AP European History - People
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
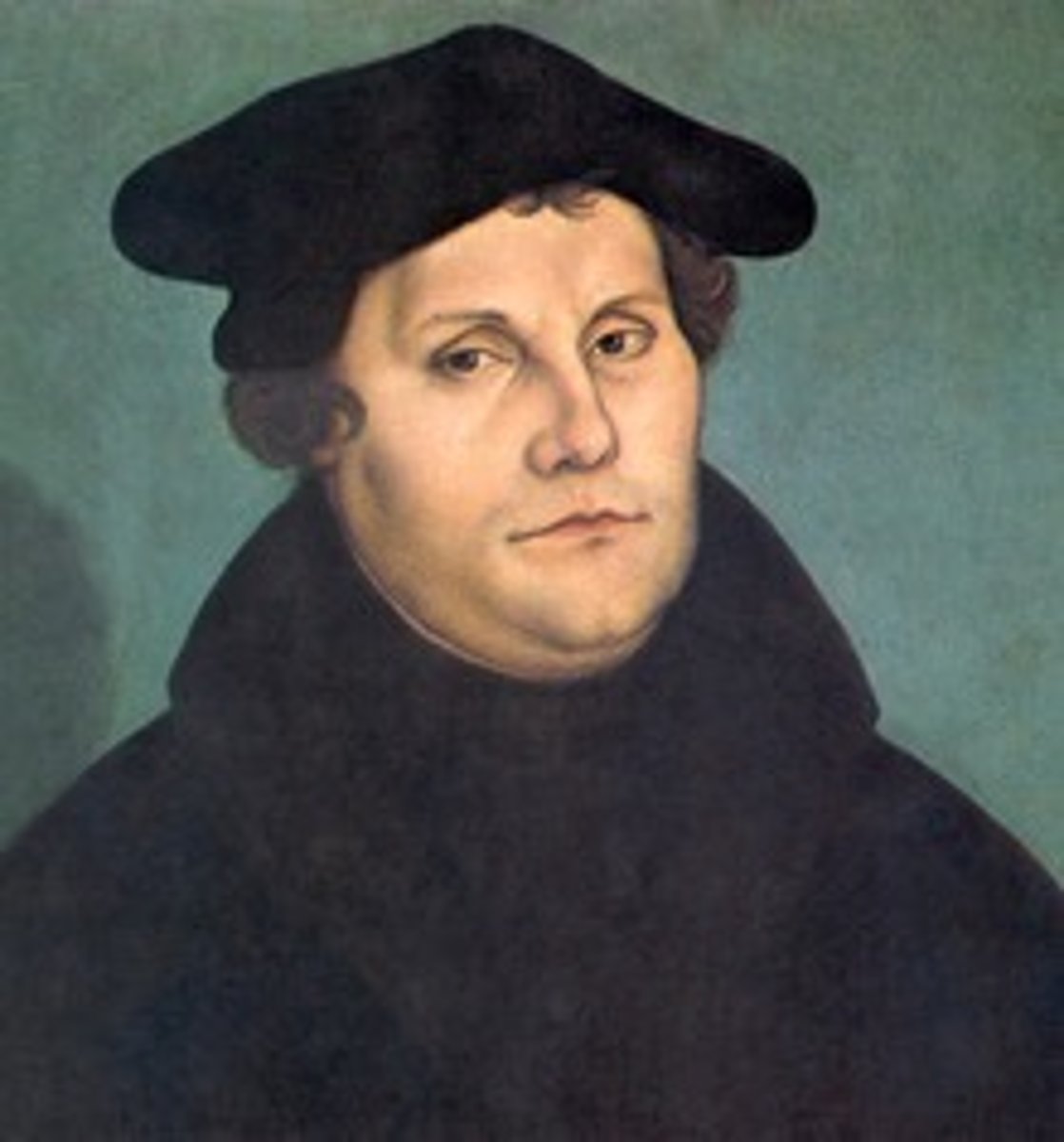
Martin Luther(1483-1546)
German Reformation
Justification by faith alone
Attack indulgences (paying for mortal sins).
1517, posting of 95 thesis.
Diet of Worms(1521) - met with HRE Charles V, didnt go that well
Did not support peasant social revolution.

Henry VIII (r. 1509-1547)
English
"Defender of the Faith"
Pope Leo X allowed his divorce
Made himself head of the Church of England Reformation.
Had many wives
Act of Supremacy
created Church of England.

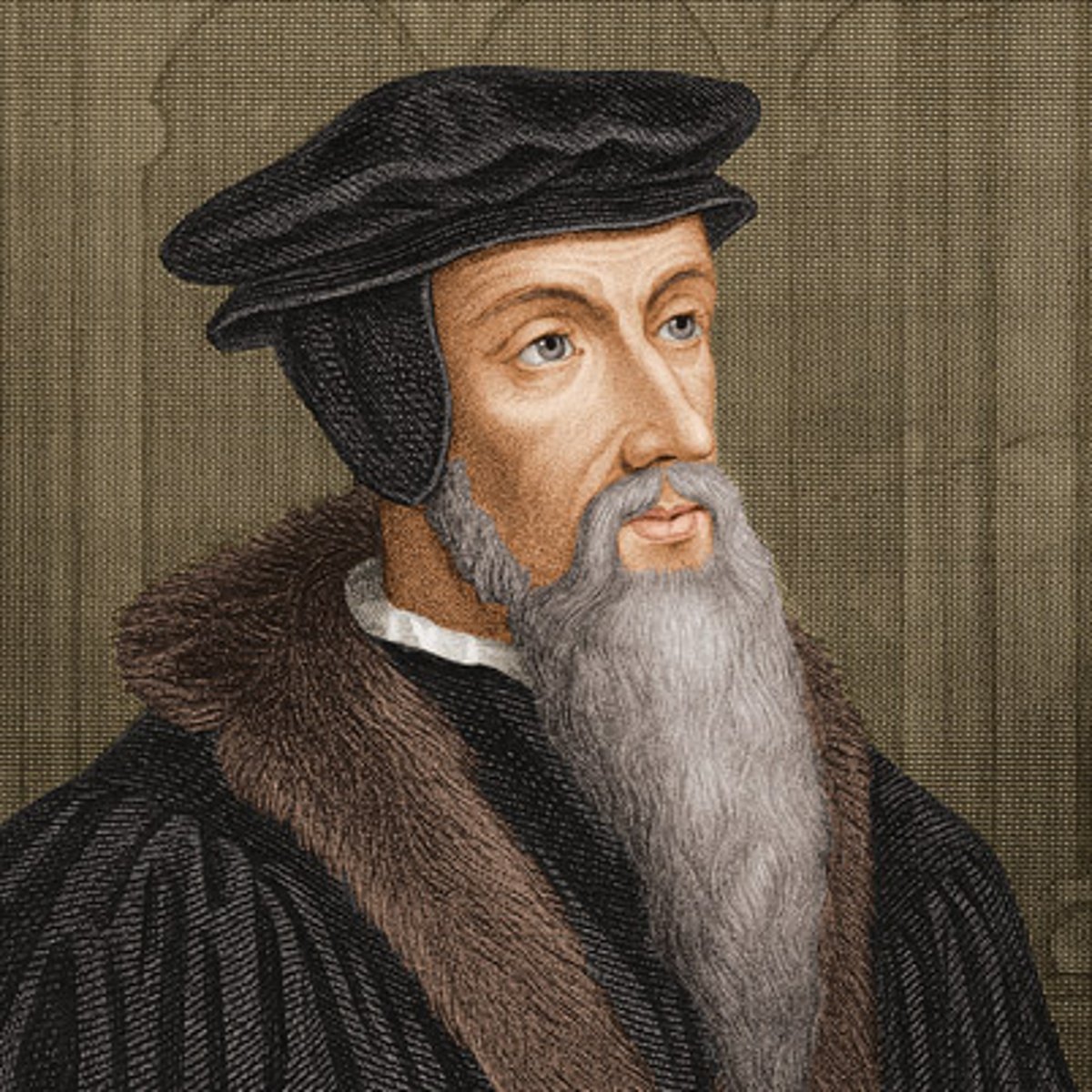
John Calvin (1509-1564)
French
Book: The Institutes of Christian Religion
Reformation
Calvanism

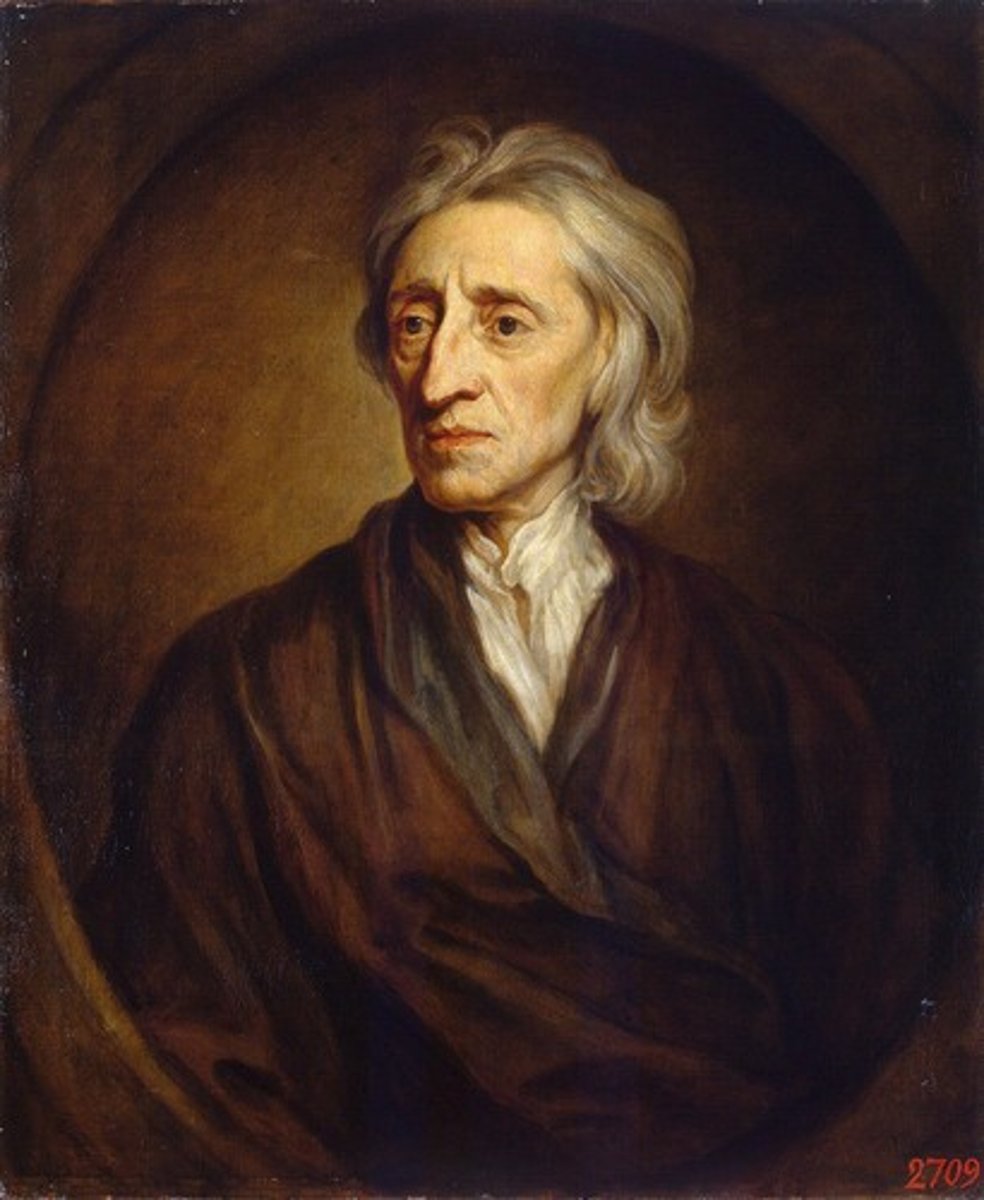
John Locke (1632-1704)
English philosopher
Tabula Rasa: the idea that people are born with no prior knowledge
Thought people had the right to Life, Liberty, and Property
Government's purpose was to protect these rights
If the govt. wasn't working for the people then the people could overthrow it and make a new government

