**OSCE questions
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
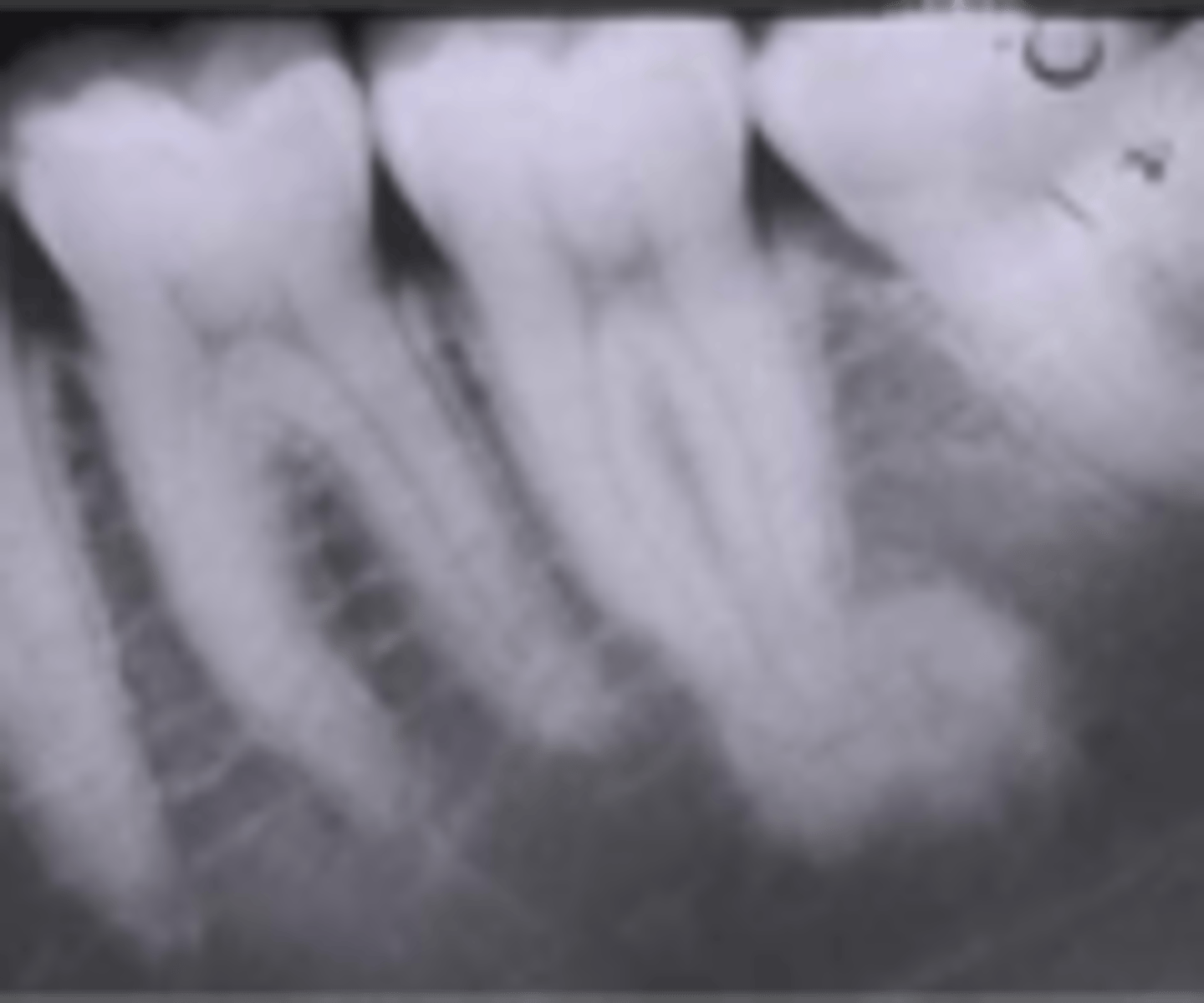
a. 5-6
* RATIONALE: only the pts permanent first molars have erupted (6yrs)
what is the approximate age of this patient?
a. 5-6
b. 7-8
c. 9-10
d. 11-12
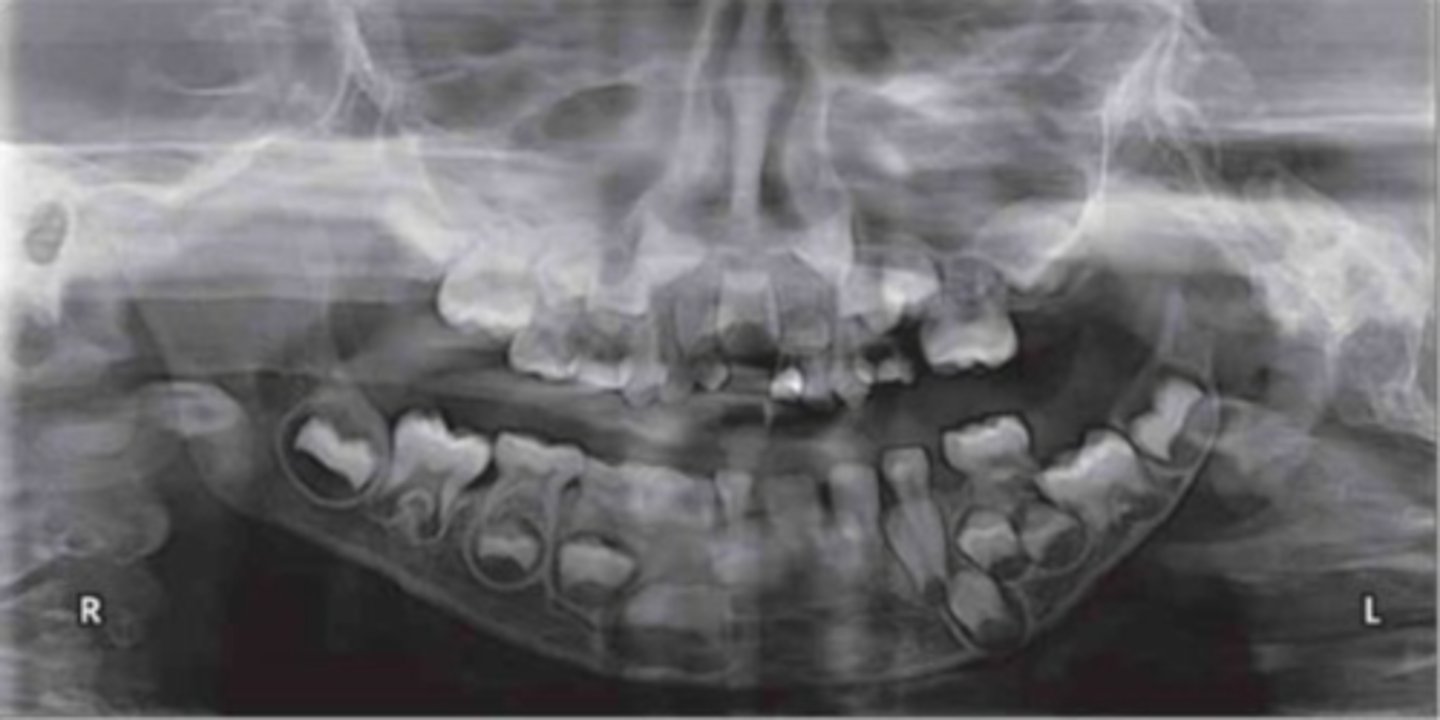
b. 7-8
* RATIONALE: pts 1st molars are in (6yrs) and central/lateral incisors are in (7-8yrs)
what is the approximate age of this patient?
a. 5-6
b. 7-8
c. 9-10
d. 11-12
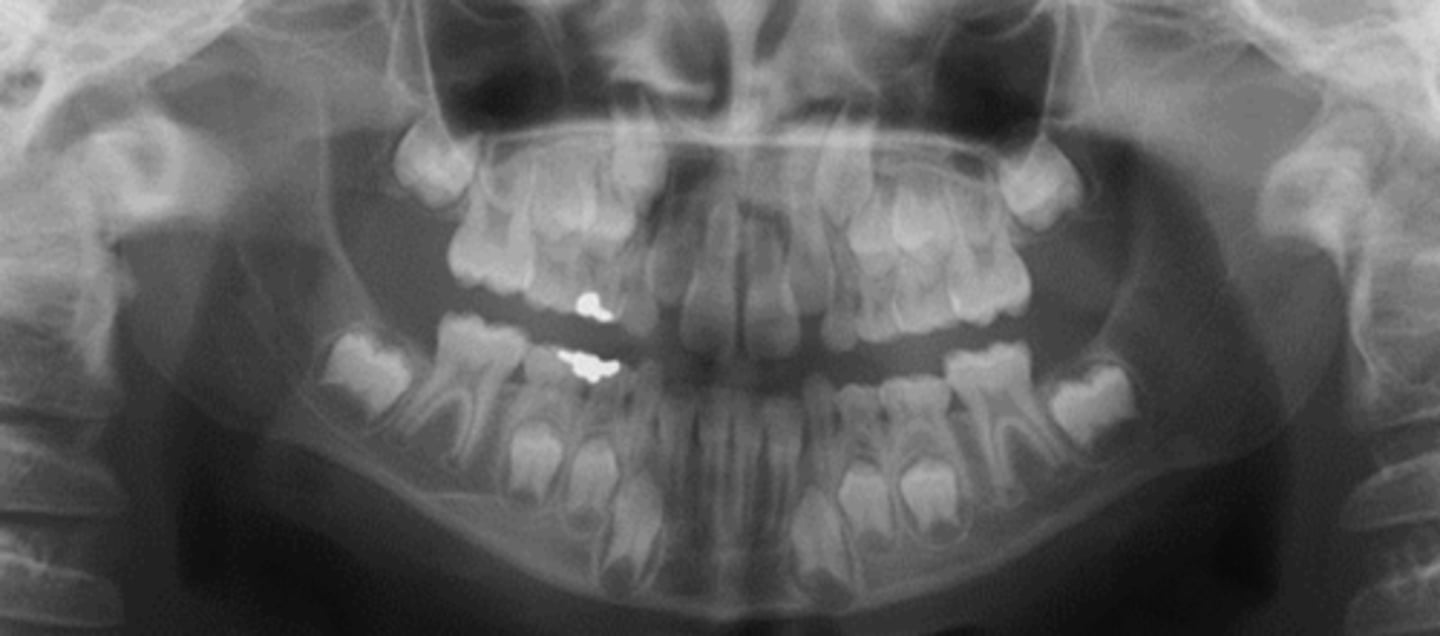
c. 10-11
* RATIONALE: first molars (6yrs), centrals/laterals (7-8yrs), canines (man-9yrs, max-11yrs), premolars/2nd molars (10-11yrs)
what is the approximate age of this patient?
a. 6-7
b. 8-9
c. 10-11
d. 12-13
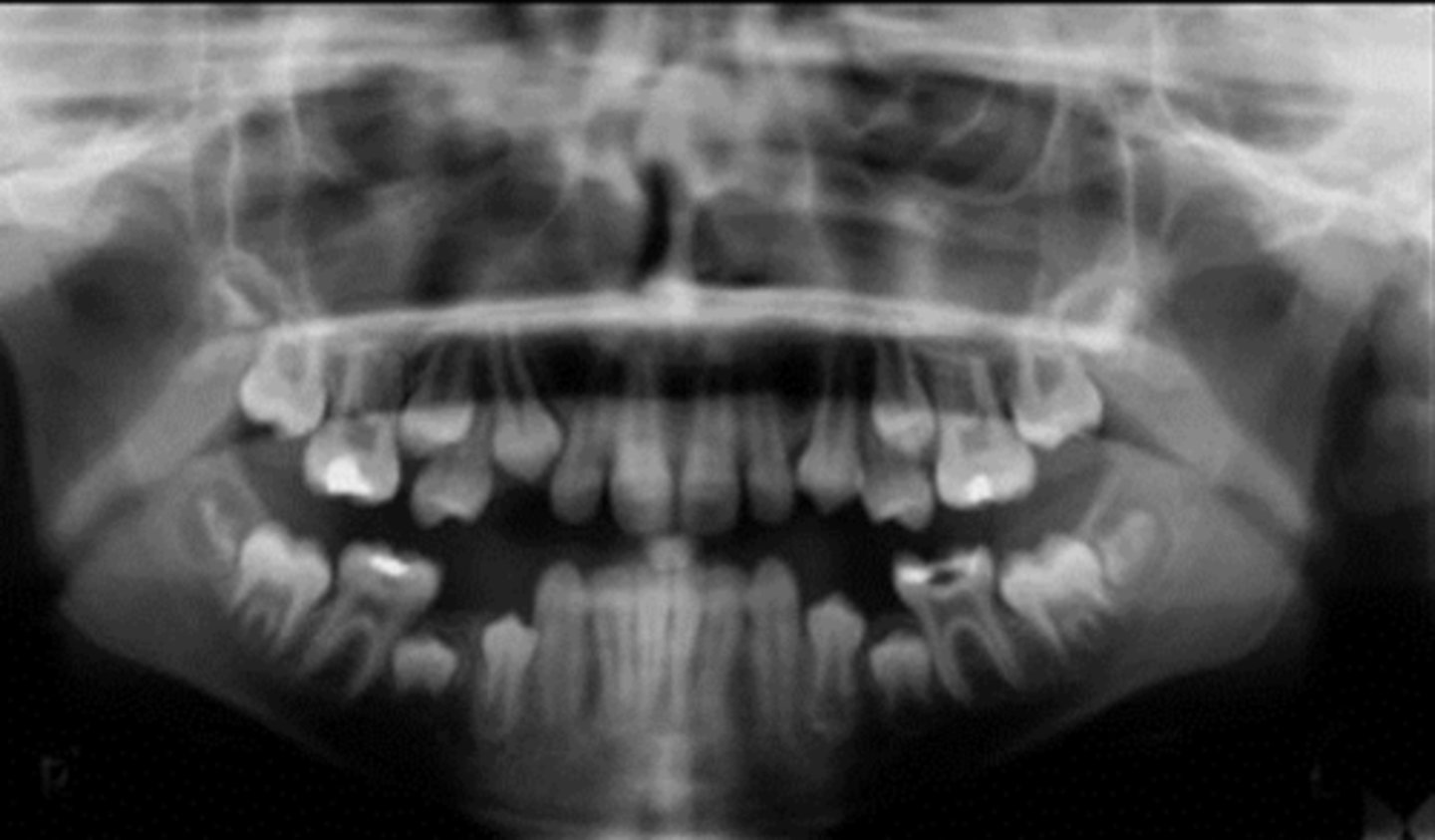
b. 7-8
what is the approximate age of this patient?
a. 5-6
b. 7-8
c. 9-10
d. 11-12
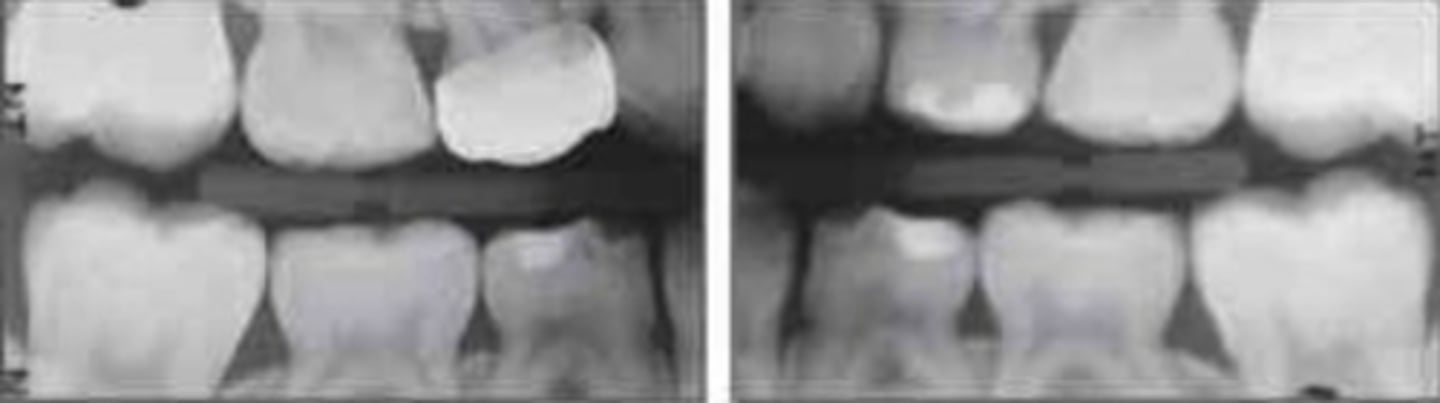
c. 11-12 years old
Note: 12 year old molars are partially erupted and deciduous F is exfoliating, therefore the patient is between the ages 11-12
what is the approximate age of this patient?
a. 7-8
b. 9-10
c. 11-12
d. 13-14
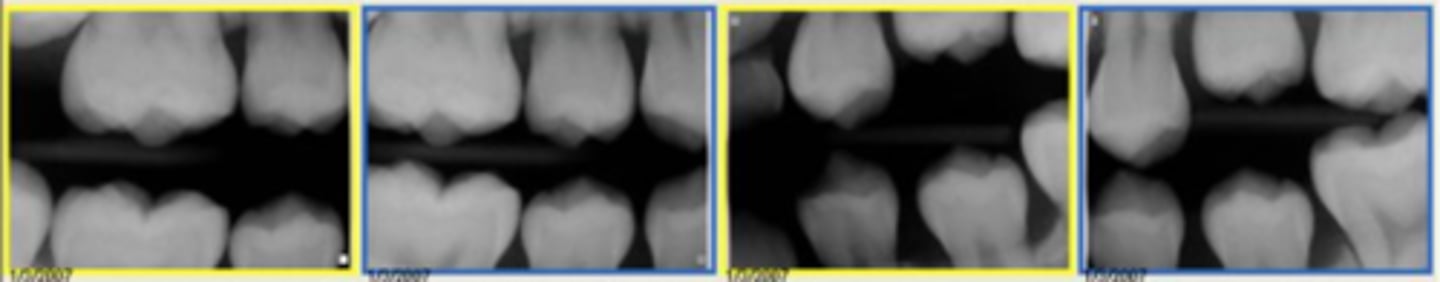
c. #20
what permanent tooth will replace primary tooth K?
a. #13
b. #19
c. #20
d. #21
zygomatic process (malar bone)
AKA: U shape or Zygoma
what are the arrows pointing at?
