Chapter 1: Financial Statements and Business Decisions
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Just Lecture; Come back before final to edit w/ lecture and Smartbooks notes!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Accounting
system that collects and processes (analyzes, measures, and records) financial info about an organization and reports that info back to decision makers
Accounting Entity
organization for which financial data are to be collected
Accounting Period
time period covered by financial statements
Audit
examination of financial reports to ensure that they represent what they claim and conform with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)
Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position)
reports the amount of assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity of any accounting entity of AT A POINT IN TIME
Basic Accounting Equation (Balance Sheet Equation)
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ (Shareholders’) Equity
Faithful Representation
requires that info be complete, neutral, and free from error
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
measurement and disclosure rules used to develop the information in financial statements
Income Statement (Statement of Income, Statement of Earnings, Statement of Operations)
reports revenue - expenses of the accounting period
Internal Controls
process by which a company provides reasonable assurance regarding reliability of company’s financial reporting, effectiveness and efficiency of its operations, and compliance with applicable laws and regulations
Notes (Footnotes)
provide supplemental information about the financial condition of a company, WITHOUT, financial statements cannot be fully understood
Primary Objective of Financial Reporting to External Users
provide financial information about the reporting entity that is useful to existing and potential investors, lenders, and other creditors in making decisions about providing resources to the entity
Relevant Information
information that can influence a decision; has a predictive and/or feedback value
Statement of Cash Flows (Cash Flow Statement)
reports inflows and outflows of cash during the accounting period in the categories of operating, investing, and financing
Statement of Stockholders’ (Shareholders’) Equity
statement reports changes in each of the company’s stockholders’ equity accounts during the period
Internal Decision Makers (Accounting System)
what managers are often called; need information about the company’s business activities to manage operating, investing, and financing activities of the firm
Managerial/Management Accounting
developing accounting information for internal decision makers; typically require continuous, detailed information because they must plan and manage the day-to-day operations of the organization
External decision makers (Accounting System)
stockholders and creditors, need info about company’s business activities to assess whether the company will be able to pay back its debts with interest and pay dividends
Financial Accounting
accounting for external decision makers
Business Activities Include
- Financing Activities
- Investing Activities
- Operating Activities
Financing Activities
borrowing or paying back money to lenders and receiving additional funds from stockholders or paying them dividends
Investing Activities
buying or selling items such as plant and equipment used in production of beverages
Operating Activities
day-to-day process of purchasing raw tea and other ingredients from suppliers, manufacturing beverages, delivering them to customers, collecting cash from customers, and paying suppliers
Two Parts of Accounting System
- External Financial Reports
- Internal Management Reports
External Financial Reports
one part of the accounting system, periodic statements and related disclosures
Internal Management Reports
one part of the accounting system, detailed plans and continuous performance report
Examples of External Decision Makers
Creditors and Investors
Examples of Internal Decision Makers
Managers
Who Uses Financial Statements?
- managers within a firm (ex: credit managers + supply chain managers)
- employee’s unions
- company human resources
How Credit Managers Use Financial Statements
use customer’s statements to decide whether to extend credit to customers
How supply chain managers use financial statements
analyze supplier’s statements to see whether the suppliers have resources to meet demand and invest in future development
How company human resource managers use financial statements
