Bio260 Unit 4 Resource 1 - Plant & Animal Nutrient Acquisition
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ask abt 14, 30, 36-37
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Nutrients
provides energy, contributes to body structure, and/or reg chem processes in body
non-essential can be made by animals
essential cannot be made, supplied from food
4 classes of essential nutrients
amino acids
fatty acids
vitamins
minerals
General info about AA
we req 20 AA and can make all but 8
plants make all 20
used for immediate metabolism (plants) & protein synthesis (animals)
General info about fatty acids
lipids are req for membranes and energy storage
use for energy, as membrane component, and as signaling molecules
General info about Vitamins
org compounds req in small amounts
13 are essentail for humans
plants make all essential vit
General info about Minerals
inorg compounds req in trace amounts
inorganic substances that help satisfy essential metabolic and structural functions in organisms
sometimes categorized as macrominerals or microminerals/trace elements
all plant essential nutrients are minerals
AA in Plants
plants can also take AA directly from soil
made from intermed of glycolysis, Citric Acid cycle, and assimilated inorg N (nitrate and ammonium)
most plants are incomplete in AA composition
ppl who eat plant proteins need to eat specific plant combos to get all essential AAs
stored in central vac
transported in phloem to dvlping vegetative reproductive sink tissues
transport of AA from plant cells is mediated by transport proteins in plants
AA biosynthesis in animals
non-essential AA made from intermed of glycolysis and citric acid cycle
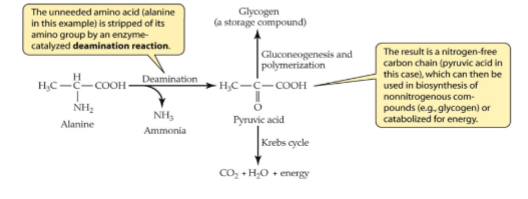
What happens to AA in animal bodies?
AA not stored in animal bodies, they circulate in blood and are taken up by cells to make proteins
liver removes excess AA + detoxifies it by removing amino group
highly toxic ammonia forms during
remaining C chain of AA can be used to make carbohydrates or lipids
Lipids in Plants vs Animals
plants
store fats and oils in forms of triglycerides
use lipids as carbon storage
animals
store excess sugars as fats in adipose tissue
store excess glucose as glycogen in liver and muscles
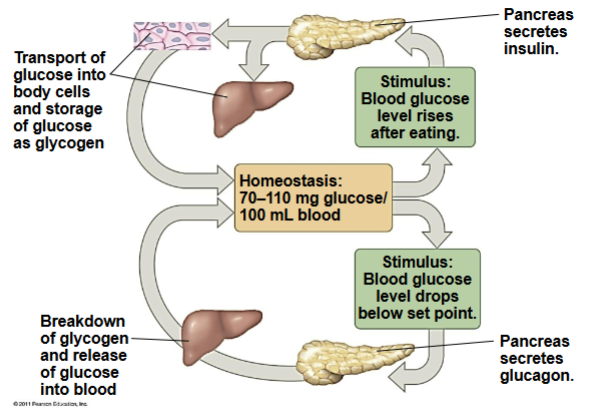
insulin is used to inhibit production of glucose
used for high blood sugar
glucagon is used to increase blood glucose
used for low blood sugar
What happens to dietary fat?
packaged into chylomicrons in the intestine initially and then delivered to muscle and adipose tissue
remaining lipids in chylomicron remnants are routed to the liver as triglycerides
What is triacylglycerol?
most common lipid in plants and animals
What are fatty acids?
