Energy, Power & Resistance
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:59 PM on 2/6/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
Open Switch
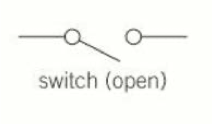
2
New cards
Closed Switch
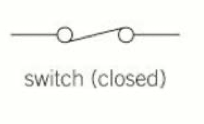
3
New cards
Cell
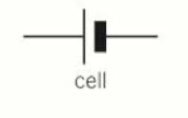
4
New cards
Voltmeter
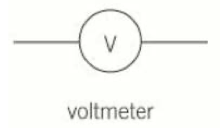
5
New cards
Ammeter
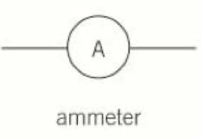
6
New cards
Thermistor
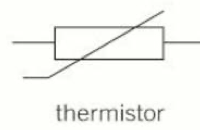
7
New cards
Battery
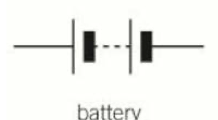
8
New cards
Diode
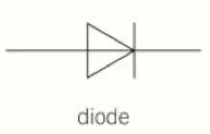
9
New cards
Resistor
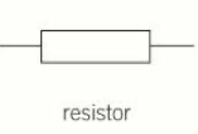
10
New cards
LDR
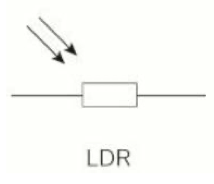
11
New cards
LED
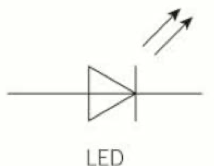
12
New cards
Capacitor

13
New cards
Variable Resistor
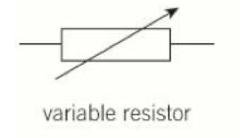
14
New cards
Lamp
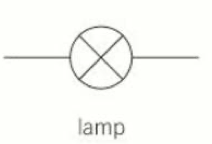
15
New cards
Fuse
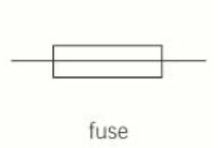
16
New cards
What are circuit symbols used for?
To represent components in electrical circuits
17
New cards
How should circuit symbols be drawn?
Clearly and carefully with correct directions
18
New cards
How should wires be drawn in circuit diagrams?
As straight lines
19
New cards
How should junctions be drawn?
At 90° angles
20
New cards
What does an open switch symbol represent?
A break in the circuit
21
New cards
What does a closed switch symbol represent?
A complete circuit
22
New cards
What is a cell?
A single source of emf
23
New cards
What is a battery?
Two or more cells in series
24
New cards
What does a voltmeter measure?
Potential difference
25
New cards
How is a voltmeter connected?
In parallel
26
New cards
What does an ammeter measure?
Current
27
New cards
How is an ammeter connected?
In series
28
New cards
What does a resistor do?
Limits the current in a circuit
29
New cards
What does a variable resistor do?
Allows resistance to be changed
30
New cards
What is an LDR?
A resistor whose resistance depends on light intensity
31
New cards
What is a thermistor?
A resistor whose resistance depends on temperature
32
New cards
What does an LED do?
Emits light when current flows through it
33
New cards
What does a diode do?
Allows current to flow in one direction only
34
New cards
What does a capacitor do?
Stores electrical charge
35
New cards
What does a fuse do?
Breaks the circuit if current is too large
36
New cards
What does a lamp symbol represent?
A filament bulb
37
New cards
What is potential difference?
Energy transferred per unit charge
38
New cards
What is the equation for potential difference?
V = W/Q
39
New cards
What are the units of potential difference?
Volt V
40
New cards
What does 1 volt mean?
1 joule of energy transferred per coulomb
41
New cards
What happens to charge carriers across components?
They lose energy
42
New cards
What is electromotive force?
Energy supplied per unit charge
43
New cards
What is the equation for emf?
ε = W/Q
44
New cards
What energy transfer occurs in a cell?
Chemical to electrical
45
New cards
What are the units of emf?
Volt V
46
New cards
What is an electron gun?
