Anatomy & Physiology 2 Exam 2
1/213
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
214 Terms
salivary amylase
initiates the breakdown of starch
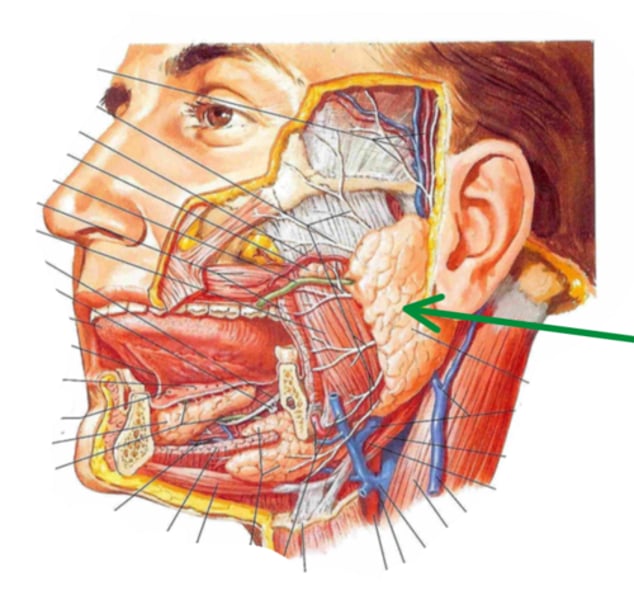