use as basis for contract negotiations over pay rates and can serve as a basis for calculating employee bonuses
The Four Basic Financial Statements
Balance Sheet
Income Statement
Statement of Stockholders’ (Shareholders’) Equity
Statement of Cash Flows
Characteristics of Four Basic Financial Statements
- normally prepared by profit-making orgs for use by investors, creditors, and other decision makers
- can be prepared at any point in time (year, quarter, or month) and can apply to any span (one year, one quarter, or one month)
Quarterly Reports
financial statements for external users prepared at the end of each quarter
Annual Report
financial statements for external users prepared at the end of the year
Purpose of Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position)
report the financial position (amount of assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity) of an accounting entity AT A PARTICULAR POINT IN TIME; similar to a financial snapshot indicating entity’s financial position
Characteristics of Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position)
- business entity itself, not business owners, viewed as owning resources it uses and being responsible for its debts
- heading of each statement indicates time dimension of report
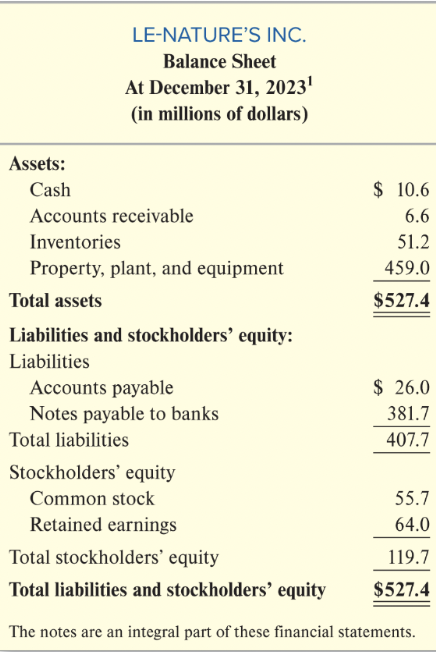
Structure Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position)
Heading
- name of entity
- title of statement
- specific date of statement (at December 31, 2023)
- unit of measure (in millions of dollars)
Resources Controlled by Company (Assets)
- amount of cash in company’s bank account (Cash)
- amounts owed by customers from prior sales (Accounts Receivable)
- ingredients and beverages ready for sale (Inventories)
- factories, production equipment, and land (PPE)
Total Amount of Company’s Resources (Total Assets)
Sources of Financing for Company’s Resources (Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity)
- financing supplied by creditors (Liabilities)
- amounts owed to suppliers for prior purchases (Accounts Payable)
- amounts owed to banks on written debt contracts (Notes Payables to Banks)
Total Liabilities
Financing Provided by Stockholders (Stockholders’ Equity)
- amounts invested in the business by stockholders (common stock)
- past earnings not distributed to stockholders (retained earnings)
Total Stockholders’ Equity
Total Sources of Financing for Company’s Resources (Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity)
Heading (Balance Sheet)
specifically identifies significant items related to statement which includes (1) name of entity, (2) title of statement, (3) specific date of statement, (4) unit of measure
Accounting Entity (Balance Sheet)
organization for which financial data are to be collected, MUST BE PRECISELY DEFINED!
Liabilities (Balance Sheet)
financing from creditors (e.g., amounts owed to suppliers, employees, banks)
Stockholders’ Equity (Balance Sheet)
financing from stockholders (e.g., common stock, retained earnings)
Assets (Element of Balance Sheet)
economic resources owned by the entity and depend on nature of operations; initially measured at the total cost incurred to acquire it but DO NOT generally show amounts for which assets could currently be sold; can be sold for cash in event company goes out of business
Common Account Titles for Assets on Balance Sheet
- Cash
- Short-term investment
- Account/Note Receivable
- Inventory
- Prepaid Expenses
- Suppliers
- Equipment
- Buildings
- Land
Accounts Receivable
when products are sold on credit with promise to pay, which is later collected in cash
Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position) Formulaic Structure
Balance Sheet
Assets
=
Liabiltiies
+
Stockholder’s Equity
Example of Content on Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position)
cash, accounts, receivable, plant and equipment, long-term debt, common stock
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity (Element of Balance Sheet)
sources of financing for the company’s economic resources
Liabilities (Elements of Balance Sheet)
indicate the amount of financing provided by creditors; company’s debts or obligations
Account Payable
arise from the purchase of goods/services from suppliers on credit without a formal written contract (or a note)
Notes Payable
to banks result from cash borrowings based on a formal written debt contract
Stockholders’ Equity (Element of Balance Sheet)
indicates amount of financing provided by owners of the business and reinvested earnings
Why creditors consider stockholder’s equity a protective “cushion”
