TEAs science (biology mostly)
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
squeak no anatomy/chemistry included :P
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
cells
the basic unit of life
tissue
made up of cells with similar structure and function
organs
made up of tissue that work together to function
organ systems
groups of organs that work together to carry out a function
organism
made up from one or more organ system
biological organization
cells
tissues
organs
organ systems
organisms
modern cell theory
the cells are the smallest living unit in all organisms
all living things are made up of cells
all cells come from other pre-existing cells
prokaryotes (PRO = NO)
examples: bacteria + archaea
characteristics →
DNA
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Cell membrane
NO NUCLEUS
NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGNELLES
ex: nucleus + mitochondria + golgi apparatus
Eukaryotes (EU = DO)
examples: fungi + protist + plants + animals
characteristics →
DNA
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Cell membrane
NUCLEUS
HAS MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES
cell membrane (plasma membrane)
separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment
characteristics →
selectively permeable
only specific materials can come in and out
keeps cells stable (HOMEOSTASIS)
homeostasis
self-regulating process by which biological systems maintain stability while adjusting to changing external environment
cytoplasm
gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell :3
cytoskeleton
network of fibers that provide structural support for the cells and organelles
helps with cellular movement
ribosomes
intercellular structures made of both RNA and protein
site of protein synthesis in the cell
can either float freely or is attached to another organelle
other words: is primarily responsible for assembling proteins using instructions encoded in mRNA
amino acids
small molecules that are the building blocks of proteins
nucleus
membrane-enclosed organelle within a cell that CONTAINS the chromosomes (DNA)
→ ONLY FOUND IN EUKARYOTES
nucleolus
area inside the nucleus of a cell that is made up of RNA and proteins and is where RIBOSOMES are made
endoplasmic reticulum
large structure that serves many roles in the cell including
calcium storage
protein + lipid synthesis
lipid metabolism
comes in 2 forms… ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM and SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
rough endoplasmic reticulum
provides surface area for chemical reactions + protein synthesis/transport
rough appearance due to the surface being covered in ribosomes
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
makes cellular products like hormones and lipids
detoxification, a vital process for liver cells
smooth appearance due to the lack of ribosomes
golgi apparatus (UPS/USPS)
helps process and package proteins and lipid molecules, especially PROTEINS destined to be exported from the cell
ENZYME ASSISTANCE:
receives materials from transport vesicles that detach from the ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC R
→ enzymes modify molecules and organize them
mitochondria (POWERHOUSE of the cell)
generates most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell’s biochemical reactions.
→ generates on GLUCOSE
other words: generates ATP energy through cellular respiration
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level
chloroplast
plant cell
→ saclike organelle with a double membrane that services as a site for photosynthesis
gets its green appearance from the pigment they absorb from light energy
photosynthesis
energy from the sun that’s converted into chemical energy for growth
lysosomes
the cells waste disposal system
→ contain digestive enzymes that break down excess/worn-out cells + macros
may be used to DESTROY VIRUSES + BACTERIA
Maintain cellular cleanliness + recycle materials that can be reused by the cell
vacuole
large fluid-filled sacks found in (MOSTLY) plant cells and some animal/fungal cells
functions →
storing nutrients
maintaining hydrostatic pressure within the cell (plant)
help sequester (isolate) waste/harmful products (animal)
Mitosis
cell division that results in TWO daughter cells; each having the SAME NUMBER and kind of chromosomes
differences from meiosis:
leads to SOMATIC CELLS (body cells)
Meiosis
cell division that results in FOUR daughter cells each with HALF THE NUMBER of chromosomes of the parent cell
differences from mitosis:
produces REPRODUCTIVE CELLS, known as gametes (sperm/eggs)
included the stages TWICE (prophase 1/2, metaphase 1/2, anaphase 1/2, and telophase 1/2)
2n
both mitosis + meiosis start off as a DIPLOID CELL (2n) , which simply means two complete set of chromosomes
how many chromosomes do we have?