parotid gland
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
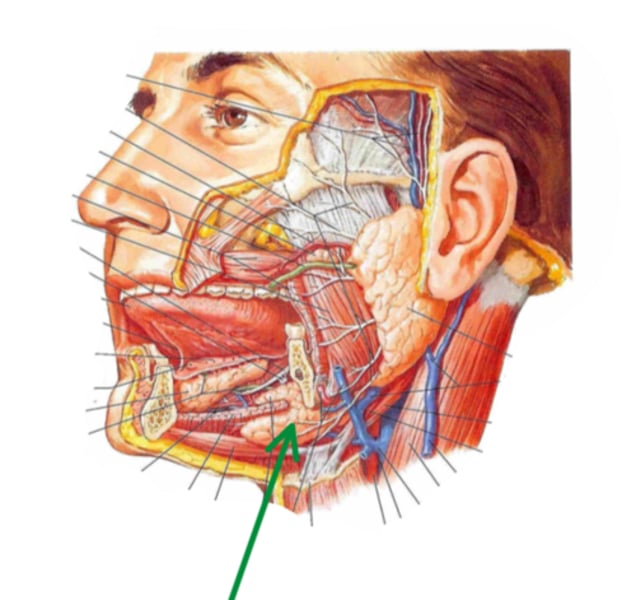
submandibular gland
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
