respiratory system
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
3 types of respirations
ventilation → movement of air and out of resp. passages in lunges
gas exchange —>
diffusion of O2 and CO2 thru capillaries in lungs
O2 and CO2 transport to and from body cells
diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and body cells
cell respiration —> constantly aerobic for catabolic processes to make ATP and Co2
properties of gas-exchange surface (5)
area of cell membrane → larger = greater exchange of O2 and CO2
respiratory surface must be kept moist → its covered by film of moisture for diffusion to occur (CO2 and O2 must be in solution)
thin → diffusion distance must be small - mostly single layer of cells
permeable → O2 and CO2 can diffuse freely
concentration difference between O2 and CO2
pathway of air
nostrils
nasal passages/nasal cavity
pharynx [passageway for food + air connects with trachea + esophagus]
larynx (vocal cords)
treachea
thoracic cavity
two bronchi
terminal bronchioles
alveolis
what structures in noses are important for its respiratory functions (3.5)
tiny hairs (cilia) → stop dust and foreign particles from entering
walls are lined with muscous membranes → moisten air/trap partiles
large # of capillaries → warm the air
warming helps protect delicate tissues of lungs
what is a part of the larynx that is crucial (3)
vocal cords (elastic ligaments) held by cartilaginous materal
air causes vocal cords to vibrate - sound
epiglottis prevents chocking
what is the important structures and functions of trachea (2.5)
supported by semi-circular rings - prevent trachea from collapsing and food to esophagus
passages of upper respiratory tract lined with ciliated mucous membrane - traps foreign membrane
continual movement of cilia propels material back into nose + throat to be expeleld by coughing or sneezing
bronchi structures/division (3.5)
divides into 2 bronchi
1 bronchus enters each lung and bifurcates (divides) into bronchioles
no cartilage and cluster of alveolies
composed of cartilage and ciliated mucous cells
lungs (right 3, left 2) 5.5
nerves + dense network of blood-filled pulmonary capillaries
each lung surrounded by pleural membrane
seals lungs in thethoracic cavity from rest of body
inner layer ADHERES firmly to surface
thin film of fluid sealed between 2 layers of pleura and holds together in breathing
is pleural layers seal is broken and air gets in, lungs dont adhere and lung collapses
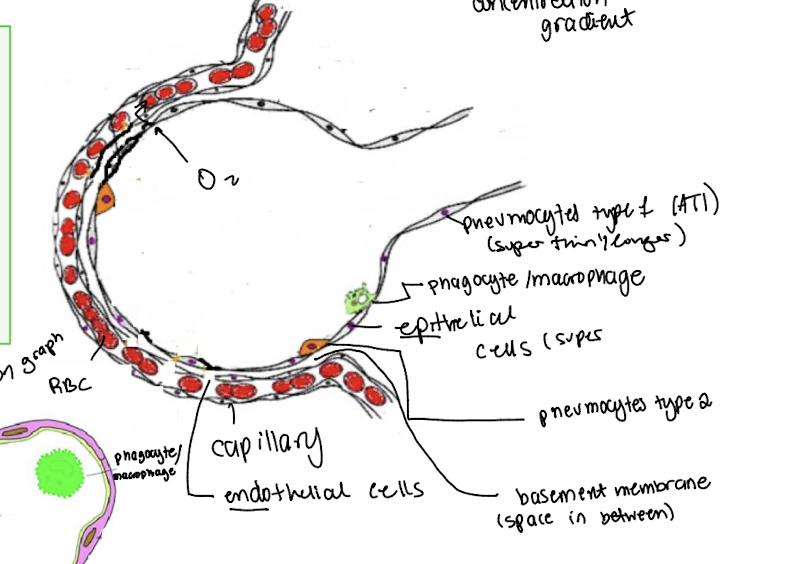
function and structure of alveoli (3.5)
lungs have 300 million alveolis → HUGE SA for gas exchange
70 m² → 40x the SA of skin
spherical shape → larger SA