A device that produces a beam of electrons
47
New cards
What is the cathode in an electron gun?
A heated metal filament
48
New cards
What process releases electrons from the cathode?
Thermionic emission
49
New cards
Why is the electron gun in a vacuum?
To prevent collisions with air particles
50
New cards
What accelerates electrons towards the anode?
A large potential difference
51
New cards
Why does the anode have a small hole?
To form a narrow electron beam
52
New cards
What energy transformation occurs during acceleration?
Electrical potential energy to kinetic energy
53
New cards
What equation links electron speed and p.d.?
eV = ½mv²
54
New cards
What assumptions are made in eV = ½mv²?
Negligible initial KE and no energy losses
55
New cards
What is resistance?
Opposition to the flow of charge
56
New cards
What is the equation for resistance?
R = V/I
57
New cards
What are the units of resistance?
Ohm Ω
58
New cards
What does 1 ohm mean?
1 volt per ampere
59
New cards
How is resistance measured experimentally?
Using voltmeter and ammeter readings
60
New cards
How are voltmeters connected in resistance experiments?
In parallel
61
New cards
How are ammeters connected in resistance experiments?
In series
62
New cards
How is resistance found from an I–V graph?
Inverse of the gradient
63
New cards
State Ohm’s law.
Current is proportional to p.d. at constant temperature
64
New cards
What condition is required for Ohm’s law?
Constant temperature
65
New cards
What is an ohmic component?
A component that obeys Ohm’s law
66
New cards
What does an ohmic I–V graph look like?
Straight line through the origin
67
New cards
What is a non-ohmic component?
A component that does not obey Ohm’s law
68
New cards
Why do metals become non-ohmic at high current?
Increased heating increases resistance
69
New cards
Why does heating increase resistance in metals?
More lattice vibrations cause more collisions
70
New cards
What is a fixed resistor?
A component with constant resistance
71
New cards
How do wires behave in circuits?
Like low-resistance fixed resistors
72
New cards
Why is a filament lamp non-ohmic?
Resistance increases as filament heats
73
New cards
How does the I–V graph of a filament lamp curve?
Gradient decreases as current increases
74
New cards
What is a diode made from?
Semiconductor material
75
New cards
How does a diode conduct?
In one direction only
76
New cards
What happens in reverse bias?
No current flows
77
New cards
What is the resistance in reverse bias?
Effectively infinite
78
New cards
What is the threshold voltage of a diode?
Minimum p.d. needed to conduct
79
New cards
Why does resistance fall after threshold?
Increased charge carrier density
80
New cards
What does NTC stand for?
Negative temperature coefficient
81
New cards
What happens to resistance in an NTC thermistor as temperature increases?
It decreases
82
New cards
Why does resistance decrease in an NTC thermistor?
More charge carriers are released
83
New cards
What are thermistors used for?
Temperature sensing circuits
84
New cards
Is a thermistor ohmic?
No
85
New cards
What happens to LDR resistance as light intensity increases?
It decreases
86
New cards
Why does LDR resistance decrease in bright light?
More charge carriers are released
87
New cards
What are LDRs used for?
Light sensing circuits
88
New cards
What is resistivity?
A material property linking resistance length and area
89
New cards
What is the equation for resistivity?
ρ = RA/L
90
New cards
What are the units of resistivity?
Ohm metre Ω m
91
New cards
How does resistivity depend on shape?
It does not
92
New cards
How does resistivity depend on material?
It depends only on the material and temperature
93
New cards
How does resistivity change with temperature in metals?
It increases
94
New cards
Why does resistivity increase in metals with temperature?
Increased ion vibrations cause more collisions
95
New cards
How does resistivity change with temperature in semiconductors?
It decreases
96
New cards
Why does resistivity decrease in semiconductors?
Charge carrier density increases
97
New cards
How is resistivity measured experimentally?
By measuring R L and A
98
New cards
How is cross-sectional area measured?
Using vernier calipers or micrometer
99
New cards
Why take multiple diameter readings?
To reduce uncertainty
100
New cards
What is electrical power?
The rate of energy transfer