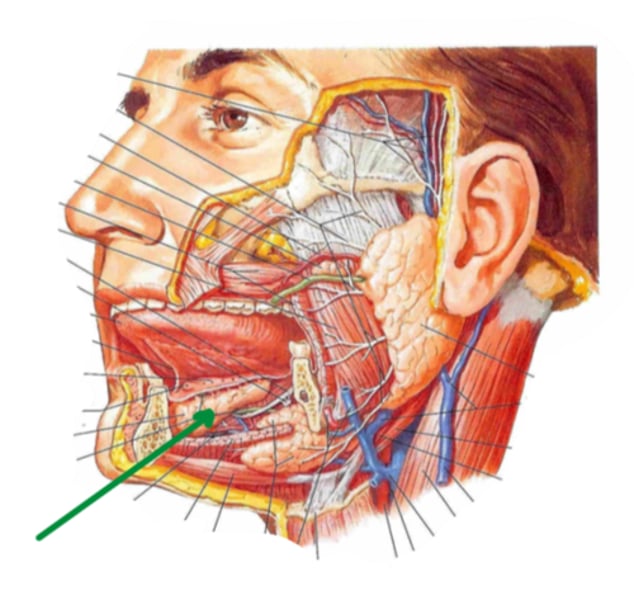
sublingual glands
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
esophagus
identify the structure
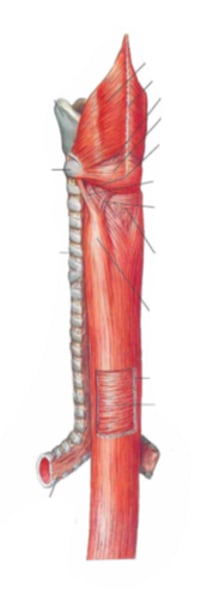
cervical region