46 chromosomes
23 from our mom
23 from our dad
Interphase
cells replicate their chromosomes
→ still referred to as 46 chromosomes because they are simply copies known as CHROMATIDS that remain joined at the region called the CENTROMERE doubling the chromatid number to 92
technically not a part of the mitosis/meiosis process, but is crucial for chromosome replication and sets the stage for what’s to come
mitosis (PROPHASE)
initial stage when it comes to division (pro = before)
→ chromosomes become visible as they condense + thicken
meiosis (PROPHASE 1)
→ chromosome condensation occurs and will also begin pairing up in HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES
allows for the exchange of genetic material between chromosomes through CROSSING OVER, which results in RECUMBENT chromosomes important for genetic diversity
homologous chromosomes
equal in size/gene type/location
one came from the mother and the other from the father
mitosis (METAPHASE) (think MIDDLE)
ps: the nuclear envelope that was previously enclosed in the nucleus has been dismantled (pulled apart)
→ chromosomes align in the middle of the cell’s center; forming a single row
meiosis (METAPHASE 1)
→ chromosomes align in the middle of the cell’s center, BUT maintain their homologous pairs, creating a pair of chromosomes standing together in the middle (NOT A SINGLE ROW)
mitosis (ANAPHASE) (think = AWAY)
→ CHROMATIDS are separated and drawn to the opposite ends of the cell by spindle fibers
REMEMBER NOT CHROMOSOMES
meiosis (ANAPHASE 1)
→ CHROMOSOMES are separated and drawn to the opposite ends of the cells by spindle fibers
homologous chromosomes are separated as it allows for the random assortment of chromosomes, contributing to GENETIC DIVERSITY among offspring
REMEMBER NOT CHROMATIDS THAT ARE FOR MITOSIS
mitosis (TELOPHASE)
→ chromosomes reach the opposite sides of the cell; forming new nuclear envelopes around the chromosomes and setting the stage for the CREATION OF TWO BRAND NEW CELLS
*mitosis
meiosis (TELOPHASE 1)
→ chromosomes reach the opposite sides of the cell, forming new nuclear envelopes around the chromosomes and setting the stage for the CREATION OF TWO BRAND NEW CELLS
*meiosis
mitosis (CYTOKINESIS)
→ the division/splitting of the cytoplasm and is going to FINALIZE the cell division process
results: two identical, diploid cells (both have 46 chromosomes)
meiosis (CYTOKINESIS)
→ the splitting of the cytoplasm of the cell
meiosis (PROPHASE 2)
→ chromosome condensation in both cells
less eventful compared to prophase 1 as there are no more homologous pairs
meiosis (METAPHASE 2) (think MIDDLE)
→ chromosomes align in the middle of the cell’s center, forming a single row
similar to mitosis metaphase
meiosis (ANAPHASE 2) (think AWAY)
→ CHROMATIDS are separated and drawn to the opposite ends of the cells by spindle fibers
in anaphase 1 they were still chromosomes, however, it is important to remember that they are not chromatids :3
meiosis (TELOPHASE 2)
→ chromosomes reach the opposite sides of the cell, forming new nuclear envelopes around the chromosomes leading to the creation of new cells
meiosis (CYTOKINESIS) again..
→ splitting of the cytoplasm again
results: four non-identical (DISTINCTIVE) cells/gametes
men: sperm
women: eggs
→ both are haploid cells carrying half of the chromosome count of the original cell (23 chromosomes)
other info: the fusion of sperm and an egg creates a diploid cell (fertilized egg known as a zygote)
summary of mitosis vs meiosis
mitosis results in TWO genetically identical diploid daughter cells
meiosis produces FOUR genetically unique haploid cells
heredity
the passing on of physical or mental characteristics genetically from one generation to another
examples: height, hair color, eye color, risk of certain diseases, etc.
