Organization of the Human Body
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Anatomy
Branch of biology concerned with bodily structure of organisms
Physiology
Branch of biology concerned with normal functions of organisms
Levels of Structural Organization
Chemical, Cellular, Tissue, Organ, Organ Systems, Organism
Chemical
Atoms & Molecules
Cellular
Cells (specialized structures/functions)
Tissues
Groups of cells and materials that perform specific functions
Types of Tissues
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous
Organ
Types of tissues joined together to perform specific functions, recognizable shape
Organ Systems
Related organs with a common purpose
Organism
Living individual, levels from chemical to systems working as one
Basic Life Processes
Metabolism, Responsiveness, Movement, Growth, Differentiation, Reproduction
Metabolism
Sum of all chemical processes that occur in the body
Anabolism
Buildup of substances (Glycogenesis or protein synthesis)
Catabolism
Breakdown of substances (Glycogenolysis or proteolysis)
Responsiveness
Ability to detect and respond to changes (Nerve cells generate electrical signals)
Movement
As a whole, individual organs, single cells, structures in cells
Growth
Size of organism, cells, # of cells
Differentiation
Unspecialized to specialized (stem cells, RBC)
Reproduction
Formation of new cells or organism
Homeostasis
State of balance in the body with respect to functions and composition of fluids and tissues
An organism is said to be in homeostasis when its internal
environment:
Optimal concentrations of nutrients, gases, ions and water, maintains optimal temperature, maintains optimal pressure for the health of the cells
Internal Feedback System (maintains homeostasis)
Circular sequence of events where info about the status of a situation is reported to a central control unit
Components of Feedback Loop
Receptor, Control Centre, Effector
Receptor
Senses the change in the variable
Control Centre
Compare value to reference point, provides response
Effector
Makes changes to the variable
Negative Feedback Loop
Response where the stimulus makes changes that reverse/reduce the stimulus
Examples of Negative Feedback Loop
Temperature receptors feel cold - stimulates shivering
High BP - stimulates vasodilation
Positive Feedback Loop
Stimulus causes an increase in the original stimulus. Does NOT maintain homeostasis
Examples of Positive Feedback Loop
Childbirth - hormones released during labour increase contractions
Clotting - Platelets gather and release an enzyme that promotes platelet aggression
Stress
Any stimulus that creates an imbalances in the internal environment. Can lead to dysfunction.
Supine
Prone
Lateral Recumbent (L/R)
Fowler’s
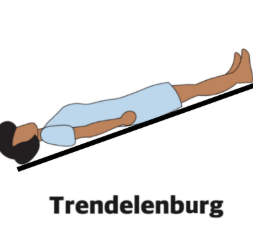
Trendelenburg
Regional Names
Head (cephalic), Neck (cervical), Trunk, Upper Extremities, Lower Extremities
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
RUQ, LUQ, RLQ, LLQ
Abdominopelvic Regions
Right & Left Hypochondriac, Epigastric, Right & Left Lumbar, Umbilical, Right & Left Inguinal (Iliac), Hypogastric (Pubic)
Anterior
Near the front of the body
Interior
Near the back of the body
Superior
Near the head
Inferior
Away from the head
Medial
Nearer to the midline
Lateral
Farther from the midline
Ipsilateral
On the same side of the body
Contralateral
On the opposite of the body
Intermediate
Between two structures
Proximal
Nearer to the origin of structure
Distal
Farther from the origin of structure
Superficial
Towards or on the surface of the body
Deep
Away from the surface of the body
Anatomical Position
Facing forwards, palms forwards
