Lecture 1: Nucleic acids and DNA replication
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
Rise per base
______ ________ _____ pair is a measure of the distance along the DNA helix axis, representing how much the DNA molecule extends in length with each added base pair.
h
rise per base pair aka __
3.4 A
Rise per base pair (h) = ____ ___
twist
"Number of base pairs per turn" refers to the count of specific DNA base pairs (adenine-thymine or guanine-cytosine) that make up one full 360-degree ____ of the DNA double helix
peak, peak
Number of base pairs per turn is amount of base pairs from ____ to ____
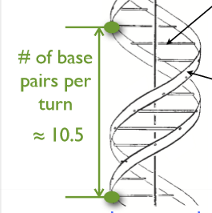
10.5
Number of base pairs per turn =
3 billion
Number of base pairs in human genome is ___ ______ in the form of one complete set of 23 of chromosomes
6
Most human cells are diploid so they contain twice as much DNA (~__ billion base pairs).
23, 46
"23 chromosomes" refers to the haploid number of chromosomes in a human cell, which is the number of chromosomes found in a gamete (sperm or egg cell), not the typical 46 found in most other body cells. Each human gamete contains __ single chromosomes (22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome), which combine with a gamete from the other parent to form a complete set of __ chromosomes (23 pairs) in a new individual.
alleles
Genes are expressed through the interaction of the two gene copies, called _____, which can have different outcomes depending on their relationship. In some cases, one dominant allele can completely mask a recessive one, but both are still present in the DNA. In other scenarios, different alleles can blend (incomplete dominance), or both can be expressed simultaneously to create distinct traits (codominance). The precise pattern of expression also depends on gene regulation, which uses factors to turn genes on or off, and epigenetic modifications that control gene accessibility without changing the DNA sequence.
two
Why Having Two Copies Matters
Having __ copies of each gene, one from each parent, provides a significant advantage:
Redundancy: If one copy of a gene is mutated and doesn't function properly, the other functional copy can often compensate, preventing disease or negative effects.
Genetic Diversity: This redundancy allows for greater genetic variation within a population, and it gives one gene copy the freedom to mutate and potentially develop new, beneficial functions.
protein
in most genes, both alleles are expressed. Each allele is transcribed into RNA and translated into ___. Dominance, co-dominance, and incomplete dominance don’t usually come from “switching one allele off,” but from how the gene products (proteins, RNAs, etc.) interact to create the phenotype.
functional, nonfunctional
1. Dominance (complete dominance)
Both alleles are expressed, but often one allele makes a ___ protein while the other makes a ______ protein (due to a mutation).
masks
1. Dominance (complete dominance)
If having just one functional copy is enough to produce the normal trait, the functional allele ___ (phenotypic effect not visible) the effect of the nonfunctional allele.
dominant
1. Dominance (complete dominance)
Example: In pea plants (Mendel’s peas), the purple-flower allele produces pigment enzyme, while the white-flower allele makes a defective enzyme. One working copy makes enough pigment, so the purple allele is ____.
visible
1. Dominance (complete dominance)
👉 Here, the “recessive” allele is expressed, but its protein doesn’t contribute to the __ phenotype.
strong
1. Dominance (complete dominance)
Masking doesn’t mean turning off or silencing an allele. It means the phenotype from one allele is ___ enough (or sufficient) that the phenotype of the other allele isn’t seen.
effect
2. Incomplete dominance
Both alleles produce protein, but one copy of the functional allele isn’t enough to reach the full ____.
intermediate
2. Incomplete dominance
The result is a phenotype _____ between the two homozygotes version (RR - ex full product vs rr - ex no product).
half
2. Incomplete dominance
Example: Red × White snapdragons → Pink heterozygotes. The red allele produces pigment enzyme, the white allele doesn’t, and a heterozygote only makes __ as much pigment. Half-pigment looks pink, not red.
functional
2. Incomplete dominance
👉 Both alleles are expressed, but the “dose” of _____ protein is lower, leading to blending.
Having two functional alleles = maximum product (strong trait), ex red snap dragon bc full pigment.
Having zero functional alleles = no product (weak or absent trait), ex white snap dragon, no pigment.
Having one functional allele = in-between level of product (intermediate trait), ex pink snap dragon bc half pigment.
distinct
3. Codominance
Both alleles produce ____ functional proteins that can be detected independently.
visible
3. Codominance
Example: Human ABO blood group. The IA allele makes one type of sugar on red blood cells, IB makes another, and i makes none. A person with IAIB expresses both sugars—so both alleles’ effects are __ at once.