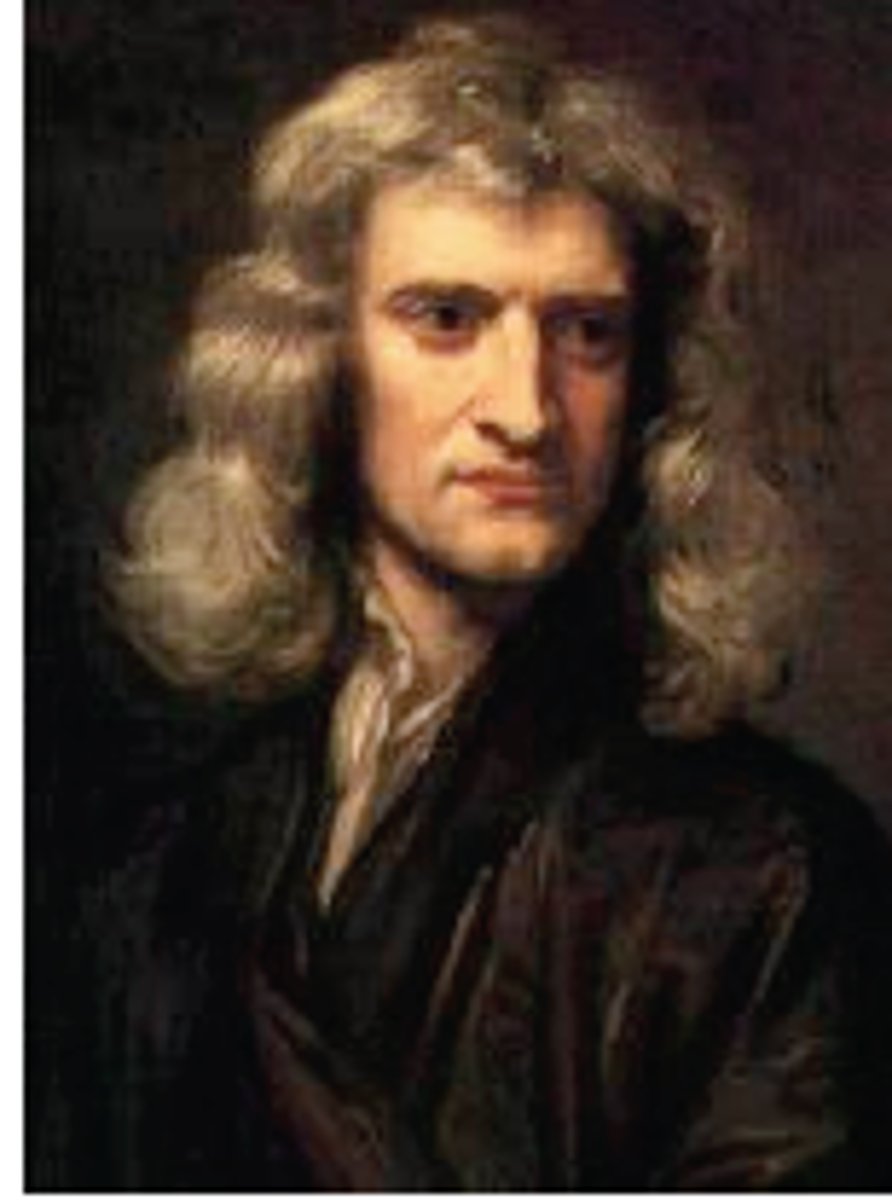
Isaac Newton (1642-1727)
English
Mathematician and physicist
Book: Principia (1687)
Laws of Motion
Laws of Gravity

Napoleon (1769-1821)
French general and emperor
Rose through the ranks of army after the French Revolution
Crowned himself emperor (1804)
Lost two-thirds of his army in a disastrous invasion of Russia
His final loss to Britain and Prussia:Battle of Waterloo
He was exiled to the island of St. Helena

Louis XIV (r.1643-1715)
Sun King
Divine Right
Versailles used to manipulate nobles. Mercantilism
Politique
Revoked Edict of Nantes
War of Spanish Succession.
Absolutism.

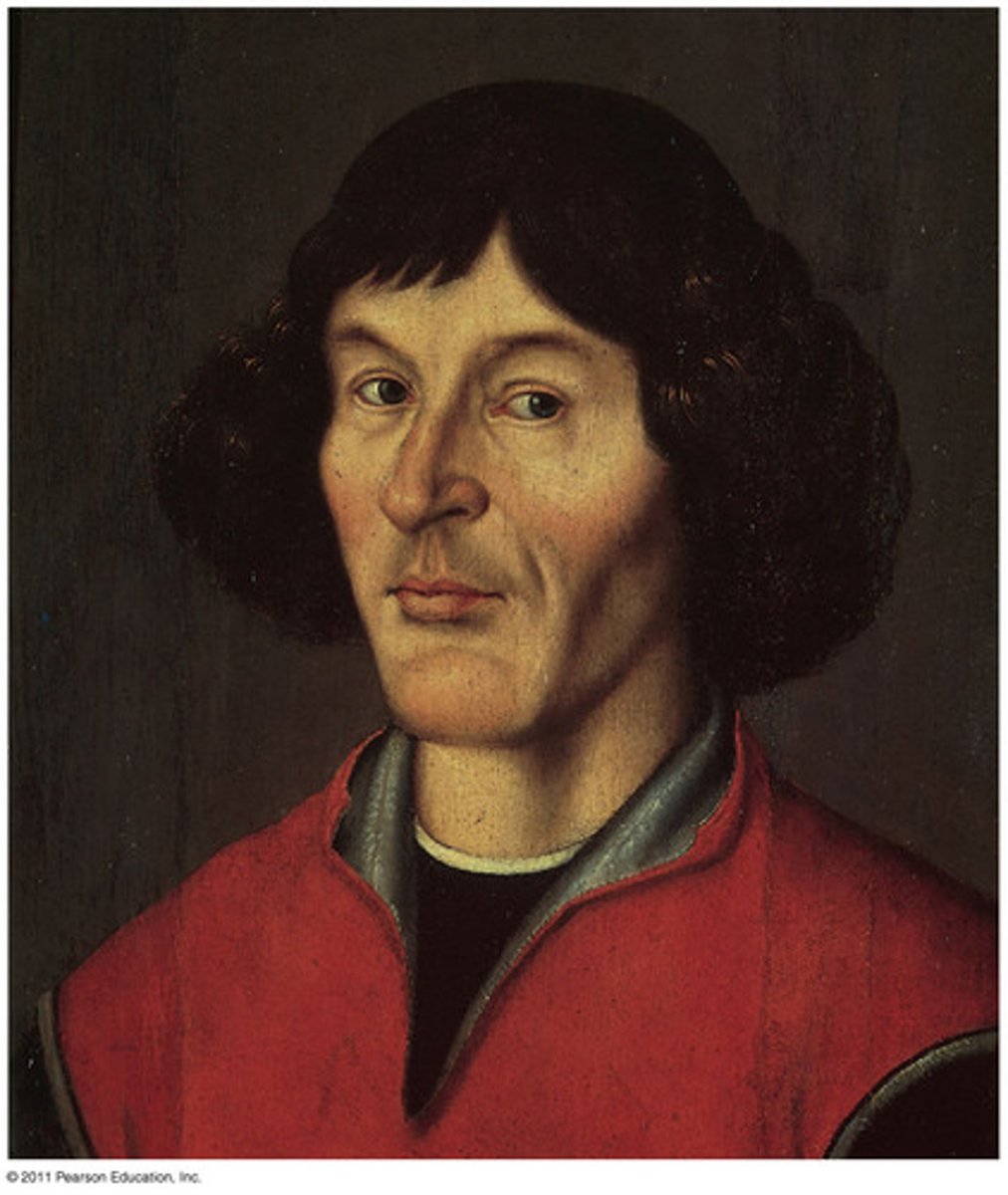
Copernicus & Galileo
Scientific Revolution. 1473-1543 Heliocentric Universe. On the Revolution of Heavenly Spheres. (1564-1642, Telescope, Math)

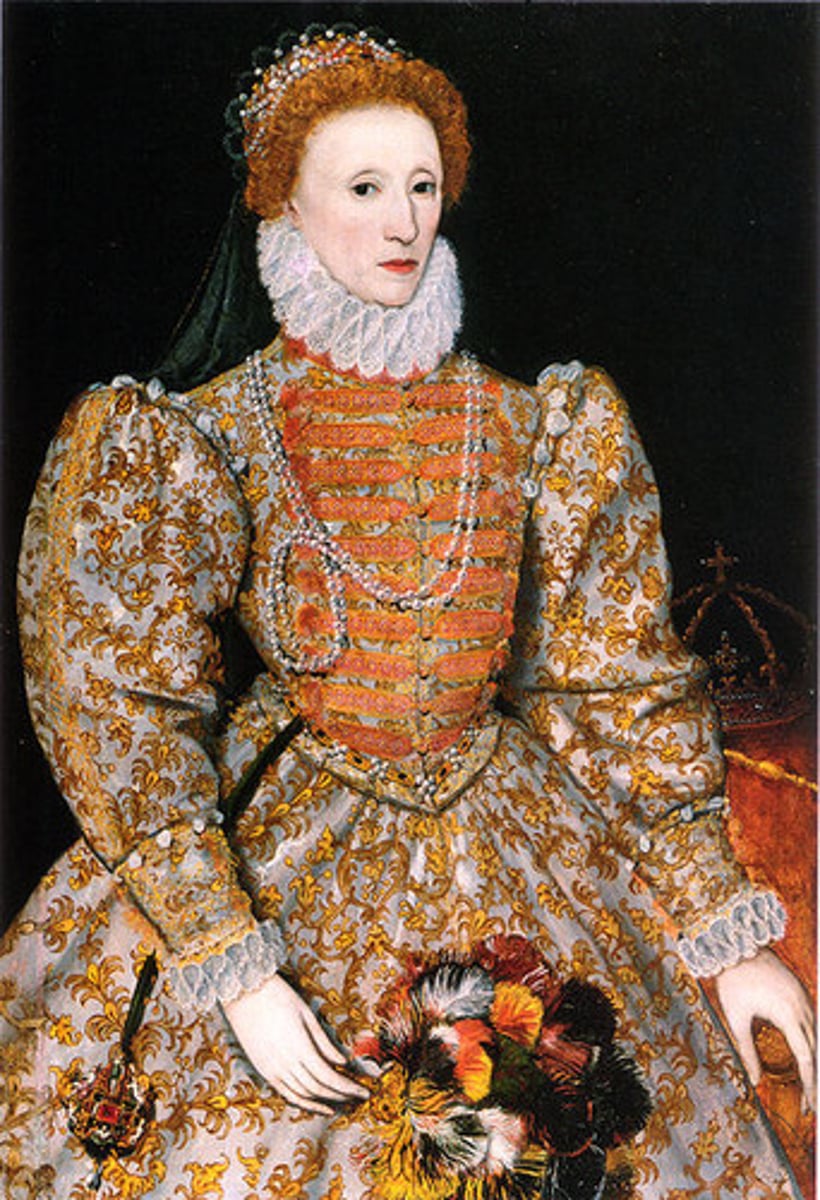
Elizabeth I
(1558-1603) Politique. 39 articles made moderate protestentism official religion of england. Executed Mary queen of scots. Failed Spainish Armada.

Peter the Great
(1682-1725) Romanov Dynasty. Westernization. Beginning in 1689 Peter gives Russia a crash course in Western ways. He sent Russians to the West to study, brought foreigners into Russia. Taming Streltsy and Boyars. Developed a navy. Founded St. Petersburg. Politique.

Adam Smith
(1723-1790) Enlightenment. Economist. Capitaism. The Wealth of Nations (1776). Selfish Economic Interests. Laissez- Faire - limited role of government in economic life. Invisible Hand.

Metternich
..., Austrian foreign minister who basically controlled the Congress of Vienna. Wanted to promote peace, conservatism, and the repression of liberal nationalism throughout Europe.

Marx
..., developed "scientific socialism", said that productive forces and economic relationships together made up the foundation of society. therefore, classes would conflict until the 'golden age' of communism took over