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
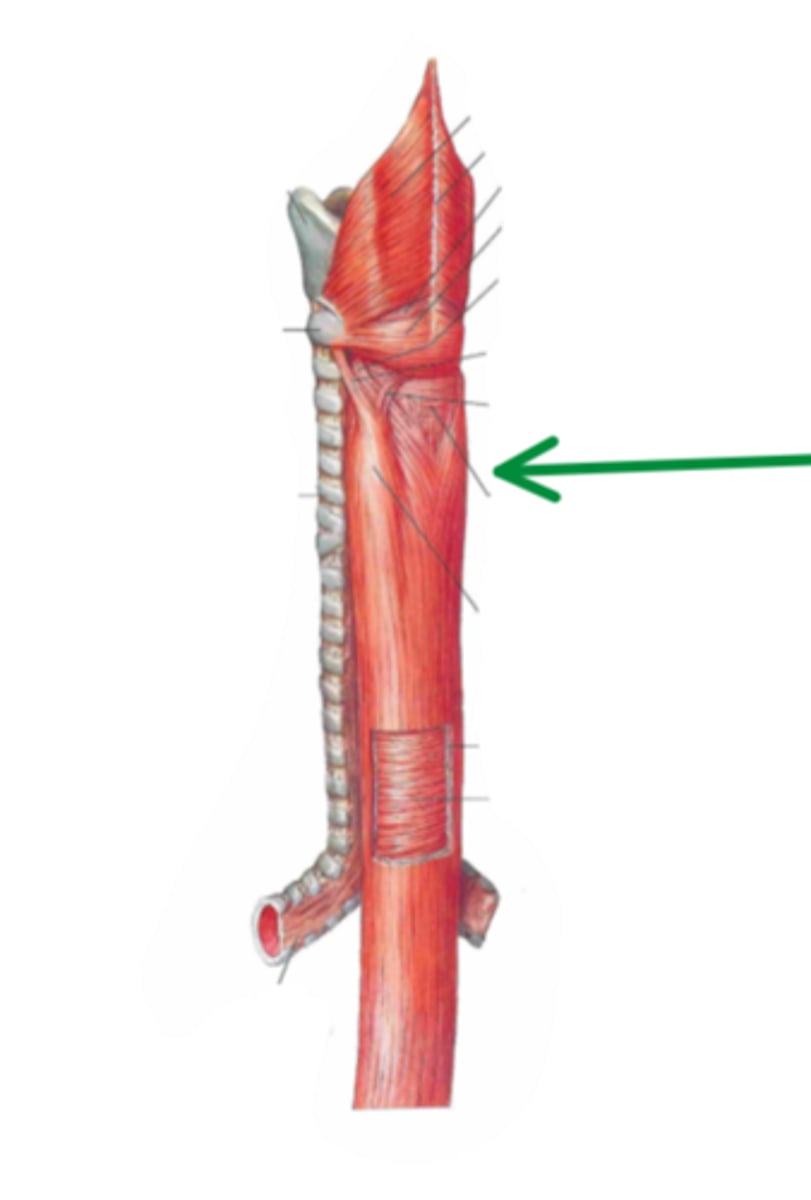
thoracic region
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
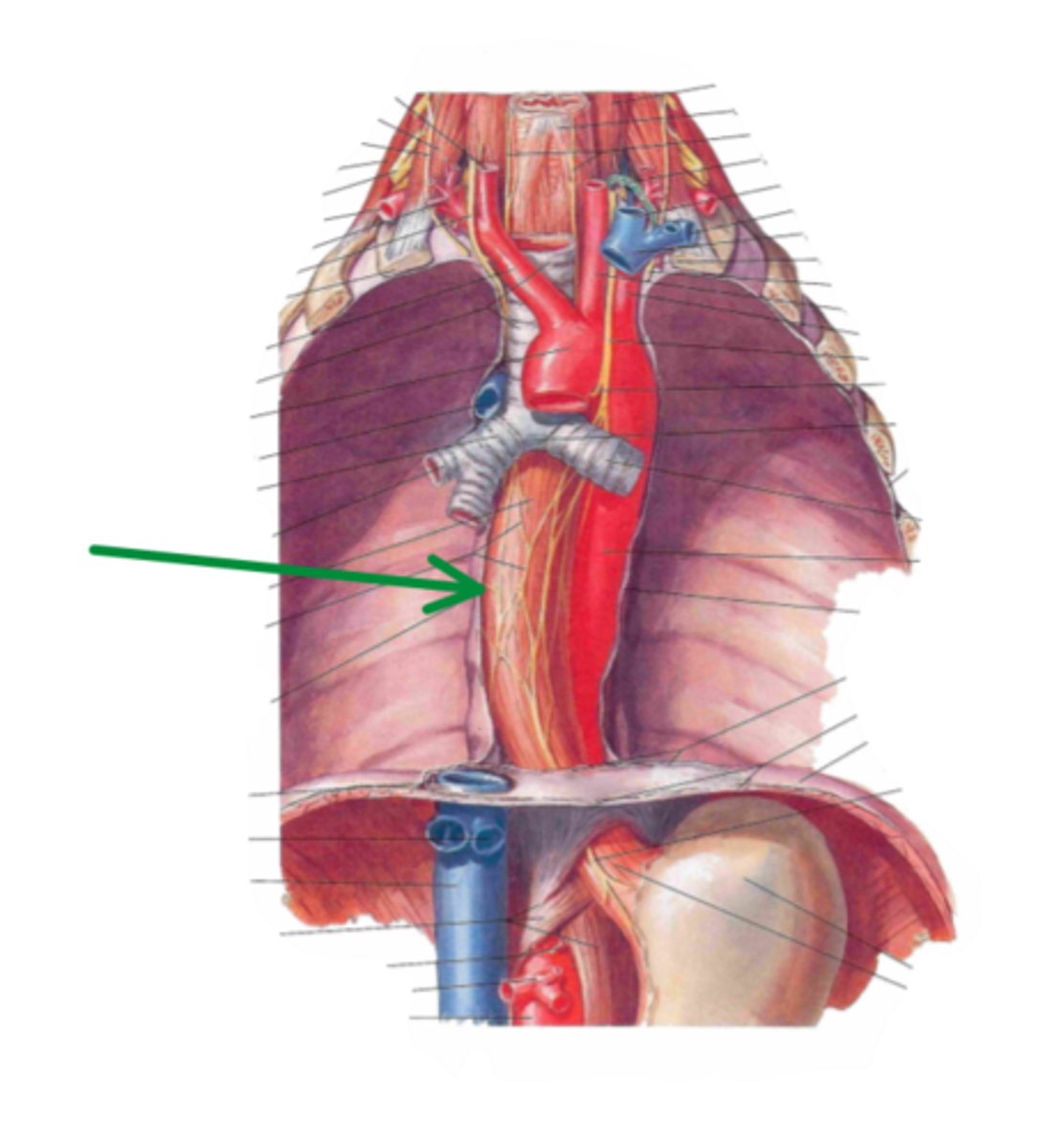