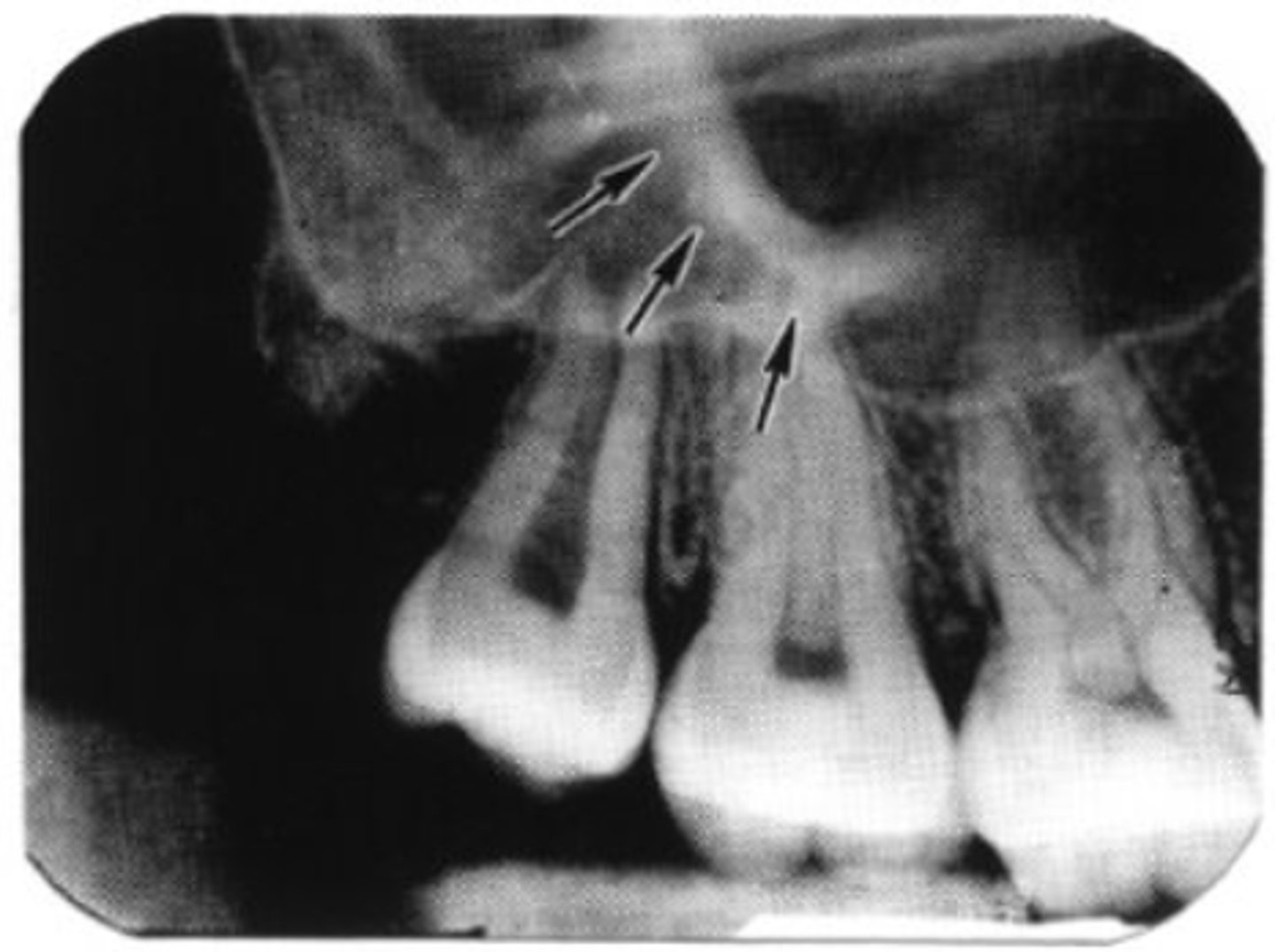
the zygomatic process (zygoma)
what is the white "U" shape above #2?
b. Fast pulse, dizziness
Your patient is suffering from hypoglycemia. Which of the following most likely describes their symptoms?
a. Slow pulse, dizziness
b. Fast pulse, dizziness
c. Slow pulse, confusion
d. Fast pulse, loss of appetite
low blood sugar
hypoglycemia
(HIGH or LOW) blood sugar
c. 70
hypoglycemia
low blood sugar less than _____ mg/dl
a. 50
b. 65
c. 70
d. 90
- mild to mod: dizziness, moodiness, hunger, headache, confusion, rapid heartbeat
- severe: fainting, unconsciousness, seizures
hypoglycemia signs and symptoms include:
- provide glucose tablet
- provide fruit juice
- pt should improve in 10-15 minutes
hypoglycemia
management of hypoglycemic condition:
provide glucagon - 1mg intramuscularly
- if pt loses consciousness, call emergency
hypoglycemia
if pt is unconscious, what should you do?
c. tredelenburg
your patient is showing symptoms that they are about to pass out. the patient is NOT diabetic. what position should you place the patient in?
a. upright
b. semisupine
c. tredelenburg
d. supine
a. upright
your patient is showing symptoms that they are about to pass out. the patient IS diabetic. what position should you place that patient in?
a. upright
b. semisupine
c. tredelenburg
d. supine
coughing, breathing difficulties, wheezing, and cyanosis
asthma signs and symptoms include:
short acting bronchodilator (beta-2 receptor agonist) such as albuterol
asthma asthma attacks are generally managed with what?
- positions pt upright with arms forward
- administer 1 puff from inhaler, repeat in 5 min if necessary
- administer O2
- assess and record vitals
- call 911 if no improvement in 5 minutes
asthma treatment of asthma:
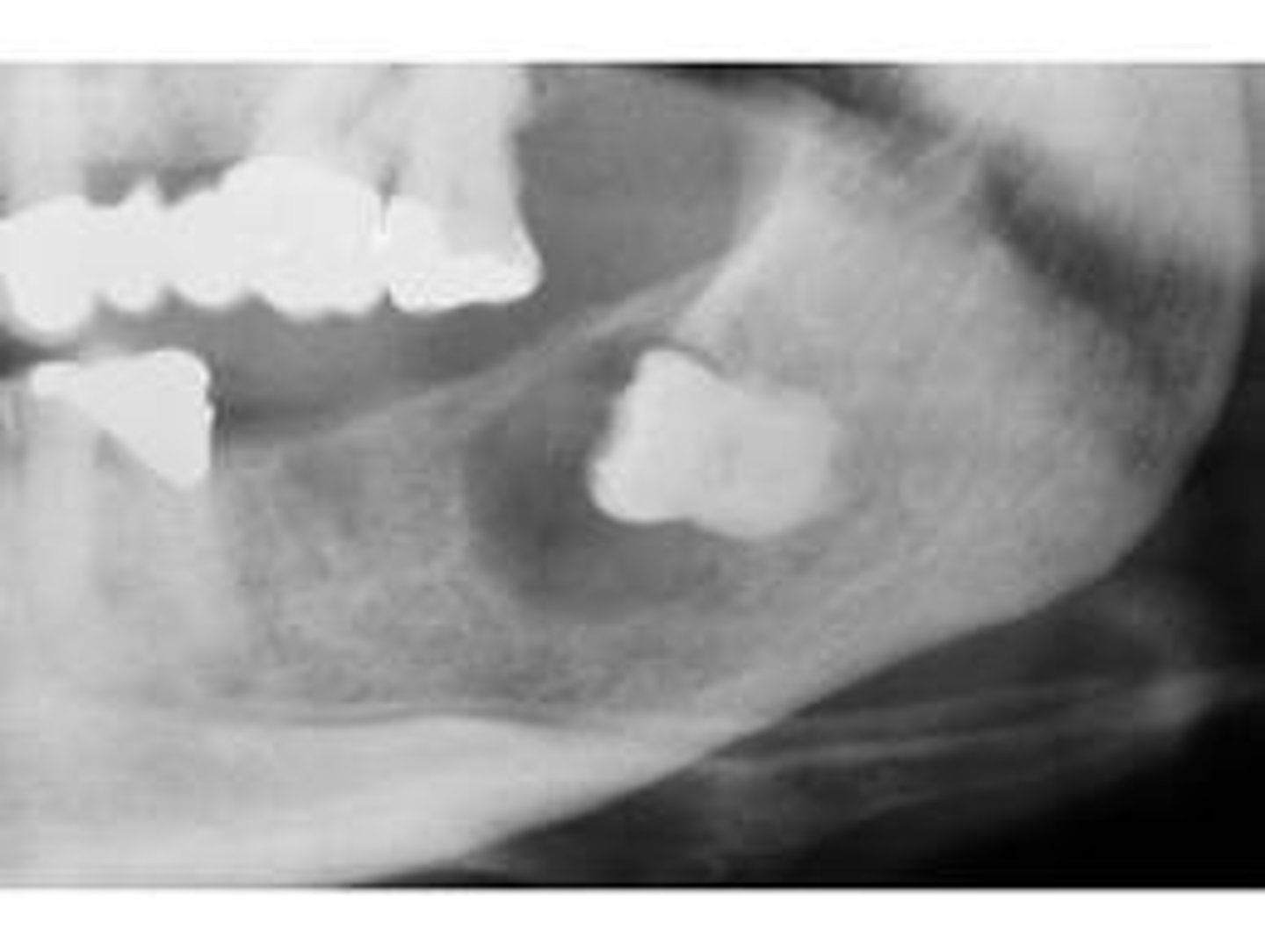
c. dentigerous cyst
NOTE: a dentigerous cyst commonly appears around the crown of an impacted mandibular third molar.
**a primordial cyst does not have a tooth associated with it so this cannot be a primordial cyst!!
the radiolucency in this radiograph appears to be a:
a. abscess
b. primordial cyst
c. dentigerous cyst
d. eruption cyst
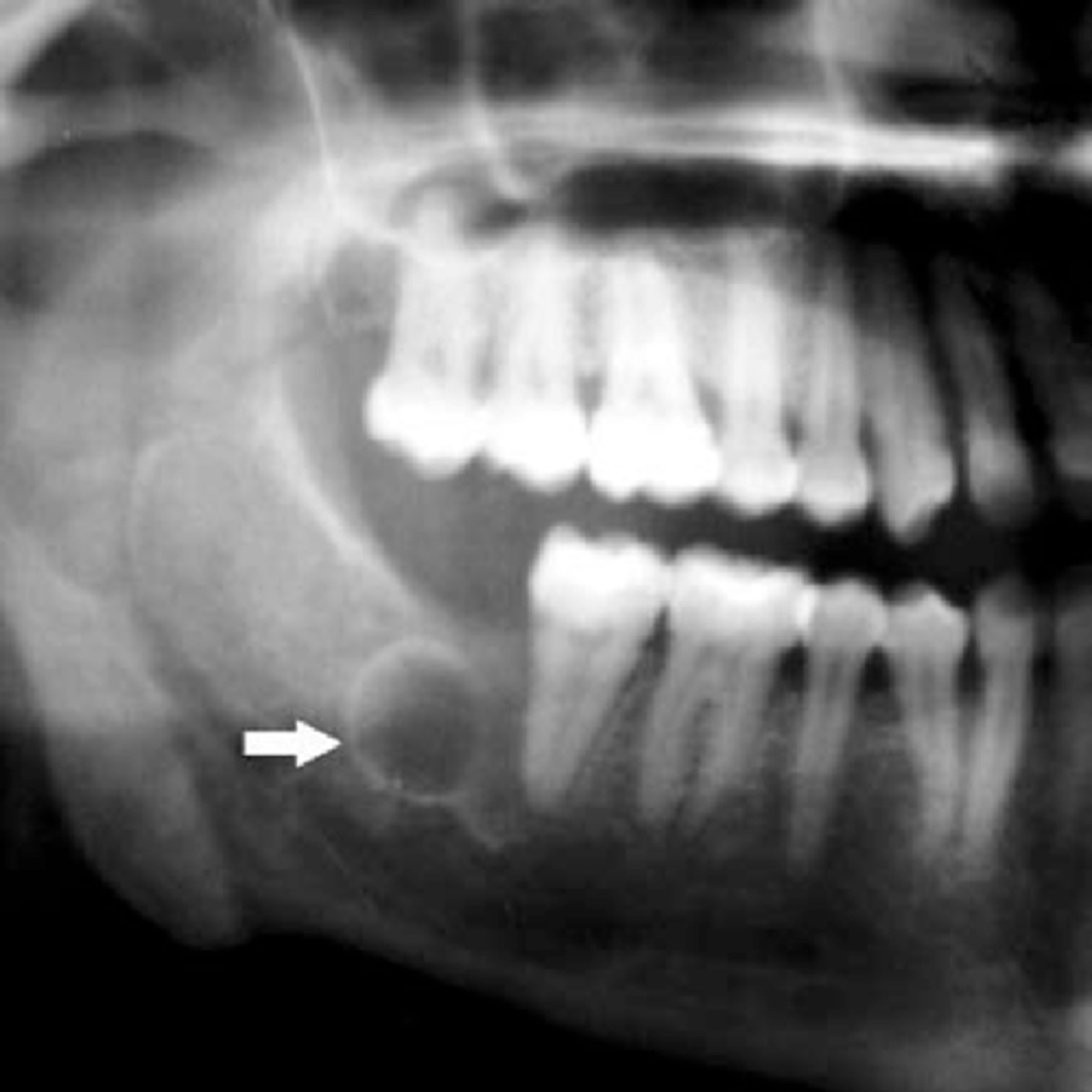
a follicular cyst
a dentigerous cyst is also known as what?
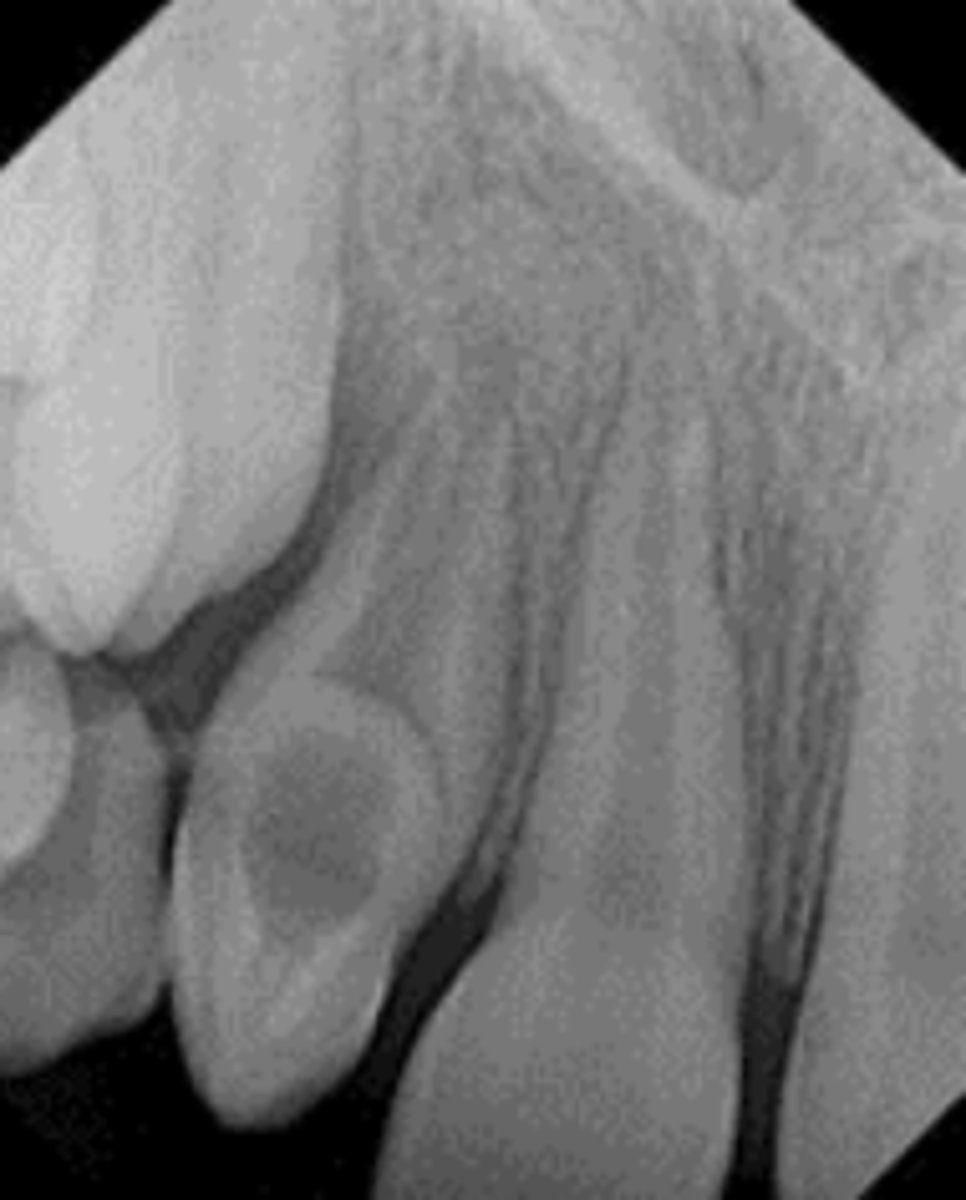
b. primordial cyst
NOTE: a primordial cyst is found in an area where a tooth should have formed but is missing
the radiolucency in this radiograph appears to be a:
a. abscess
b. primordial cyst
c. dentigerous cyst
d. eruption cyst
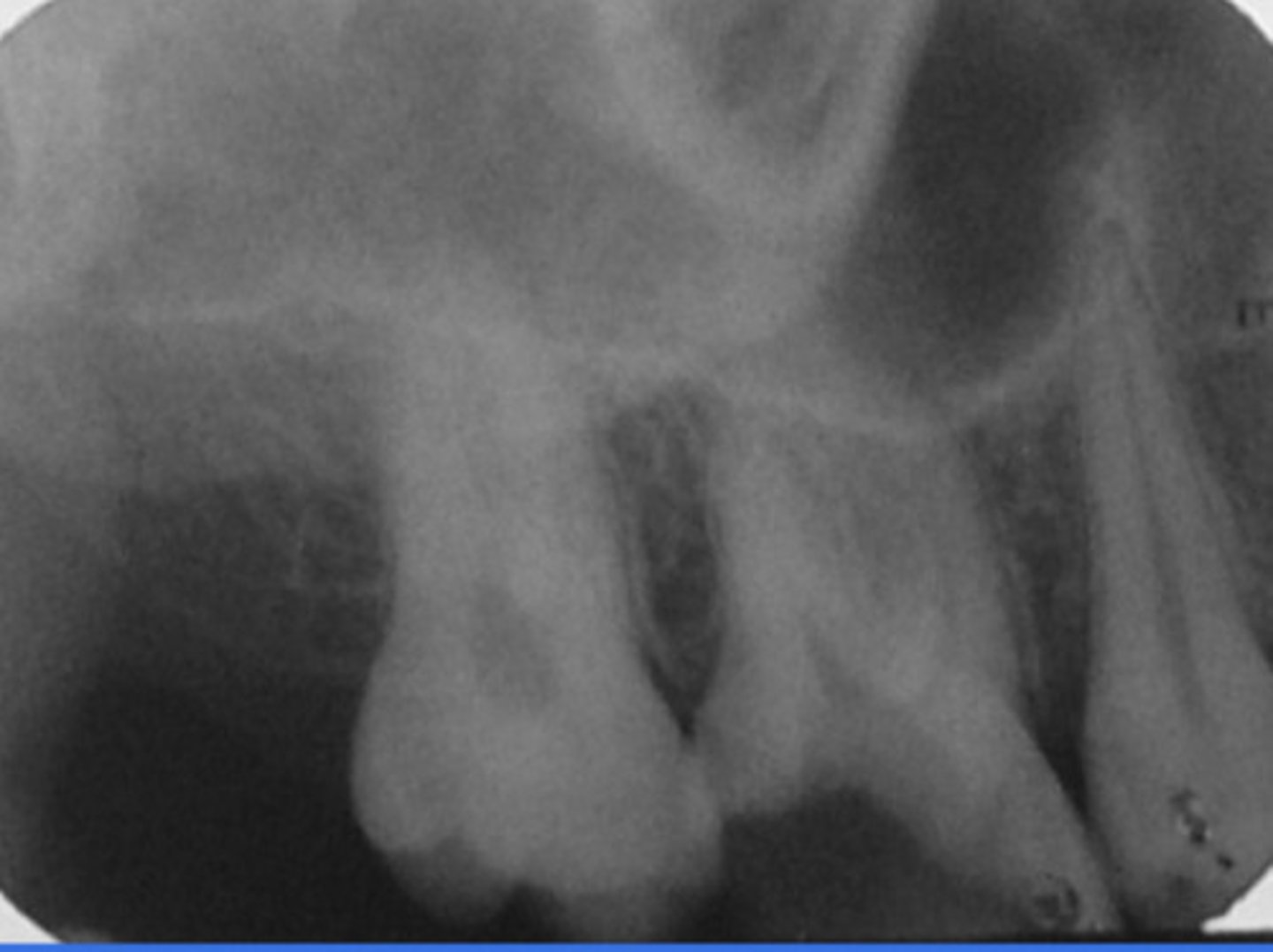
dens invaginatus (Dens in dente)
AKA: tooth within a tooth
what is a condition found in teeth where the outer surface folds inward?