👉 Here, the proteins don’t mask each other—they coexist.
allele, heterozygote, both
3. Codominance
✅ So when we say “the proteins don’t mask each other—they coexist,” we mean:
Each __ produces its own fully functional product.
Both products are visible in the ______.
The phenotype shows ____ traits at the same time, not one hidden, and not a blend.
20 A
diameter of DNA = ____ ___
sugar-phosphate backbone
The ___-_____ ______ of DNA is a structural framework formed by alternating deoxyribose (sugar) and phosphate groups, linked by covalent phosphodiester bonds.
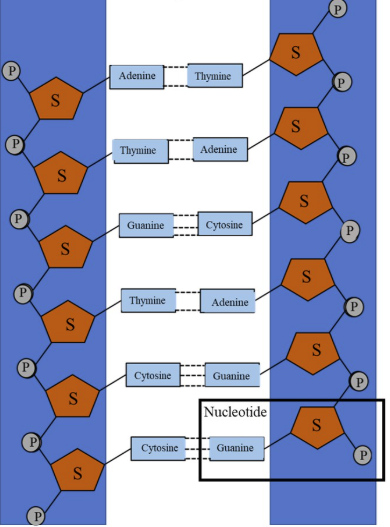
base pair
A DNA ___ _____ consists of two nitrogen-containing bases—adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), or cytosine (C)—held together by hydrogen bonds on opposite strands of the DNA molecule. These pairs, specifically A with T and G with C, form the "rungs" of the DNA double helix, providing the structure and carrying the genetic information within the DNA sequence.
right
B-form DNA is a ____-handed double helix
right
A right-handed double helix is the standard structure of DNA, where the two strands spiral around an axis in a clockwise direction. You can visualize it like a spiral staircase; as you move up or down, your ____ hand would follow the turns of the staircase.
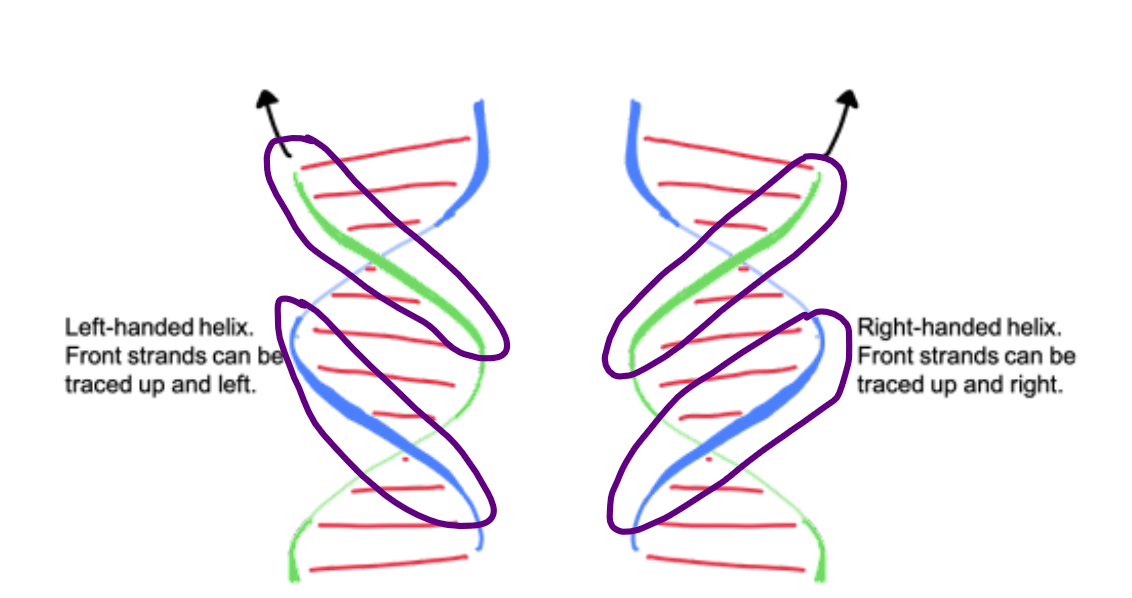
UP
Right handed helix: Front strands can be traced ___ and right
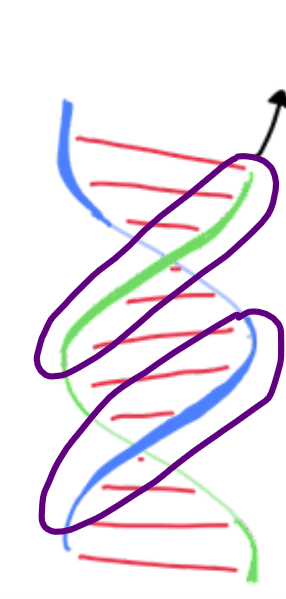
UP
Left handed helix: Front strands can be traced __ and left
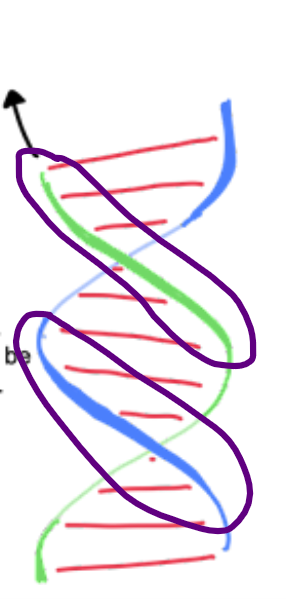
UP
Right hand rule: think of each DNA strand as a spiral staircase. Fingers point towards the path you take to move __.