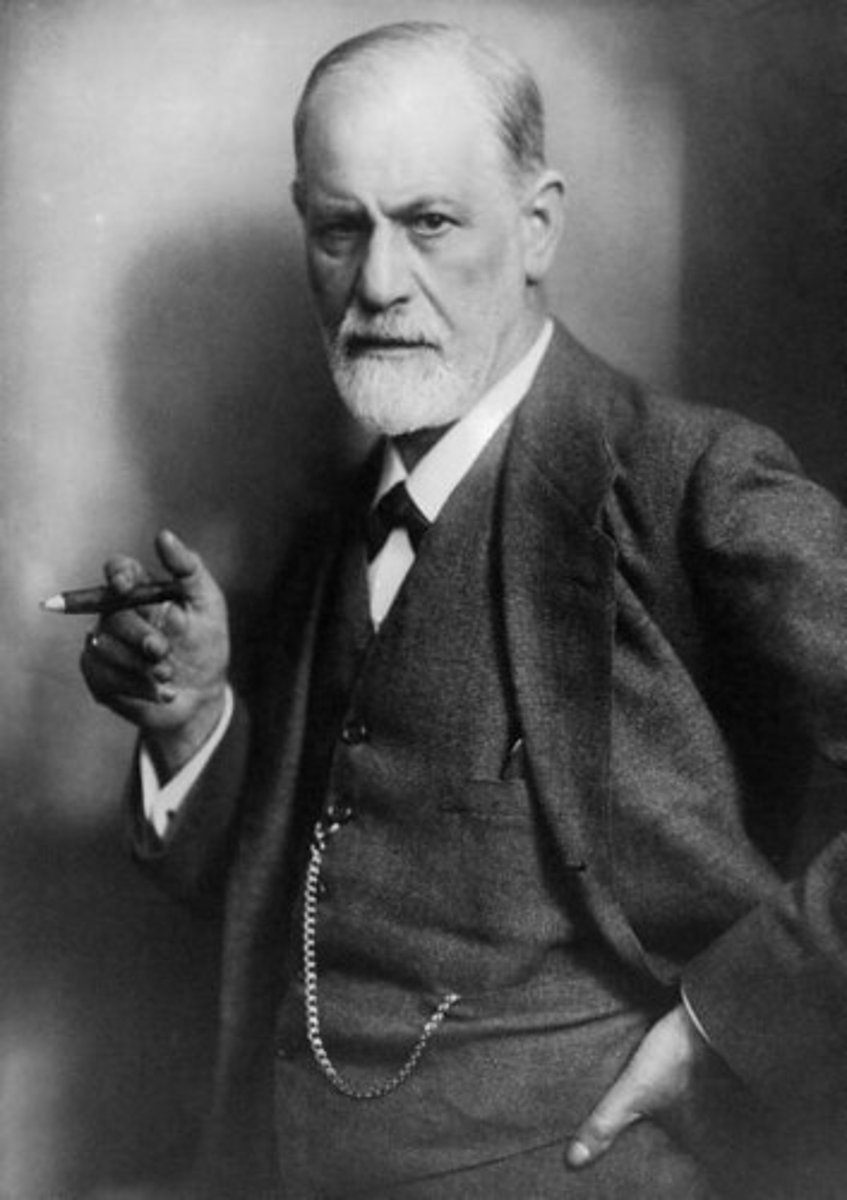
Darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection (1809-1882)
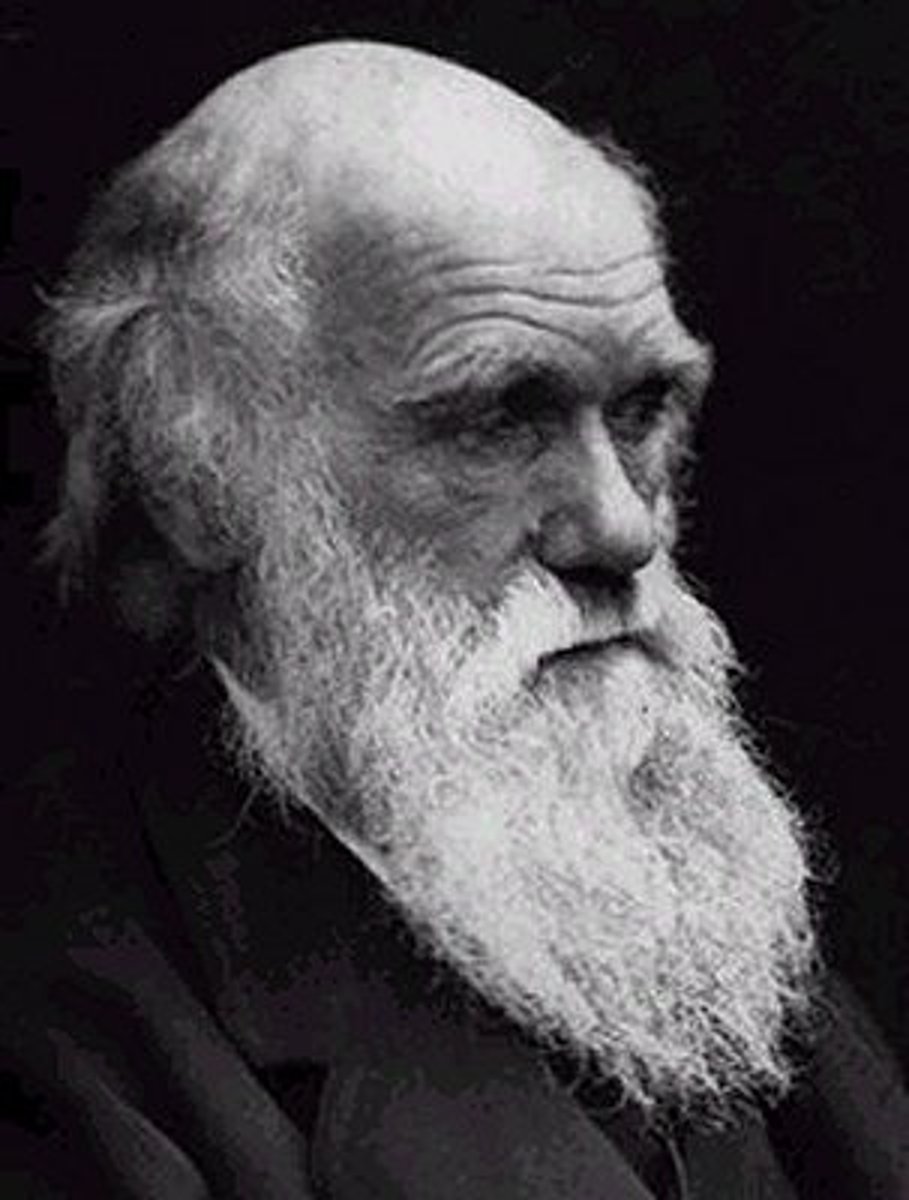

Bismark
The Prussian minister-president who came from a Junker family. He was the architect of the unification of Germany. He wanted to loosen Hapsburg grip on German affairs and establish Prussia as a respectable and dominant power.
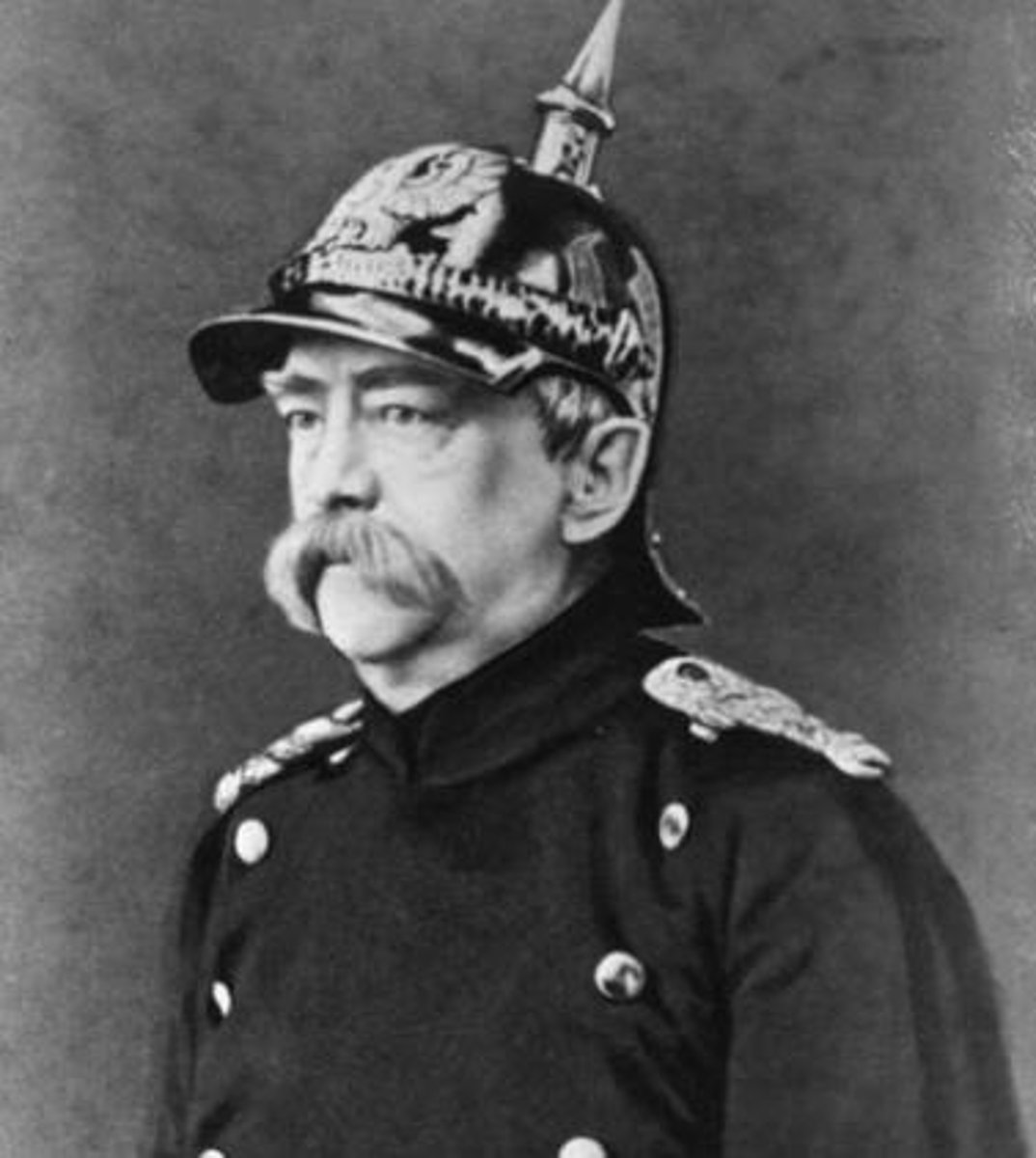

Lenin
founded the Communist Party in Russia and set up the world's first Communist Party dictatorship. He led the October Revolution of 1917, in which the Communists seized power in Russia. He then ruled the country until his death in 1924.
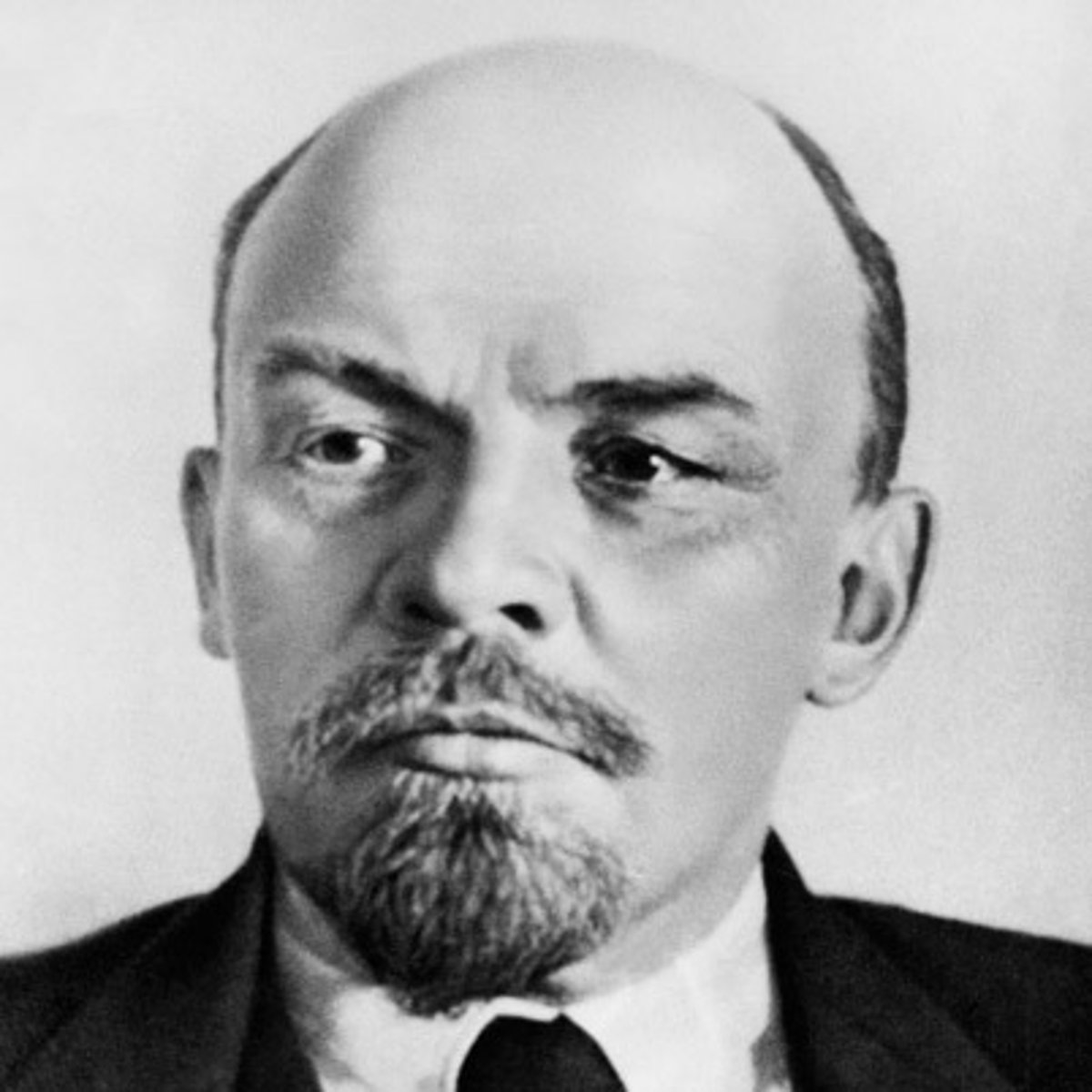

Freud
Psychologist who developed psychoanalysis, a method of probing the unconscious mind, frequently by analyzing dreams. He believed that humans were driven by unconscious pleasure-seeking forces.

