Biology Unit 1 - Biomolecules
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
polar/hydrophilic
electrons not equally shared (item w/higher EN takes more). Polar substances are hydrophilic - they dissolve in water.
● nonpolar/hydrophobic
Electrons equally shared (equal EN or symmetrical). Nonpolar substances are hydrophobic - they do not mix with/dissolve in water.
● adhesion
attractive forces between molecules of different substances (polar/charged)
● cohesion (why surface tension?)
attractive forces (water to water) - creates high surface tension because water pulls together more than it is pulled towards the air
● hydrogen bond
intermolecular weak attraction (not a real bond) between partially positive hydrogen and other partial/fully negative charged atoms. Intermolecular - does NOT hold water molecule together.
● electronegativity
How much an atom can attract electrons from other atoms towards itself
● heat capacity
how much heat needed to increase temperature (water has hydrogen bonds, so it is very hard to get them to move and therefore it has a high specific heat capacity)
● density - ice and water
mass/volume ex: ice is less dense than water because when water freezes, the molecules stop moving and form a rigid structure with empty spaces due to hydrogen bonds. This makes ice much less dense than water.
● pH scale
how acid or basic a substance is - 1 = most acidic, 14 = most basic
● atom
smallest unit of matter
● ion
positively/negatively charged atom (positive = cation, negative = anion)
● molecule
A group of atoms bonded together
● element
type of atom
● functional group
group of atoms - give similar properties onto other dissimilar molecules (hydroxyl /amine/carboxyl groups)
● polymer
at least 2 monomers
● monomer
smallest unit of a biomolecule
● dehydration synthesis
When multiple monomers form into one polymer with water as a byproduct.# of H20 molecules = #of monomers -1
● hydrolysis
When a large polymer breaks down into smaller pieces with the addition of water
● polymerization
joining monomers to form a polymer
● de-polymerization
Process of breaking down a polymer into monomers
● positive control
something you know will test positive to compare with what you are testing
● negative control
something you know will test negative to compare with what you are testing
● DNA/RNA - atoms, monomer and polymer, function
Chonp, nucleotides, DNA, RNA, store and transmit genetic info
● hemoglobin
An iron-containing protein in red blood cells
intramolecular vs intermolecular
intra - inside forces(ionic/covalent bonds), inter - outside. forces (LDF, dipole-dipole, hydrogen)
why is water the universal solvent?
dissolves many substances (polar)
why is carbon important?
can bond 4 times w/ other atoms (single, double, triple), can bond w/ itself and H,O,N, carbon skeletons can be really long and make rings
What are carbohydrates made of?
C, H, O
what is the ratio for simple sugars?
1:2:1
types of carbs
sugar, starch, fiber (cellulose) - mostly polar
monosaccharides
monomer - simple sugars
polysaccharides
polymer - complex sugars
functions of carbs
store energy (short term), structural support (cell walls) in plants
what are lipids made of?
mainly C and H, also O, N, P
3 meanings of fat in biology
fat tissue , fat cells (adipocytes), lipids (fat molecules)
what are lipids
fat molecules - insoluble in water (non-polar - hydrophobic), includes cholesterol, glycolipids, etc.
