AH Biology - Unit 2 - KA5(a) - Niches
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is an ecological niche?
An ecological niche is a multidimensional summary of tolerances and requirements of a species.
What are the two types of niche?
The two types of niche are:
Fundamental niche
Realised niche
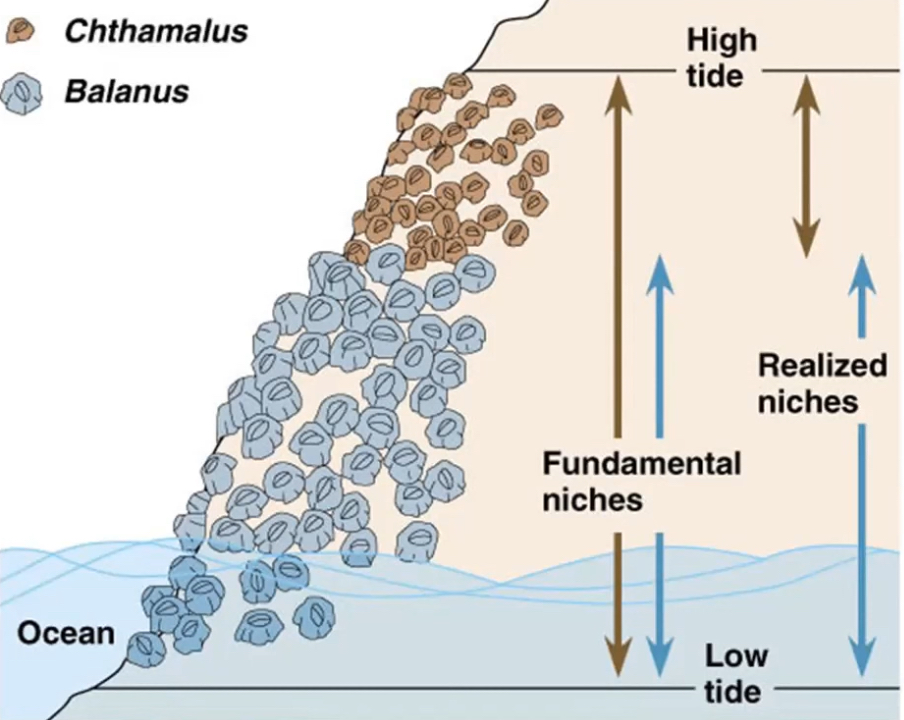
What is a fundamental niche?
A fundamental niche is the niche a species would occupy in the absence of any interspecific competition.
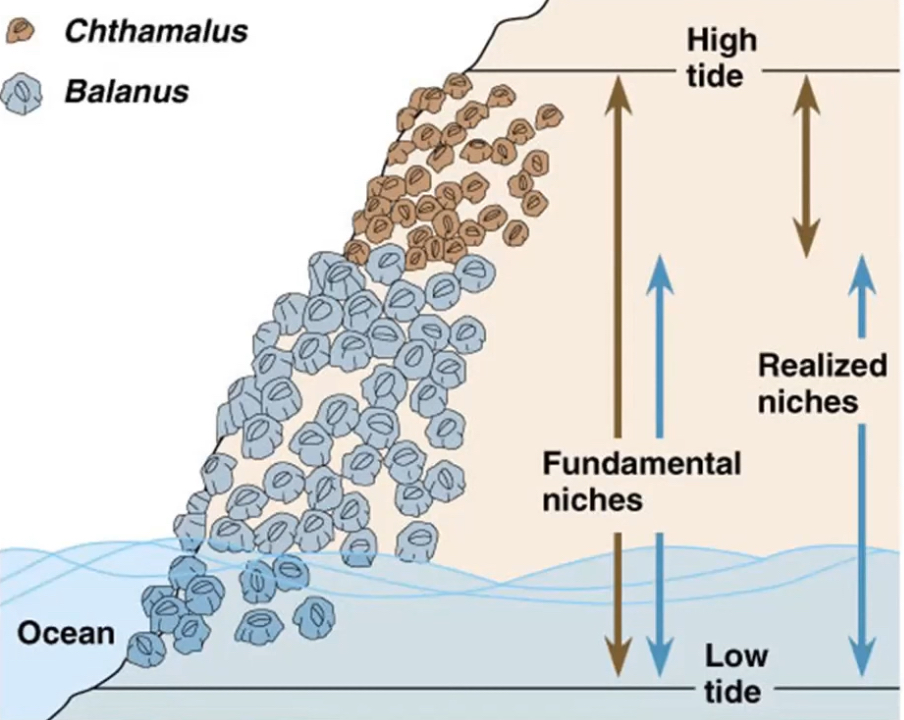
What is a realised niche?