Medici Family
Wealthiest Florentine Family. Financed much of the Renaissance. Powerful Italinan family. Most famous member: Catherine de Medici
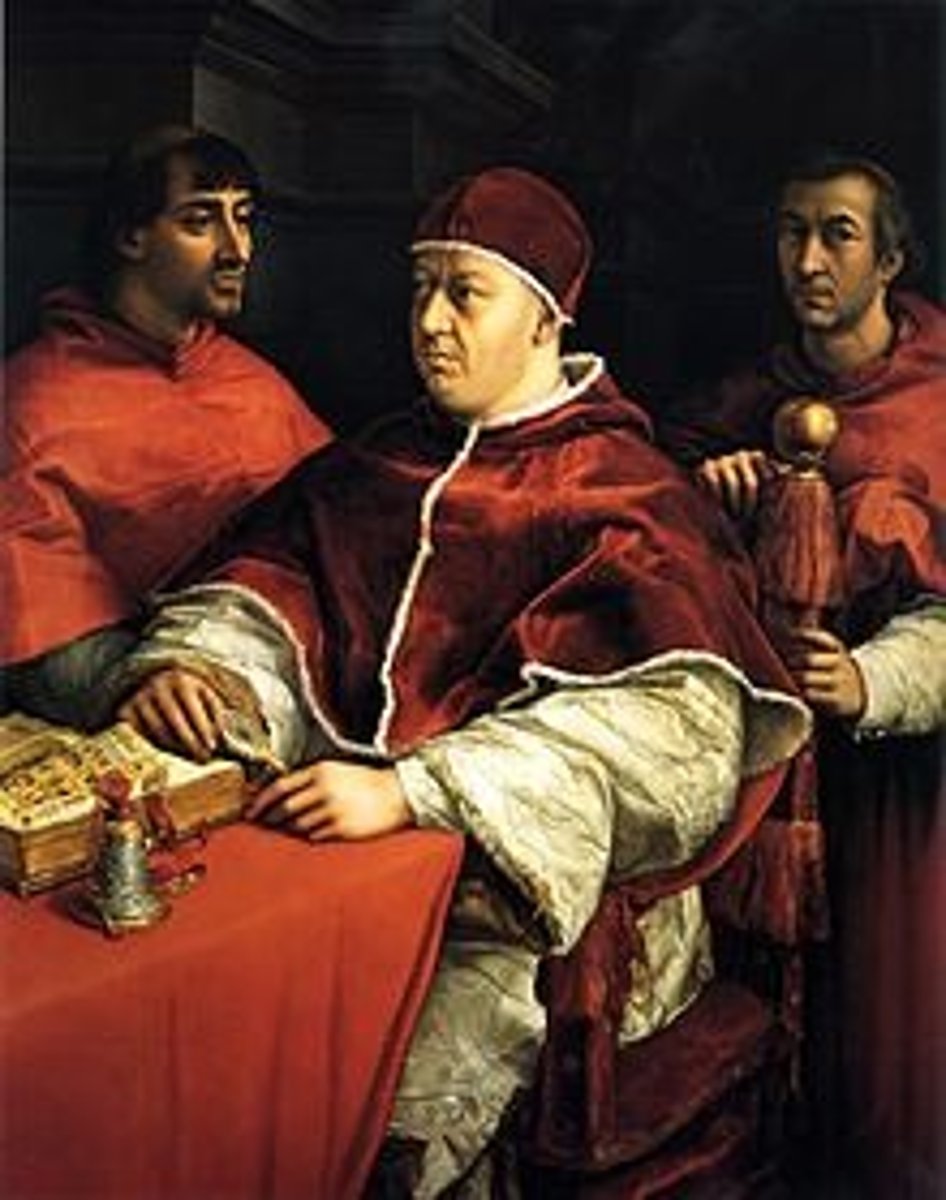

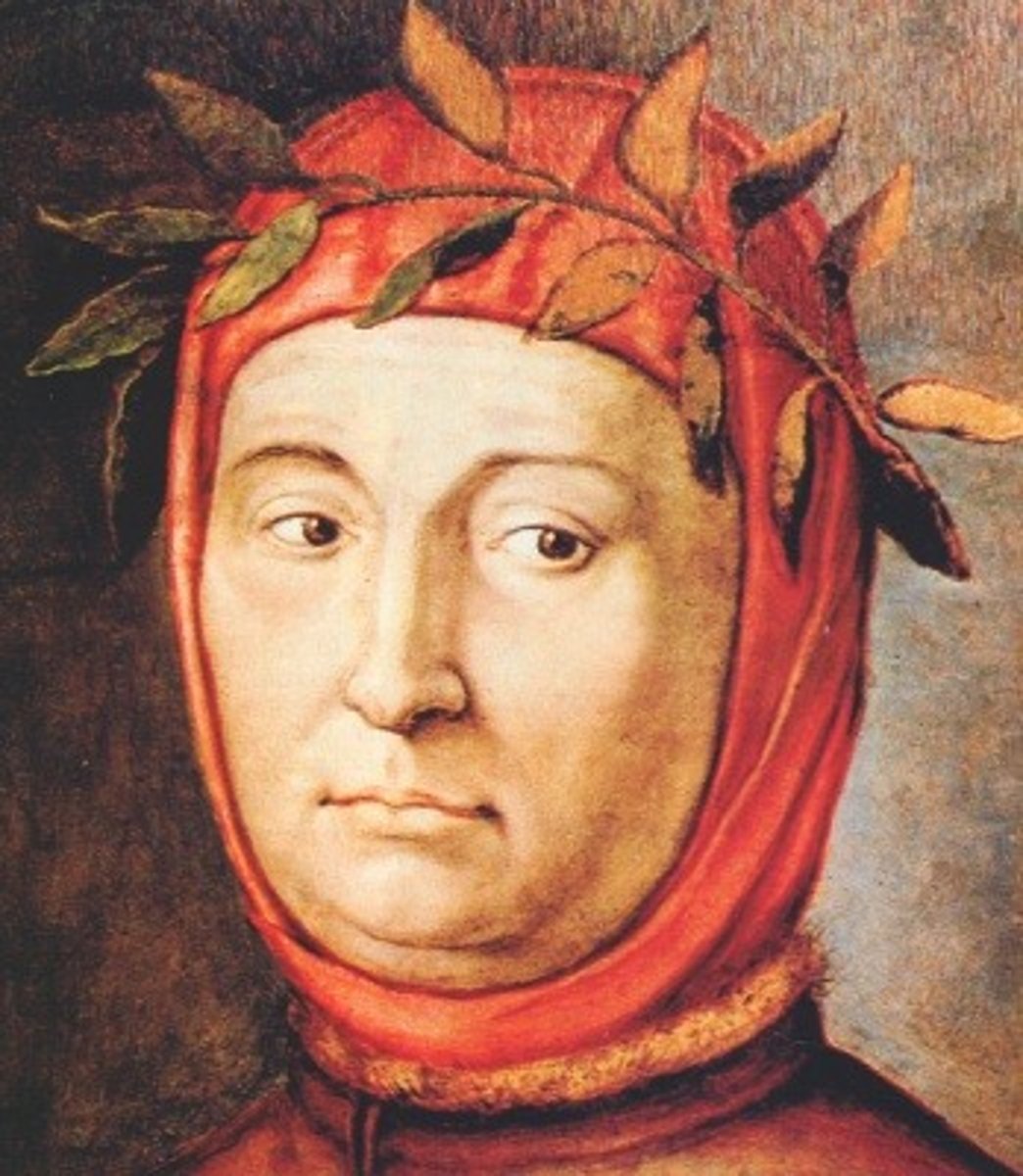
Petrarch
one of the earliest and most influential humanists. "father of Renaissance humanism" great poet

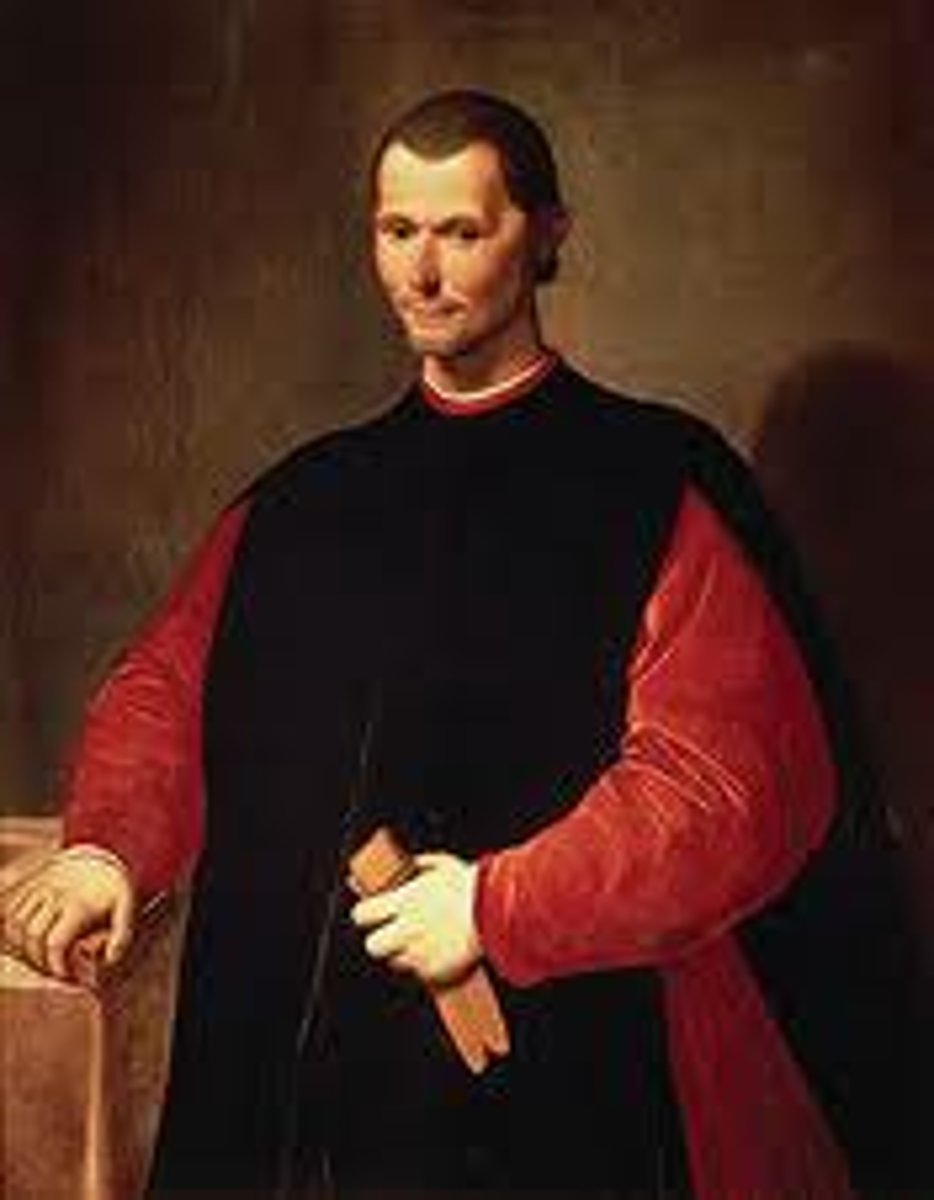
Machiavelli
Wrote "The Prince", a book that recommended harsh and arbitrary rule for princes

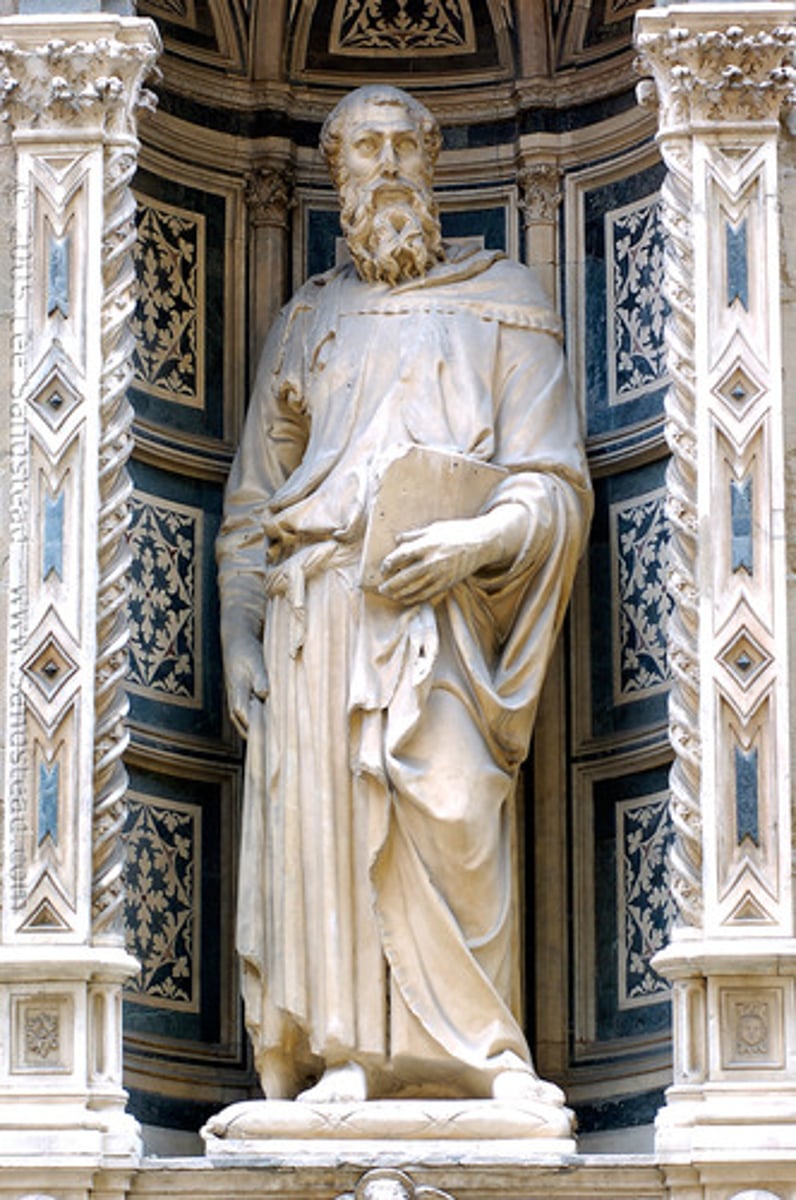
Donatello
Florentine sculptor famous for his lifelike sculptures (1386-1466)