abdominal region
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
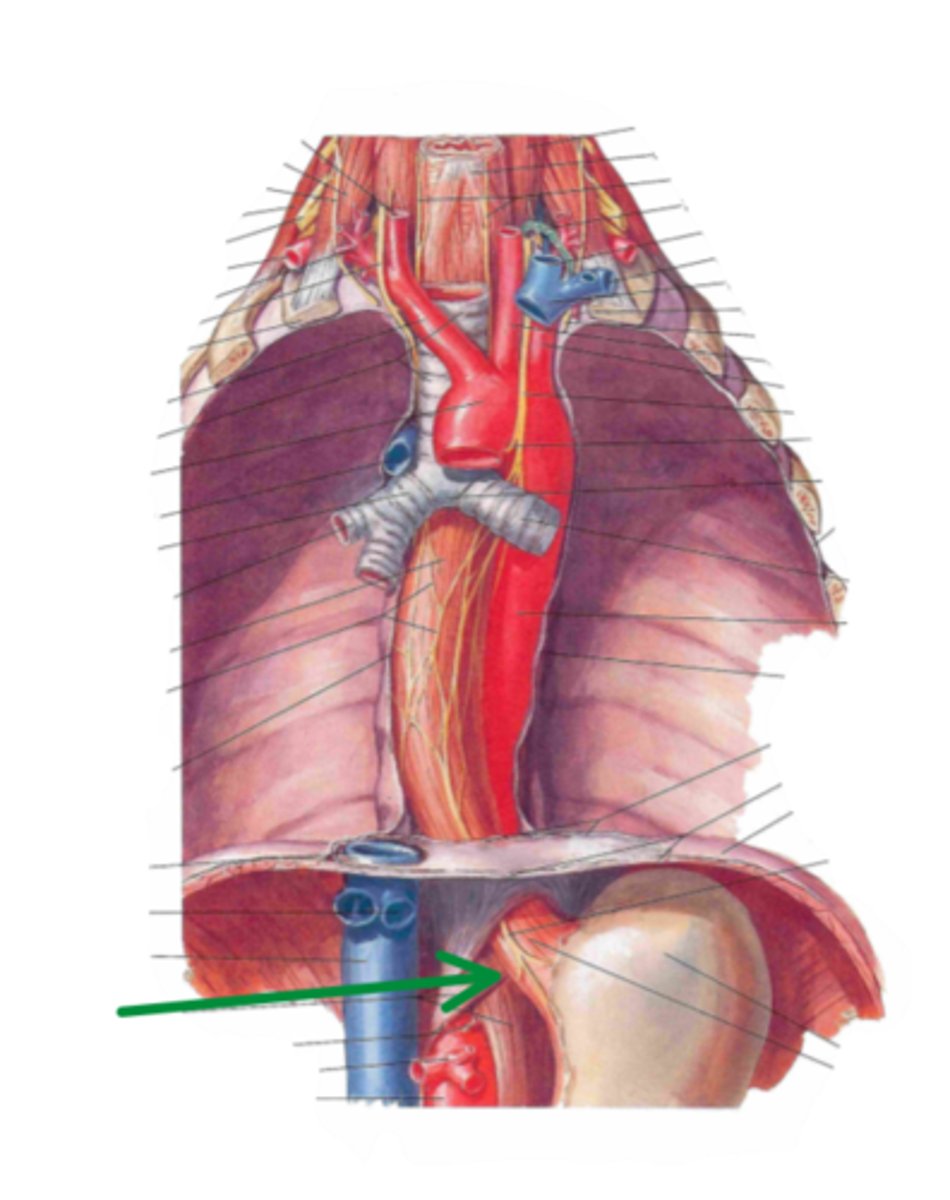
gastro-esophageal junction
esophagus joins the stomach at