→ DNA is responsible for coding the traits that define us
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
self-replicating material that is present in NEARLY all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes
→ fall into the category of nucleic acids
feature 3 critical components
Deoxyribose (a sugar)
a Phosphate group (known as the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA)
nitrogenous base
has 4 types of bases (A, T, C, and G)
Adenine
Thymine
Cytosine
Guanine
nucleic acid
one of our essential biomolecules is composed of building blocks known as nucleotides
Pairing of nucleotide bases
Adenine and Thymine
REMEMBER → APPLE in the TREE
Cytosine and Guanine
REMEMBER → CAR in the GARAGE
DNA structure
consists of TWO strands with nucleotides aligned along each side of them
→ in the center the bases of opposite stands are going to pair up, connected by HYDROGEN BONDS
structure of DNA will twist into a DOUBLE HELIX SHAPE
REMEMBER: nucleotides
nucleotide bases are held together with HYDROGEN BONDS
genes
segments of DNA create genes
→ a unit of heredity which is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristics of the offspring
structural genes
specific regions of DNA correspond to individual genes capable of encoding proteins
→ CRUCIAL TO TRAIT EXPRESSION
ex: human eye color/hair color
other functions:
transport
structure support
enzymatic activity (facilitates synthesis for several substances)
defense mechanisms
regulatory genes
non-coding regions 😽
→ produce proteins or RNAs that control the expression of other genes
Gene regulation: used to control timing, location, and amount in which genes are expressed
genes can be activated and deactivated through various mechanisms
IMPORTANT (genes)
despite all of our body cells containing a complete DNA code only specific gene segments may be used with certain genes being activated and others being deactivated (gene regulation)
gene regulation
used to control the timing, location, and amount in which genes are expressed
chromosomes
DNA is compacted/organized into these structures
→ a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes
consists of DNA coiled around a protein scaffold
humans consist of 46 chromosomes
23 from mom / 23 from dad
relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes
Chromosomes are composed of DNA, and genes are specific segments of chromosomes that dictate individual traits
REMEMBER →
chromosomes are long strands of DNA wrapped around proteins called histones
Genes are located ON these chromosomes and act as instructions to produce proteins that determine characteristics
what best describes the function of regulatory genes in gene expression
they produce proteins or RNAs that control the expression of other genes
→ REMEMBER
regulatory genes are responsible for producing proteins and RNAs + play a crucial role in controlling expressions (enhance/inhibit gene expression)
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
→ a nucleic acid present in ALL living cells whose principal role is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins
in eukaryotes, RNA is located INSIDE and OUTSIDE of the nucleus
RNA structure
is SINGLE-SIDED + has one single strand of nucleotides
there is an absence of oxygen molecules
there is a different sugar base (RIBOSE)
contains the nitrogenous bases of...
Adenine
Uracil (replaces thymine from DNA)
Cytosine
Guanine
pairing of nucleotide bases
ADENINE + URACIL
APPLE UNDER the tree
CYTOSINE + GUANINE (same)
CAR in the GARAGE
the 3 different types of RNA
mRNA
rRNA
tRNA
mRNA (messenger)
carries genetic information to make proteins
→ can exit the nucleus and allow it to transport the genetic blueprint to the RIBOSOMES to produce proteins
composed of an RNA sequence that MIRRORS the DNA template + goes under ALOT of editing before working
rRNA (ribosomal)
found in ribosomes + serve as a location for protein synthesis
tRNA (transfer)
the primary function is to take amino acids to the ribosome + ensure that they align correctly with the corresponding mRNA codons to create a POLYPEPTIDE CHAIN
other words: an adaptor molecule that decodes an mRNA into a protein
protein synthesis unfolds through…
2 principal phases
transcription
translation
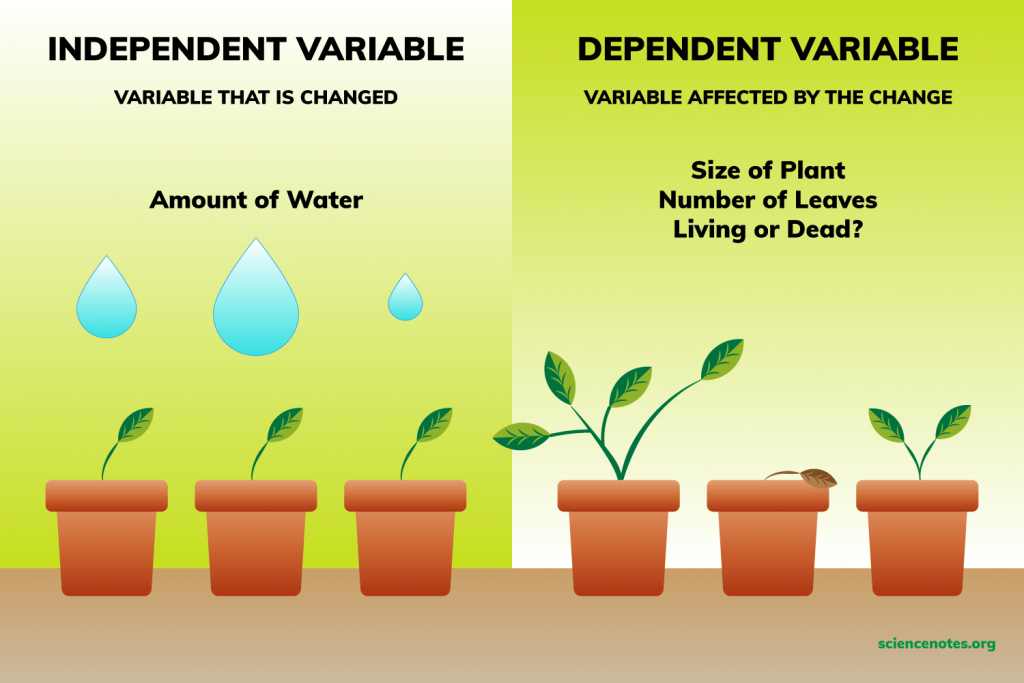
independent variable
VARIABLE THAT IS CHANGED
example → the amount of water poured on plants
dependent variable
variable affected by the change
example → the size of the plant, the number of leaves, or whether the plant is dead/alive
extra info: RNA
while DNA hold the instructions for traits it cannot be expressed with RNA
remember → RNA translates DNA’s genetic code into proteins
transCription (think = C comes before L)
involves converting DNA into a messenger strand; this takes place in the nucleus where DNA is found.