because creditors’s claims legally come before those of the owner. if a company goes out of business and its assets are sold, proceeds of sale must be used to pay back creditors before stockholders recieve any money
Common Stock
part of stockholder’s equity, investment of cash and other assets in the business by stockholders
Total Stockholders’ Equity
part of stockholder’s equity, sum of common stock + retained earnings
Retained Earnings
amount of earnings (profits) reinvested in the business (and thus not distributed to stockholders in the form of dividends)
How to Get Retained Earnings
A company earns revenue
Subtract all expenses to arrive at its net income (profit)
Subtract any dividends paid to shareholders
Remaining profit can be used for growth, debt reduction, or other financial needs
Income Statement (Statement of Income, Statement of Earnings, Statement of Operations)
reports the accountant’s primary measure of performance of a business, reports for SPECIFIED PERIOD OF TIME
Income Statement (Statement of Income, Statement of Earnings, Statement of Operations) Formula
Net Income = Revenues = Expense
Net Income/Net Earnings vs Profit
While profit is widely used for measure of performance, accountants prefer to use net income rather than profit
Revenues
normally are amounts expected to be received for goods and services that have been delivered to a customer, whether or not customer has paid for the goods/services
Expenses
resources used (incurred) by entity to earn accounting period’s revenue
Net Income
revenues earned - expenses incurred
Accounting Period
time covered by the financial statements (i.e., one year)
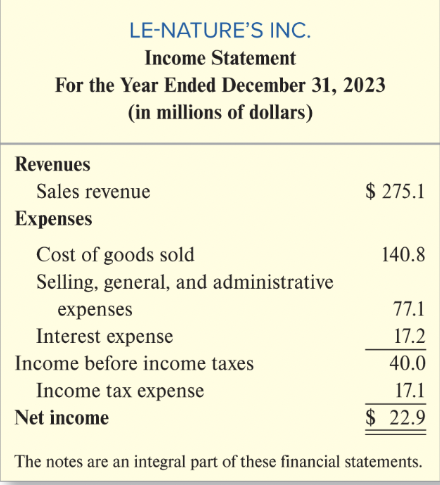
Income Sheet General Structure
Heading
Name of Entity
- Title of the Statement
- Accounting Period
- Unit of Measure
Revenues
- Cash and promises received from sale (Sales Revenue)
Expenses
-Cost to produce beverages sold (Cost of Goods Sold)
- Other operating expenses such as utilities, delivery costs, etc (Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses)
- Cost of using borrowed funds (Interest Expense)
- Revenues Earned - Expenses EXCEPT for income taxes (Income Before Income Taxes)
- Income taxes on period’s income before income taxes (Income Tax Expense)
Net Income (revenues earned - expenses incurred
characteristics of expenses
- expenses reported in one accounting period may be paid for in another accounting period
- some require the use of another resource, such as an inventory item, which may have been paid for in a prior period
statement of stockholders’ equity
reports the changes in each of the company’s stockholders’ equity accounts DURING ACCOUNTING PERIOD
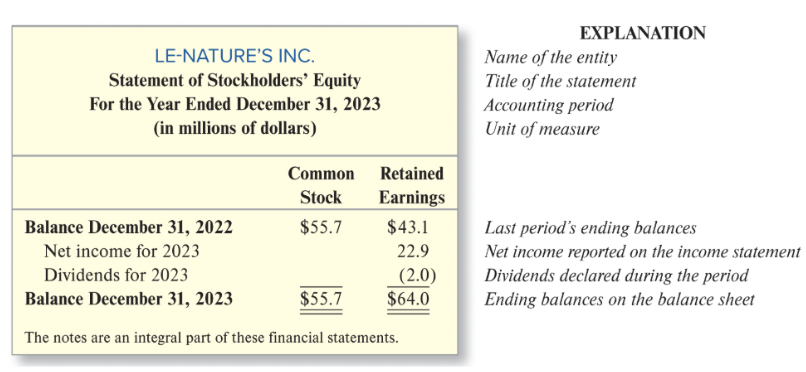
statement of stockholders’ equity general structure
name of entity
title of statement
accounting period
unit of measure
[common stock and retained earnings columns]
last period’s ending balances
net income reported on income statement
dividends declared during the period
ending balances on the balance sheet
retained earnings column
reports the way that net income and the distribution of dividends affected the company’s financial position DURING accounting period; INCREASED by net income earned during year
statement of stockholders’ equity formula
beginning retained earnings + net income - dividends = ending retained earnings
Elements of Statement of Stockholders’ Equity
- starts with the beginning balances in stockholders’ equity accounts, lists the increases and decreases, and reports resulting end balances
- retained earnings portion of statement indicates relationship of the income statement to the balance sheet
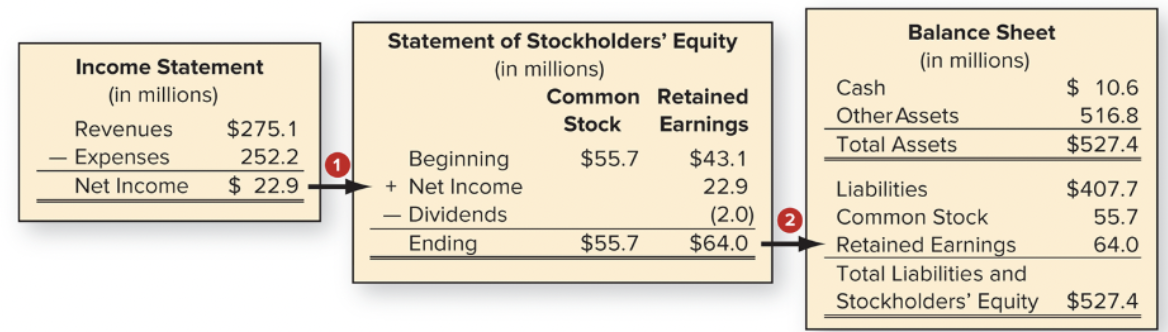
Relationship among the income statement, statement of stockholders’ equity, and balance sheet
1. Net income from income statement results in an increase in ending retained earnings on the statement of stockholders’ equity
2. Ending retained earnings from statement of stockholders’ equity is one of the two components of stockholders’ equity on balance sheet
3. Income statement explains, through statement of stockholders’ equity, how operations of company improved/harmed financial position of company during year
statement of cash flows (cash flow statements)
reports inflows and outflows of cash DURING ACCOUNTING PERIOD in the categories: operating, investing, and financing activities
Note About Reported Revenues (Cash Flow Statement)
reported revenues do not always equal cash collected from customers because some sales may be on credit
The Cash Flow Statement Equation(s)
describes causes of change in cash reported on balance sheet from end of last period to end of current period; sources can be pos or neg
Statement of Cash Flows General Structure