dens invaginatus (Dens in dente)
AKA: tooth within a tooth
what condition is found in this image?
b. elongation
what is the radiographic error?
a. foreshortening
b. elongation
c. improper horizontal angulation
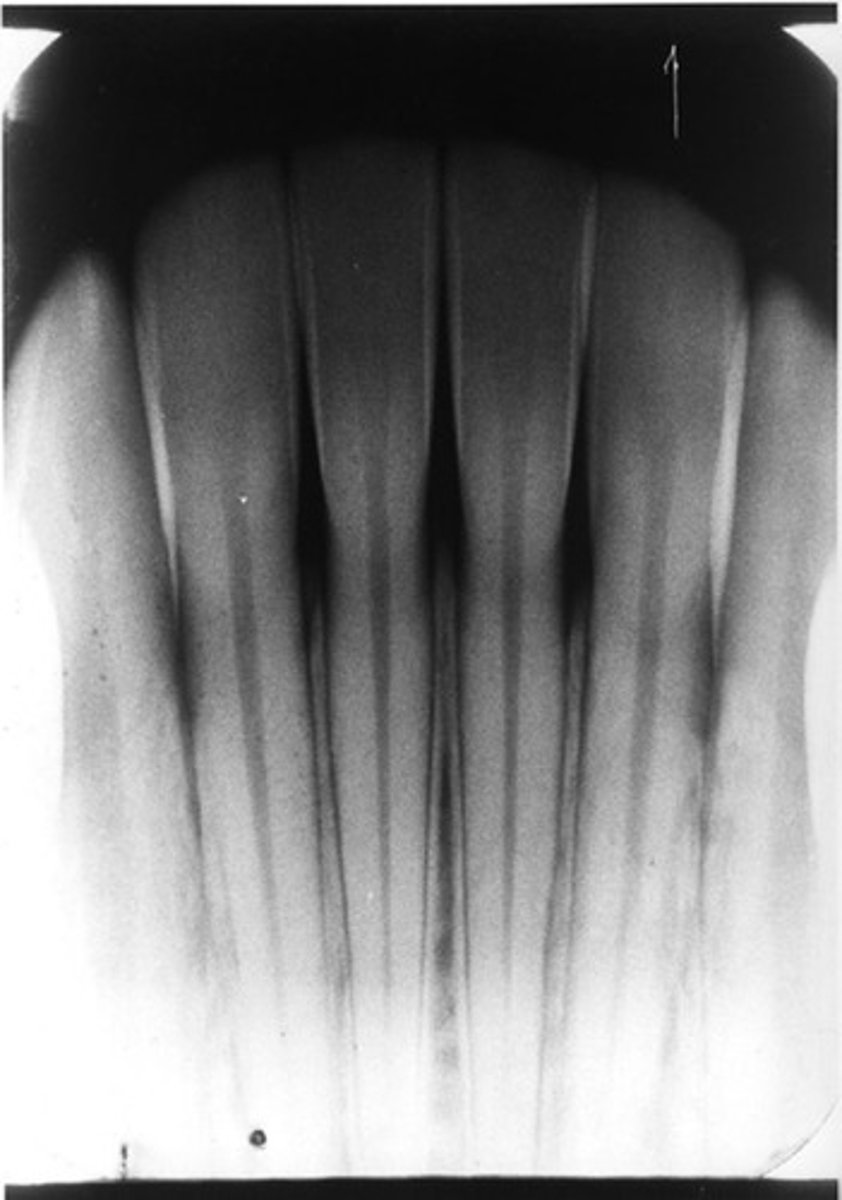
c. increase vertical angulation
the teeth look longer than normal in this radiograph. what should the clinician do to prevent this error next time?
a. increase horizontal angulation
b. decrease horiztonal angulation
c. increase vertical angulation
d.. decrease vertical angulation
1. b (hypertension)
2. d (depression)
3. a (anxiety/depression)
4. e (arthritis)
5. c (allergies)
6. b (hypertension)
match the following medications with its corresponding medical condition. some choices may be used twice.
1. thiazide diuretic (Hydrochlorothiazide) : _____
2. fluoxetine (Prozac) : _____
3. Alprazolam (Xanax) : ______
4. Medrol Dosepak : _______
5. Claritin : _______
6. Lisinopril: ______
a. anxiety/panic disorders
b. hypertension
c. allergies
d. depression
e. arthritis
complete airway obstruction
the patient in your chair starts to clutch his throat and can't talk. what type of airway obstruction does this incident best describe?
perform abdominal thrusts (AKA Heimlich maneuver) until the object is expelled or pt loses consciousness
your patient is conscious with partial airway obstruction and poor air exchange. what should you do?
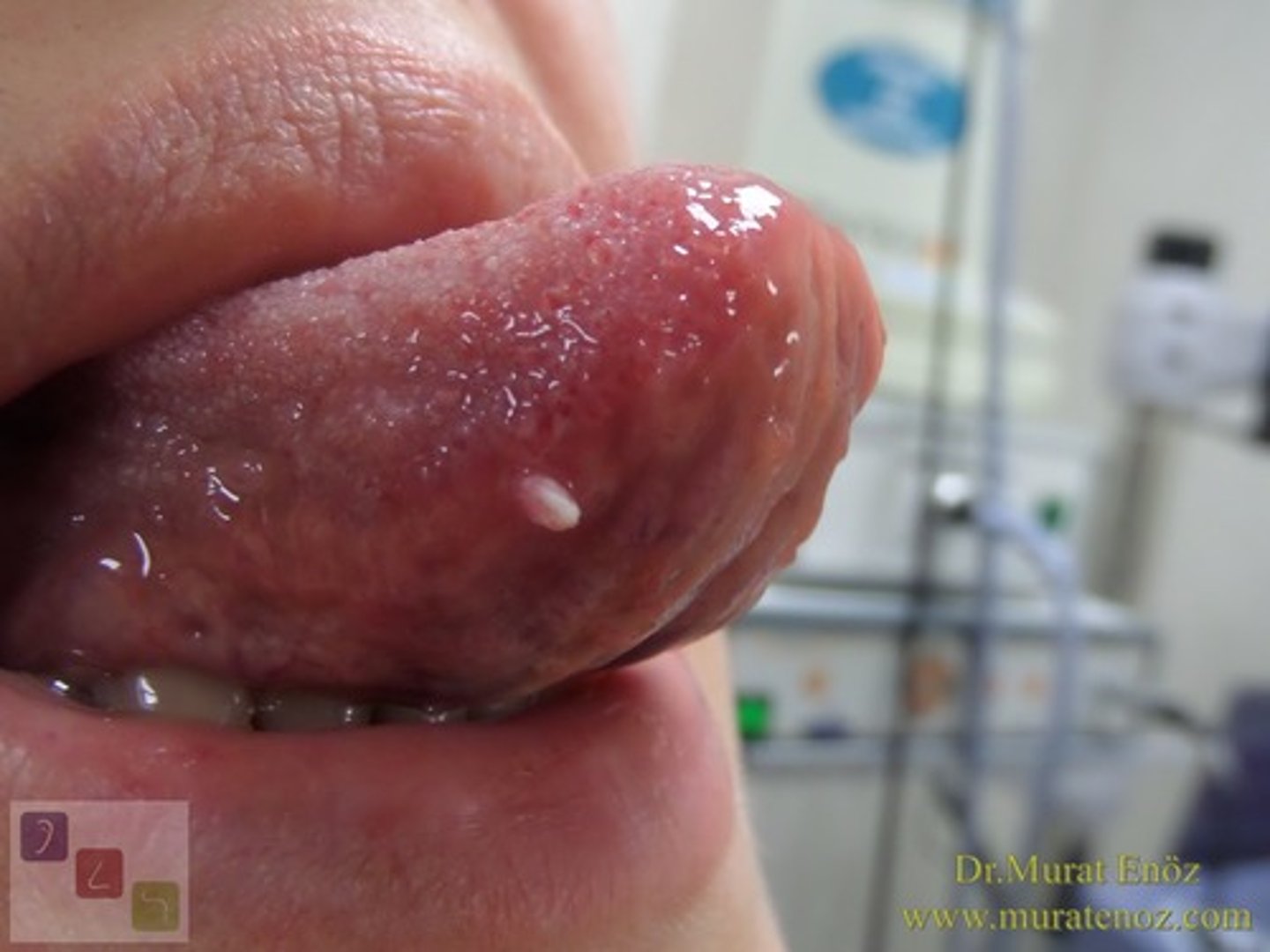
irritation fibroma
- tumor-like growth of scar tissue, normal in color, non-compressible
- commonly found on tongue, buccal mucosa and lips
what lesion is pictured above?
- unilateral facial muscle paralysis
- affects the 7th (facial) cranial nerve
- mobility on unaffected eye
- inability to close eye on affected side
- hereditary
- most pts recover in 3 weeks to 6 months
what are characteristics of Bell's palsy?
- blood vessel in brain is blocked/ruptured preventing oxygen from reaching that part of the brain
- risk factors: hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes, coronary diseases, obesity
- symptoms: sudden weakness uni/bilaterally, difficulty speaking, severe headache, dizziness, loss of balance, visual impairment, drooling on affected side
- do not treat for 6 months post attack
what are characteristics of a cerebrovascular accident (CVA - stroke)?
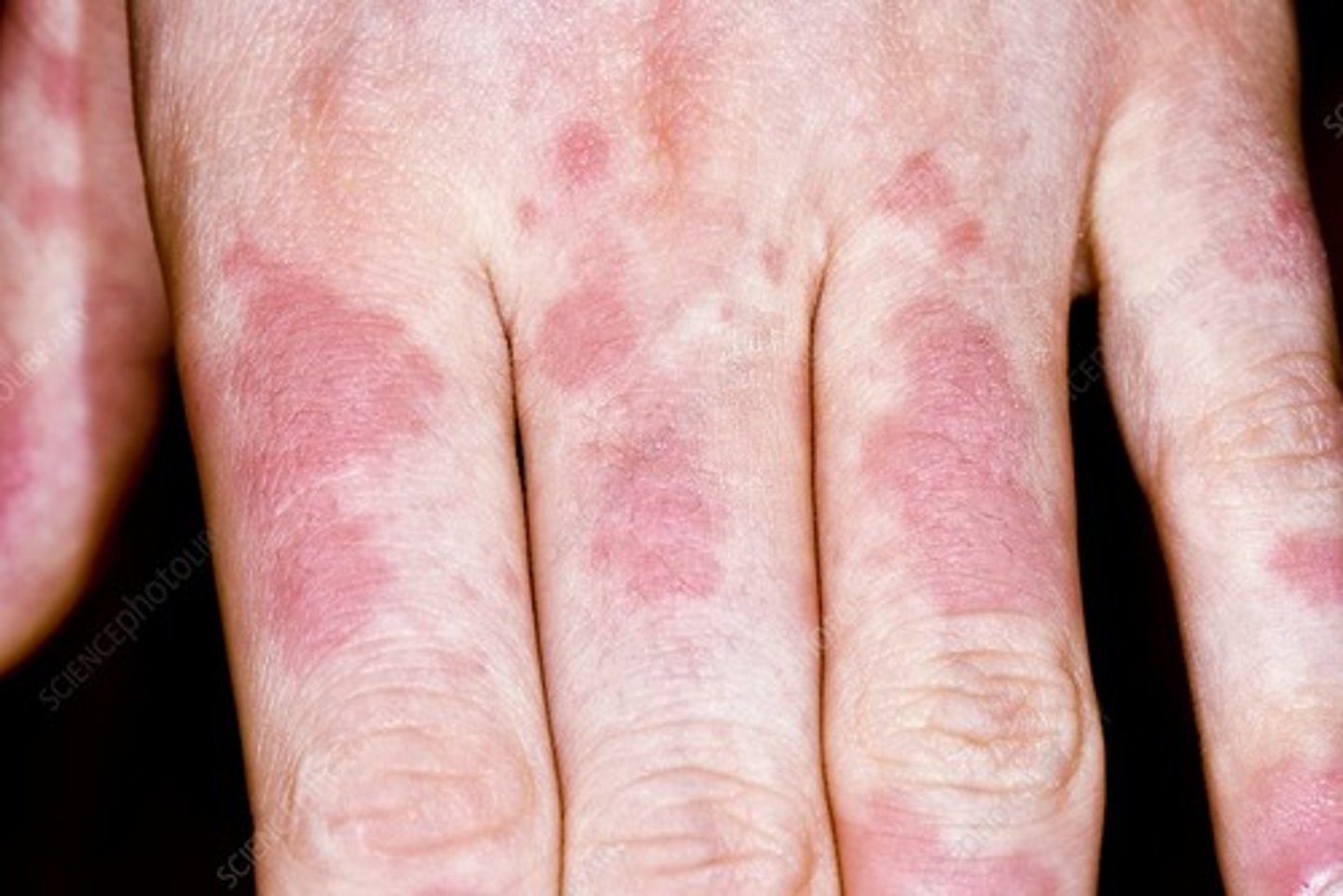
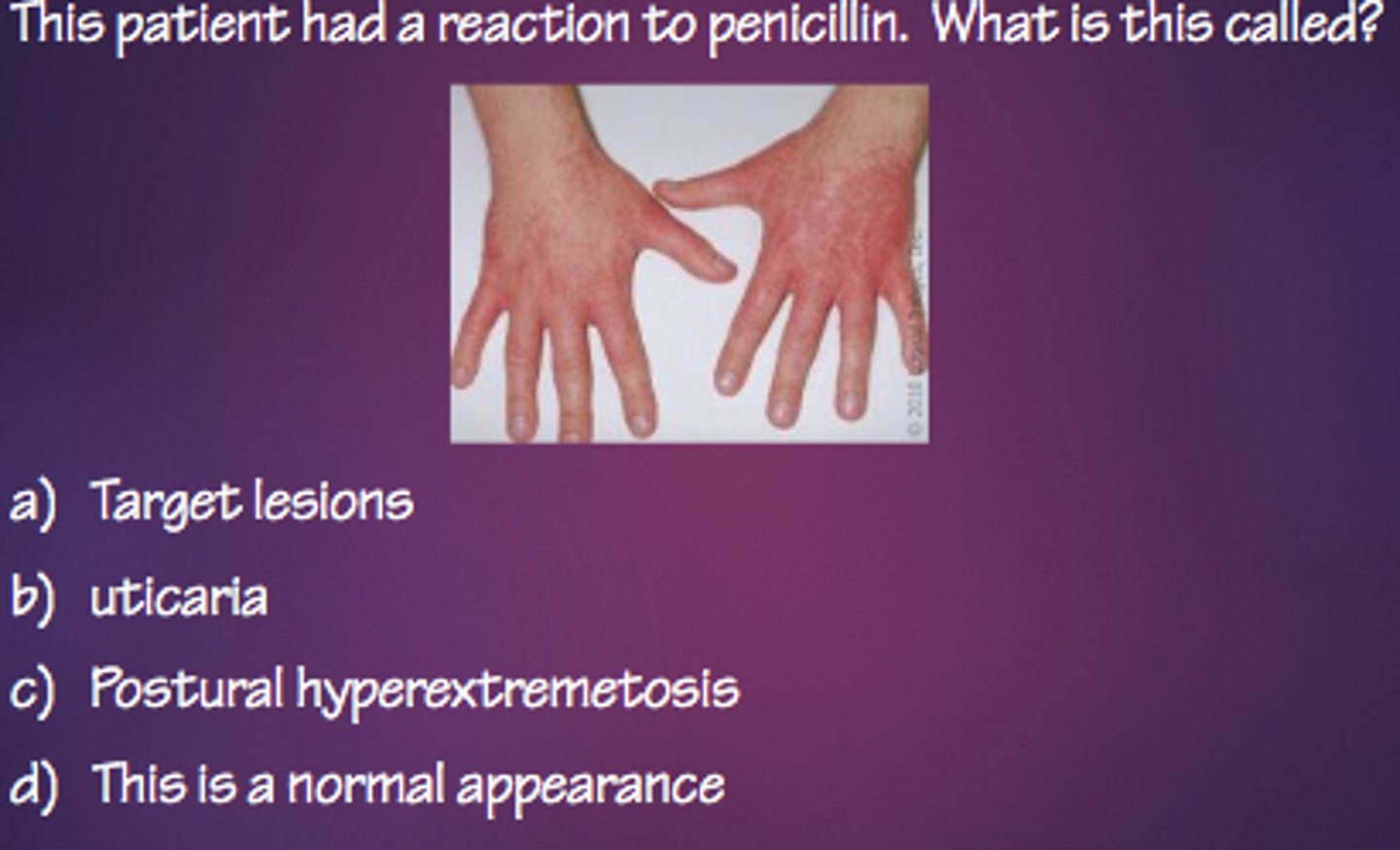
c. urticaria
this patient had an allergic reaction to penicillin and reported rashes on their hand. what is this condition known as?