→ RNA polymerase (an enzyme) attaches matching RNA bases to the DNA templates to create a single-stranded molecule of mRNA
transLation (remember C comes before L)
where ribosomes assemble the proteins
in other words→ the process of translating the sequence of a mRNA to amino acids during protein synthesis
in the cytoplasm, you’ll find multiple tRNA molecules that are responsible for carrying amino acids (protein’s building blocks)
the mRNA will serve as a guide that determines which tRNA needs to be brought to a ribosome + which amino acid needs to be assembled to form a protein
each tRNA will search for bases that match its mRNA strand.
After finding matching bases the tRNA contributes its amino acids to the growing protein chain
result → a creation of an amino acid chain, assembled in a specific sequence that is dictated by the mRNA
codons
a sequence of THREE consecutive nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule that codes for a specific amino acid
what component is essential for initiating the transcription of a gene into mRNA in eukaryotic cells?
RNA polymerase
reads the DNA sequence of a gene and creates a complimentary mRNA strand
what is the role of mRNA in protein synthesis?
it serves as a template for assembling amino acids into proteins
mRNA = MESSENGER as it carries genetic code from DNA during transcription to the ribosome
allele
a variant of a gene often recognized by letters
in other words → an alternative form of a gene that arises by mutation and are FOUND IN THE SAME PLACE ON A CHROMOSOME
recessive allele
trait not expressed if there is a dominant allele
→ expressed as a LOWERCASE LETTER
dominant allele
trait will be expressed due to its dominance
→ expressed as a UPPERCASE LETTER
genotype
refers to the two alleles present at a specific locus in the genome + refers to the ENTIRE GENETIC MAKEUP of an individual
the two types of genotypes
homozygous genotype
homozygous DOMINANT (FF)
homozygous RECESSIVE (ff)
heterozygous genotype
heterozygous DOMINANT (Ff)
monohybrid cross
genetic mix between two individual genotypes which result in an opposite phenotype for a certain trait
→ mono signifies that we are focusing on a SINGLE TRAIT
phenotype (think p → physical)
an individual’s OBSERVABLE TRAITS produced by the interaction of the genotype
examples → height, eye color, and blood type
extra info on punnet squares
they offer predictions BASED on PROBABILITIES not certainties!!
they do not guarantee anything :0)
dihybrid cross
cross between two individuals for two observed traits that are controlled by two distinct genes (two different alleles)
mendel’s law of independent assortment
suggests that traits are inherited independently of one another
→ there is NO genetic link between X and Y
example: just because someone has black hair it doesn’t mean they like to BLANK
incomplete dominance
one allele is not completely dominance over the other
codominance (co = working together)
both traits show up in codominance
→ both alleles are expressed equally in the phenotype + independently
Basic macromolecules
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
and nucleic acids ( i guess.)
monomer
basically a building block (a smaller unit)
elements in the carbs
think CHO
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
elements in lipids
think CHO
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
*lipids
elements in proteins
think CHON
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
elements in nucleic acids
think CHONP
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
phosphorus
carbohydrates
biomolecule consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
THINK → cellulose, starch, and sugars
monomer: MONOSACCHARIDE (simple sugar) like glucose
disaccharide (di → two)
when TWO monosaccharides link together
carbohydrate rule!!!
if the word ends in -OSE it most likely indicates a carb
examples:
glucOSE
fructOSE
maltOSE
sucrOSE
lactOSE