single layer very thin cells epithelium
structures and functions type 1 penumocytes- AT1 (4)
very small and thin (0.15 um diametter) since adapted for gas exchange
surrounded by many pulmonary capillaries diffuse very short distance less than 0.5 um away) → increase rate of gas exchange
passive transprot (due concentration gradient)
AT1 have very little cytoplasm, mitochondria and other organelles
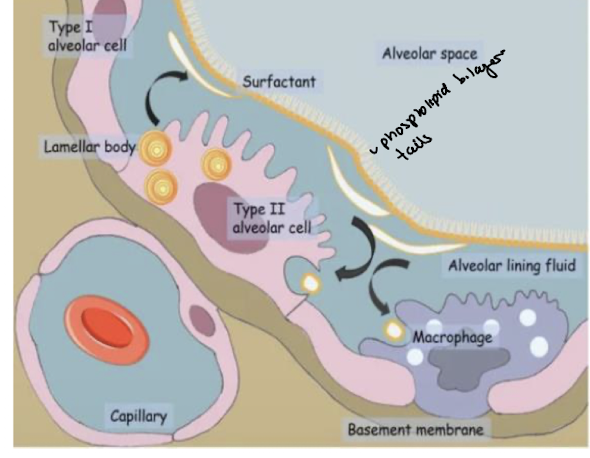
structure and function type II - pneumocytes AT2 (5.5)
SO MANY (90%) of these rounded cells that onyl take up 5% of alveolar SA
secrete fluid to keep inner surface moist - gasse sdissolve
thicker than AT1 - 10um diameter - dense cytoplasm, more mitochondira, rER/RER and lysosomes
many phospholipids synthsized in cytoplasm and stored in lamellar bodies} - secreted by exocytosis
they form a single layer on outer surface of film mositure - hydrophilic haeds facing water and tails air of alveolus
proteins secreted by lamellar bodies are dispered between phospholipid molecules
layer acts as a surfactant to reduce surfance tnesions and prevents sides of alveoli from sticking together when air exhaled
what other types of cells are in lungs (not pneuomocytes)
some contain collagen fibres - strengthen lung tissue
elastic fibres limit inhlaation and cause passive exhalation
boyles law
decreasing volume of gas → more collisions between gas molecules
higher # of collisions increases with pressure
what is the pressure of a single gas?
partial pressrue
gases move from aresas of higher pressure to areas of lower pressure
combination of two structures in rib cage
pump handle - lifts up away from pump (ribs moving UP and AWAY from spine )
bucket handle - lift away from the sides of the bucket (ribs moving outward LATERALLY)
both braodens the rib cage in all directions
muslces of diaphragm and intercoastal muscles
diaphragm is a muscle layer separating thoracic cavity from abdominal cavity
intercoastal muscles - associated with ventral surface of rib cage
what happens sudinrg inspiration/inhalation (5.5)
the diaphragm contracts downwards + flattens → enlargement of thoracic cavity and pushes abdomen wal out
muscles in abdomen relax
the external intercostal muscles contract - ribs upwards and outwards - away from body
internal intercostal muscles relax - pull back into their elognated state
increase in volume of thoracic cavity → decrease in air pressure within space (air has more space to move)
pressure OUTside lungs is much greater than pressure of of air WITHIN lungs
due to partial pressure laws
percent values of inhaling O2 and CO2 vs exhaltion concentration
inhalation
O2 = 21 %