a. allergies
b. contact dermatitis
c. urticaria
d. psoriasis
b. urticaria
the patient had a reaction to penicillin. what is this called?
a. target lesions
b. urticaria
c. postural lhyperextremetosis
d. this is a normal appearance
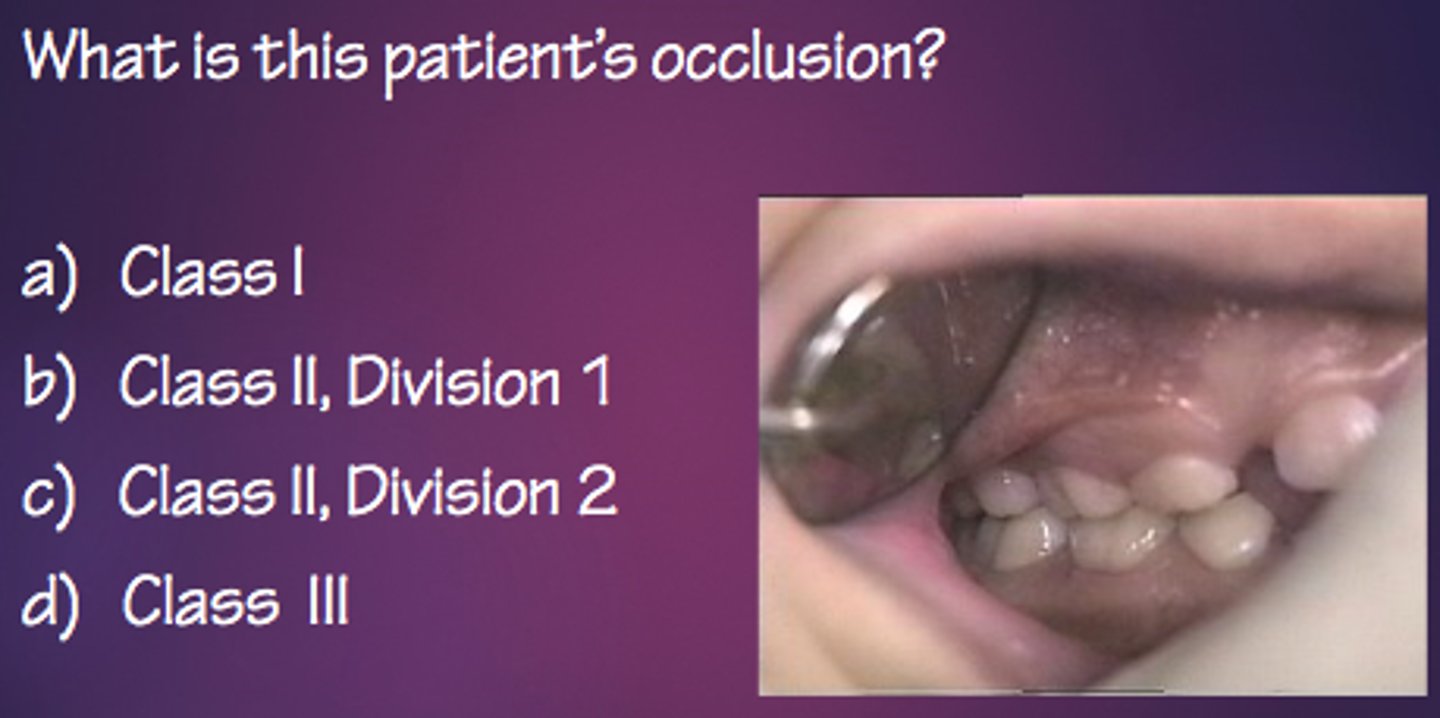
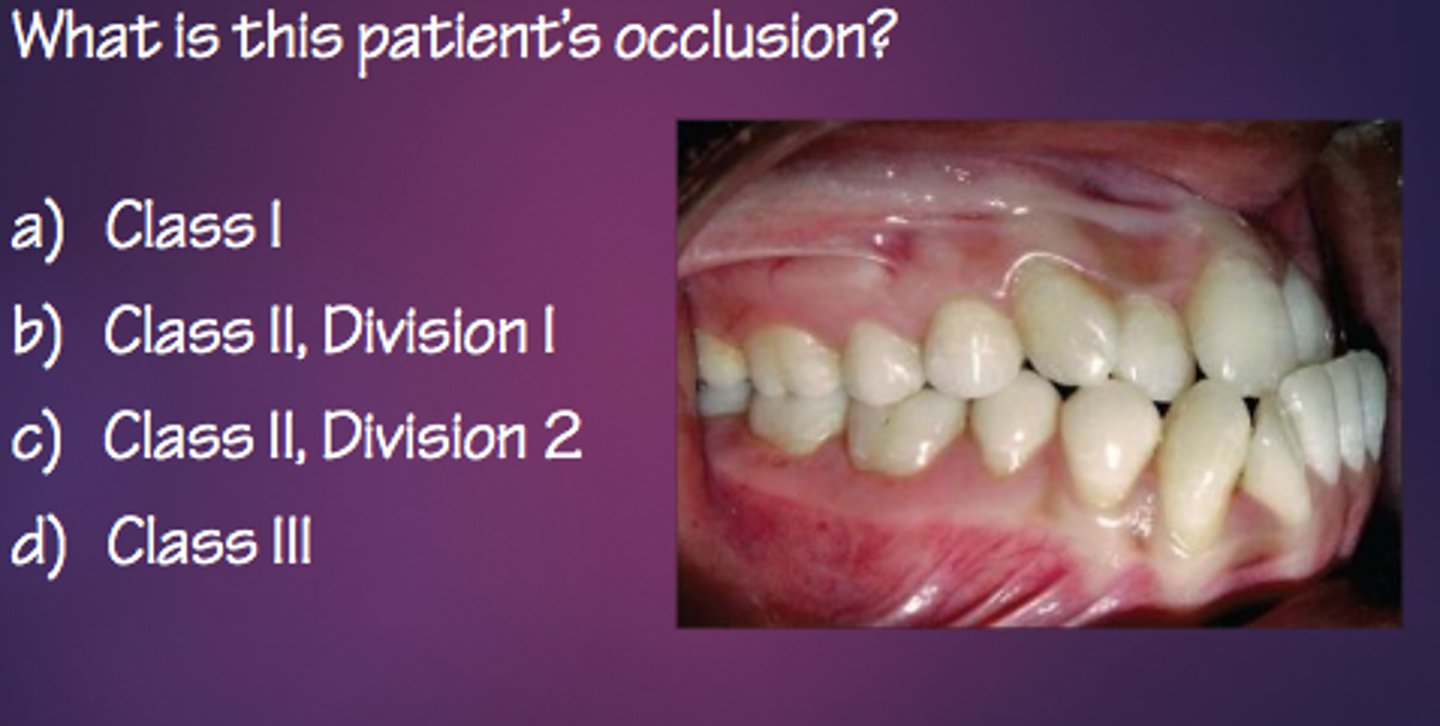
a. class I
what is this patient's occlusion?
a. class I
b. class II, division 1
c. class II, division 2
d. class III
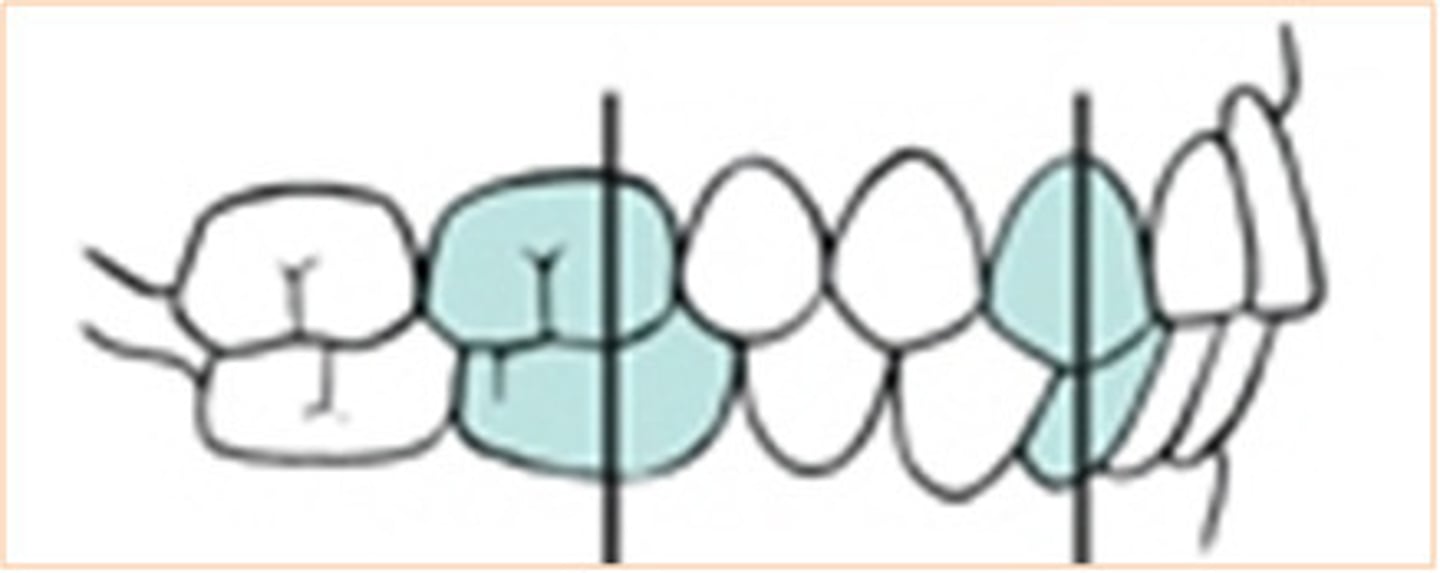
a. class I - pt has a mixed dentition
b. class II, division 1
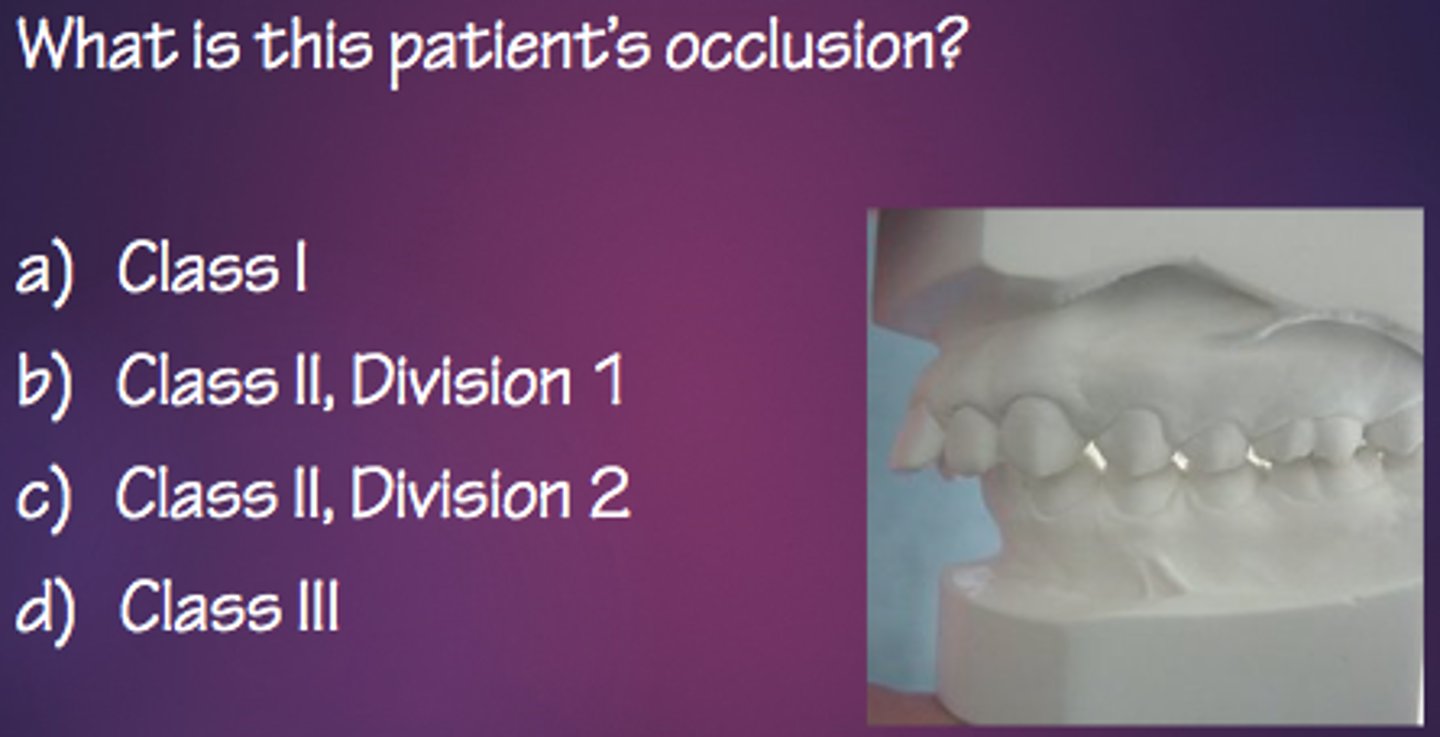
d. class III
- contaminated needles
- anesthetic capsules
- matrix bands
- scalpel blades
- ortho wires/bands
- endo instruments
what are examples of items that would be placed into a sharps container?
- paper towels
- barriers
- gloves
- masks
- drapes
what are examples of items that would be placed into normal trash?
- sharps
- items that drip of saturated blood and/or saliva
- hard and soft tissues removed from pts mouth
what are examples of items that would be placed into a biohazard container?