curl
The "right-hand rule":
Point your right thumb along the axis of the helix (up or down). If your fingers ____ in the direction the helix twists, then it is a right-handed helix.
-10
1 A = 1 × 10^__ m
-9
1 nm = 1 × 10^__ m
-6
1 um = 1 × 10^__ m
-3
1 mm = 1 × 10^__ m
RNA-RNA, RNA-DNA
DNA and RNA conformations: B-form, A-form(___-____ or ___-___), Z-form
helix sense
the term _____ ______ refers to the direction of the twist in a helical or spiral structure. Helices can be either right-handed (clockwise) or left-handed (counter-clockwise).
right
Helix sense B-form:
right
Helix sense A-form:
left
Helix sense Z-form:
20 A
Diameter B-form: ~
26 A
Diameter A-form: ~
18 A
Diameter Z-form: ~
10.5
bp/turn B-form:
11
bp/turn A-form:
12
bp/turn Z-form:
3.4 A
rise/bp B-form:
2.6 A
rise/bp A-form:
3.7 A
rise/bp Z-form:
pucker
The sugar ring in a nucleic acid (like DNA or RNA) isn't perfectly flat. It's a 5-membered ring (a furanose ring) that can twist into various non-planar shapes, a distortion called _____.
endo
"____" means "inside" or "inward"
inner
In this context, the C2' carbon is displaced towards the endocyclic (____) side of the sugar ring, which is typically towards the 5' carbon
steric
sugar pucker Relieves ___ and electronic clashes: A flat, five-membered deoxyribose ring would force many atoms and their substituents to be eclipsed, or directly lined up with one another. This creates unfavorable steric and electronic repulsions between adjacent atoms, which an energetically unstable conformation. By becoming non-planar, the ring adopts a staggered conformation that significantly reduces these clashes, leading to a more stable, lower-energy conformation.
C-2’
sugar pucker conformation B-form: __-__ endo
C-3’
sugar pucker conformation A-form: _-_ endo
C-2’, C-3’
sugar pucker conformation Z-form: __-__ endo for C,T and ___-__ endo for A,G
glycosidic
A _______ bond is a type of ether bond that links a carbohydrate molecule (the glycone) to another group (the aglycone), which can be another sugar or a non-sugar molecule
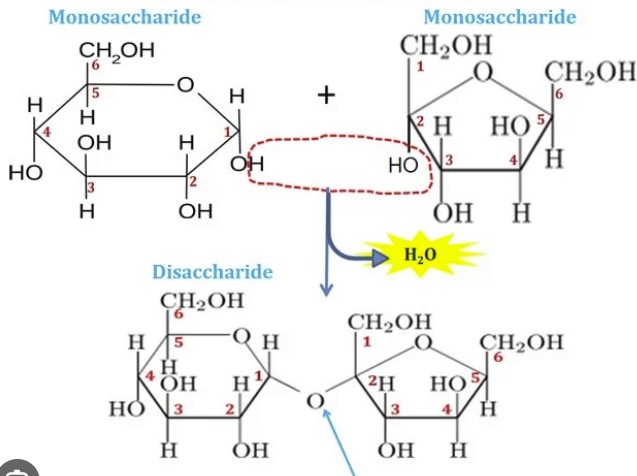
carbohydrate
In chemistry, a _____ is an organic compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with the general formula Cₙ(H₂O)ₙ.
ether
_____ bond: The oxygen atom is single-bonded to two carbon atoms, each part of an organic chain (like an alkyl or aryl group).