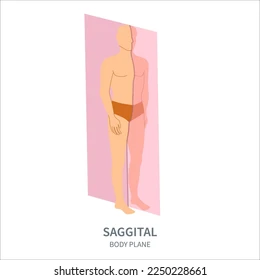
Midsagittal
Through the midline
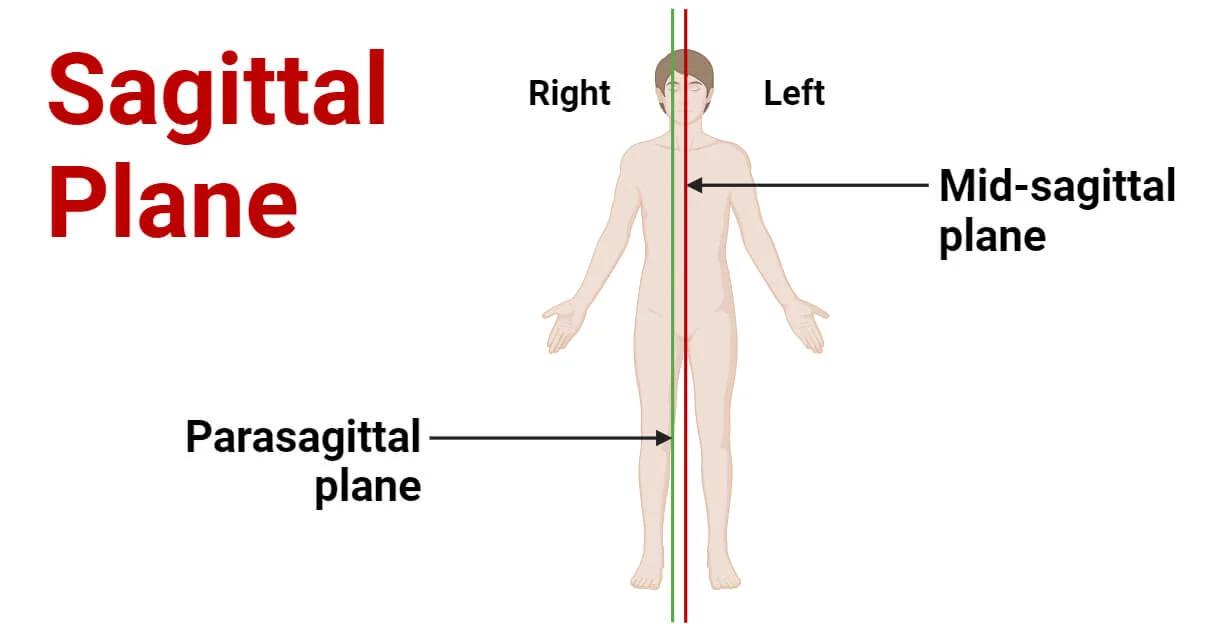
Parasagittal
Slightly left or right from midsagittal
Frontal
Front & Back
Transverse
Top & Bottom
Oblique
Any angle
Body Cavities
Spaces within the body that protect and support internal structures (Cranial, Vertebral, Thoracic, Abdomino-Pelvic)
Cranial Cavity
Formed by cranial bones, contains brain
Vertebral Cavity
Formed by vertebral column, contains spinal cord and spinal nerves
Pleural Cavity
Fluid-filled space surrounding lungs and chest wall
Pericardial Cavity
Fluid-filled space surrounding heart
Mediastinum
Region surrounding heart between lungs
Abdominal Cavity
Contains digestive organs
Pelvic Cavity
Contains reproductive organs and rectum
Retroperitoneal Organs
Behind/outside peritoneum membrane, contains urinary organs
Serous Membrane
Double layered membrane with serous fluid
Visceral Layer
Attached to “viscera” (internal organs)
Parietal Layer
Attached to wall of the cavity
Pleural Membrane
Serous membrane of pleural cavity, lubricates lungs against wall of pleural cavity, air/blood can get trapped
Pericardium
Fibrous sac that encloses the heart, has outer fibrous layer and inner double layered serous membrane
Peritoreum
Serious membrane of abdominal cavity
Parts of Integumentary System
Skin, hair, nails, sweat/oil glands
Purpose of Integumentary System
Protection, temperature regulation, elimination of waste, makes vitamin D, sensory
Parts of Skeletal System
Bones, joints, cartilage
Purpose of Skeletal System
Protection, support, movement (muscles), produce RBC, stores minerals/lipids
Parts of Muscular System
Skeletal, smooth, cardiac muscle
Purpose of Muscular System
Produces movement, stabilizes body position, circulates blood/fluid, generates heat
Parts of Nervous System
Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory tissues
Purpose of Nervous System
Generates action potential, regulates body activities, feedback systems
Parts of Endocrine System
Hormone producing glands; pituitary, hypothalamus, adrenal, thyroid
Purpose of Endocrine System
Regulates body activities by releasing hormones (chemical messengers transported in the blood to targeted tissues)
Parts of Respiratory System
Lungs, trachea, bronchi, pharynx
Purpose of Respiratory System
Gas exchange between environment and blood cells CO2/O2, helps regulate acid base balance
Parts of Cardiovascular System
Heart, blood, vessels
Purpose of Cardiovascular System
Pumps blood to all tissues in the body, carries O2 and nutrients to cells, transports cellular waste for elimination, regulation of acid base, temperature and water content
Parts of Digestive/Gastrointestinal (GI) System
Esophagus, stomach, intestines, pancreas, gallbladder, salivary glands
Purpose of Digestive/Gastrointestinal (GI) System
Physical and chemical breakdown of food, absorbs nutrients, eliminates waste
Parts of Urinary/Renal System
Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra
Purpose of Urinary/Renal System
Produces, stores, eliminates waste, regulates blood volume, chemical composition, acid base balance, body mineral balance, production of blood cells
Parts of Lymphatic & Immune System
Lymphatic fluids, lymph vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils
Purpose of Lymphatic & Immune System
Returns proteins and fluids to blood, carries lipids from GI tract to blood, produces lymphocytes that protect against disease
Parts of Reproductive System
Gonads, testes, ovaries, uterus, vagina, penis
Purpose of Reproductive System
Production of sperm and eggs, reproduction of a new organism