goiter
when we are palpating the center of the neck, we are feeling for:
TMJ - crepitus
when we perform a bilateral palpation near the tragus we are feeling for:
thyroid gland
when you palpate the neck and the patient swallows you are checking the:
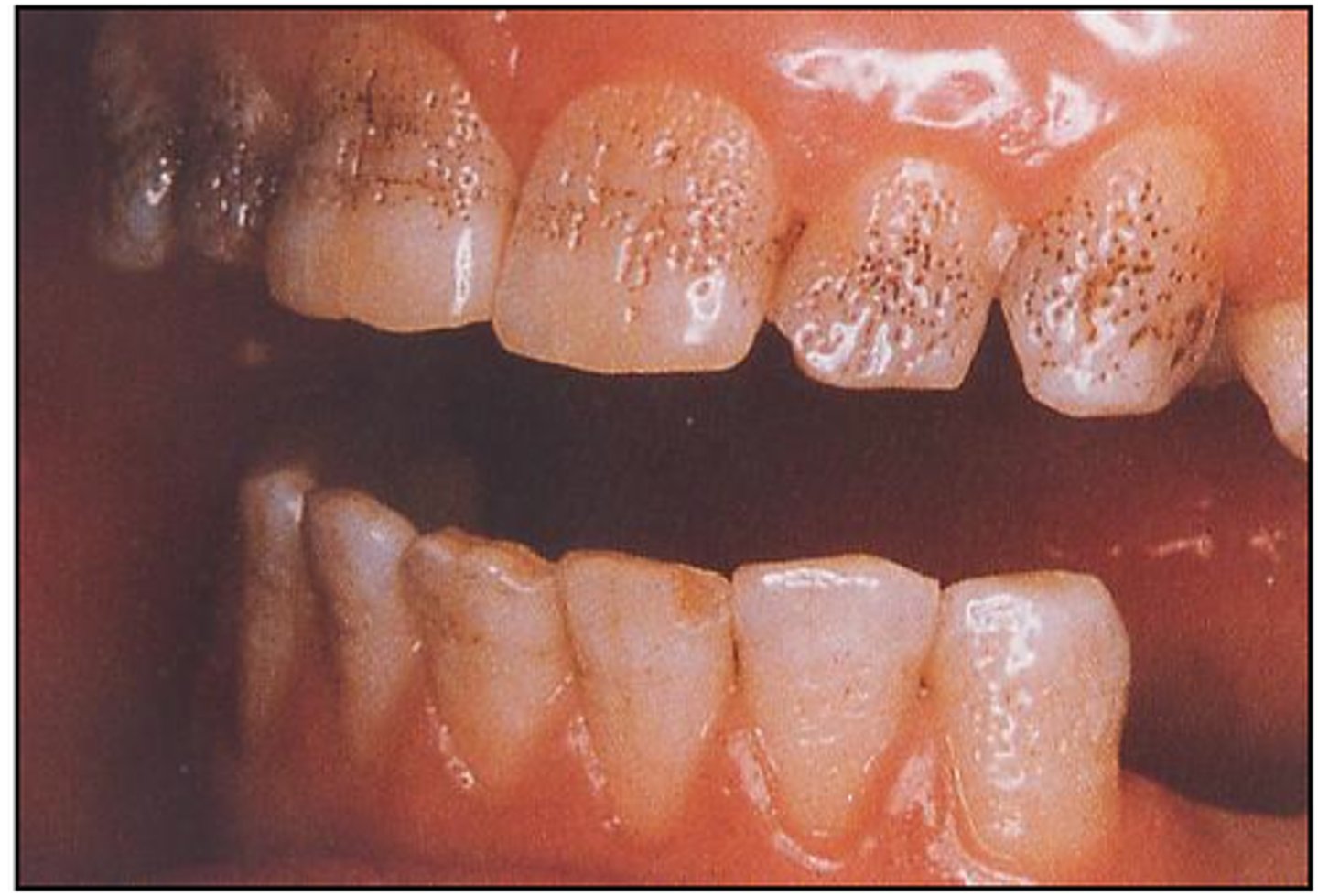
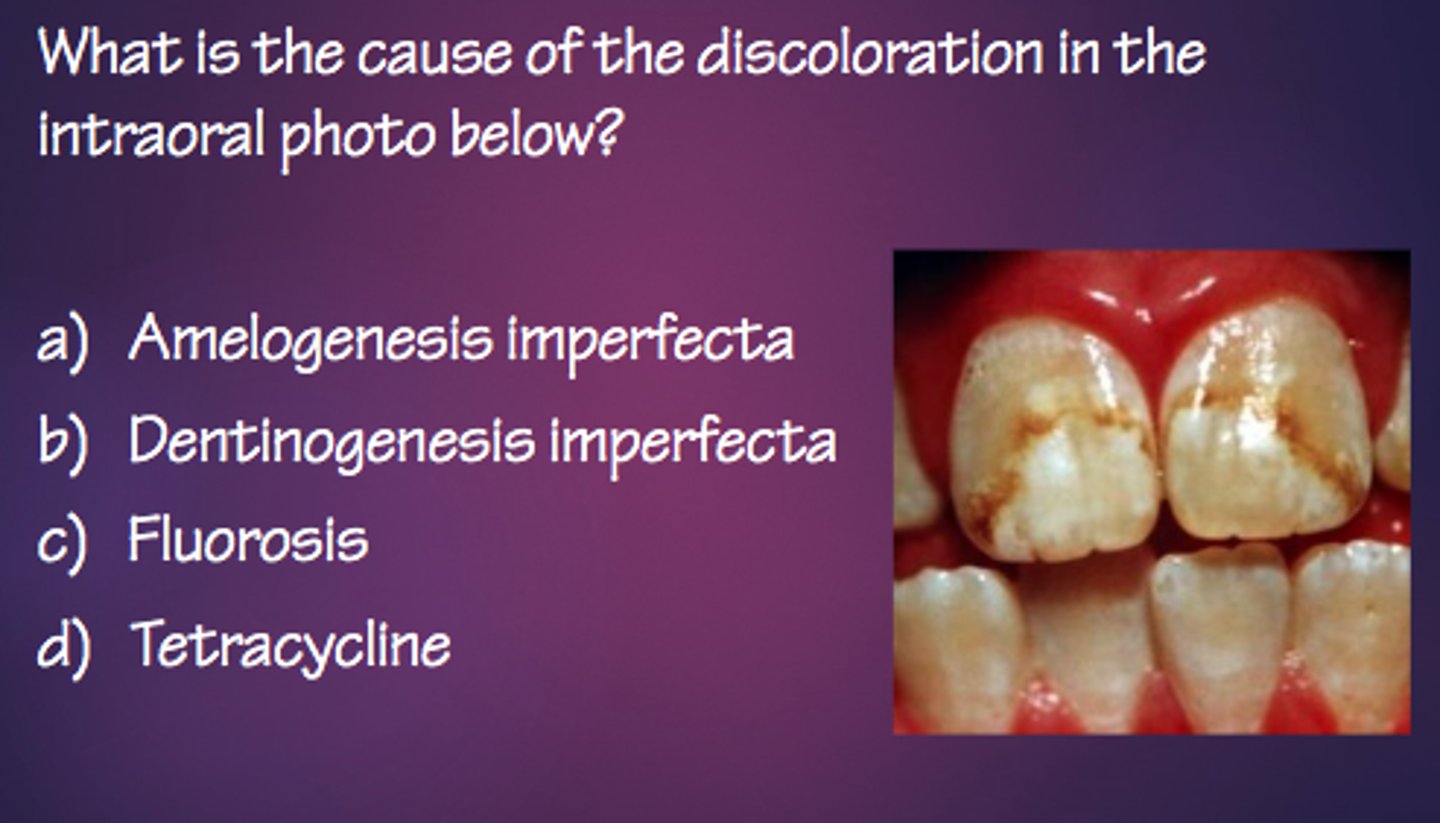
c. amelogenesis imperfecta
what condition is shown in the picture?
a. dentinogenesis imperfecta
b. fluorosis
c. amelogenesis imperfecta
d. tetracycline
c. amelogenesis imperfecta
what condition is shown in the picture?
a. dentinogenesis imperfecta
b. fluorosis
c. amelogenesis imperfecta
d. tetracycline
c. fluorosis
aspirin burn
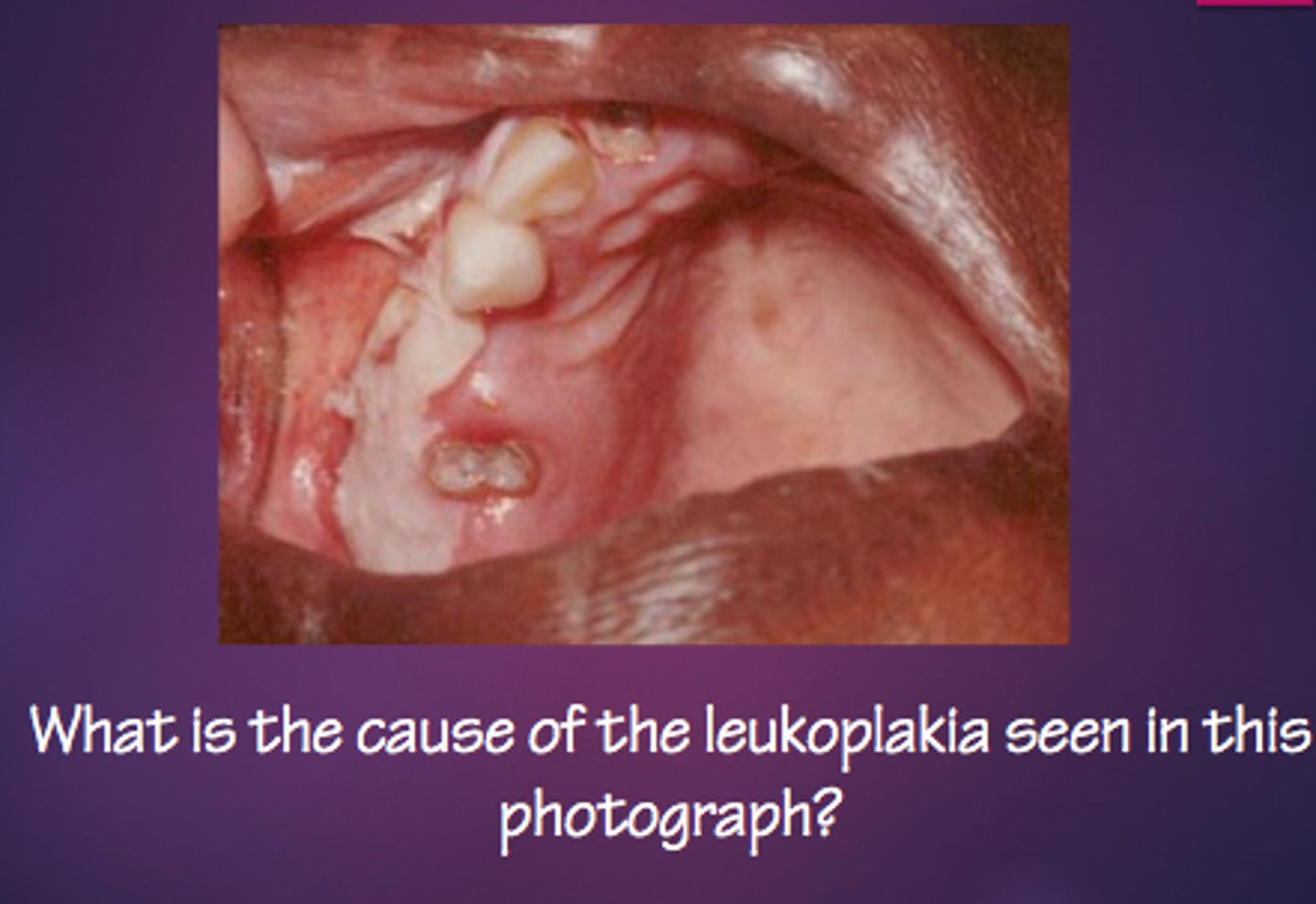
aspirin burn
a patient comes in and complains of tooth pain and has wrinkled white buccal mucosa that can be easily peeled off. what condition does the patient present with?
c. leukoedema
what condition is pictured?
a. linchen planus
b. leukoplakia
c. leukoedema
d. linea alba
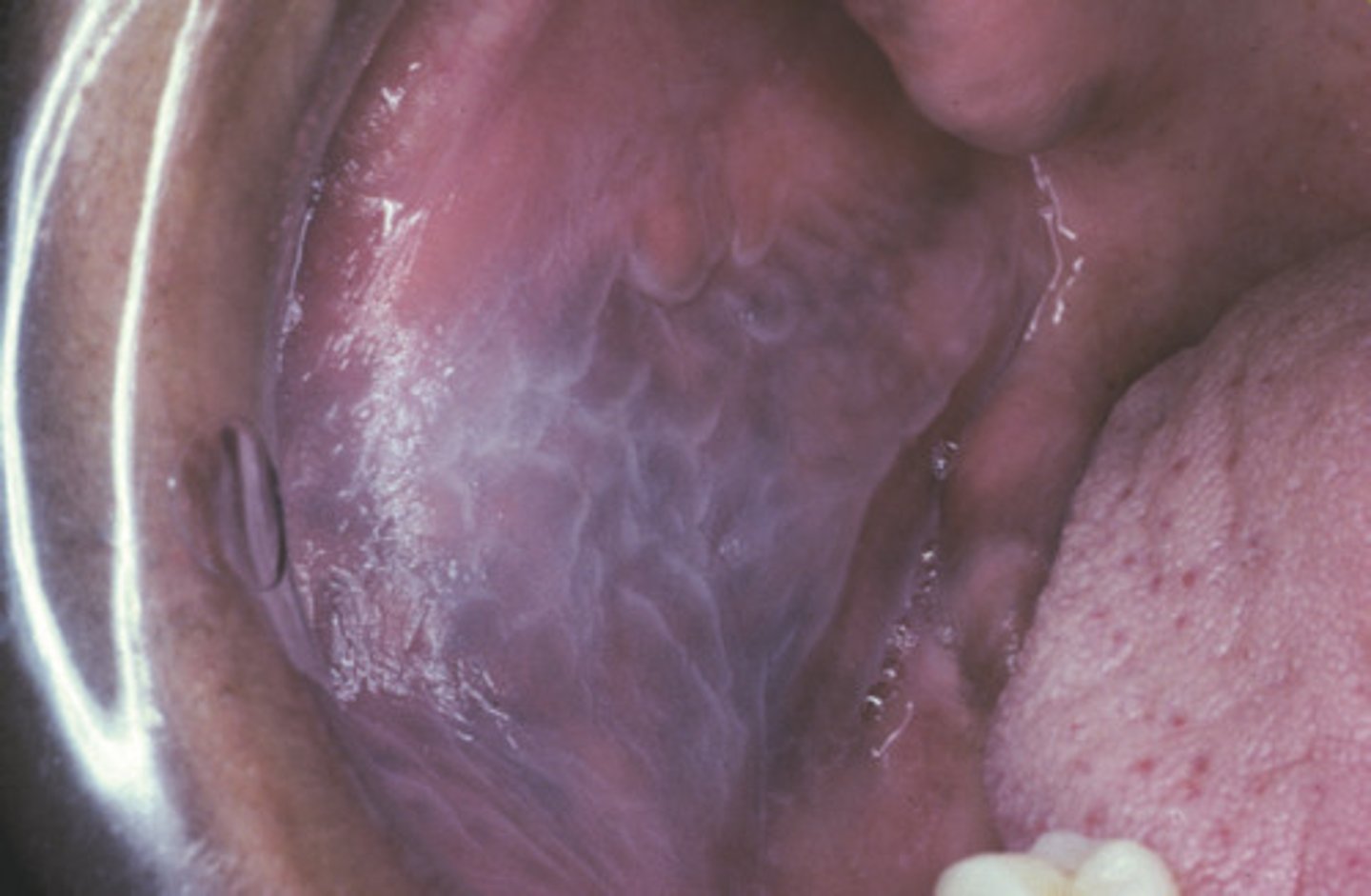
c. leukoedema
a patient comes in with this on their buccal mucosa and it does not wipe off. what is the condition?
a. linchen planus
b. leukoplakia
c. leukoedema
d. linea alba
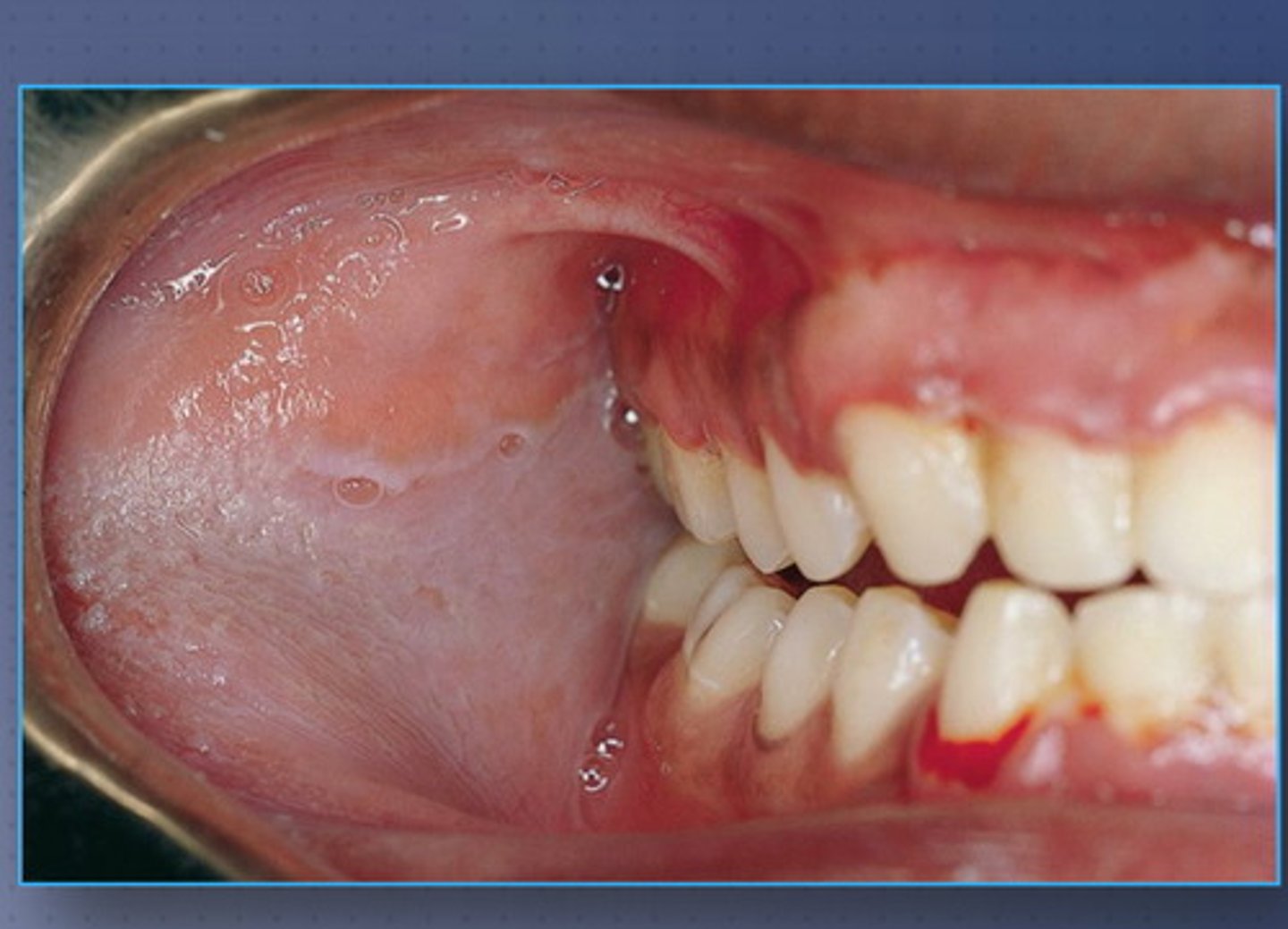
b. leukoplakia
this lesion is caused by Epstein Barr virus. it cannot be wiped off. what is the condition?