lipid monomer
fatty acids and glycerol
lipid polymer
triglycerides, phospolipids, steroids
functions of lipids
store energy (long term) --> convert sugars to fats, insulation, organ cushioning, make cell membranes, waterproofing
glycerol + 3 fatty acids
triglyceride + 3 H20
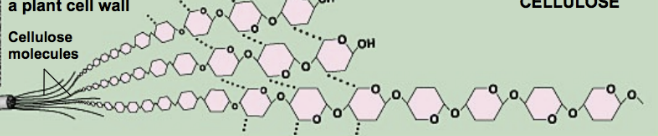
cellulose
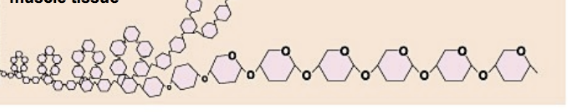
glycogen
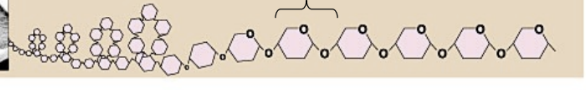
starch
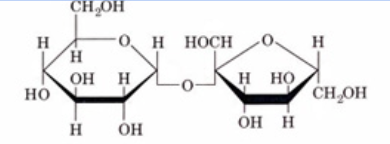
disaccharide (sucrose)
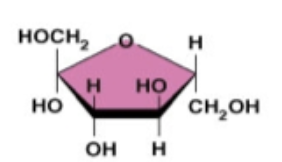
fructose (HOCH2)
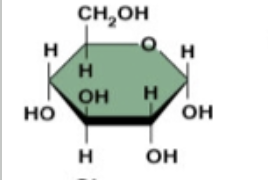
glucose (no HOCH2)
types of fat
saturated - single bonds, harder to break down (stable), solid at room temp, unsaturated - fatty acids (1+double bonds), liquid at room temp, trans fat- artificially created,makes unsaturated fats solid
phospholipids
main molecules that make up cell membranes - 2 fatty acid chains and phosphate group (non-polar - make barrier, oil beads up and makes droplets)c
cholesterol
lipid that is different from fat, part of cell membrane
phospholipids have
polar head, nonpolar tail
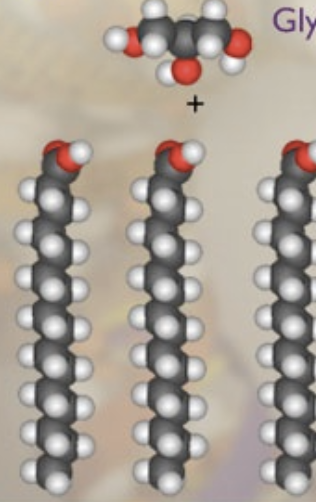