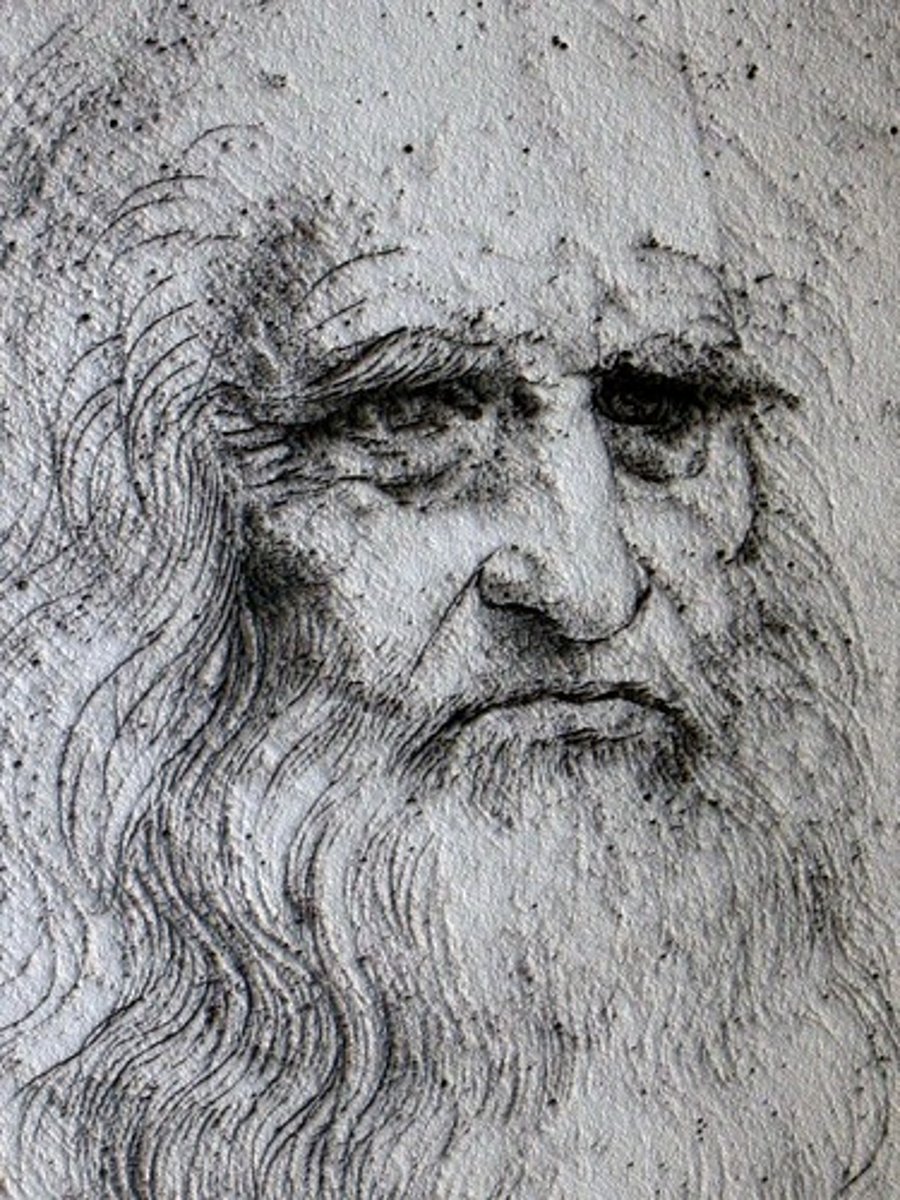
Leonardo da Vinci
Italian painter and sculptor and engineer and scientist and architect

Michelangelo
famous painter and sculptor who painted the ceiling of the Sistene Chapel in the Vatican and statue of David

Raphael
Italian painter whose many paintings exemplify the ideals of the High Renaissance (1483-1520)
Botticelli
Italian painter of mythological and religious paintings (1444-1510)
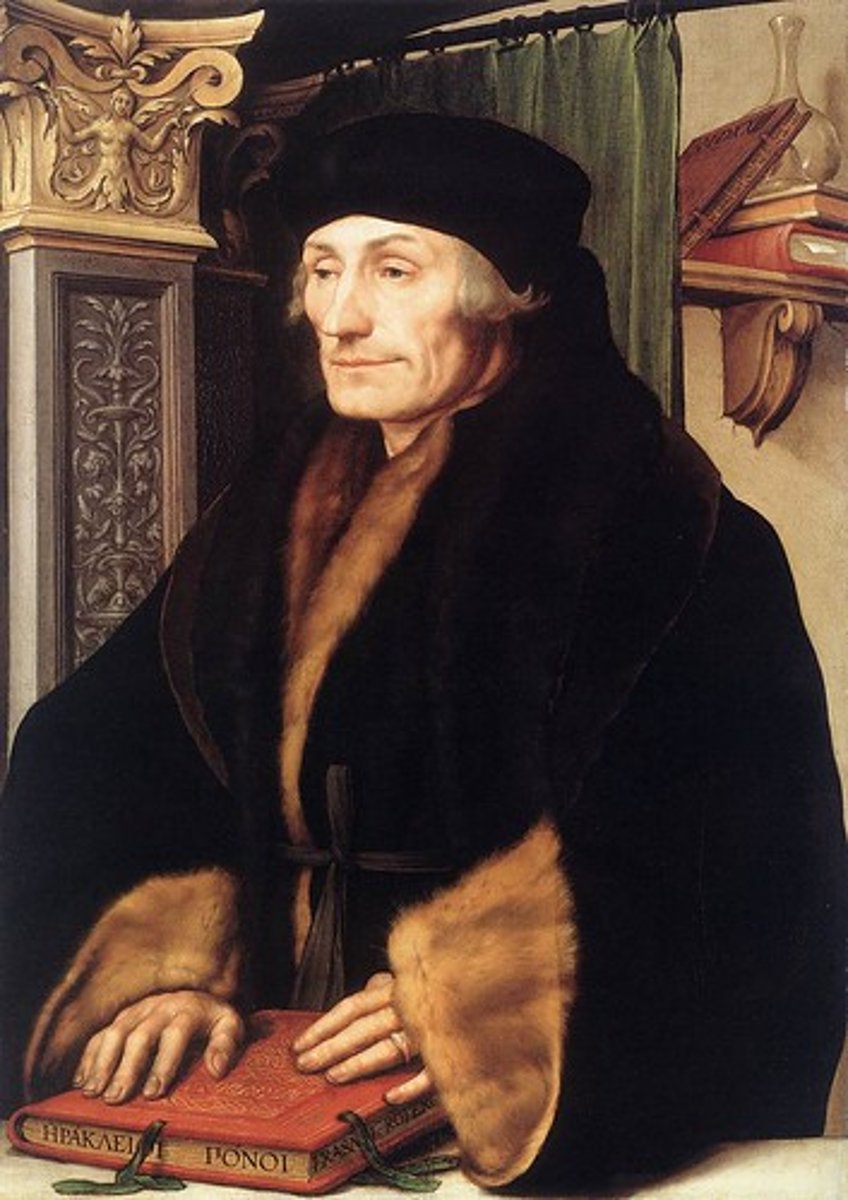
Erasmus
Renaissance. Most famous of Northern Humanists. Religious reformer. Prince of Humanists

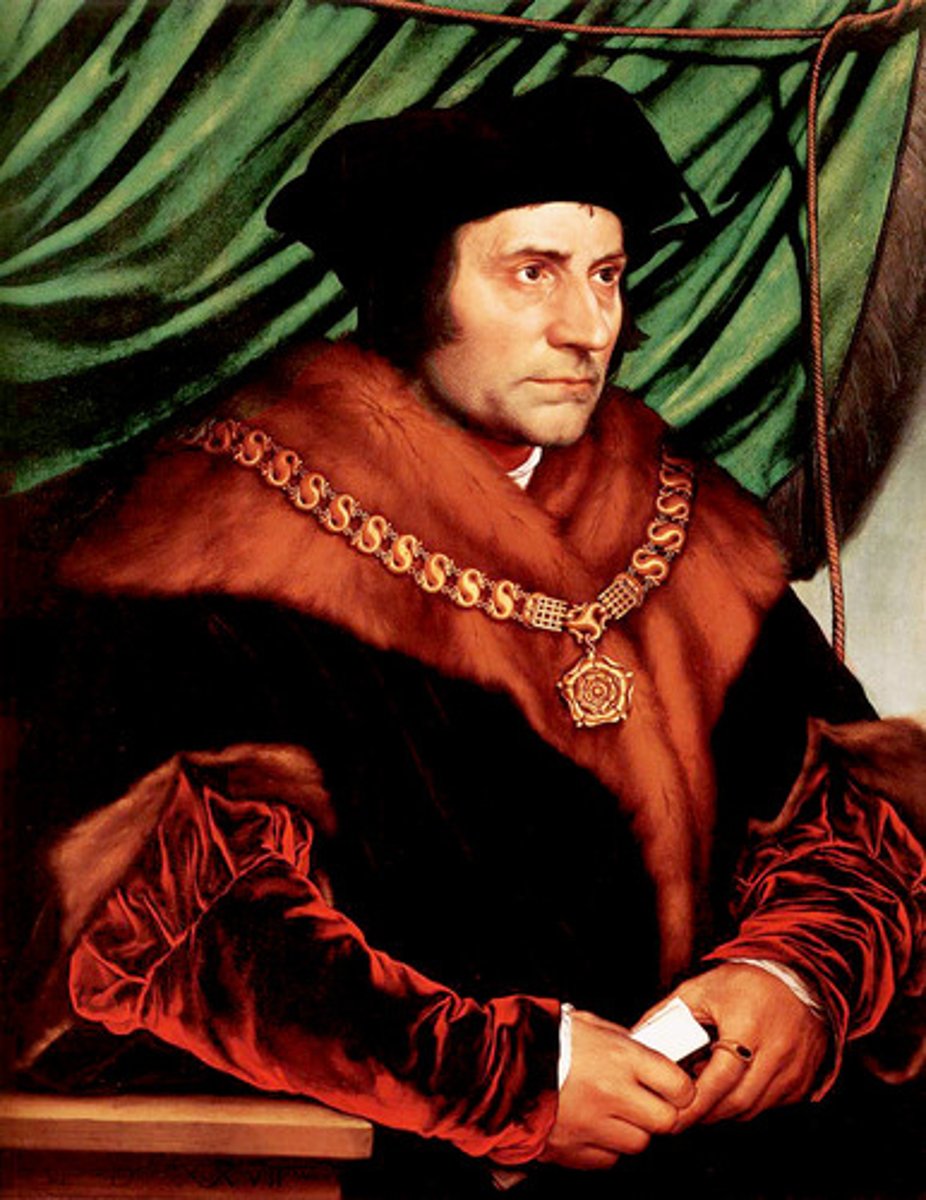
Thomas More
Renaissance. Most famouus English Humanists. Wrote Utopia critizing contemporary society.

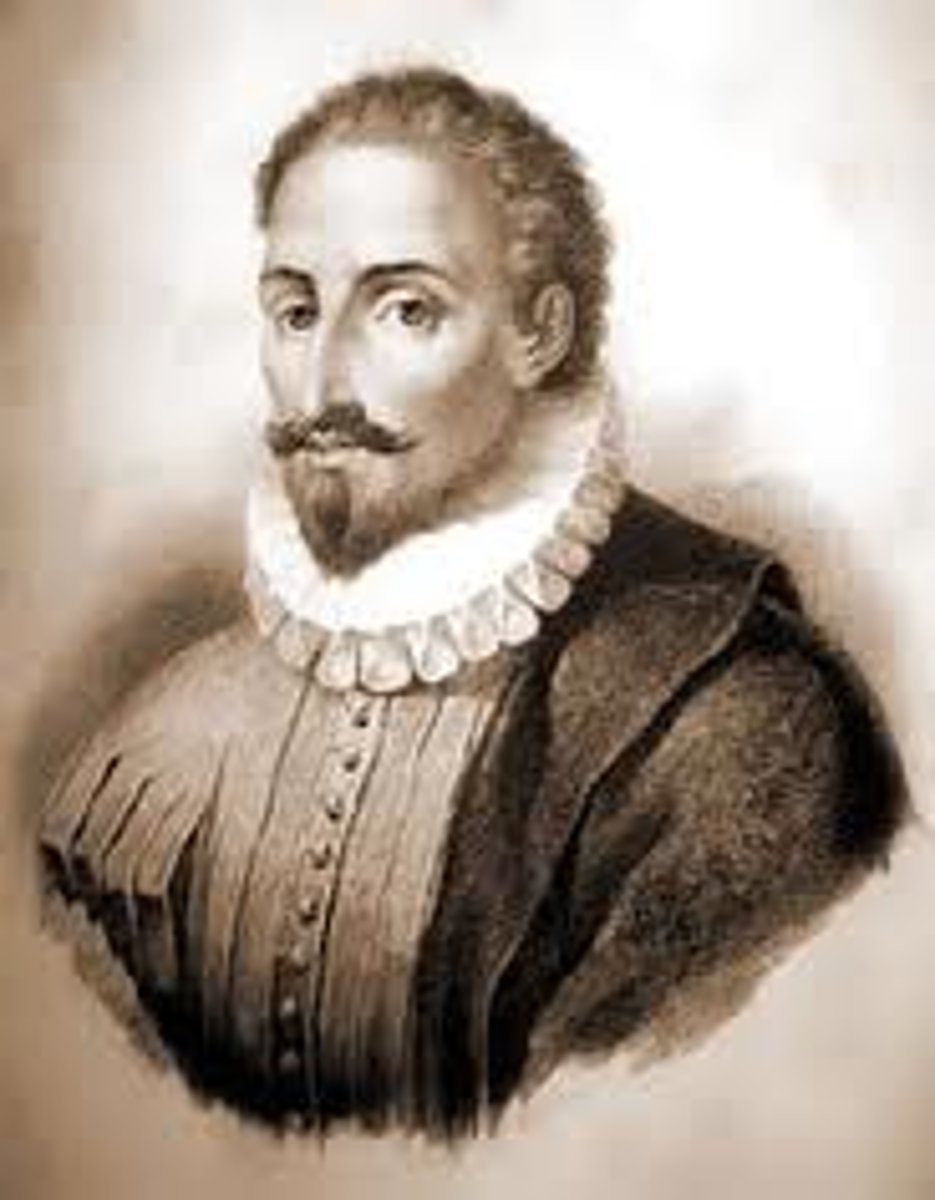
Cervantes
Renaissance. Spanish writer best remembered for 'Don Quixote' (1547-1616)

Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn
Religious Wars. Influential Dutch artist (1606-1669)
Van Eyck
Northern Renaissance. Artist. Arnolfini Wedding

Mary I queen of england
Religious wars. Undid alot of her brothers pro-protestent acts. Was extremly violent against protestents

Ignatius Loyola
Founded the Society of Jesus (jesuits), resisted the spread of Protestantism, Counter Reformation

Prince Henry the Navigator
Age of Discovery. Portugese prince who sponsered portuguese exploration of African coast

Vasco de Gama
Age of Discovery. Portuguese explorer and the first person to navigate a route to the East and India

Cortez and Pizarro
Age of Discovery. Spanish Conquistadors who conquered the Aztec and Incans

Philip II
King of Spain and Portugal and husband of Mary I

James I
Paths to Constitutionalism succeeded Elizabeth I; he alienated the British Parliament by claiming the divine right of kings and by raising taxes without permission. Problems with puritans (1566-1625)

Charles I
(1625-1649) Continued to raise taxes and alienate parliment and have Catholic sympathies. Didnt call parliment for a while, short parliement then long parliment then english civl war.