a. linchen planus
b. leukoplakia
c. leukoedema
d. linea alba
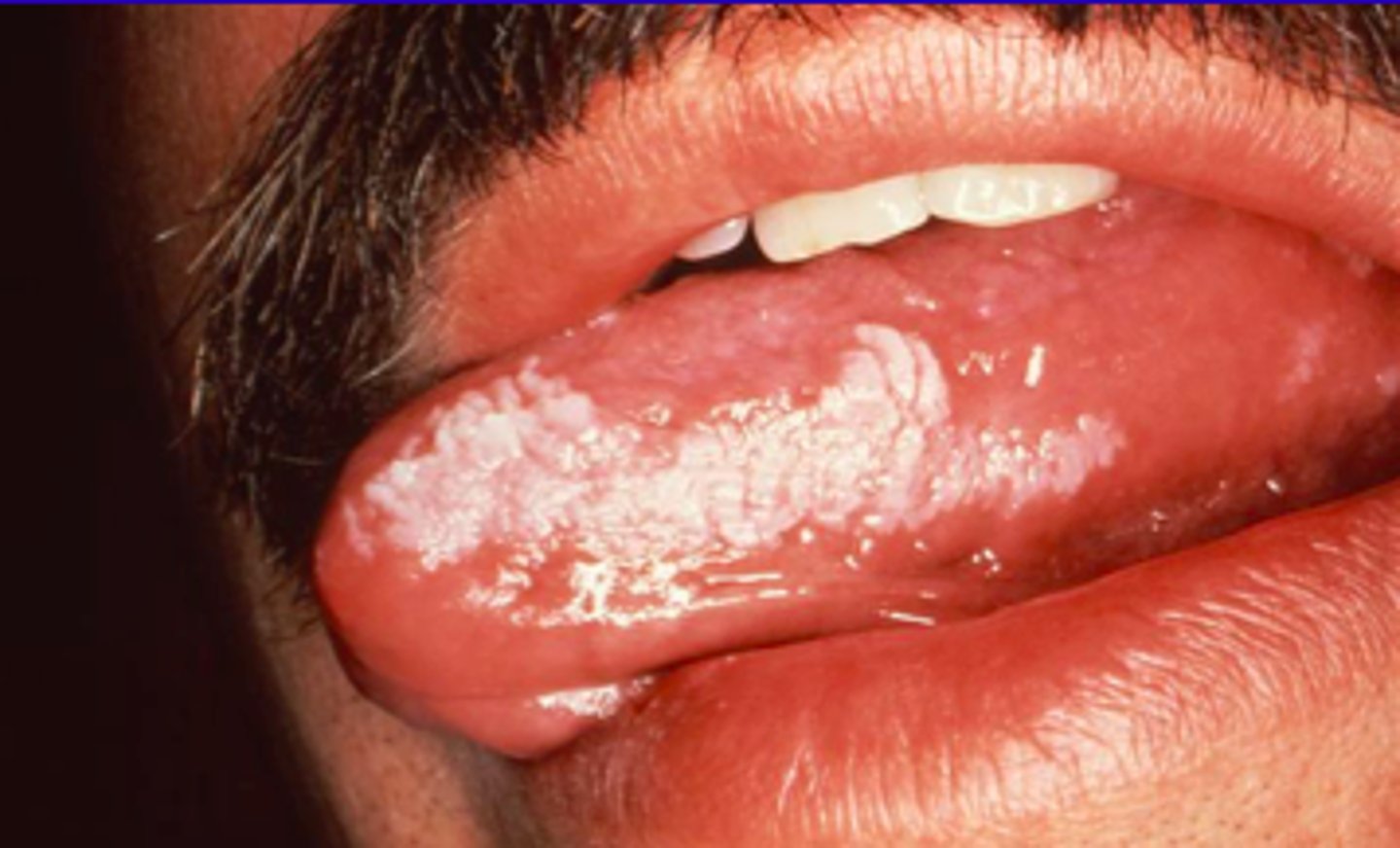
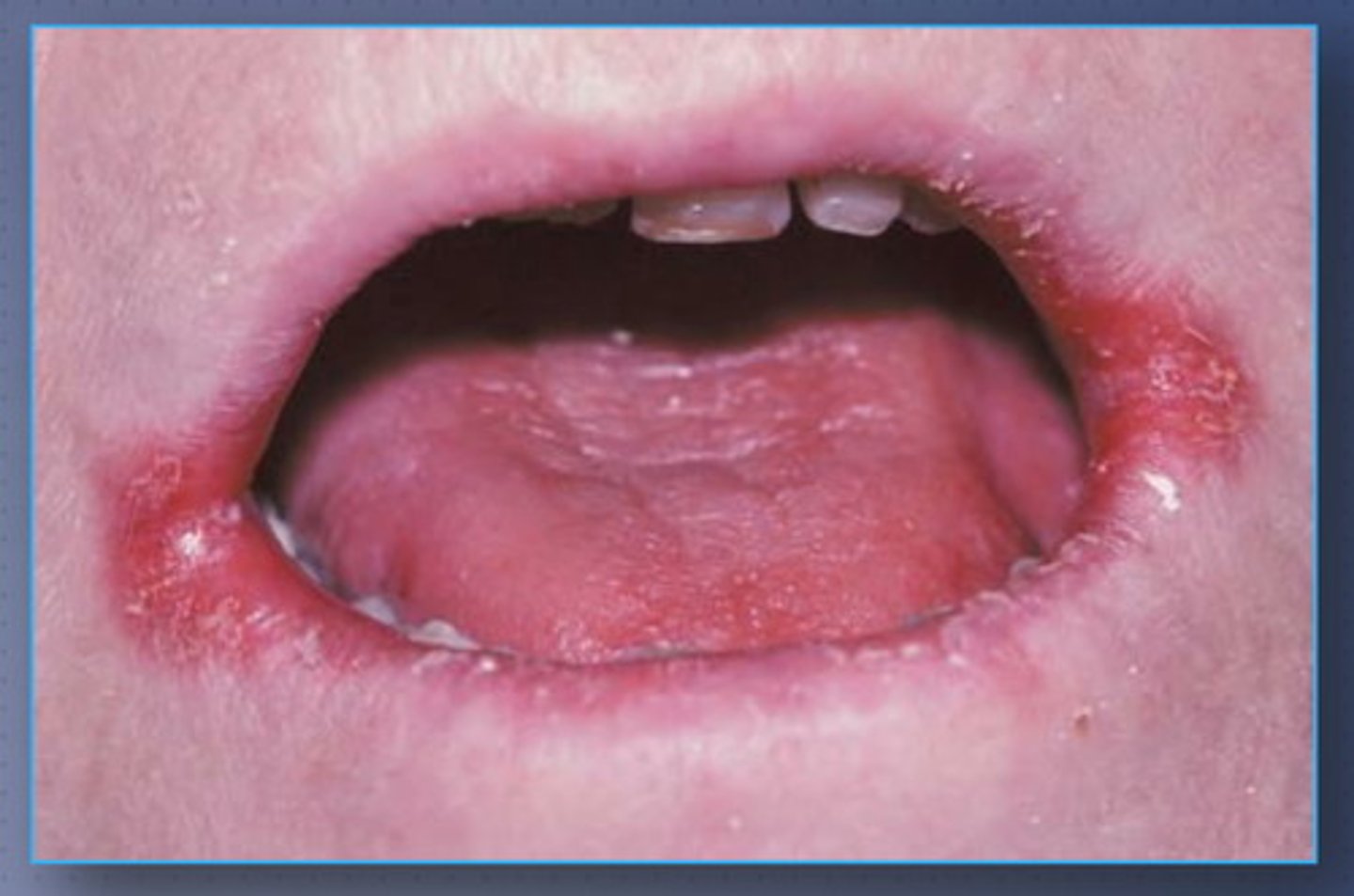
condition: angular chelitis
caused by: candida albicans
what is the condition that is pictured? what causes this?
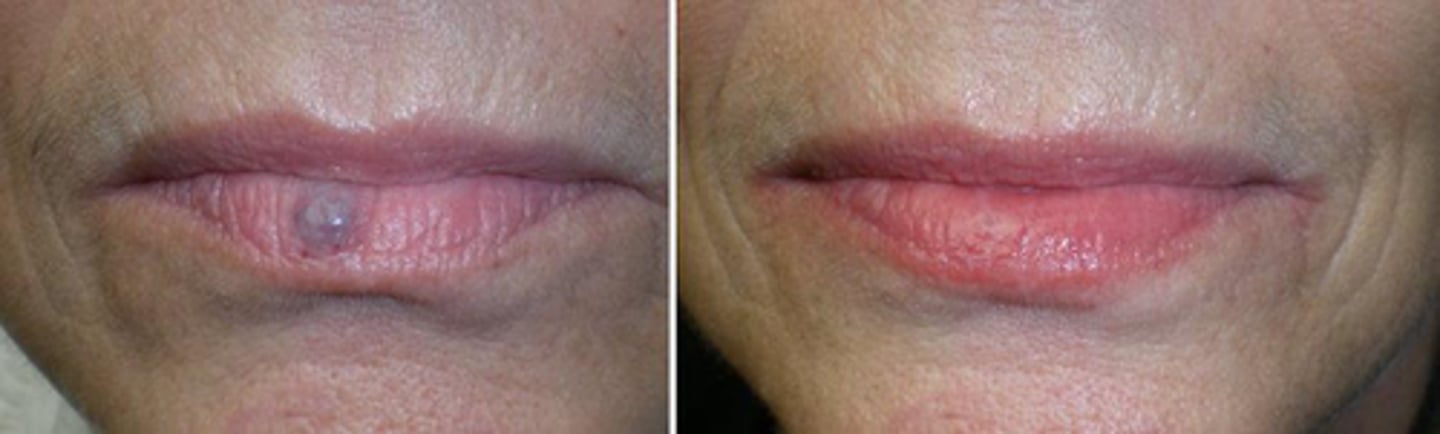
b. hemangioma
* this answer makes the most sense because the other options are caused by trauma, a hemangioma is present at birth
a blue lesion that appears on the lower lip, pt states it has been present from birth. what is the lesion?
a. hematoma
b. hemangioma
c. mucocele
d. fibroma
c. 14-21 minutes
how long is Oraqix effective?
a. 5-10 minutes
b. 10 minutes
c. 14-21 minutes
d. 30 minutes
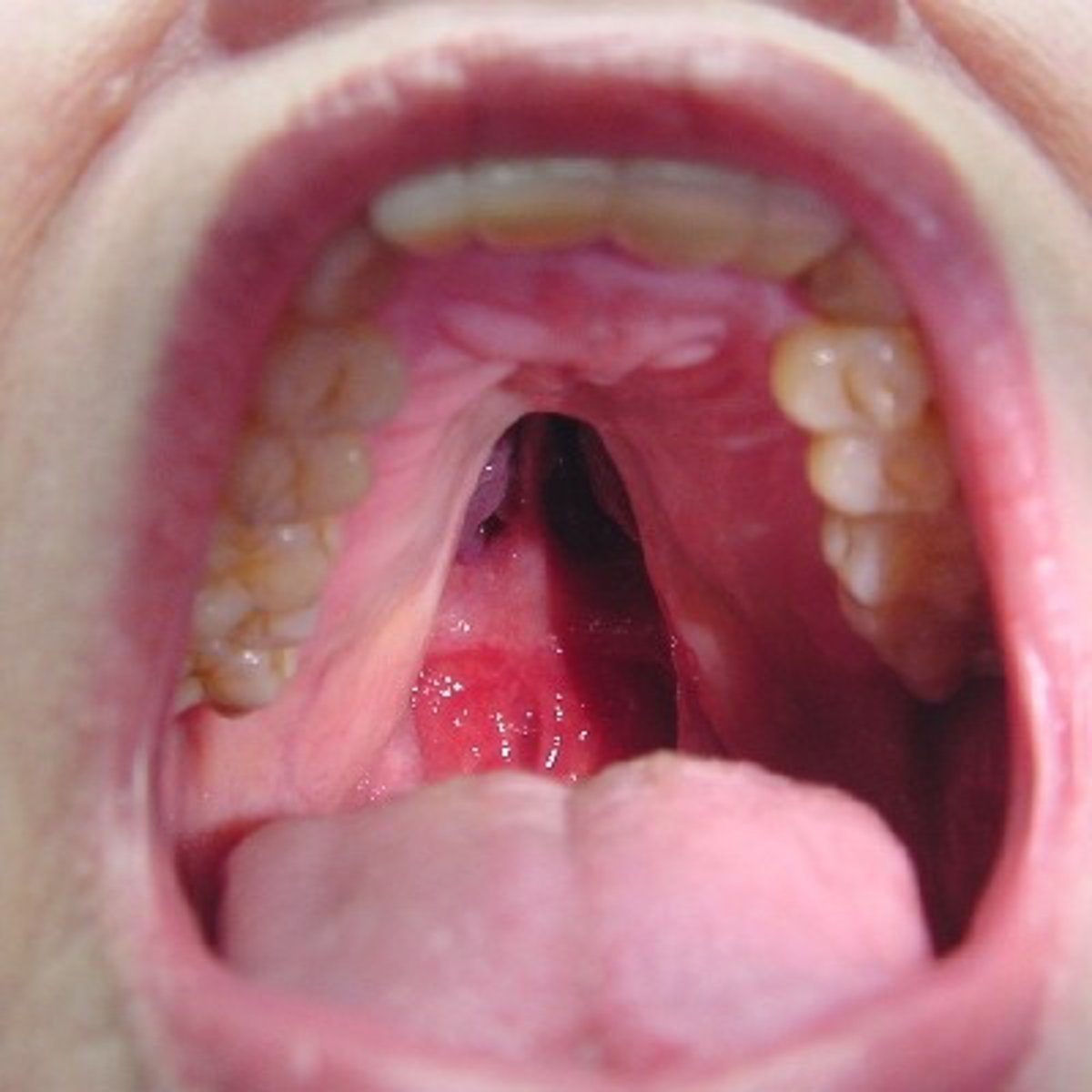
cleft palate
what is the most significant thing related to this picture? (primary concern in this patient)
contact the orthopedic surgeon
a patient comes in and states they recently had hip replacement surgery. does this patient require a premed?
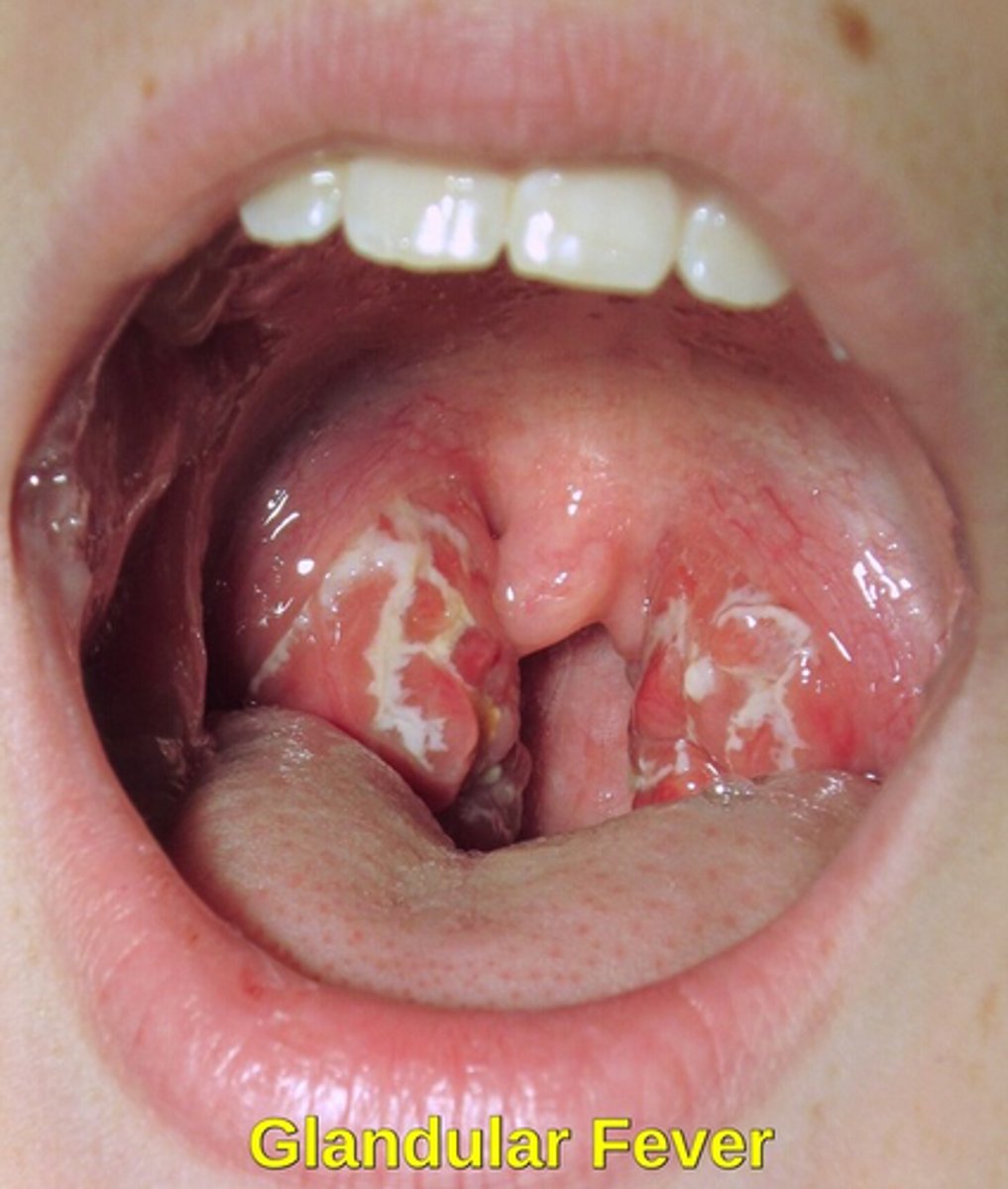
mononucleosis
a patient presents with Epstein Barr virus. his intra oral lesions are examples of what?
Vancomycin
what is the agent of choice for the treatment of invasive MRSA?
anticoagulant
what is the best type of therapy for the treatment of deep venous thrombosis?
1. linea alba - no
2. leukoplakia - yes
3. leukoedema - no
4. rhomboid (geographic tongue) - maybe if an anti-fungal does not work
5. cancer on tongue - yes
which of these conditions require a biopsy? (there will be pictures on the exam)
1. linea alba - (yes/no)
2. leukoplakia - (yes/no)
3. leukoedema - (yes/no)
4. rhomboid (geographic tongue) - (yes/no)
5. cancer on tongue - (yes/no)
1. abrasive toothpaste - no
2. toothpick in plastic holder - no
3. proxy brush metal - no
4. manual toothbrush - yes
5. powered toothbrush - yes
6. dental tape - yes
7. floss threader - yes
8. interdental brush - no
which of the following OPT aids can a patient with an implant use?