glycerol + 3 fatty acids
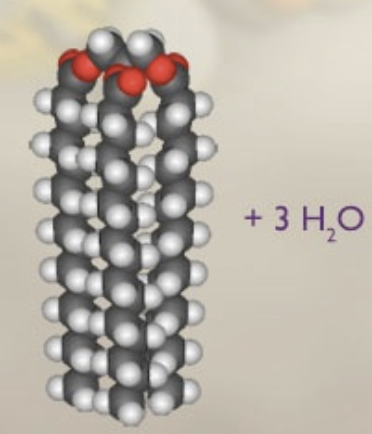
triglyceride
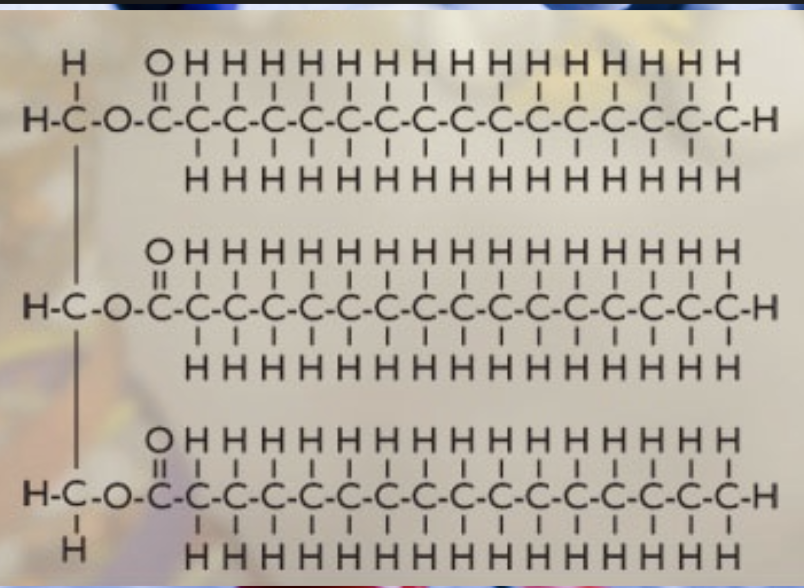
triglyceride
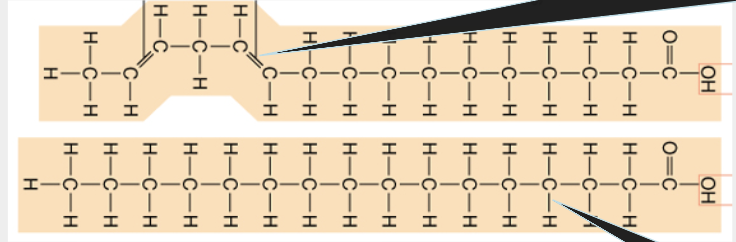
unsaturated, saturated fat
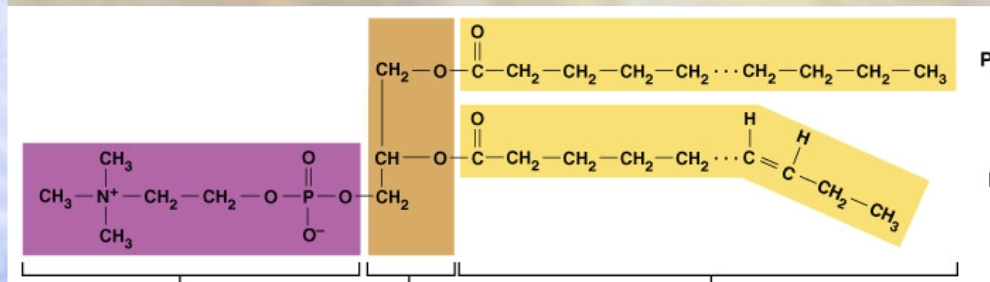
phospholipid
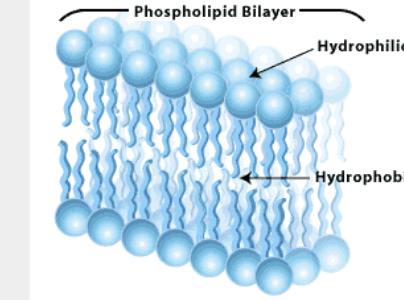
cell membrane
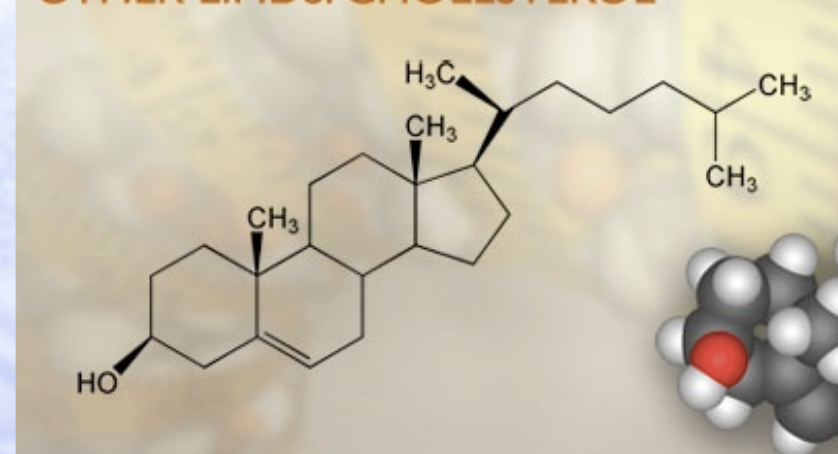
cholesterol (it has ch3)
types of protein
meat, eggs, fish, dairy, nuts, legumes
elements in proteins
C, H, O, N, S
protein monomer
amino acids
protein polymer
polypeptide
groups. in. amino acid -
amine group (nitrogen, left) r side chain, carboxyl group (C,O, OH)
functions of proteins
do+be work - hormones, antibodies, hemoglobin, ferritin, actin and myosin - storage, transport, protection, hormonal, contractile, receptors, enzyme, structural
amino acids held together by…
peptide bonds (between C-N - H+OH removed andbecome H20)
#of bonds in protein =
#of amino acids -1
4 levels of protein structure
primary - peptide bonds btwn amino acids, secondary - hydrogen bonds. w/N+O molecules, tertiary - folding of polypeptides, quaternary - multiple polypeptides