3 families based on presence of DB in the hydrocarbon chain
saturated: H or straight chains w/ no DB
monounsaturated: has 1 DB b/w adjacent C atoms
polyunsaturated aka PUFA: has more than one DB b/w adj C atoms
omega-6 (n-6)
omega-3 (n-3)
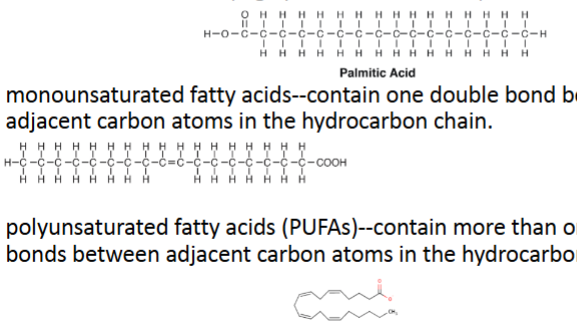
Fatty acids in plants
usually straight chain, unsat-carbocyclic acids w/ even # of C
syn in plastids and assembled in endoplasmic reticulum
only plants can make omega-3 and omega-6
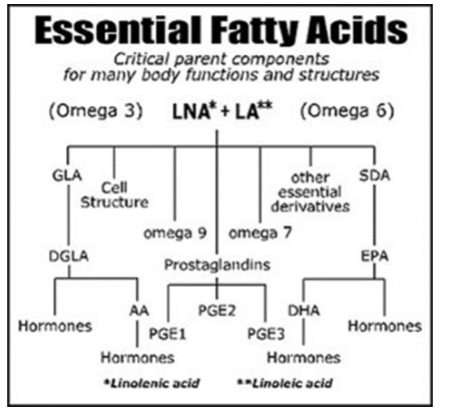
Essential fatty acids in animals
can make most of the fatty acids needed
98% of ingested fatty acids are in the form of triacylglycerol
essential polyunsat fatty acids: linoleic, linolenic, and arachidonic acids
deficiencies in fatty acids are rare
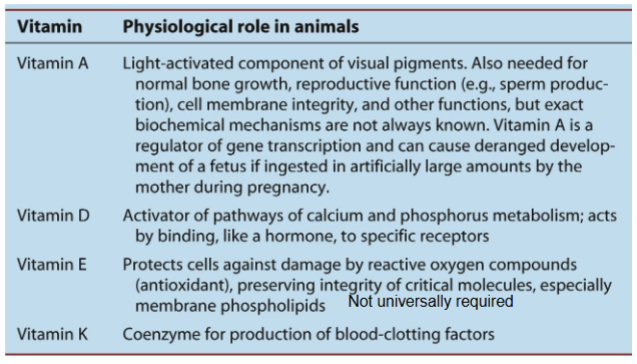
Vitamins in animals
organic molec reg in diet in small amounts
13 vitamins are essential to humans
vit E: protects fatty molec
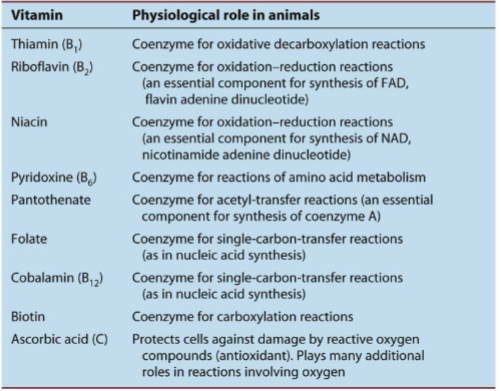
Vitamins in plants
B vitamins may be converted into enzyme cofactors in plants
reduce oxidative stress
water soluble vitamins
B1: thiamine
B2: riboflavin
B3: niacin
B6: key role in nitrogen metabolism
B8: biotin
Vit C: antioxidant
fat soluble vitamins
pro-vit A: cartenoid vit A doesn’t exist in plants
vit E: important in nutrient transport
vit K1: electron carrier supp photosyn
vit D: not found in plants but is in fungi and yeast
Where is Vit D acquired?
synthesized in the skin upon exposure to sunlight & other forms of DVB radiation
additional sources are from supplements, w/ small amounts coming from food like protein and dairy.
