CHEM 1150 EXAM 2 QUESTIONS
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
when light shines through a double slit, a pattern of bright and dark lines appear
waves of light interfere constructively when they arrive in-phase and destructively when they arrive out of phase
hydrogen produces emission lines with the following wavelengths: 410, 434, 486, 656. Where would you expect to see the absorption lines for hydrogen on its absorption spectrum
the absorption lines for hydrogen would appear at exactly the same wavelengths because the energies of the photons emitted and absorbed by hydrogen are the same
What is the evidence that supports the claim that light can act as a particle?
WHen light shines on metal there is a thershold frequency, below which no electrons are ejected from a metal
An MRI machine operates at a frequency of 30 kilohertz what wavelength radiation does this correspond to?
1×10^4
What wavelength of light in nm would break a O=O bond?
240 nm
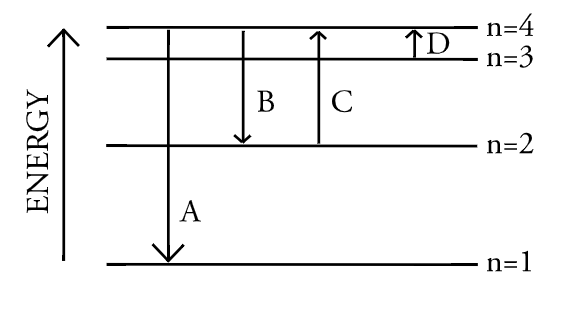
The diagram represents energy transitions for an electron in an atom. Which arrow corresponds to the emission of a photon with the longest wavelength?
B
Why must we consider the wave properties of an electron, but not the wave properties of macroscopic objects
The wavelength of the electron is similar in size to the atom and affects its properties, whereas the wavelength of the macroscopic object is much smaller than the object and does not affect its properties
Difference about the valence electrons in F and Cl
the valence electrons have different energies and are in different size orbitals
Condensed electron configuration of Selenium
[Ar]4s23d104p4
Consider K+ and Cl- which is larger?
Cl is larger because fewer protons are attracting the same number of electrons as in K+
Atomic radius decreases from left to right across a row on the periodic table
because the relative attraction between the protons and the outer electrons increases
Two Elements 1 and 2 are in the same row of the periodic table but not next to each other.
Element 1 has a larger atomic radius than Element 2, which of the following are most likely
to be true about their relative ionization energies and why?
Element 2 has a larger ionization energy and electrons in Element 2 are more strongly attracted to the nucleus
n=3. which orbitals can you occupy
4s, 4p, 4d
quantum numbers that describe d orbitals or l=2
-2, -1, 0, 1, 2
what is true about 1s, 2s, and 3s
The s orbitals in higher energy levels are larger in size
.On average the electrons in 2s and 3s orbitals are further away from the nucleus than 1s electrons and hence less stable.
Higher energy s orbitals have more nodes or regions of space where electrons cannote exist
Atoms become larger
and zeff stays the same as the number of core electrons increase. the greater repulsion causes the atoms to expand in size
atomic absorption spectra are caused by
electrons moving to higher energy levels after absorbing photons of energy equal to the energy difference between the levels