Oliver Cromwell
English general and statesman who led the parliamentary army in the English Civil War. established Puratin Republic

Charles II
Reset status quo. Had catholic sympathies. Tried to work with parliement

James II
..., English king from 1685-1688. He made enemies with Parliment when he displayrd his Catholic faith, appointed Catholics to offices within the government, and had a Catholic son who would be heir to the throne. He was depsoed in 1688

William and Mary
..., These people were the king and queen of England after the Glorious Revolution that recognized the supremacy of the English Parliament

Catherine de Medici
wife of Henry II, influenced her sons after the end of there father's rein. She placed an alliance with the ultra-Catholics (the militant Catholics), which was led by the second most powerful family in France, The Guise Family. She permitted the Guise Family their own independent army,which they would use to take out the other religions residing within the French Borders. This led to the civil wars in France and also the St. Bartholome's Day Massacre.

Henry IV (of Navarre)
French Bourbon king. A POLITIQUE. Converted from Calvinism to Catholicism to support his country. ("Paris is worth a Mass"). Proclaimed the EDICT OF NANTES. LAID FOUNDATION FOR FRANCE TO BECOME THE STRONGEST EUROPEAN POWER IN THE 17TH CENTURY

Cardinal Richelieu
This was the man who influenced the power of King Louis XIII the most and tried to make France an absolute monarchy

Jean-Baptiste Colbert
An economic advisor to Louis XIV; he supported mercantilism and tried to make France economically self-sufficient. Brought prosperity to France.

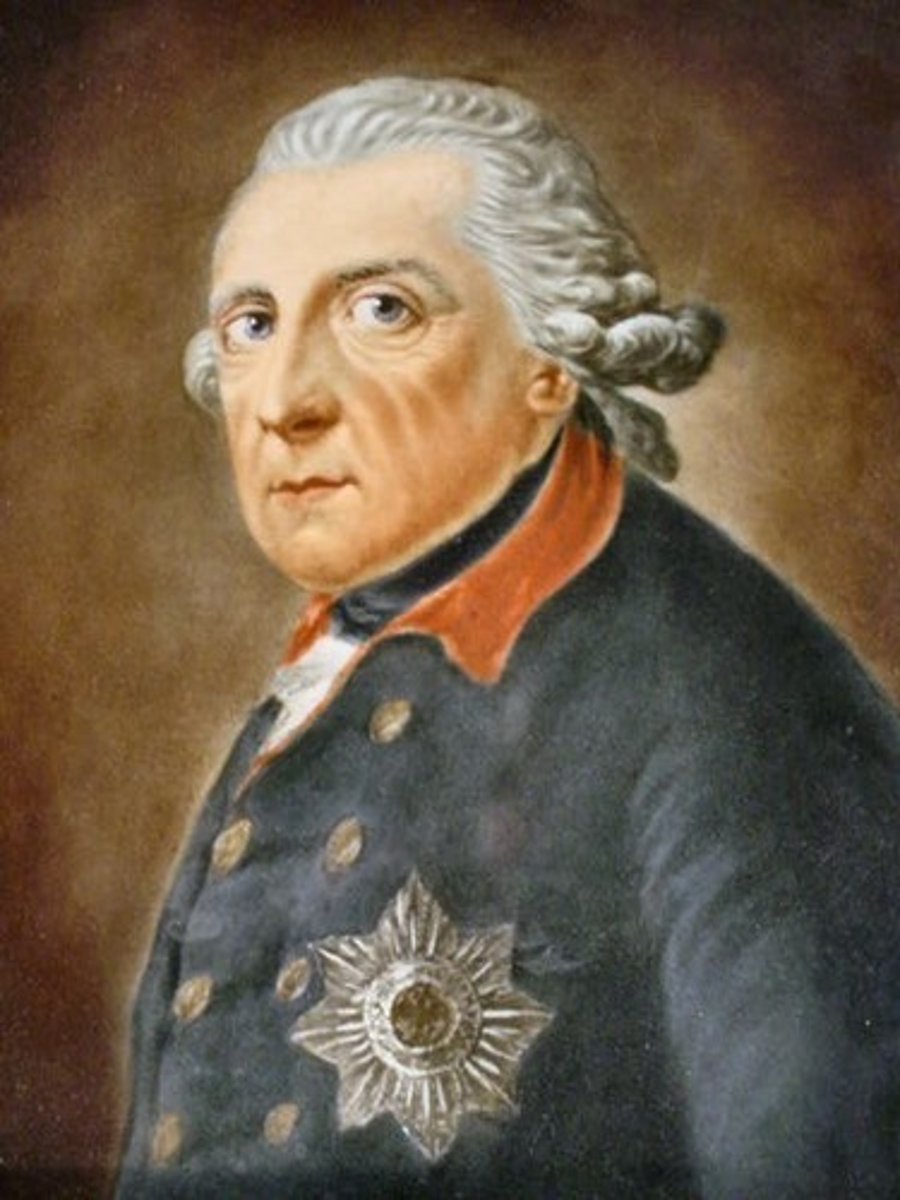
Fredrick II (the Great)
King of Prussia, fought the War of Austrian Succession and the Seven Years War against Maria Theresa

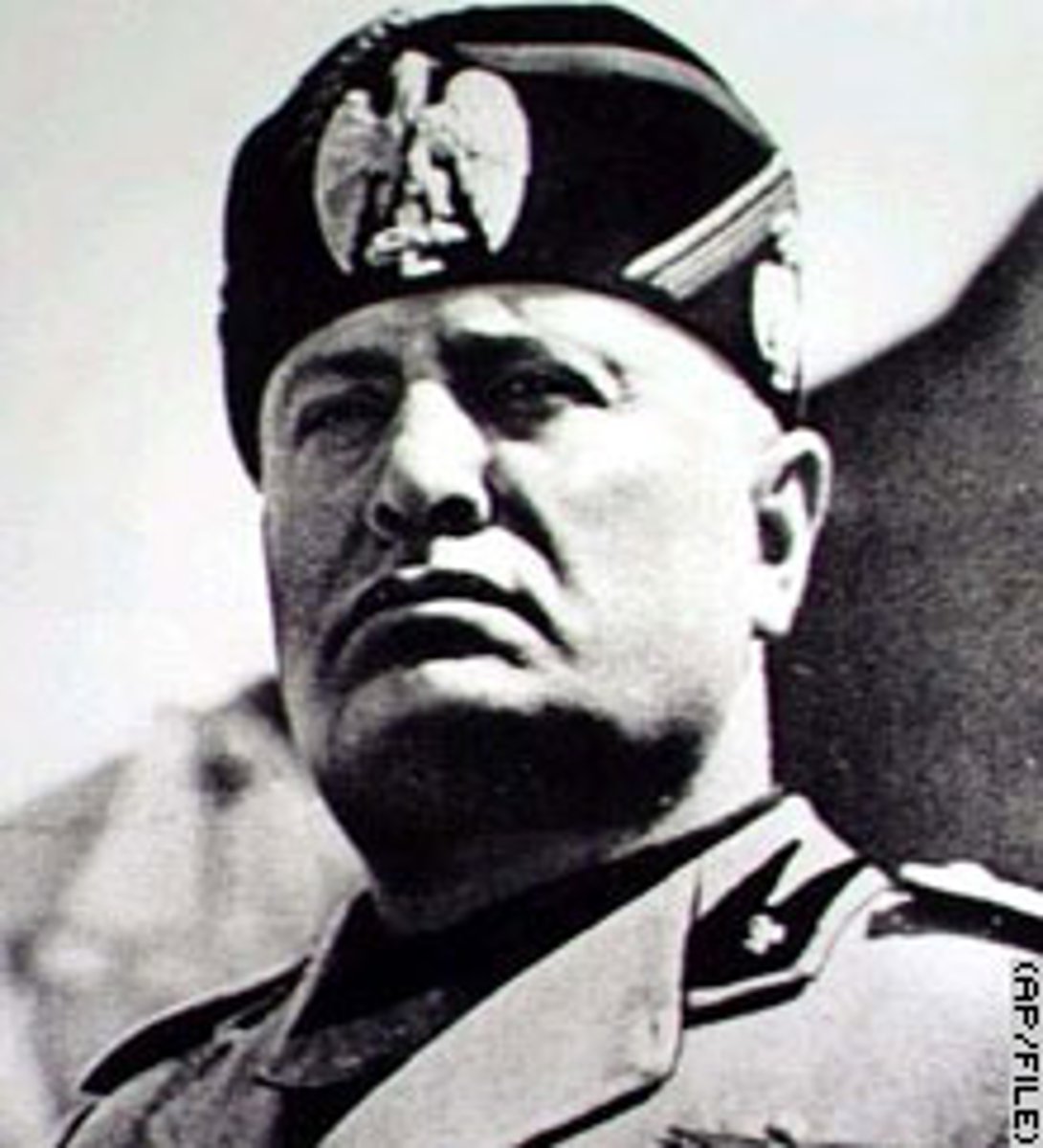
Benito Mussolini
Fascist dictator of Italy (1922-1943). He led Italy to conquer Ethiopia (1935), joined Germany in the Axis pact (1936), and allied Italy with Germany in World War II. He was overthrown in 1943 when the Allies invaded Italy. (p. 786)

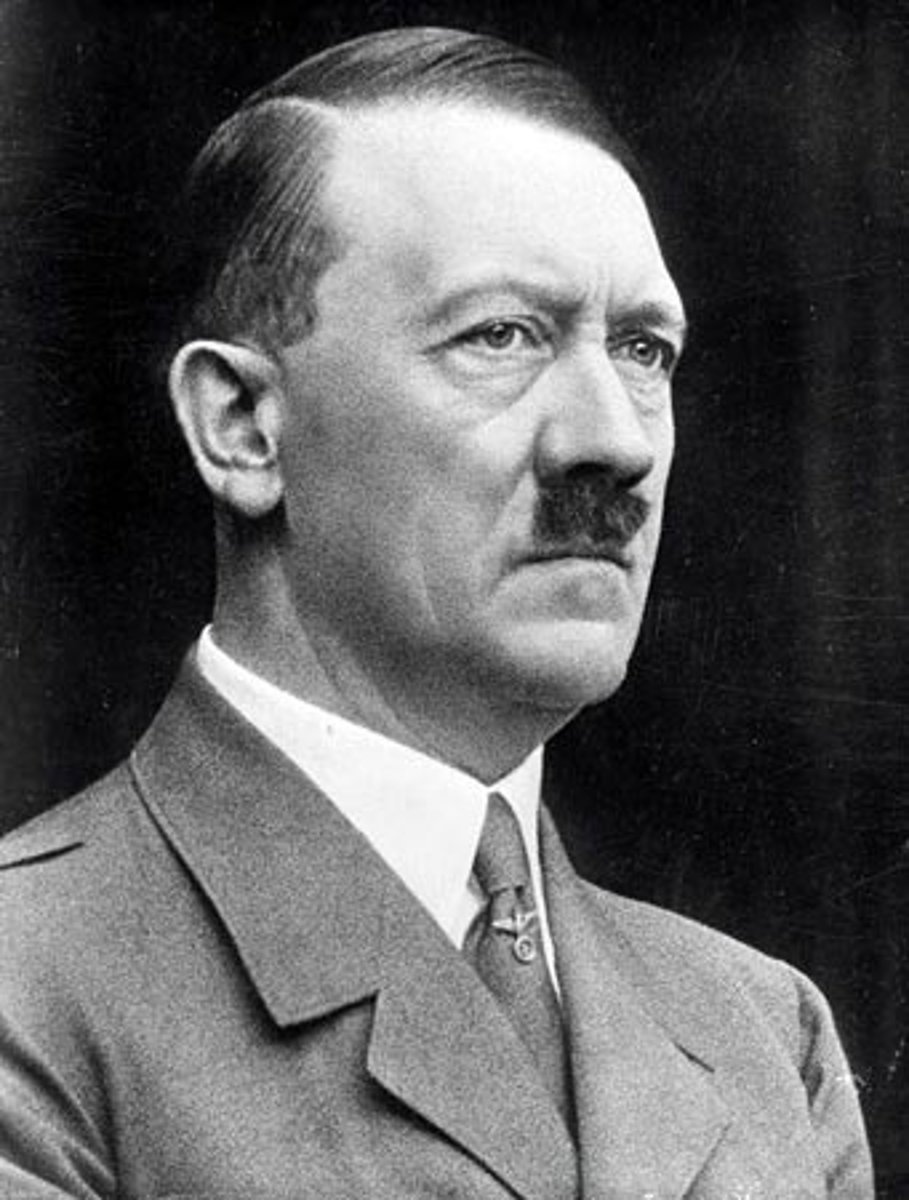
Adolf Hitler
This dictator was the leader of the Nazi Party. He believed that strong leadership was required to save Germanic society, which was at risk due to Jewish, socialist, democratic, and liberal forces.