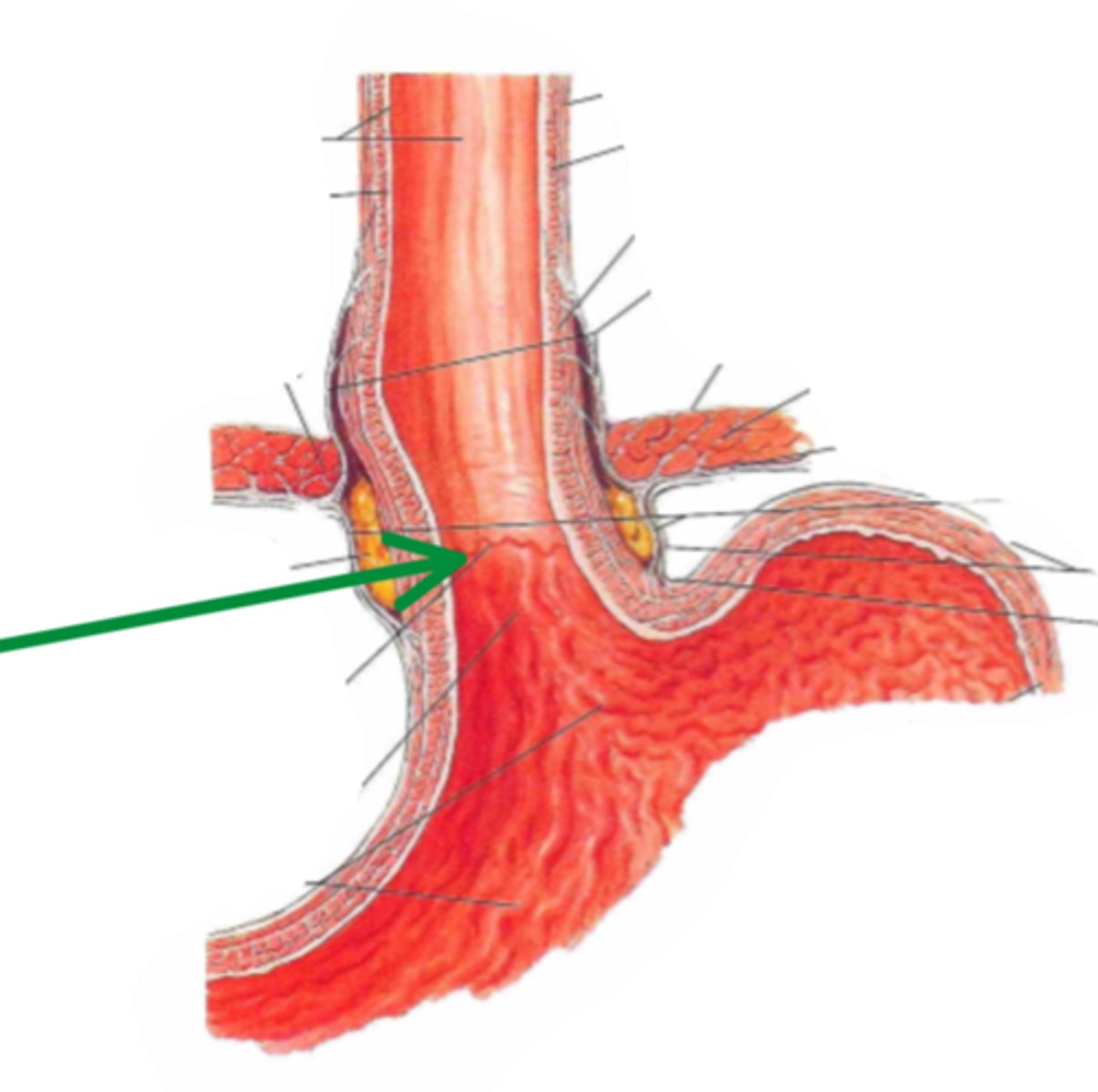
cardiac opening
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
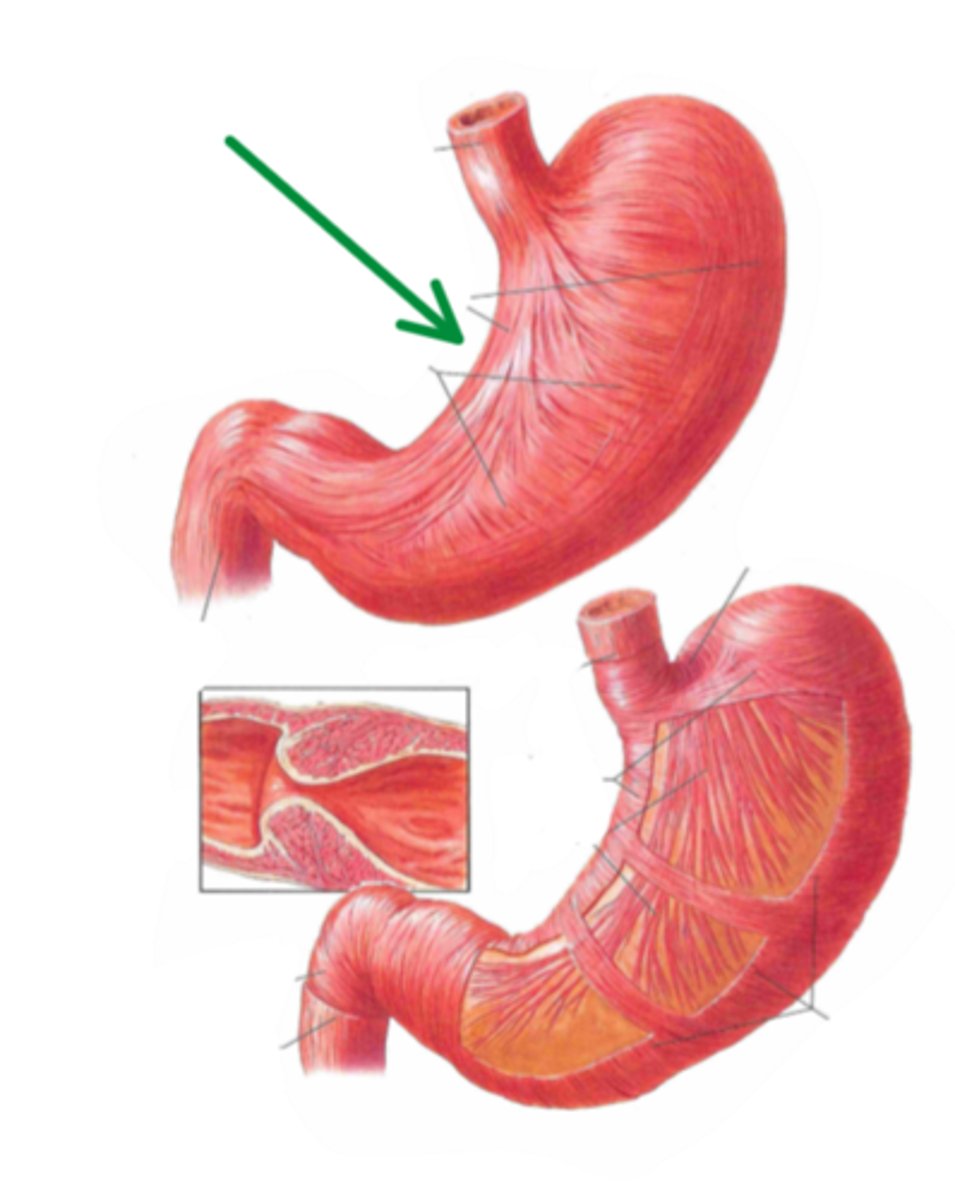
lesser curvature
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