Adaptations of vasc plants
adaptations for acquiring resources were key steps in evolution of vasc plants
plants grew taller and had flat broad appendages
more cells and needed more water, nutrients, and improved anchoring system
evol of xylem and phloem made it possible to dvlp roots and shoots
made long-distance transport (from bottom to top) of water, minerals and products of syn possible
more roots = better anchor
root sys formed symbiotic relationships w/ bacteria, cyanobac, or fungi
increase shoot length = more distance b/w roots-water and nutrients-leaves-sources of sugar
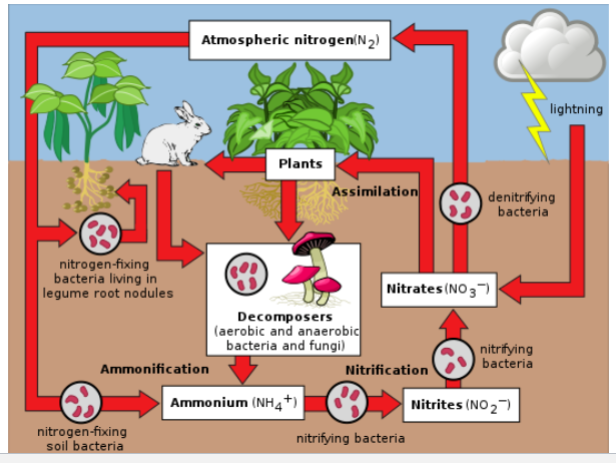
How does nitrogen pass thru in biochem cycle?
atmosphere has 78% of nitrogen
acquiring N req breaking stable triple covalent bond b/w 2 N atoms to make ammonia or nitrate
aka nitrogen fixation
plants provides sugar from photosyn that are used by nitrogen-fixing microorg for energy
in exchange for C sources, microbe provides fixed N to host plant for growth
Biological nitrogen fixation
NH3 + H20 → NH4+ + HO-
done by bac or cyanobac
N fixing bac forms symbiotic assoc
req anaerobic conditions, host makes root nodules in legumes
ammonia (NH3) dissolves in water to make ammonium (NH4+)
ammonium is absorbed and then stored in vac (b/c toxic) then converted to AA
Convert nitrate (NO3) to nitrite (NO2) in cystol
transport NO2 into chloro → red to ammonium (NH4+)
nitrate is the most important b/c plants and animals consume it
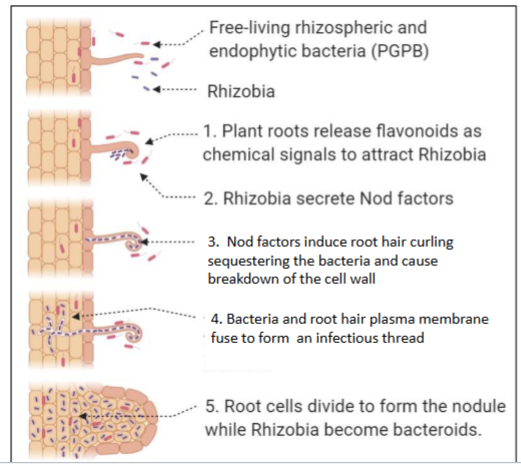
What is mycorrhizal?
a fungi that helps nutrient uptake by roots or broad range of angisperms
mycorrhizal fungi form a mycorrhiza
the tiny hyphae of mycorrizal fungi extend reach of roots into surr soil and start acquiring nutrients (esp. Phosphorus)
in return, plants provide carbohydrates to fungi
Other mineral absorption
plants take in sulfur from sulfates in the soil or as sulfur dioxide thru stomata
used in AA, proteins, and oils
root hairs take in phosphates from soil by symporter; made into sugar, phospholipids, and nucleotides
ferric iron is taken from soil and then is used as a comp. in many enzymes (cytochromes in e-transport)
also involved in syn of chlorophyll