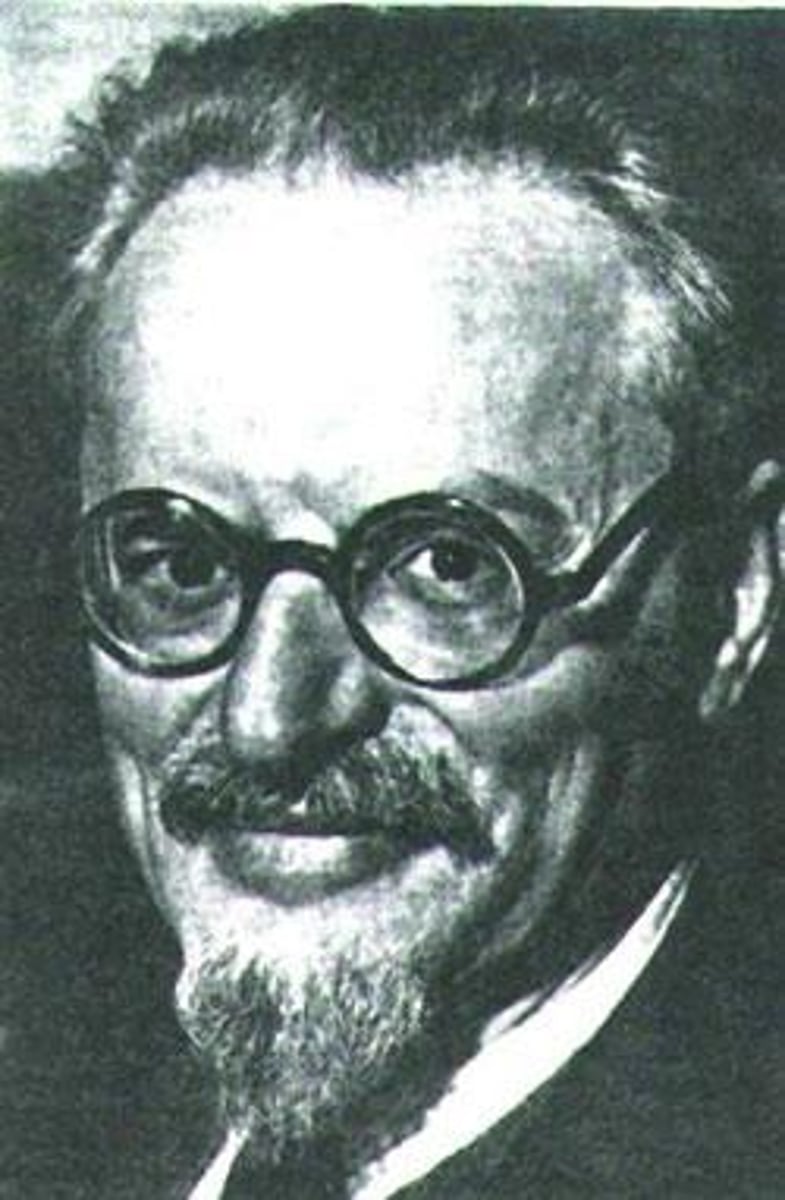
Leon Trotsky
Russian revolutionary intellectual and close adviser to Lenin. A leader of the Bolshevik Revolution (1917), he was later expelled from the Communist Party (1927) and banished (1929) for his opposition to the authoritarianism of Stalin

Stalin
Russian leader who succeeded Lenin as head of the Communist Party and created a totalitarian state by purging all opposition

Winston Churchhill
(1874-1965) Prime Minister of Great Britain during World War II.

Catherine the Great
An enlightened despot who ruled over Russia. She is responsible for many positive changes in Russia, as well as securing the country a warm water port.

William of Orange
Age of Religious wars. Led calvinist movement in the Netherlands. Helped unite Netherlands against the Spanish in hope for independence (Pacification of Ghent).

Brahe
He believed that other planets revolved around the Sun, but that the Sun and Moon revolved around the Earth.

Kepler
German astronomer who first stated laws of planetary motion (1571-1630)

Harvey
Circulation of blood

Pascal
French mathematician and philosopher and Jansenist

Thomas Hobbes
wrote "Leviathan" and believed people were naturally cruel, greedy, and selfish; he also believed only a powerful governemnt could keep an orderly society

Francis Bacon
(1561-1626) English politician, writer. Formalized the empirical method. Novum Organum. Inductive reasoning.

Descartes
"I Think, Therefore I am", (1596-1650) French philosopher, discovered analytical geometry. Saw Algebra and Geometry have a direct relationship. Reduced everything to spiritual or physical.

Montesquieu
(1689-1755) wrote 'Spirit of the Laws', said that no single set of political laws was applicable to all - depended on relationship and variables, supported division of government

Voltaire
French writer who was the embodiment of 18th century Enlightenment (1694-1778)
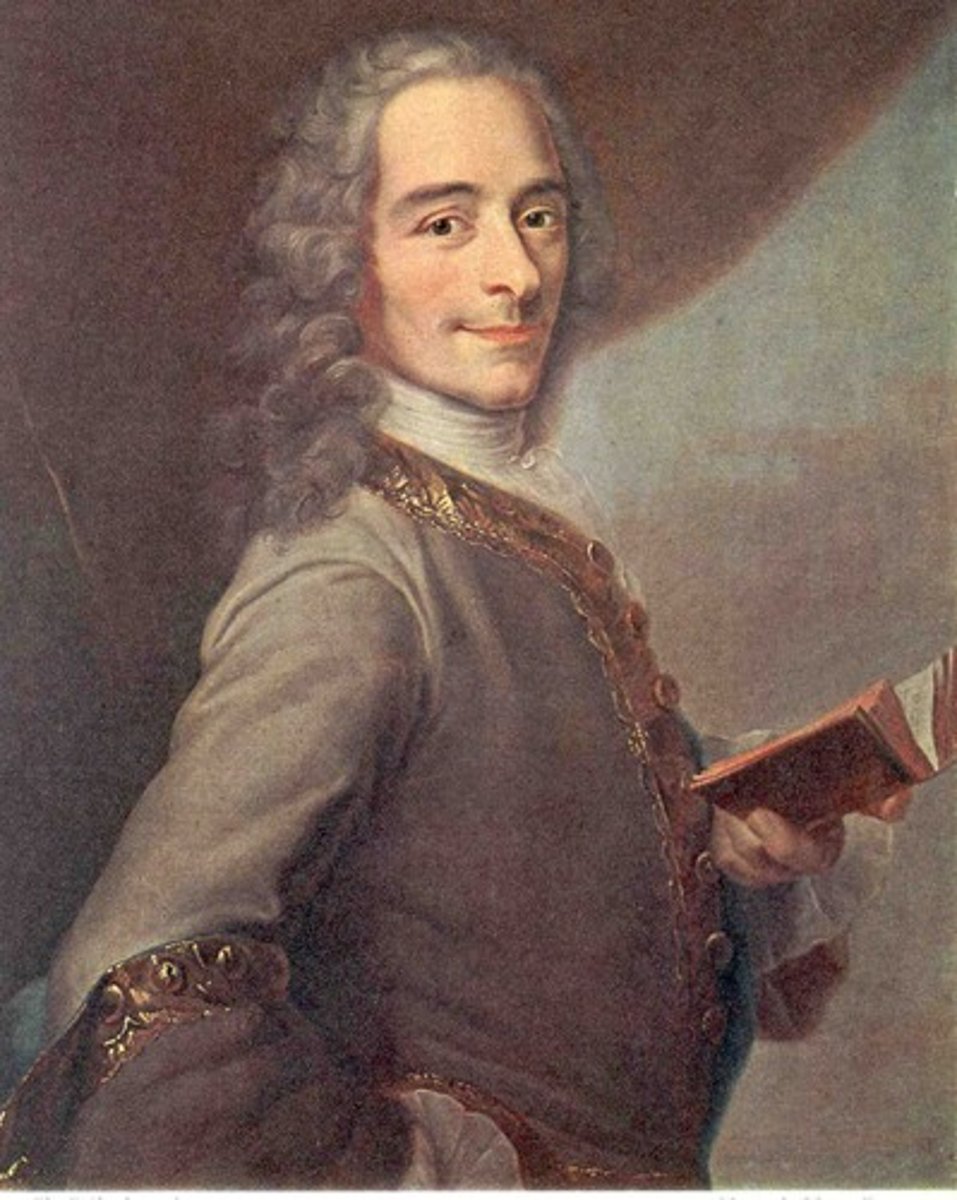

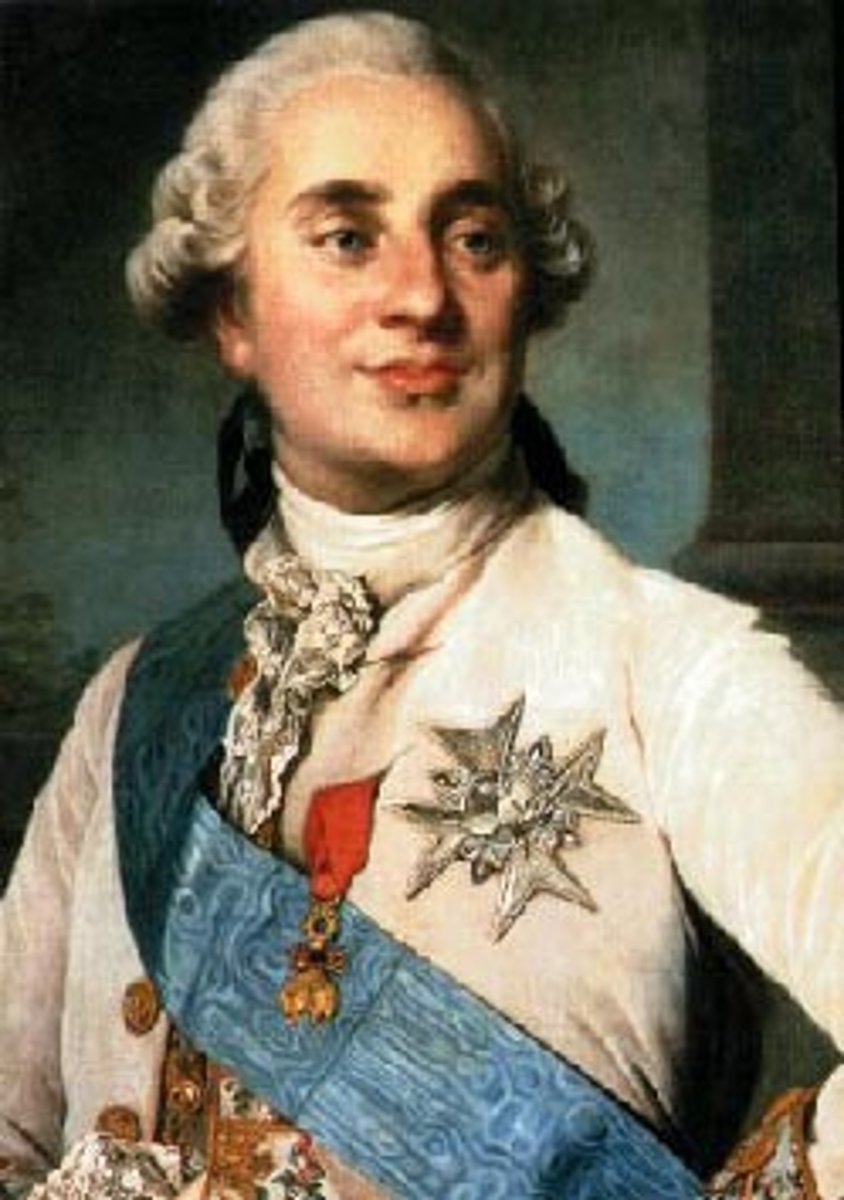
Louis XVI
- King of France (1774-1792). In 1789 he summoned the Estates-General, but he did not grant the reforms that were demanded and revolution followed. Louis and his queen, Marie Antoinette, were executed in 1793.