proteins are “done” at
either tertiary or quaternary
denaturation
loss of biological activity (proteins aren’t alive, but if they are unfolded they don’t do anything
causes of denaturation
change in ph, temp change, change in ionic strength, dissolved/change in solubility
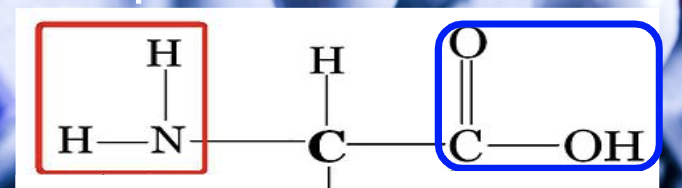
amino acid
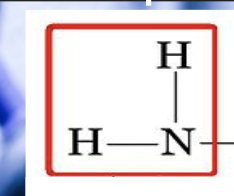
amino group
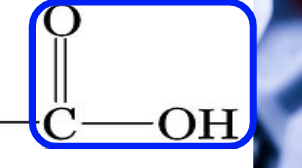
carboxyl group
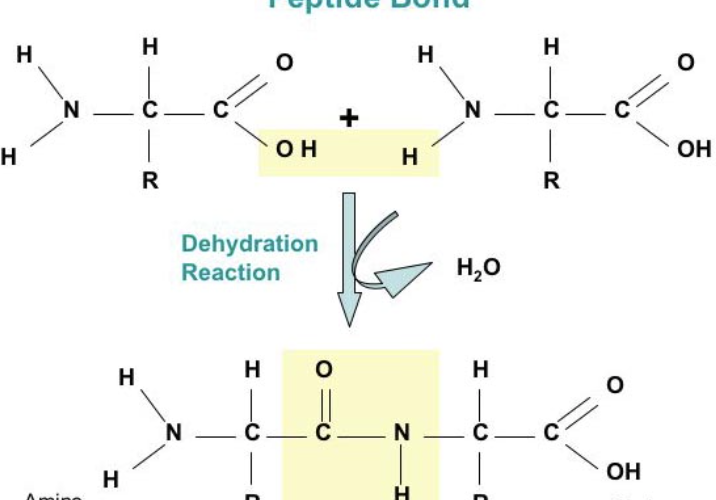
peptide bond (c+n)
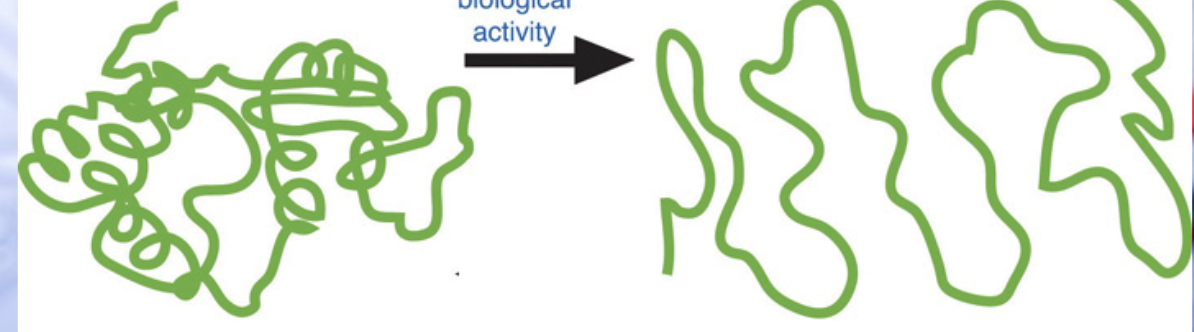
denaturation
water’s properties
adhesion, cohesion, high specific heat, ice floats, surface tension, universal solvent
functions of amino and carboxyl group
Amino group - can accept H+ ions (basioc) and charged
Carboxyl group - releases H+ ions (acidic
Groups combine to form peptide bond
why does shape matter for biomolecules?
Lipids = long chains with lots of bonds = more energy but harder to break down
Carbohydrates - very simple structure and much easier to break down, but less bonds so less energy
polar/nonpolar (symmetrical/asymmetrical) changes solubility