1. Introduction to Intelligence
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are implicit theories of intelligence?
the layperson’s definition
drive the way in which people perceive and evaluate their own intelligence and that of others
What was the procedure of Steinberg et al. (1981)? first and second experiment. What were the conclusions
asked 3 groups of people (those in college library, waiting in supermarket, waiting for a train) to list behaviour characteristics of intelligence, academic intelligence, everyday intelligence, unintelligence
second group rated behaviour lists from experiment 1 on how well they reflected aspects of intelligence
from both experiments: 3 dimensions of intelligence
What are the three dimensions of intelligence identified through sternbergs 2 experiments
practical problem solving
verbal ability
social competence
What the aspects of practical problem solving identified in sternbergs initial 2 studies?
analyse
reasoned decision making
flexible thinking
effective solutions
What the aspects of verbal ability identified in sternbergs initial 2 studies?
good vocabulary
confident use
communicates effectively
good reading comprehension
What the aspects of social competence identified in sternbergs initial 2 studies?
good knowledge of themselves and others
can use this knowledge to successfully navigate relationships
good interpersonal skills
good balance of independence and interdependence
What are the 6 dimensions of intelligence identified in sternbergs later research (1985)?
practical problem solving
verbal ability
intellectual balance and integration (making connections between topics and concepts, identify differences)
goal orientation and attainment
contextual intelligence (able to learn from experiences, understand and interpret current environment)
fluid thought
What are the main differences in the values associated with intelligence between western and non-western cultures
western cultures - value speed of processing and verbalising solutions (skills relating to individual cognition)
non-western - value consideration of family/friends, culture/spiritual needs and how wise people have succeeded previously (more focus on social, cultural, historical aspects)
What might cultural variations be linked with/ a result of?
linked with which aspects of intelligence are most values within a culture
often a result of deeply rooted philosophies
individual differences, sub-cultural difference
How are cultural variation in implicit theories of intelligence seen in chinese culture?
chinese value responsiveness to change, honouring parents, doing the right thing, understanding of self and surrounding world
reasoning, social skills, numeracy and memory are important, but less important than other elements
What did Yang and Sternberg find were the 5 aspects of intelligence that emerged in a Taiwanese population?
first group gave descriptors and second group rated
what emerged:
general cognitive factor intelligence
interpersonal intelligence (relating to others)
intrapersonal intelligence
(last 4 much more focussed on social interactions than western studies)
What is the cultural variation in implicit theories of intelligence seen in india?
thinking, judgement, decision making; gelled by harmony of thought resulting from self-awareness and consciousness
also appreciation of others, interest in others, politeness, modesty
What are the key aspects of theories of intelligence associated with western cultures?
individualistic: focus on the primacy of the individual
speed/ depth of mental processing
verbal abilities
emphasis on learning
good memory
good cognitive skills
What are the key aspects of theories of intelligence associated with eastern cultures?
collectivist; focus on collective nature of social obligation
similar ideas to western cultures but they apply not just to the individual, extending to social, historical and spiritual aspects of everyday life
How might intelligence be described in a 6 month old?
recognise people and object
signs of motor coordination
How might intelligence be described in a 2 year old?
verbal ability
ability to learn
awareness of people and environment
How might intelligence be described in a 10 year old?
verbal ability
problem solving
reasoning
learning
how might intelligence be described as an adult?
problem solving
verbal ability
reasoning
creativity
Why might intelligence be viewed differently at different ages?
more cognitive development
more socialisation
What are the issues with the explicit theory of intelligence?
no single definition
different experts = different opinions
some agreement
What did sternberg find differences in the explicit theory of intelligence was dependent upon?