+/- Cash flows from operating activities
+/- Cash flows from investing activities
+/- Cash flows from financing activities
[line]
Change in Cash
+ Beginning cash balance
[line]
Ending Cash Balance
Cash flow from operating activities
cash flows that are directly related to earning income (e.g., when entity pays salaries to production employees or pays bills to suppliers)
Cash flows from investing activities
cash flows that are directly related to the acquisition or sale of the company’s plant and equipment and investments (e.g., purchase of additional manufacturing equipment to meet growing demand for its products)
Cash flows from financing activities
cash flows directly related to the financing of the enterprise itself; involve receipt or payment of money to investors and creditors (except for suppliers) (e.g., LeNature borrowed additional money from bank to purchase most of new manufacturing equipment)
How to Find Ending Cash Flow
1. The pos and neg subtotals for cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities are added to determine change in cash during period
2. Change in cash during period is added to beginning cash balance
3. Results in ending cash balance (should be same amount reported on balance sheet at end of the period)
Why Bankers Consider Operating Activities Section to be Most Important
indicates company’s ability to generate cash from sales to meet its current cash needs, as any amount leftover can be used to pay back bank debt or expand
Examples of Content (Balance Sheet)
Cash, Accounts Receivable, Plant and Equipment, Long-Term Debt, Common Stock
Examples of Content (Income Statement)
Sales Revenue, Costs of Goods Sold, Selling Expense, Interest Expense
Examples of Content (Statement of Stockholders’ Equity)
Beginning and Ending Stockholders’ Equity Balances, Stock Issuances, Net Income Dividends
Examples of Content (Statement of Cash Flows)
Cash Collected from Customers, Cash Paid to Suppliers, Cash Paid to Purchase Equipment, Cash Borrowed from Banks
Who Determines Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
created by Congress, given broad powers to determine measurement rules for financial statements that publicly traded companies must provide to stockholders
Publicly Traded Companies
companies issuing stock to the public
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
given primary responsibilities that work out detailed rules that become GAAP
Accounting Standards Codification
official pronouncements of FASB, relies on conceptual framework to provide a structure for developing specific accounting standards
Conceptual framework FASB relies on to provide structure for developing specific accounting standards
- provide financial info about entity that is useful to existing and potential investors, lenders, and other creditors in making decisions about providing resources (primary objective of financial reporting)
- information must be RELEVANT to decisions of external users
- information must be a FAITHFUL representation of economic substance of company’s activity
Relevant Information
part of FASB conceptual framework, helps evaluate the company’s past behavior and predict its future activities
Faithful Representation
part of FASB conceptual framework, requires info to be complete and free from bias and other forms of error
Costs and Major Economic Consequences Companies Incur Through Preparation and Publication of Statements
- effects of selling price of a company’s stock
- effects of amount of bonuses received by management and employees
- loss of competitive info to other companies
Three-Step Process When Faced w/ an Ethical Dilemma
1. Identify benefits of decision (often to manager or employee involved)
2. Identify alternative courses of action
3. Choose one you would like your family/friends to see reported on local news (usually the ethical choice)
Three Important Steps to Assure Investors that Company’s Records are Accurate
1. Entity should maintain system of internal controls over both records and assets of company
2. Should hire outside independent auditors to audit fairness of financial statements
3. Should form a committee of board of directors to oversee integrity of other safeguards
Internal Controls
processes by which company provides reasonable assurance regarding reliability of company’s financial reporting, effectiveness and efficiency of operations, and compliance with applicable laws and regulations
Audit
examination of financial reports to ensure that they represent what they claim and conform with GAAP
Three Main Types of Business Entities
Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, Corporation