- Expression of emotion
By doing this, leading to social connectedness
Social signaling matters
Social signal: any behavior done in front of another person
- May not be intentional or consciously done
- E.g., yawn, tone of voice, interrupting, avoiding, etc.
OC individuals have habitual social signaling styles as coping responses that ends hurting relationships
OC individuals bring perceptual and regulatory biases into social situations that function to isolate them from others
- Heightened threat responding and can’t adjust flexibly
Diary cards & behavioral chain analysis: social signals
Social signals tracked on diary card; targeted in chain analyses
Social signaling matters: it is not what is said, it's "how" we say it
Compared to CBT, the emphasis on emotions and thoughts is much lower
Focused on how behaviors impact interpersonal relationships and lead to emotional loneliness
OC behavioral themes to identify social signaling targets
Inhibited/disingenuous emotional expression
Overly-cautious and hypervigilant behavior
Rigid and rule governed behavior
Aloof & distant relationships
High social comparisons with envy and bitterness
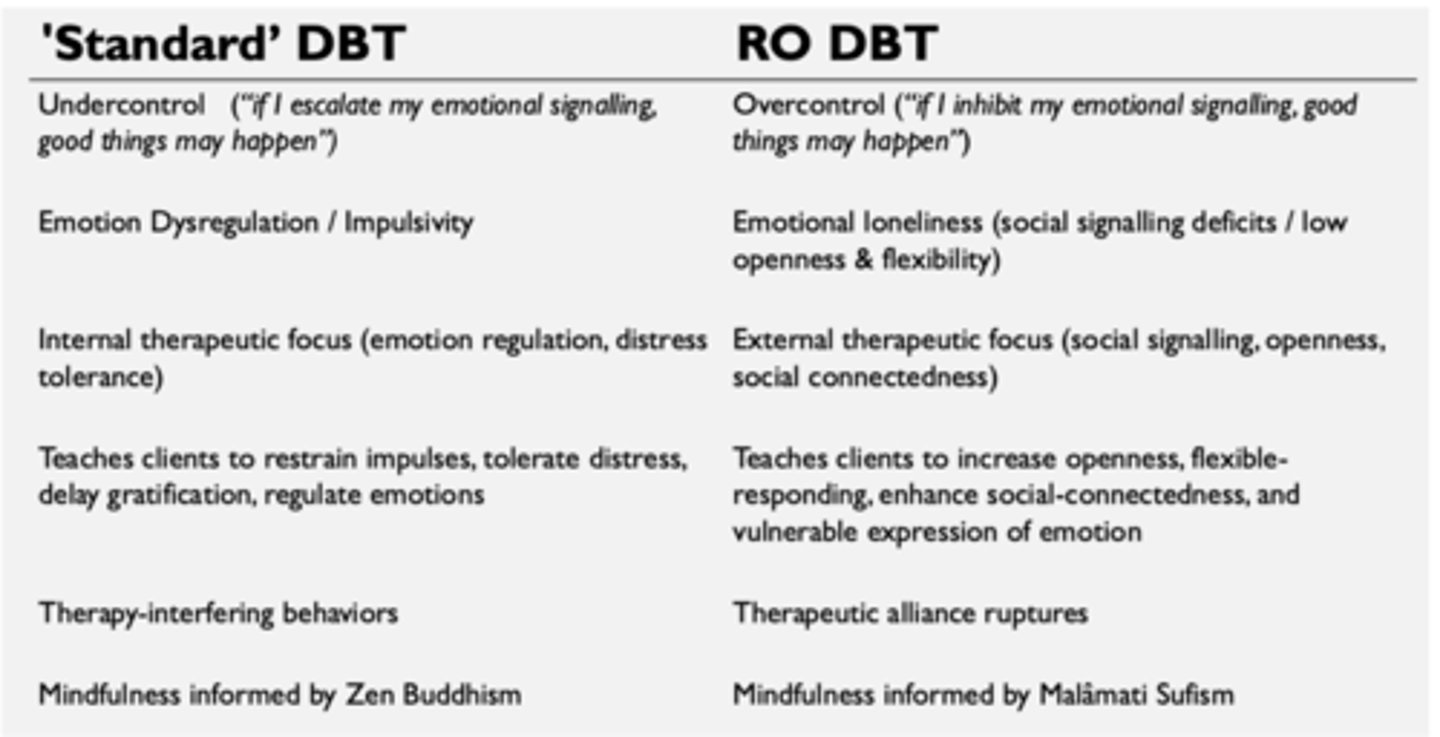
"Standard DBT" vs. RO DBT: similarities
RO DBT "emerged" from standard DBT
Both based on dialectics and behavioral principles with a biosocial model
Highlight importance of mindfulness and therapeutic relationship
Structure similar:
- Weekly individual therapy
- Weekly skills class/group
- Phone coaching
- ~30 weeks
- Therapist consultation
Individual therapy structure: treatment hierarchy, diary cards to monitor treatment targets, chain and solution analysis
"Standard DBT" vs. RO DBT: differences
undercontrol vs. overcontrol
emotion dysregulation vs. emotional loneliness
internal therapeutic focus vs. external therapeutic focus
therapy-interfering behaviors vs. therapeutic alliance ruptures
informed by Zen Buddhism vs. Malamati Sufism
Emerging research evidence
Treatment-resistant depression
Project RefraMED: multi-site RCT for treatment-resistant depression
RO-DBT associated with lower depressive symptoms, high effect size
Increasing psychological flexibility and social connectedness mechanistically led to decreased depressive symptoms
Anorexia
4 feasibility trials and case series trials: large effect sizes; increase BMI, decrease eating disorder symptoms, decrease medical problems, comorbid symptoms, cognitive inflexibility and social isolation/withdrawal
Heterogeneous overcontrolled samples (transdiagnostic)
Case series: Autism Spectrum Disorder subsample decrease in global distress
Just the skills component: RO DBT skills vs. TAU: decreased overall psychopathology, distress, and emotional suppression
Adolescents
Case series for adolescents: decreased eating disorder, depressive, anxiety, self-harm symptoms and overcontrol; increased cognitive flexibility, reward processing, emotional expression
Systematic review
Emerging evidence for adolescents and adults
While RO DBT shows promise as a treatment for disorders of overcontrol, further research is needed
Big 3+1: one skill we focus on for RO DBT
When an OC individual in novel/unsafe/feels challenged:
defensive-threat system goes on alert ->
Flexibility decreases and social signaling goes to habitual coping mechanisms
"Activate social safety": physiological signal to tell my body that I'm in a safe place
Big 3+1
1. Slow deep breath (belly breath)
2. Closed-mouth cooperative smile
3. Eyebrow wag
+1 (if seated): lean back in your chair at the start
Interpersonal skills: intimacy thermometer & match + 1
Relationship that you want to move closer with
People vary in how much intimacy they desire (set points), and that is ok
Noticing intimacy differences can be helpful in understanding some relationship issues
To increase closeness/intimacy: Match + 1
Match the other person's self-disclosure and then go one level higher by revealing more personal details, genuine opinions and emotions about yourself
Get people start showing emotions without big jumps
Match + 1 is not asking questions of about the other person
Not match + 1000