1. abrasive toothpaste - (yes/no)
2. toothpick in plastic holder - (yes/no)
3. proxy brush metal - (yes/no)
4. manual toothbrush - (yes/no)
5. powered toothbrush - (yes/no)
6. dental tape - (yes/no)
7. floss threader - (yes/no)
8. interdental brush - (yes/no)
1. give oxygen - yes
2. give tablet sublingually - yes
3. give epinephrine - no
4. lay patient supine - no
5. put patient upright - yes
which of the following should be done when giving a patient nitroglycerin?
1. give oxygen - (yes/no)
2. give tablet sublingually - (yes/no)
3. give epinephrine - (yes/no)
4. lay patient supine - (yes/no)
5. put patient upright - (yes/no)
to prevent infection - prevent bacteremia
why do certain patients require a premedication prior to dental treatment?
frequency of carb intake
what is the closest nutritional relationship that causes an increased risk for caries?
a. posterior teeth with shallow pockets
where would you use an instrument with a contra angle and short tip?
a. posterior teeth with shallow pockets
b. posterior teeth with deep pockets
c. anterior teeth with shallow pockets
d. anterior teeth with deep pockets
amoxicillin - 2g 1 hour prior to appointment
what drug is considered the standard for premedication? what is the dosage?
amoxicillin - 2g 30min to 1 hour before appt
your patient has no allergies and no know contraindications, what would you prescribe this patient?
- clindamycin : 600mg 1 hour prior
- azithromycin : 500mg 1 hour prior
- clarithromycin : 500mg 1 hour prior
if the patient is allergic to penicillin, what are other premedication options? what are their dosages?
b. ASA 2
* pts with mild systemic diseases, well controlled chronic conditions
a patient with controlled epilepsy is classified as what ASA?
a. ASA 1
b. ASA 2
c. ASA 3
d. ASA 4
b. contact dermatitis

HIV
a patient presents with these lesions on their palate. what condition does the patient have?
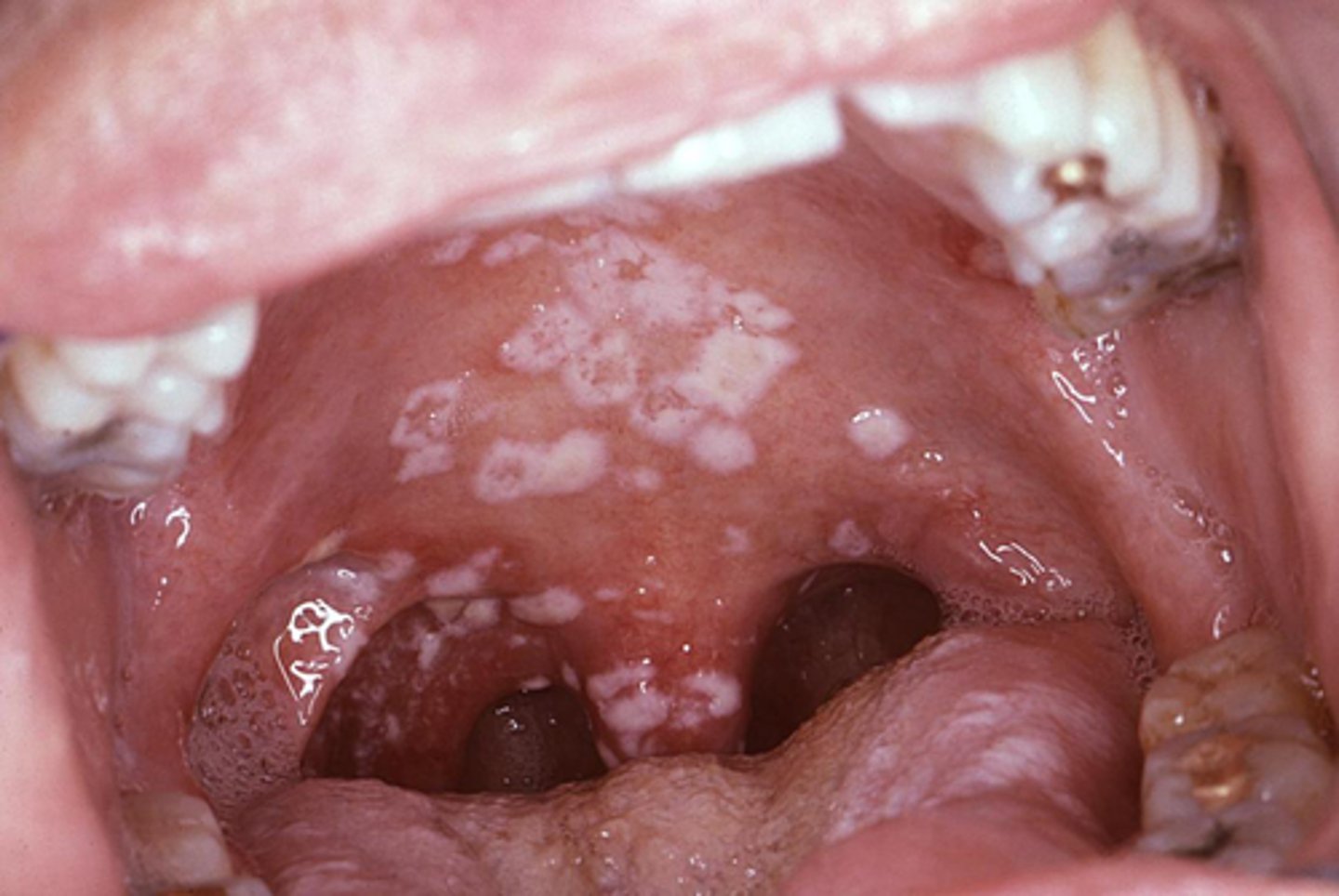
HIV
a patient presents with these lesions on their palate. what condition does the patient have?
a. neoplasm
level 1 mask : low level
N95 mask : high level
disposable gown : low level
non-fluid resistant gown : high level
face shield : high level
bonnet/hair cup : low level
label the following PPE items as either low level protection or high level protection.
level 1 mask : ___
N95 mask : ___
disposable gown : ___
non-fluid resistant gown: ___
face shield : ___
bonnet/hair cap : ___
2. minocycline
4. works immediately
6. lasts for 21 days
7. 1mg of minocycline
4 of the statements below describe this image. which 4 are the correct statements that accurately describe the image?
1. doxycycline
2. minocycline
3. works within 1 hour
4. works immediately
5. don't brush teeth for 12 hours
6. lasts for 21 days
7. 1mg dispensed
8. 5mg dispensed
d. gracey 13/14 or 17/18
what is the best instrument for scaling the distal of #30?
a. sickle scaler
b. gracey 11/12
c. gracey 15/16
d. gracey 13/14 or 17/18
furcation involvement
what is being measured in regards to the probe?
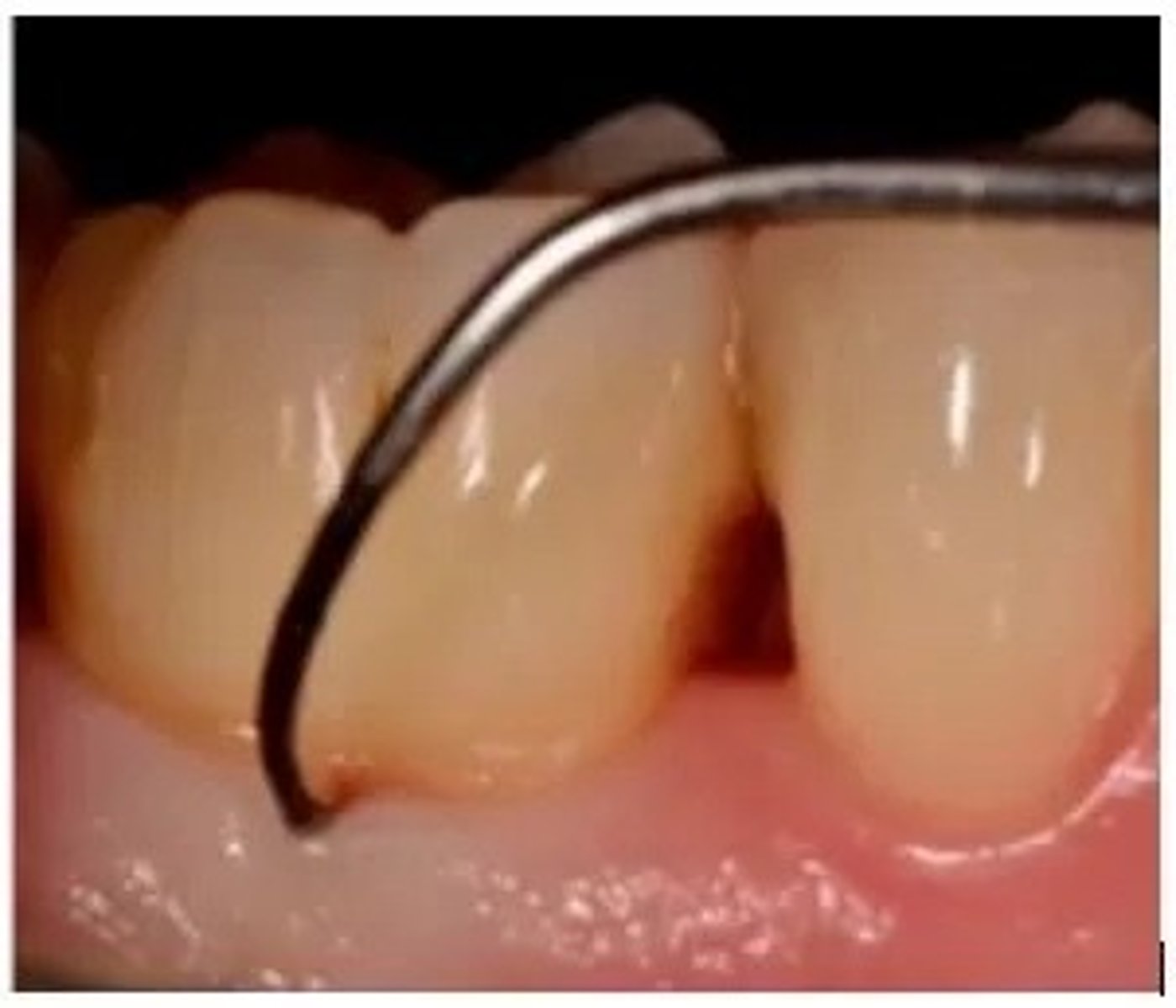
c. furcation involvement
what is being measured in regards to the probe?
a. recession
b. pocket depth
c. furcation involvement
d. clinical attachment level
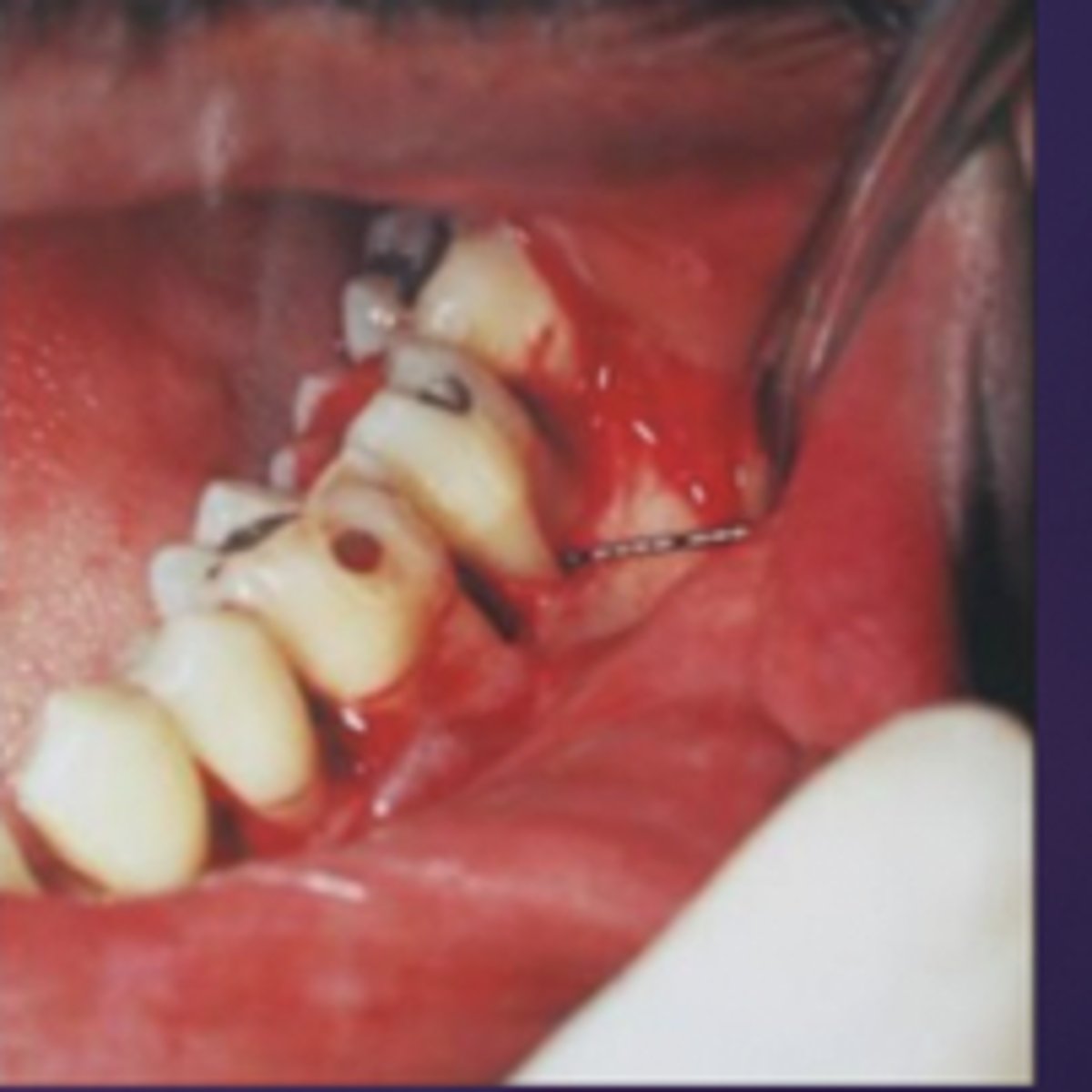
CVA - stroke
your patient loses consciousness and has one sided weakness once consciousness has been regained. what can the hygienist assumed happened?
how long has it been there?
what is the most important question for a doctor to ask before making a diagnosis?
c. 60%
alcohol sanitizing spray in a dental office should be at least what percentage?
a. 30%
b. 50%
c. 60%
d. 99%
a. activate EMS
*Unresponsive = EMS
after being called to the reception area and seeing an unresponsive patient, what do you do next?
a. activate EMS
b. start chest compressions
c. check for broken bones
d. check airway for obstruction
1. B - not needed
2. A - needed
3. A - needed
4. B - not needed
5. A - needed
6. A - needed
in regards to informed consent, mark the following statements as either needed or not needed:
1. informed consent is not needed : ____
2. legal signature of patient : ___
3. risk of treatment : ___
4. post-care instructions : ___
5. confirmation of patient competency : ___
6. understanding language : ___
A. needed
B. not needed
impaired healing
your patient states that he is taking steroids. what should you be concerned about with this patient?