Formula:
.
The general formula is R−O−R′, where R and R′ represent these organic groups.
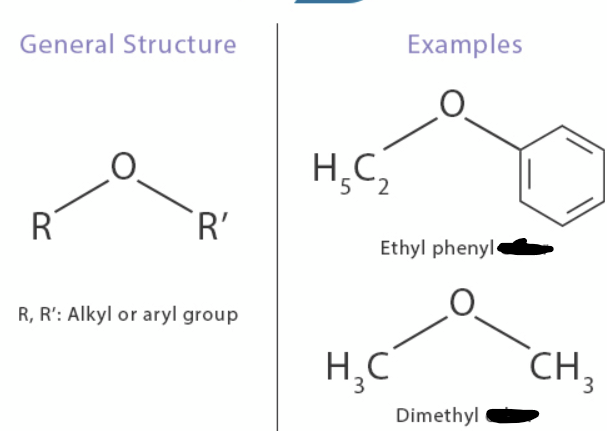
N
__-Glycosidic Bond:
.
This is the bond that connects the sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) to the nitrogenous base
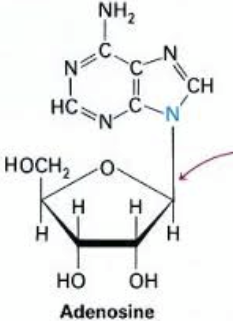
N-glycosidic
Anti and syn refer to the two distinct orientations, or conformations, of the base with respect to the sugar in a nucleoside, defined by rotation around the ____-______ bond
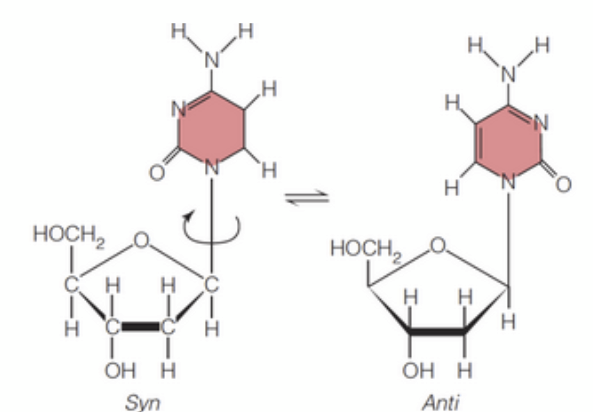
anti
The _____ conformation, where the base is rotated around the N-glycosidic bond away from the sugar's 5' carbon, is generally favored due to steric hindrance.
syn
The _____ conformation, where the base is rotated around the N-glycosidic toward away from the sugar's 5' carbon, is generally favored due to steric hindrance.
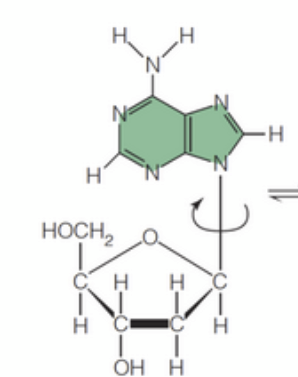
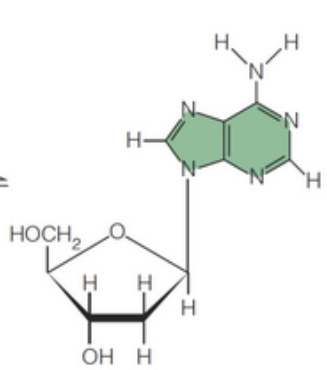
anti
Glycosyl bond formation B-form:
anti
Glycosyl bond formation A-form:
anti, syn
Glycosyl bond formation Z-form: __ for pyrimidines, _ for purines
physiological
B-form DNA
“Predominant form in DNA is +++”
The triple plus (+++) simply means: B-DNA is by far the most common/stable form under ____ conditions (normal hydration, moderate salt, neutral pH).
rare
A-form DNA
“–”
The minus sign means A-form is not normally favored.
It occurs mainly under dehydrating conditions (like crystallization in low humidity) or in RNA–DNA hybrids and double-stranded RNA.
So, the shorthand “–” = ____ under normal DNA conditions.
sequence, chemical
Z-form DNA
“+/– alternating G/C, C/G^Me”
The “+/–” means Z-DNA can form under special _____ or ____ conditions, not generally predominant.