CO2 = 0.04%
exhalation
O2 = 16%
CO2 =3-5%
both inhale + exhale of N2 and trace gases = 79%
expiration (5.5)
the diaphragm relaxes - pushed up into domed shaped
muscles in abdomen wall contract - organs + diaphragm pushed up
external intercostal muscles relax - go back to elongated state
internal intercostal muscles relax - ribs go down and in
contractions cause volume of thoracic cavity to decrease
air pressure in lungs increases and greather than outside
air rushes OUT due to partial pressure differences between 2 spaces
tidal volume (TV)
volume of fresh air normal unforced breathing cycle/ventilation (# of times that air is inspired or expried per minute)
inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
max volume of air inspired FORCEFULLY from end of tidal inspiration
deep breath
expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
max volume of air that can be expired foreccfully beyond end of tidal expiration
exhale forcefully
residual volume (RV)
volume of air remains in lungs and passageways even after maximum expiration
never leaves respiratory system - lungs would collapse
little value for gas exchange
vital capacity (VC)
max volume of air that can be expired after max inspiration
TV + IRV + ERV = VC
every min - 5-7L air moved in and out
what are the 4 feedback controls of ventailation rate
respiratory stimuli- change in arterial pressure of CO2/arterial pressure of O2, change in blood pH, change in lung partial pressure of O2
respiratory receptors - chemo (chemical factors) or baroreceptors (alveolar)
respiratory centres - located in brain stem
respiratory effectors
normal inspiration.expiration → diaphragm + external intercostals muscles
forced expiration → internal intercostals muscles + abdominal muscles
types of respiration control
voluntary respiration → people control (hold breath, speaking, singing)
involuntary respiration - controlled by negative feedback regulator
central vs peripheral chemoreceptors (4)
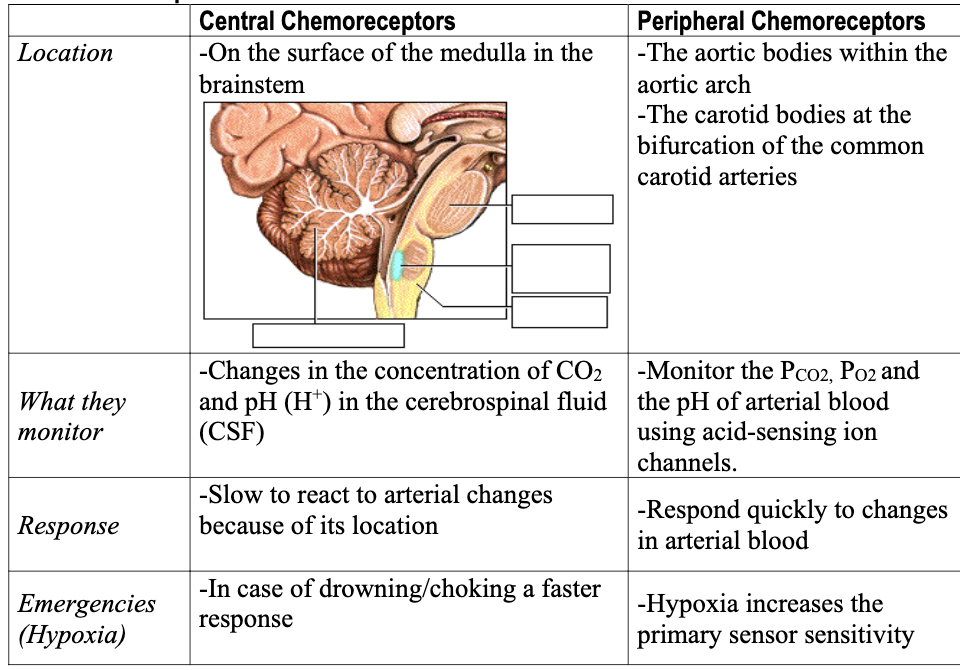
how does feedback loops react for O2 and CO2 in chemoreceptors
if too little O2 in arterial blood - breathing increases (O2 decreases)
if CO2 of cells exceeds rate exhaled, ventilation increases to match rate
CO2 and ventilation rate
after CO2 enters bloodstream and in blood → lower portion of brain
CO2 combines with water to form carbonic acid - dissociate H+ and bicarbonate ions
H+ stimulat central C.R.
lowered pH → acidosis (levels below 6.8)
a good level is 7.35-7.45 pH
greater rolle controlling rate of breathing than O2
what do chemoreflexes do
protect asphyxia (CO2 build up) and hypoxia (lack of O2 in tissues)
hypoxia → “silent killer”