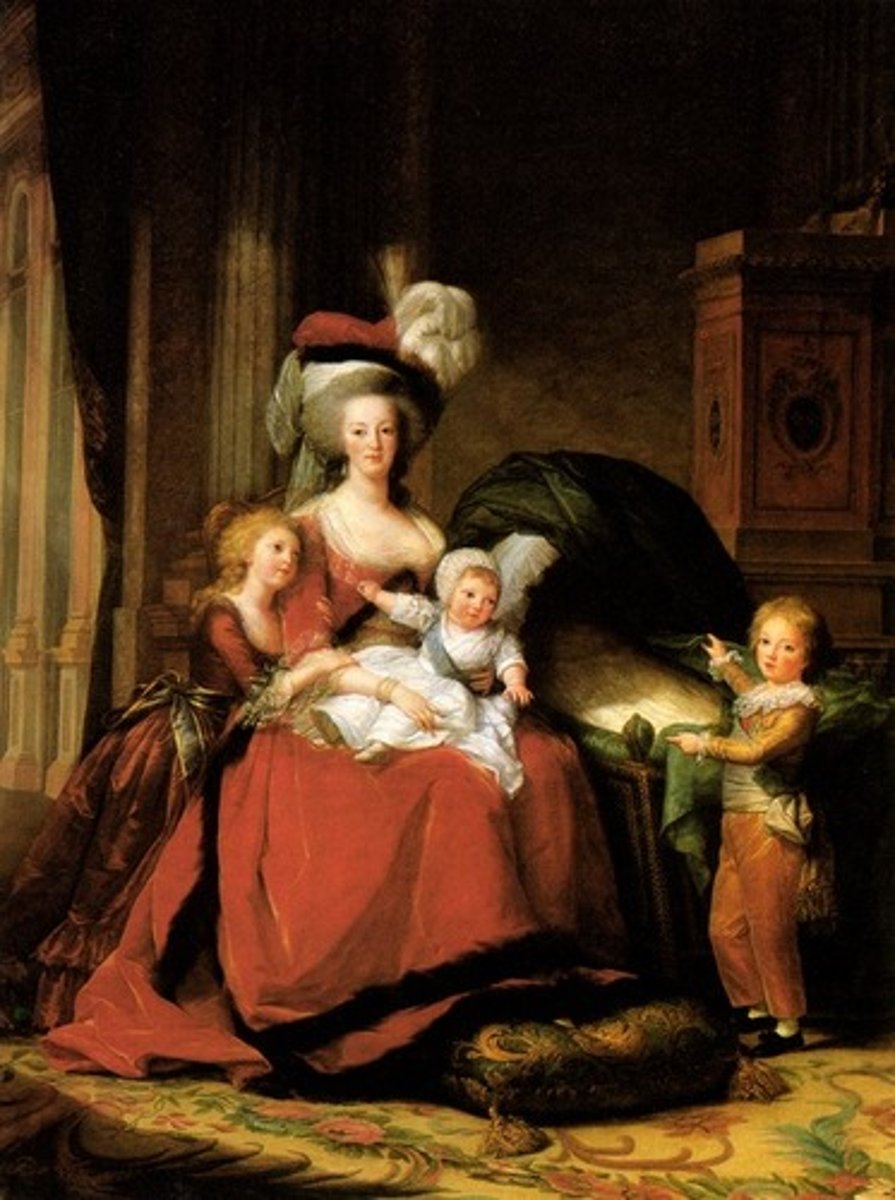
Marie Antoninette
Austrian royal who becomes Queen of France and killed during the Reign of Terror

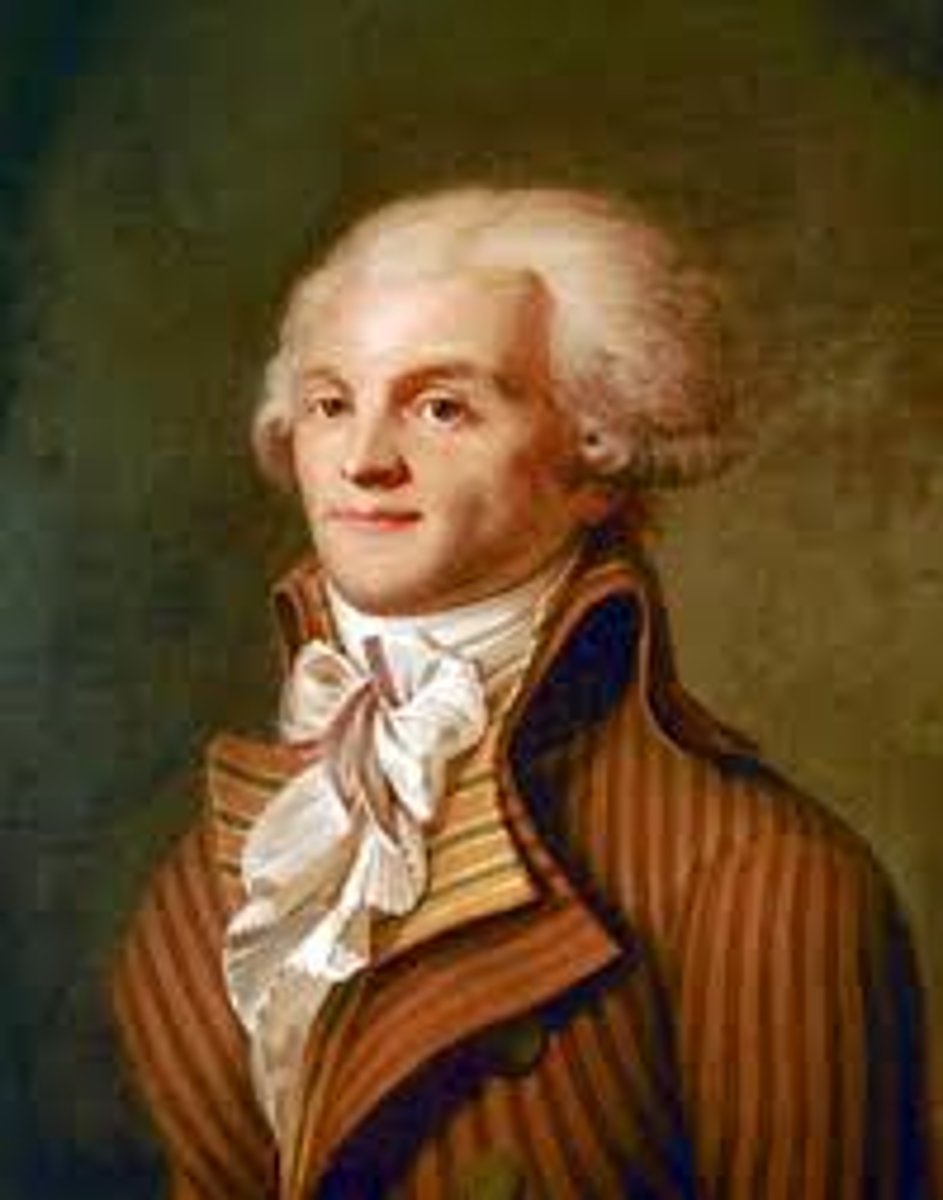
Robespierre
leader of the Committee of Public Safety who intiated the Reign of Terror

Wordsworth/Coleridge/Byron/Shelly/Neats
English Romatic Writers

Thomas Malthus
an English economist who argued that increases in population would outgrow increases in the means of subsistence (1766-1834)

David Ricardo
Principles of Political Economy (1817); "iron law of wages": rise of population means rise of amount of workers, which cause wages to fall below the subsistence level, resulting in misery and starvation. wages should not be raised
Garibaldi
United southern italy. Italian patriot whose conquest of Sicily and Naples led to the formation of the Italian state (1807-1882)

Mazzini
Giuseppe Mazzini was the first person that tried to unify all of Italy.His brand of democratic republicanism seemed too radical for the people. Austria smashed Mazzini's republicanism in 1848.

Count Cavor
prime minister of sardinia-piedmont, provoked austria into a war which led to the reunification of the northern italian states. United Italy

Alexander II
(r. 1855-1881) Emperor of Russia; advocated moderate reforms for Russia; emancipated the serfs; he was assassinated.

Captain Dreyfus
This french Jewish captain was falsely accused for spying for the Germans

William Gladstone
One of Britain's great liberal leaders, he favored expanding political rights for British men. He served several times during the mid to late 1800s.

Benjamin Disraeli
leading conservative political figure in Britain in the second half of the 19th century; took initiative of granting vote to working-class males in 1867;

Albert Einstein
physicist born in Germany who formulated the special theory of relativity and the general theory of relativity

Hebert Spencer
Social Darwinism, believed that if society was left alone it could correct it's own problems; it tends naturally toward health and ability

Archduke Francis Ferdinand
heir to the throne of Austria Hungary; assassinated .; sparked WWI

Tsar Nicholas II
Last Tsar of Russia and then end of the Romanov line. Was executed along with the rest of his family under the order of Lenin. In WWI ordered a partial mobilization against Austria-Hungary, forcing a chain reaction of mobilization.

Rousseau
French philosopher from 1712-1778 who believed that people are naturally good, but are corrupted by society. "Social Contract"

Kaiser Wilhelm (William)
Also known as Wilhelm II; he was the first king or kaiser of unified Germany.

Christine de Pisan
(1363-1434) Renassance Wrote the Renaissance's woman's survival manual ('The City of Ladies,' 1405), possibly Europe's first feminist.

Mikhail Gorbachev
Head of the Soviet Union from 1985 to 1991. Responsible for collapse of SU. Glasnot, Economic Perestroika, Army Perestroika. Did not put down 1989 revolutions

Olympe de Gouges
A proponent of democracy, she demanded the same rights for French women that French men were demanding for themselves. In her Declaration of the Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen (1791),

Emmeline Pankhurst
Leader of the WSPU (Women's Social and Political Union), which fought for women's suffrage in Britain.

Alexandra Kollontai
Russian revolutionary and diplomat, commissar for social welfare in 1918 and head of the women's section of the Communist Party

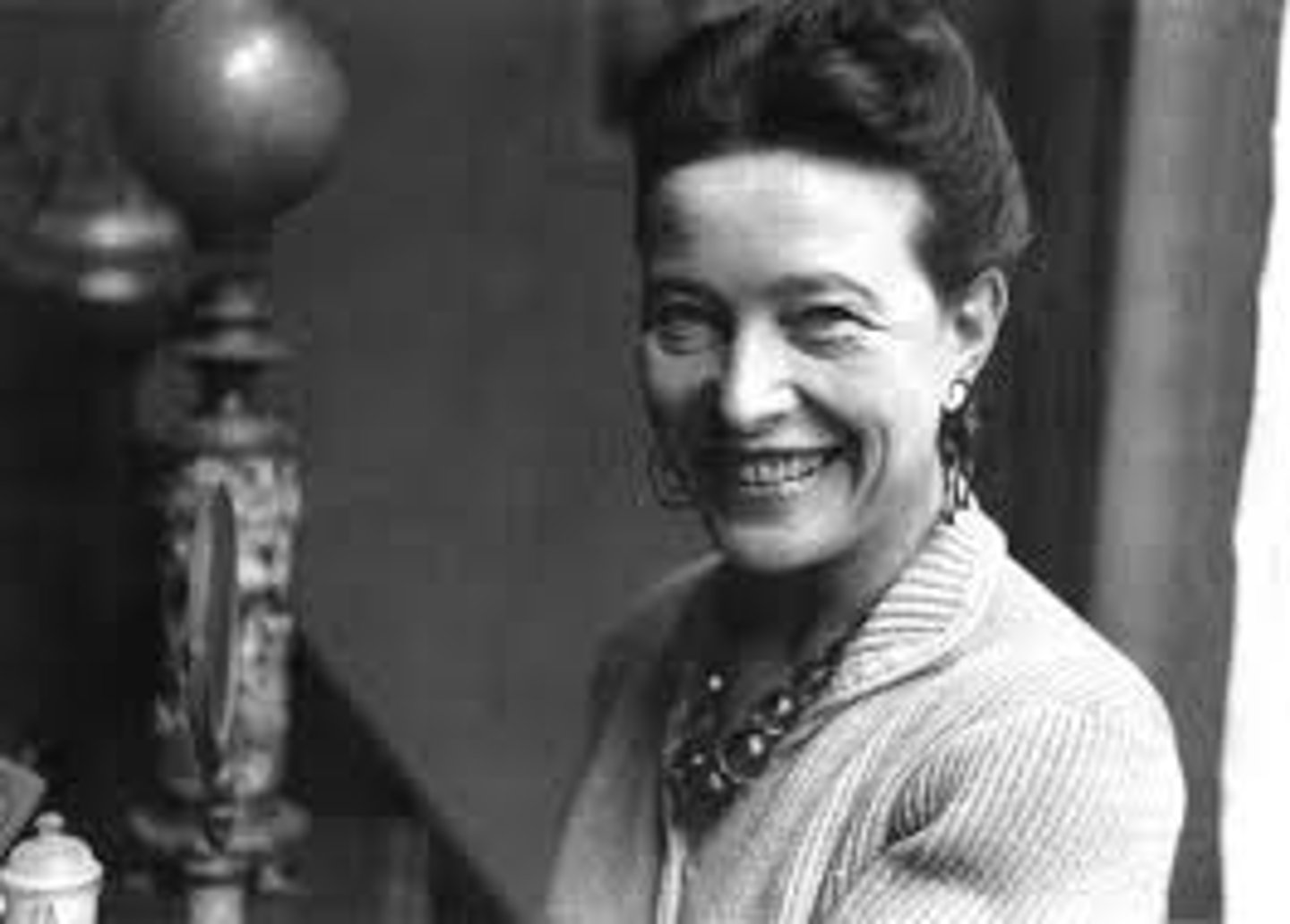
Simone de Beauvoir
French feminist and existentialist and novelist (1908-1986) Author of Second Sex