greater curvature
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
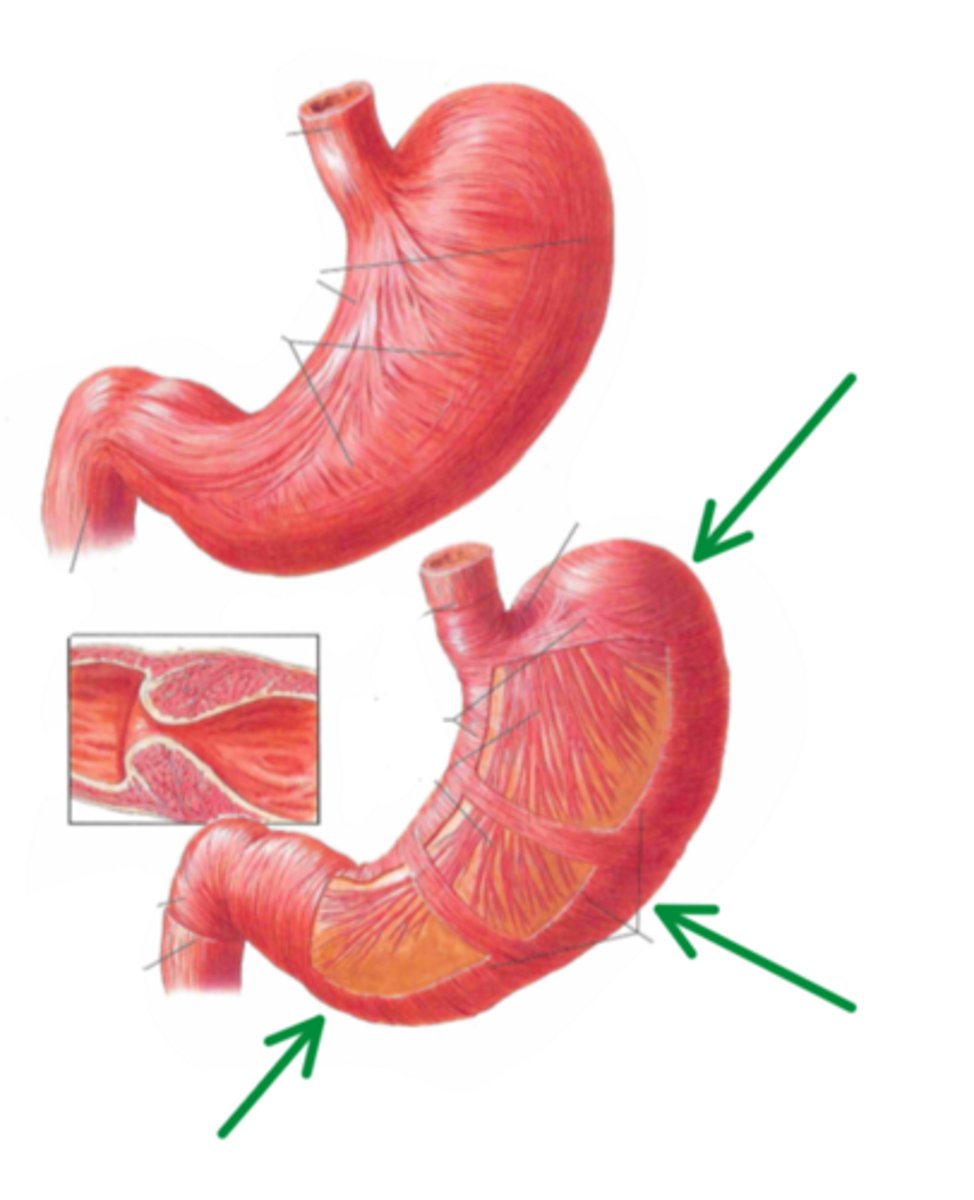
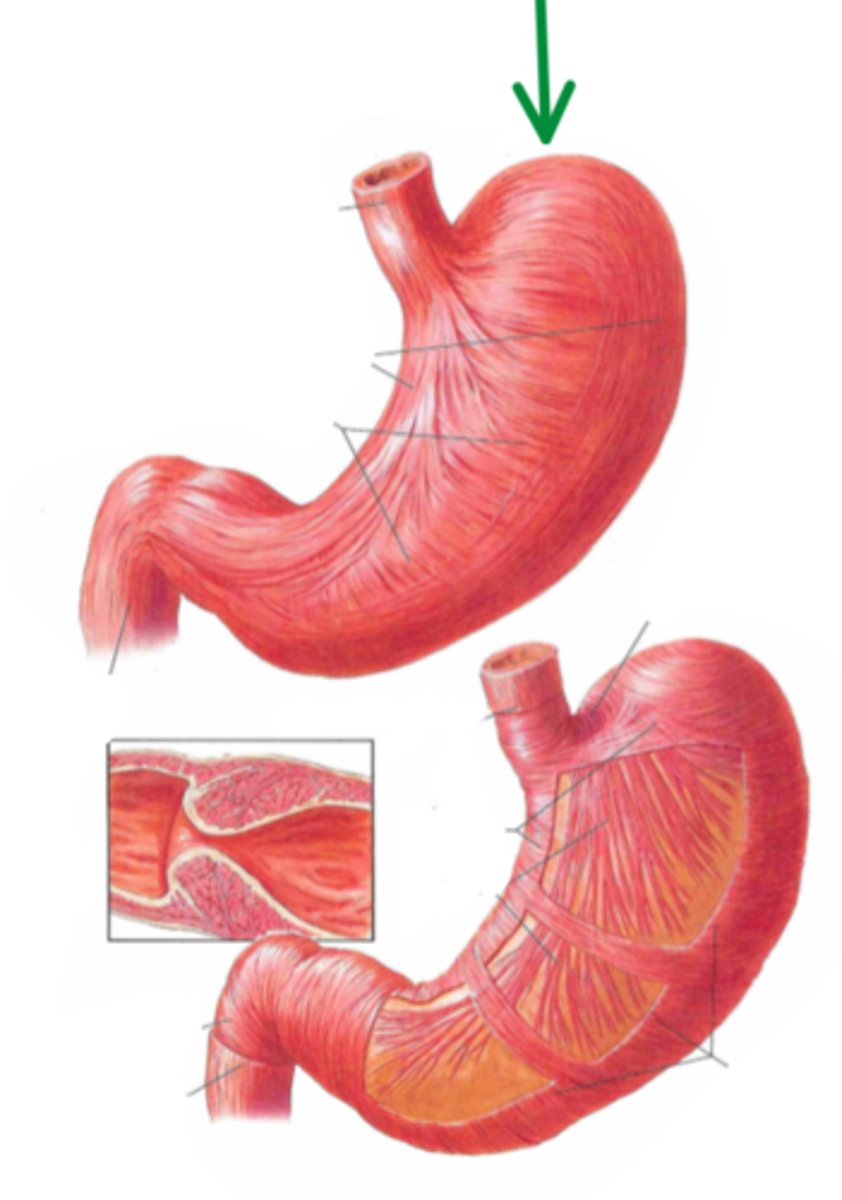
fundus