G/C, methylated
Z-DNA is stabilized by alternating ___/__ sequences because they allow the required syn–anti alternation, especially when cytosine is ____ because the methyl group adds stacking and groove stabilization, making the left-handed helix energetically favorable
unfavorable
B-form RNA (–)
“–” here means B-form is rare or ______ in RNA.
Unlike DNA, RNA usually cannot adopt the B-form because of the 2′-OH group on ribose.
The 2′-OH causes steric hindrance that prevents the sugar from adopting the C2′-endo puckering required for B-DNA.
✅ So, in RNA, B-form is basically not physiologically relevant.
predominant, stable
2. A-form RNA (+++)
“+++” indicates A-form is the ______, ___ form in RNA.
RNA duplexes (double-stranded RNA, or RNA-DNA hybrids) almost always adopt A-form geometry.
The 2′-OH group favors C3′-endo sugar pucker, which stabilizes A-form over B-form.
unfavorable, condiitons
3. Z-form RNA (–)
“–” means Z-form is rare or energetically ____ in RNA.
While theoretically possible in GC-rich RNA sequences, the steric clash from 2′-OH destabilizes Z-RNA.
Z-RNA can appear transiently under special _______ (supercoiling, protein binding, or chemical modifications), but it is generally uncommon.
nucleotides
The building blocks of DNA and RNA =
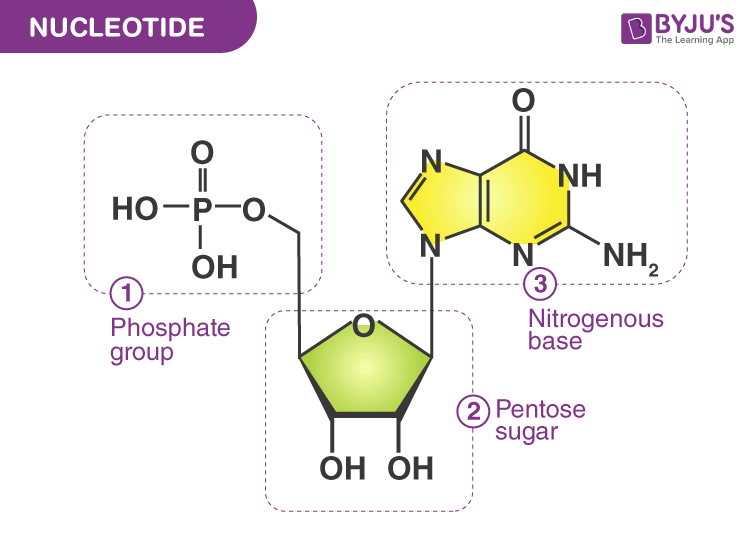
base, sugar, phosphate
A nucleotide comprises 3 components: a heterocyclic nucleobase (_____), a pentose _____, and a ____ group
nucleobase
heterocyclic ______
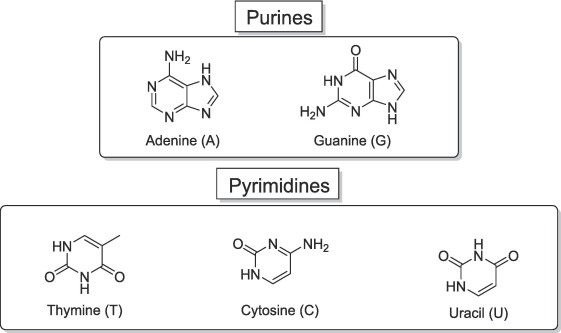
carbon
"Heterocyclic" describes a cyclic chemical compound containing at least one atom (a heteroatom) of an element other than ____ within its ring structure
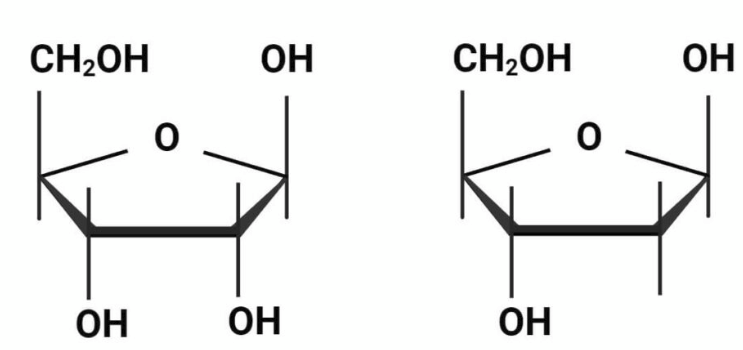
2’ OH, 2’H
Pentose sugars are five-carbon monosaccharides crucial for life, with the most well-known examples being ribose (____ ____) in RNA and deoxyribose (____ __) in DNA
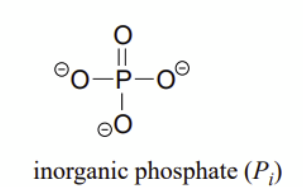
phosphate
____ group
nucleoside, nucleotide
A ____ consists of a nitrogenous base and a sugar, while a ____ also has one or more phosphate groups attached
sugar
In a nucleoside triphosphate, the three phosphate groups are designated alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ), with the alpha phosphate attached to the ____ molecule, the beta attached to the alpha, and the gamma attached to the beta
phosphate
It's called nucleoside triphosphate, not nucleotide triphosphate, because the term "nucleotide" already implies one or more ______ groups are attached to a nucleoside
pentose
Nucleotides: The C and N atoms in the bases are numbered. The C atoms in the _____ are also numbered with a prime (e.g. 5’ and 3’)
DNA, RNA