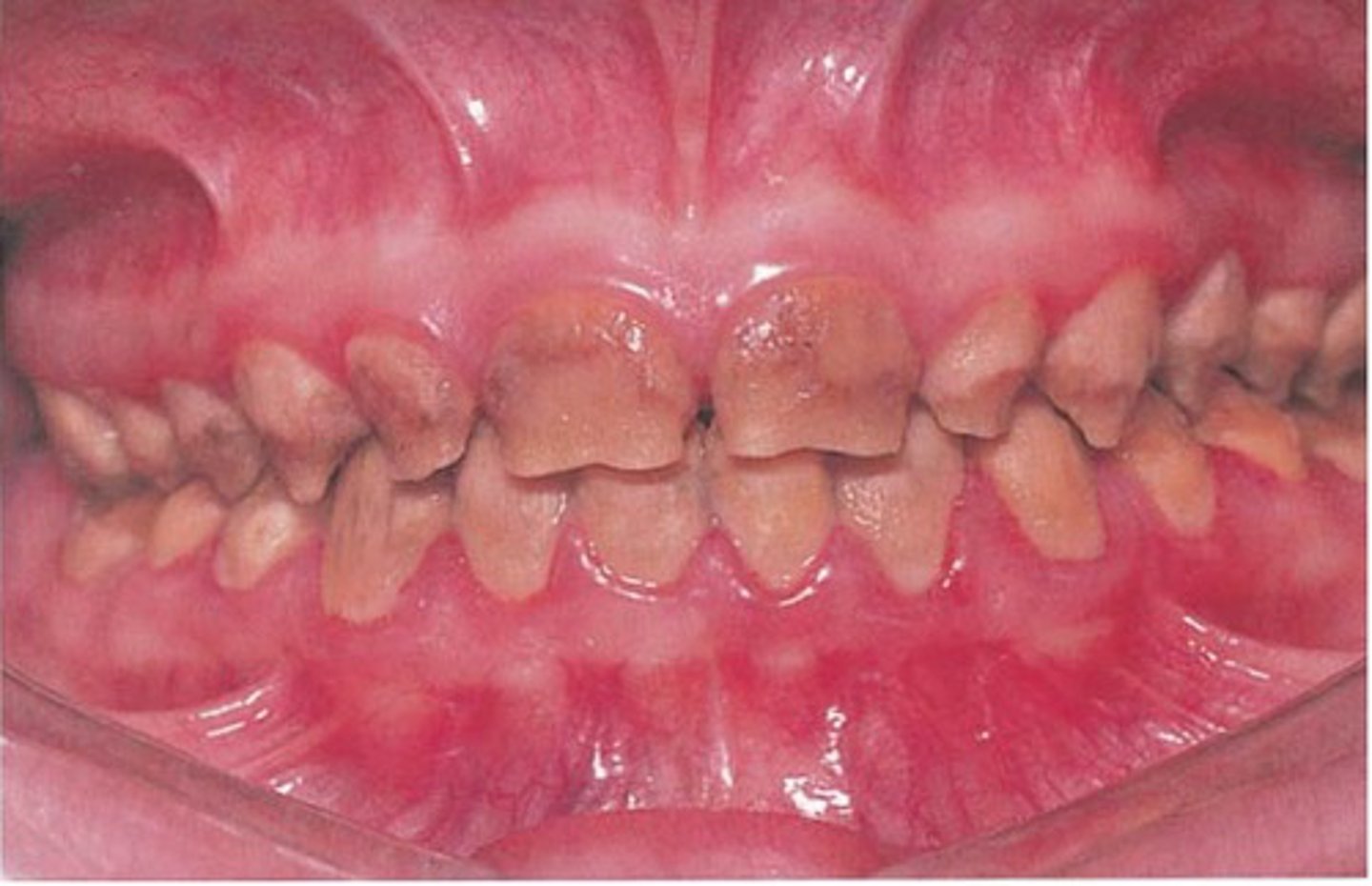
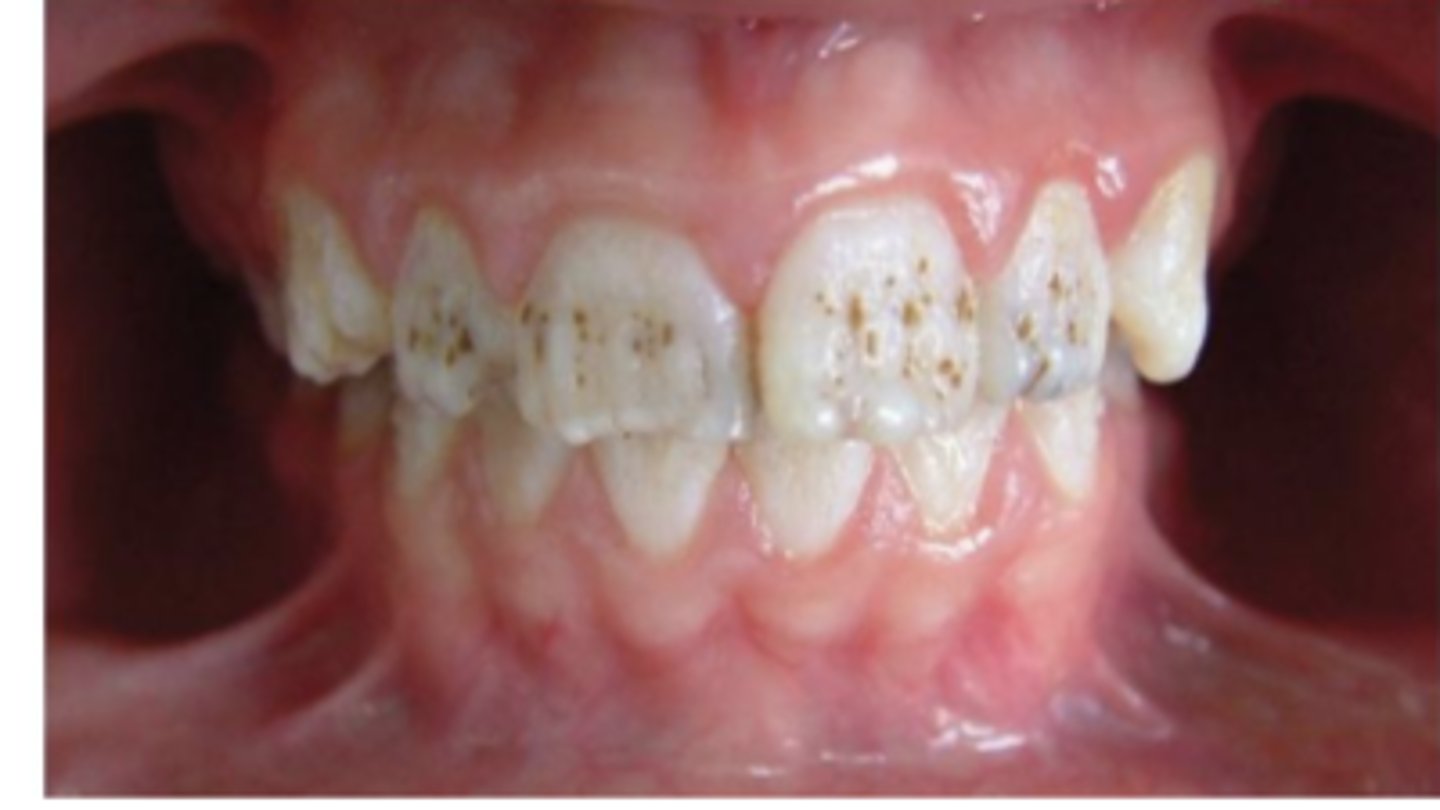
fluorosis
your patient presents with teeth as shown in the picture. the patient has no previous history of caries. what condition does this patient have?
c. gingivitis
all of the following would contribute to a patients malocclusion EXCEPT?
a. protruded teeth
b. posterior crossbite
c. gingivitis
d. open bite
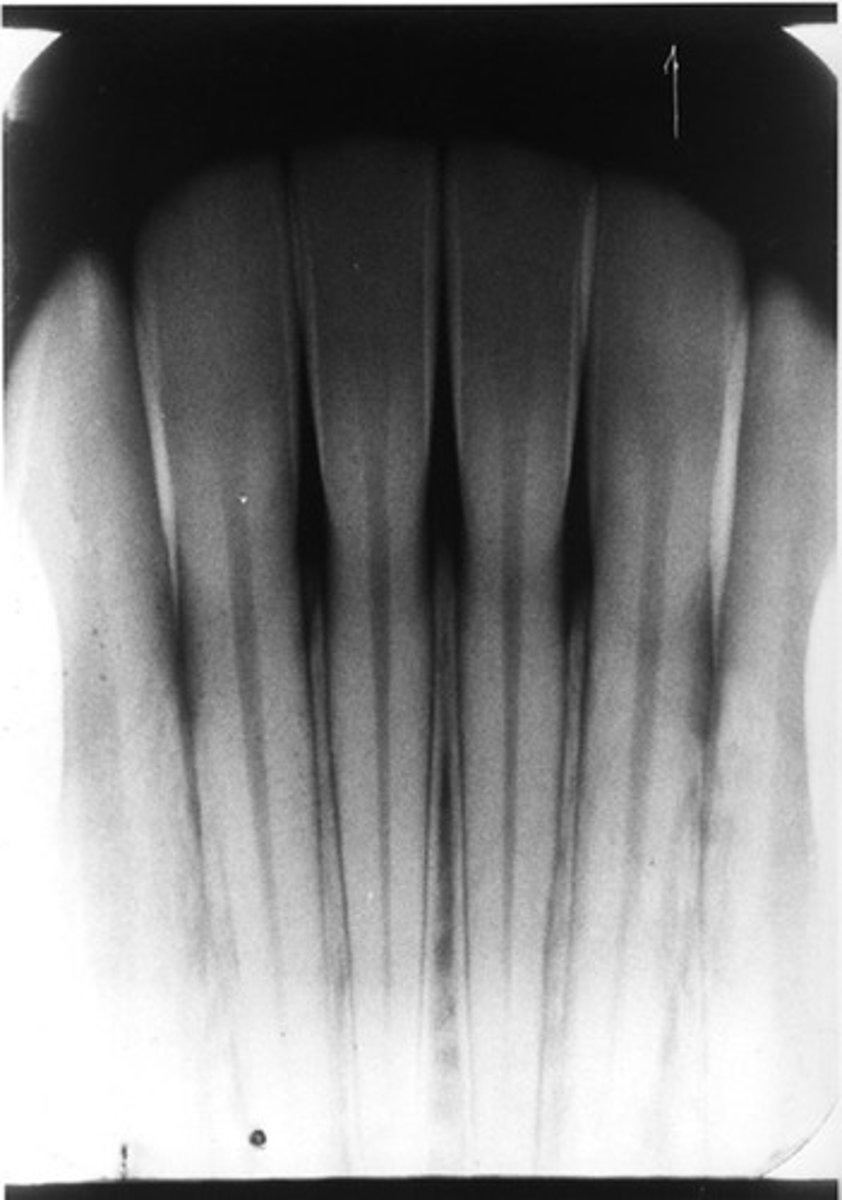
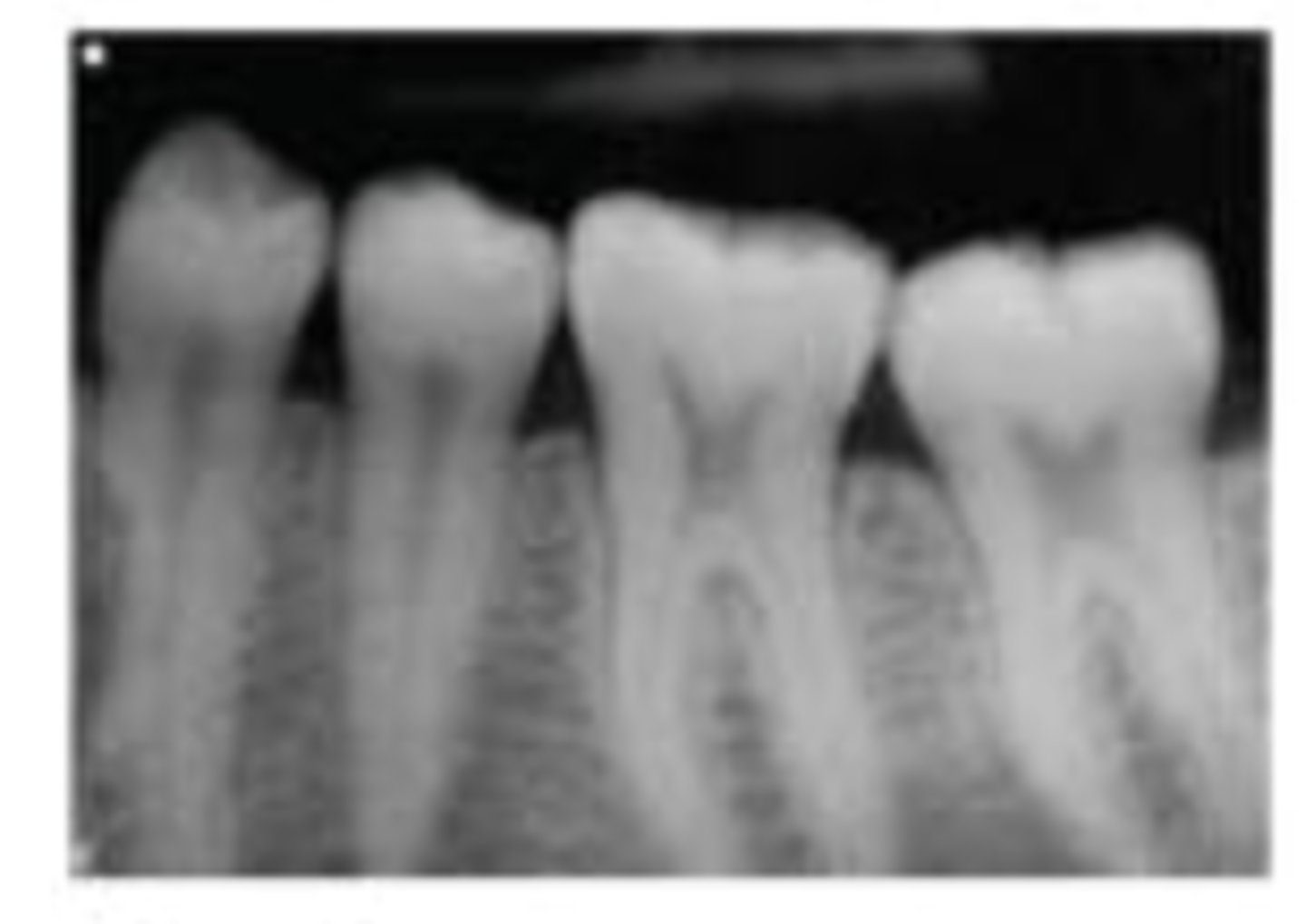
d. decreased vertical angulation
* elongation is the issue in the image and elongation is caused by not enough (decreased) vertical angulation
the following radiographic error is caused by:
a. increased horizontal angulation
b. decreased horizontal angulation
c. increased vertical angulation
d. decreased vertical angulation
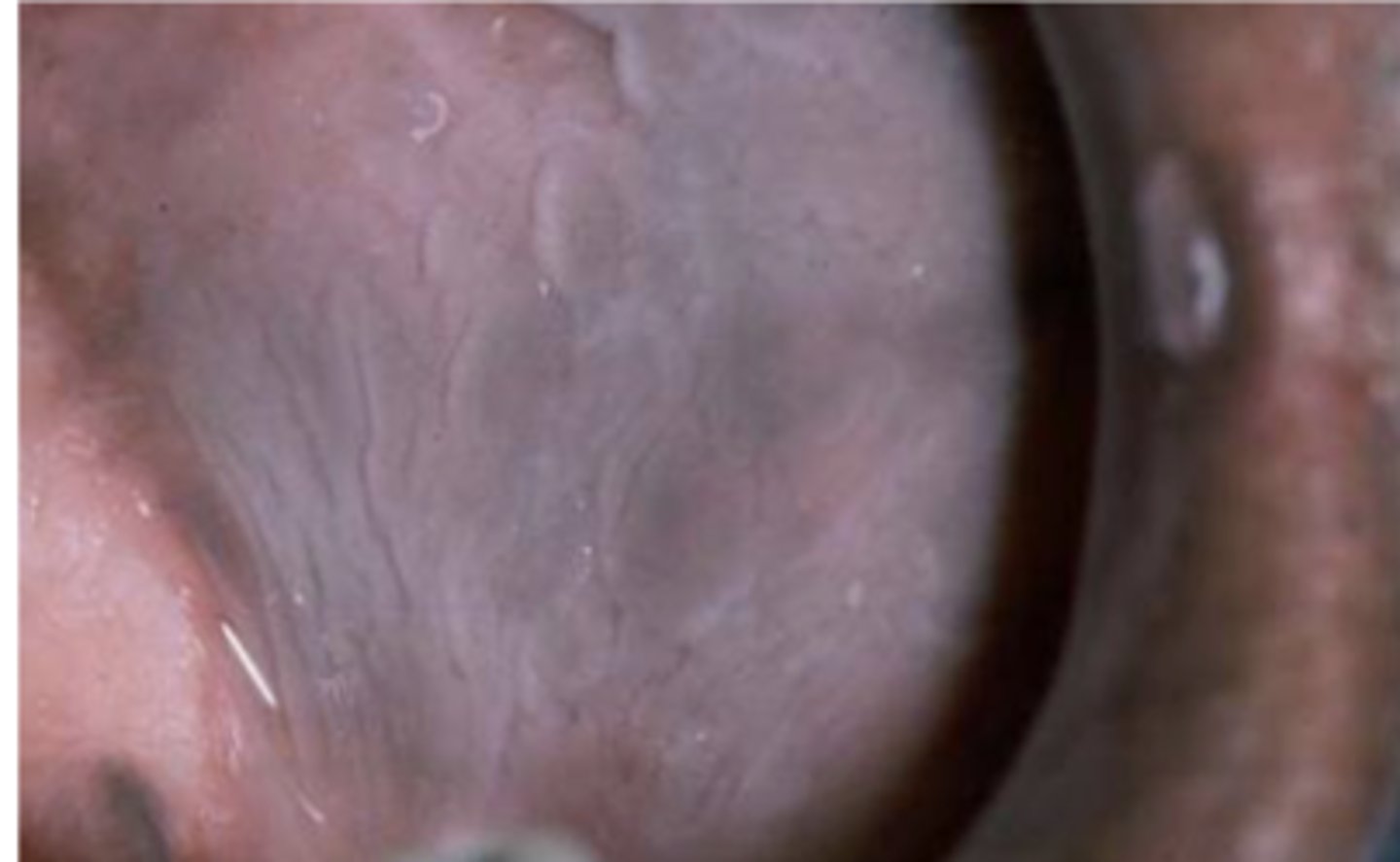
leukoedema
* leukoedema is a white/whitishgray edematous lesion of the buccal and labial oral mucosa. they may be diffuse/patchy
what condition can be seen in this image?
1 (d) systemic lupus
2 (a) pemphigus vulgaris
3 (b) steven johnson syndrome
4 (c) behcet's syndrome
match the following characteristics with its correct medical conditions:
1. Butterfly rash
2. Acantholysis
3. Toxic epidermal necrolysis
4. Ophthalmic, genital, and oral lesions
a. pemphigus vulgaris
b. steven johnson syndrome
c. behcet's syndrome
d. systemic lupus
increased bleeding
your patient reports they are taking Clopidogrel (Plavix). this patient will experience increased _______________.
do NOT pack them up using regular gloves. MUST use utility gloves
after using sharp instruments, what would you NOT do?
mask, lab coat, safety glasses, and utility gloves or impervious gloves
what would you wear in the sterilization area when handling sharp instruments?
d. refer immediately to doctor
your patient's blood pressure reading is 156/120. what would you do?
a. continue with treatment
b. wait 5 minutes, then continue with treatment
c. continue treatment and refer to doctor
d. refer immediately to doctor
b. give them an extra 300mg and wait an hour
your patient who is allergic to penicillin and needs antibiotic premed took 300mg of clindamycin an hour prior to the appointment. what do you advise?
a. give 2g amoxicillin
b. give them an extra 300mg and wait an hour
c. do nothing and proceed with treatment
c - lateral side + face
in regards to sharpening an instrument; where would you sharpen?
b. place stone at junction between face and lateral surface
how should you sharpen an instrument?
a. place stone at terminal shank
b. place stone at junction between face and lateral surface
c. place stone at back
d. toxins in biofilm
what contributes to caries in plaque and calculus?
a. inorganic irritant
b. organic irritant
c. acids within plaque
d. toxins in biofilm
the following apply:
b. primarily seen in African American women
d. posterior teeth
f. starts radiolucent but turns radiopaque
which of the following items apply to the following condition: focal sclerosis osteitis
a. primarily seen in men
b. primarily seen in African American women
c. anterior teeth
d. posterior teeth
e. starts radiopaque but turns radiolucent
f. starts radiolucent but turns radiopaque
c. focal sclerosis osteitis
this condition is related to a low-grade inflammatory reaction. what condition does this describe?
a. periodical cement dysplasia
b. concrescence
c. focal sclerosis osteitis
d. cementoma