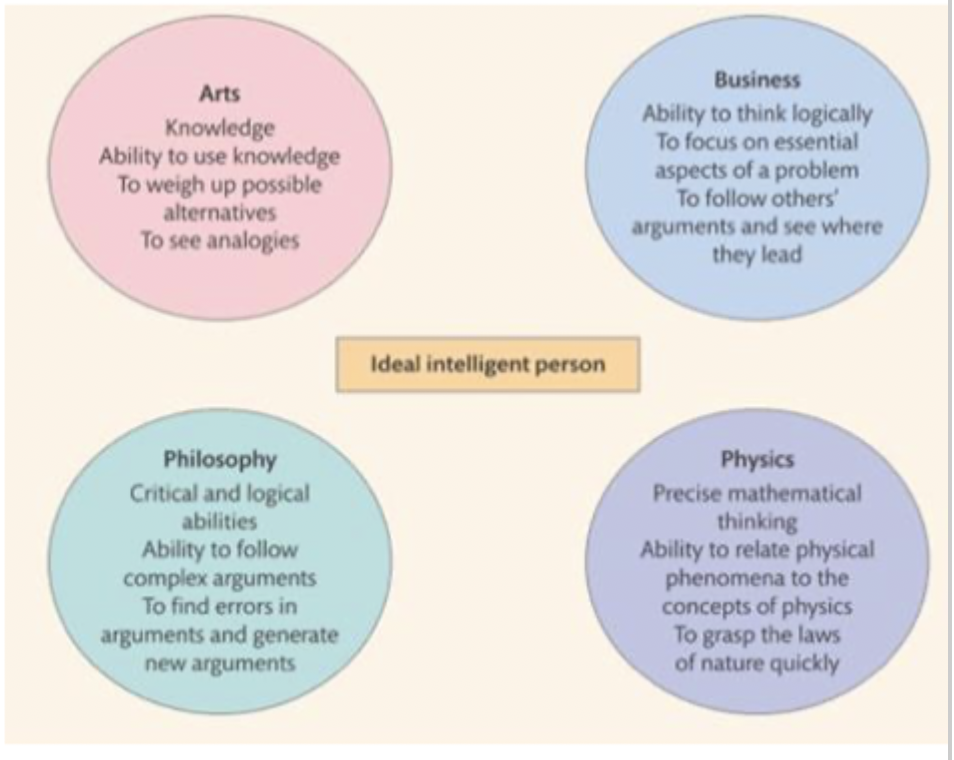
depends on the discipline
sternberg used procedure for professors of art, business, philosophy, physics - asked them to describe an intelligent person and then another group rate those traits
What was Galton’s contribution to formalised theories and tests? (1865)
first to systematically propose that people differ in intelligence
firm believe intelligence was biological and can be measured by physical means e.g. measures of senses and reaction time
Intelligence reflects peoples ability to respond to their senses

Eugenics definition
A reproductive selection process within humans that aims to create children with desirable traits
Positive eugenics definition
Encouraging reproduction in those who are perceived to have superior traits
negative eugenics
discouraging or eliminating reproduction in those perceived to have poor hereditary traits
Binet’s contribution to formalised theories and tests? (1904)
difference stance to galton: intelligence is malleable and can be developed. not necessarily a biological trait
Binet criticised intelligence testing prior to him
identified children in france who needed special eduction
developed a test scale to see how education could be tailored to children
seen as a positive influence in history of intelligence testing

What was involved in Simon-Binet’s test to determine child’s mental age?
30 short tasks that relate to everday life
shaking hands, counting coins, digit recall, word definitions. tasks got harder as you go through
What was Goddard and Terman’s contribution to formalised theories and tests? 1910s
adjusted the binet scale to be used in america but it didnt apply very well
recognised that standardisation was needed to be able to apply widely
so tried to capture a single entity of intelligence, despite no strong theory of intelligence to base it on, and no expert consensus on what intelligence is
wanted to use the scale to categorise US society, and use as part of the immigration process; all things that binet said shouldn’t be done
What was Yerkes’ contribution to formalised theories and tests? 1917
used standardised binet test to make decisions in terms of education
employed it in ww1 effort in America
Adapted this testing to give to recruits to define which role they took
offices and planning if performed well, more front line roles if performed less well
What was Spearman’s contribution to standardised theories and tests? 1920
focussed more on formalising theory, systematically looking at data
in the UK, tested local school children, gave them several different tests
the positive manifold: if child did well at one test, tend to do well on another
Why is intelligence important?