Bases of ____ could be A, C, G or T; bases of ______ could be A, C, G or U
deoxyribose, ribose
In DNA, the pentose is _______; but in RNA it is a ___ which has a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to the 2’ carbon
phosphodiester
_______ bonds link nucleotides into a large bio molecule called nucleic acid
5’, 3’
A phosphodiester bond is a covalent bond that links a phosphate group to the __ carbon of the sugar in one nucleotide and to the __ carbon of the sugar in the next nucleotide, creating the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA and RNA
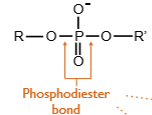
carboxylic acid, alcohol
An ester bond, or ester linkage, is a type of chemical bond (typically -COO-) formed between a _____ ___ and an ____, with a water molecule released in the process
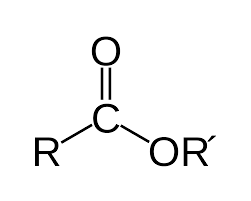
DNA
The _____ (or nucleotide sequence) can be represented as follows:
5’-AATA-3’
5’-pAATAOH-3’
AATA
5’, 3’
By convention, ssDNA is written in the ____ to (—>) __ direction from left to right
ds
__DNA may be written as:
5’-GATC-3’
3’-CTAG-5’
C1’
the covalent bond the joins a base to the __ is a glycosidic bond
negative, neutral, ionization, -1
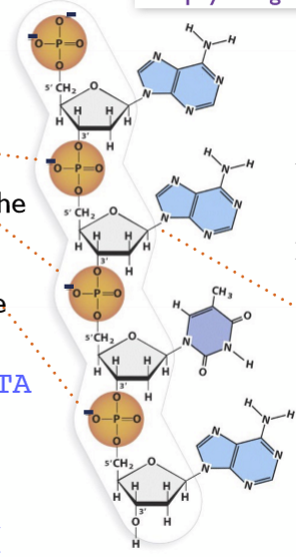
What is the net charge of this DNA molecule in physiological pH?
From the image, we can see:
Phosphate groups (PO₄²⁻)
Each phosphate in the backbone has a ____ charge at physiological pH (~7.4).
There are 4 phosphate groups in this fragment.
Bases
Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T)
At physiological pH, the nucleobases are essentially ____ (only very tiny fraction may protonate/deprotonate, negligible for net charge).
Sugar hydroxyls (deoxyribose)
No _____ at physiological pH.
Step 2: Count negative charges
Number of phosphates = 4 → each contributes __ at pH 7.4.
Net charge = -4
shorter
Sugar pucker conformation: C-2’ endo versus C-3’ endo:
In the A-from, the distance between the two phosphate groups on the 5’ and 3’ positions is ___ than that of B-form.
geometry, compact
Sugar pucker conformation: C-2’ endo versus C-3’ endo:
In the A-from, the distance between the two phosphate groups on the 5’ and 3’ positions is shorter than that of B-form. Therefore, A-form has a different helical _____ and a more __ structure
7.0 A
Distance between phosphates in B-form backbone:
5.9 A
Distance between phosphates in A-form backbone:
sp3
B form, pentose 2' is puckered (sticks out of plane of pentagon)
Hybridization state of C is __, angle btwn two bonds is 109.5
Inner angle of pentagon is 108, which is smaller than 109.5 so won't fit inside pentagon perfectly so something needs to give to accommodate angle and relieve stress