A realised niche is the niche a species actually occupies in response to interspecific competition.
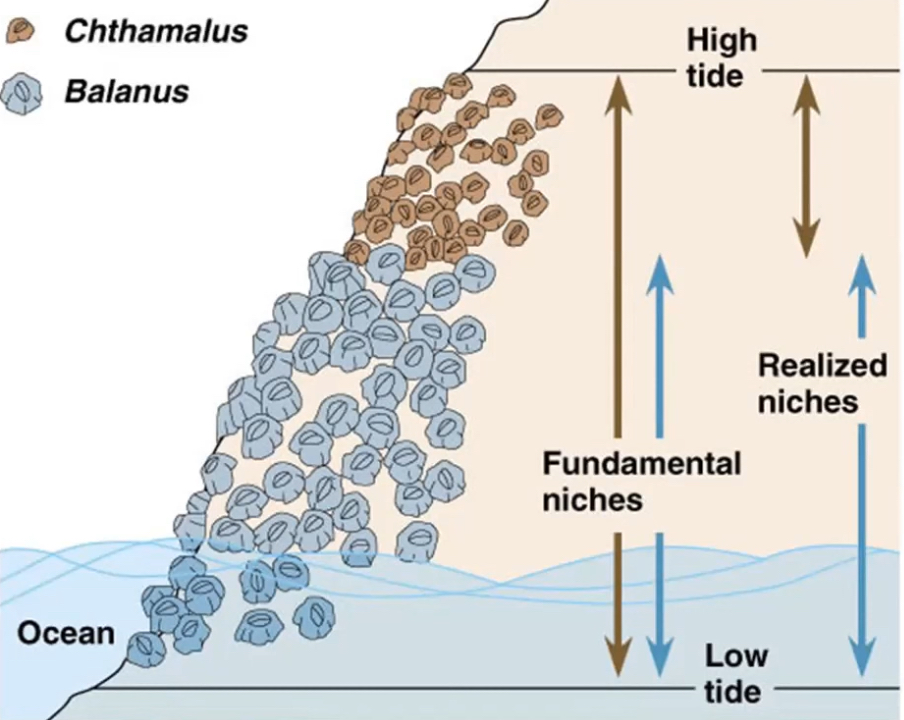
What is competitive exclusion and when does it happen?
Competitive exclusion is what occurs if interspecific competition between two species is so intense that one species declines and becomes locally extinct. Competitive exclusion occurs when the ecological niches of two species are very similar.
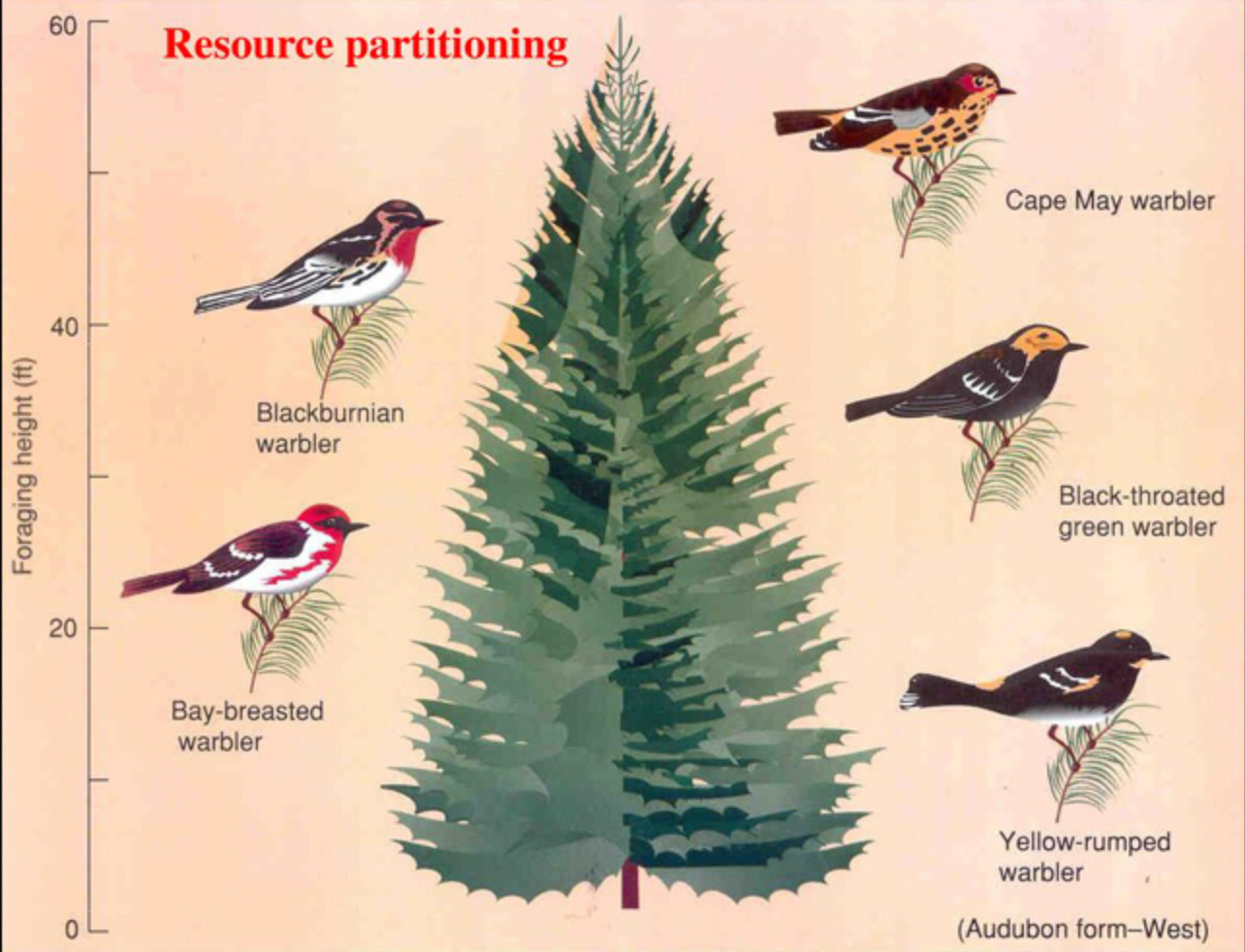
What is resource partitioning?
Resource partitioning is what happens when the realised niches of potential competitors are sufficiently different that they can use different resources in the area and can co-exist. For example, MacArthur’s warblers.
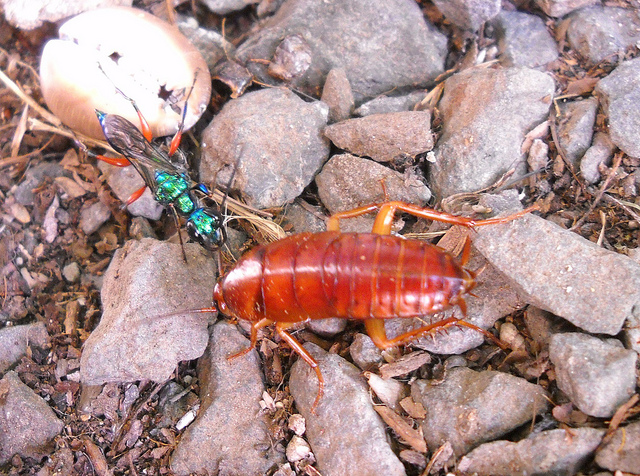
What is parasitism?
Parasitism is a symbiotic relationship between a parasite and it’s host where the parasite benefits in terms of energy and/or nutrients and the host is harmed as a result of the loss of these resources. For example, the emerald cockroach wasp (Ampulex compressa) parasitises the American cockroach (Periplaneta americana)
DELETE WHEN MErge

What are key features of a parasite’s niche?
Key features of a parasite’s niche are:
Their reproductive potential is normally much greater than their host’s.
Most are very host specific
They have a very specialised and narrow niche. As a result of this, they are degenerate, meaning they lack structures and organs commonly found in other organisms. For example, tapeworms lack a digestive system.
How are parasites classified?
Parasites are classified by where they live.
What are the two types of parasites?
The two types of parasites are:
Ectoparasites
Endoparasites
What is an ectoparasite and how are they transmitted?
An ectoparasite is a parasite found on the surfaces of the host. For example, fleas or ticks. They are transmitted by:
Direct contact
Consumption of an intermediate hosts.
Delete when merge
What is an endoparasite?
An endoparasite is a parasite found inside host tissues. For example, viruses. They are transmitted by vectors.
Delete when merge