impact on and is influenced by every aspect of life
education, work, family, friends all of these things work bidirectionally
What is involved in Dweck’s theory of fixed and growth mindset and intelligence?
what we believe about our own intelligence has an influence too
fixed mindset: entity theory
growth mindset: incremental theory
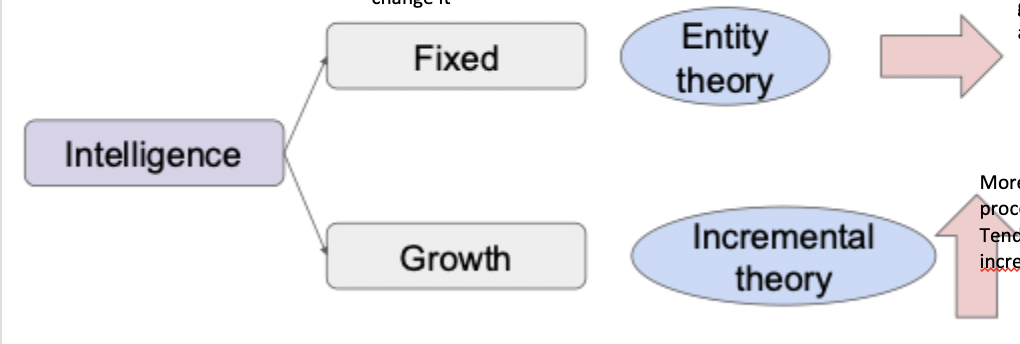
What are the characteristics of entity theory/ fixed mindset?
belief we’re born with our level of intelligence and not much we can do to change it
less likely to push themselves, less resilient, avoid challenges or give up easily
believe however much put in isn’t going to affect their achievement
What are the characteristics of incremental theory/ growth mindset?
more likely to embrace challenges and see them as a learning process
believe that their intelligence can develop and grow
tend to be more persistent and keep trying
those with incremental beliefs generally do better academically
What did Costa and Faria find conducting a meta-analysis on the role of personal implicit theories of intelligence on academic performance?
correlated with academic grades in different subjects
low but significant association between implicit theories and academic performance
particularly for subjects focused on verbal/ quantitative skills
those who viewed intelligence as fixed still showed a positive association with grades - just less strong
implicit beliefs about our intelligence are important but clearly not the only factor
How was intelligence used within the eugenics movement?
used to classify people, justify social hierarchies, support eugenics policies
aimed to “improve” human population: encourage reproduction among “fit” people and restricting reproduction among “unfit”
60,000 - 70,000 people forcibly sterilised in the USA in 20th century (until 1970s) included low intelligence
research and policies, influenced some of the atrocities enacted by the Nazi regime
How was intelligence used in immigration policies?
goddard influenced the use of intelligence measures in the US immigration process
immigrants from southern and eastern europe had lower intelligence
immigrants from northern and western europe were more intelligent
but testes were conducted in english or relied on culturally specific knowledge
many immigrants had little/ no english, limited schooling and exhausted after travelling
More history of US immigration act
US immigration act of 1924 lasted until 1965 restricted immigration from southern and eastern europe, nearly banned immigration from Asia, created immigration quotas favouring northern europeans
supporters explicitly cited intelligence test results as proof that certain ethnic groups would “lower the national intelligence”
How was ideas about intelligence implicated in soldier role allocation?
WW1 - soldiers allocated to roles based on test scores
those who scored higher were more likely to be placed in officer training or technical positions
those with lower scores were often assigned to manual labour or front line roles
immigrants and black soldiers often score lower, due to language barriers, cultural bias, and educational inequality
lead to stigma humiliation and front line deaths