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
body
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
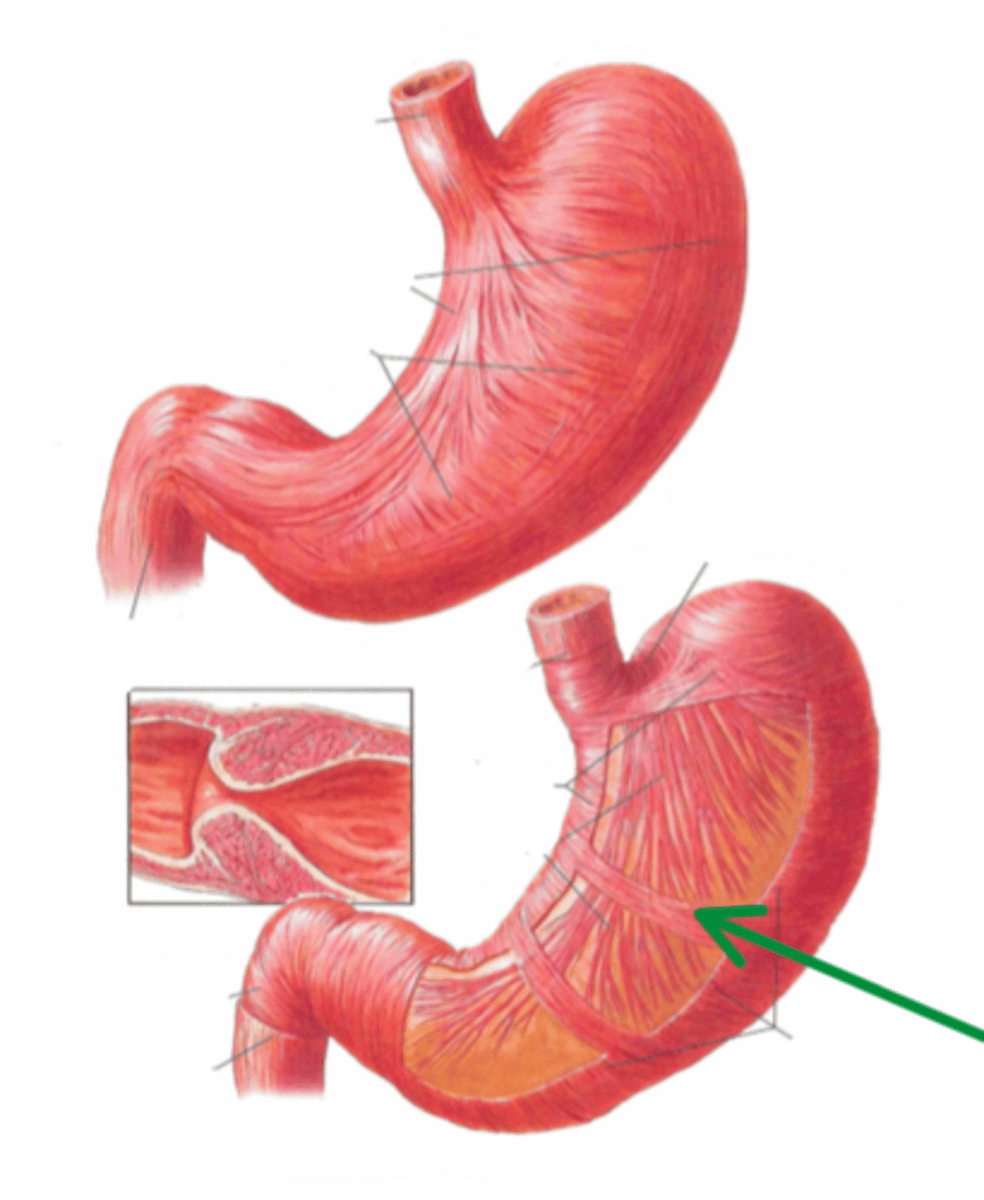
pyloric zone
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
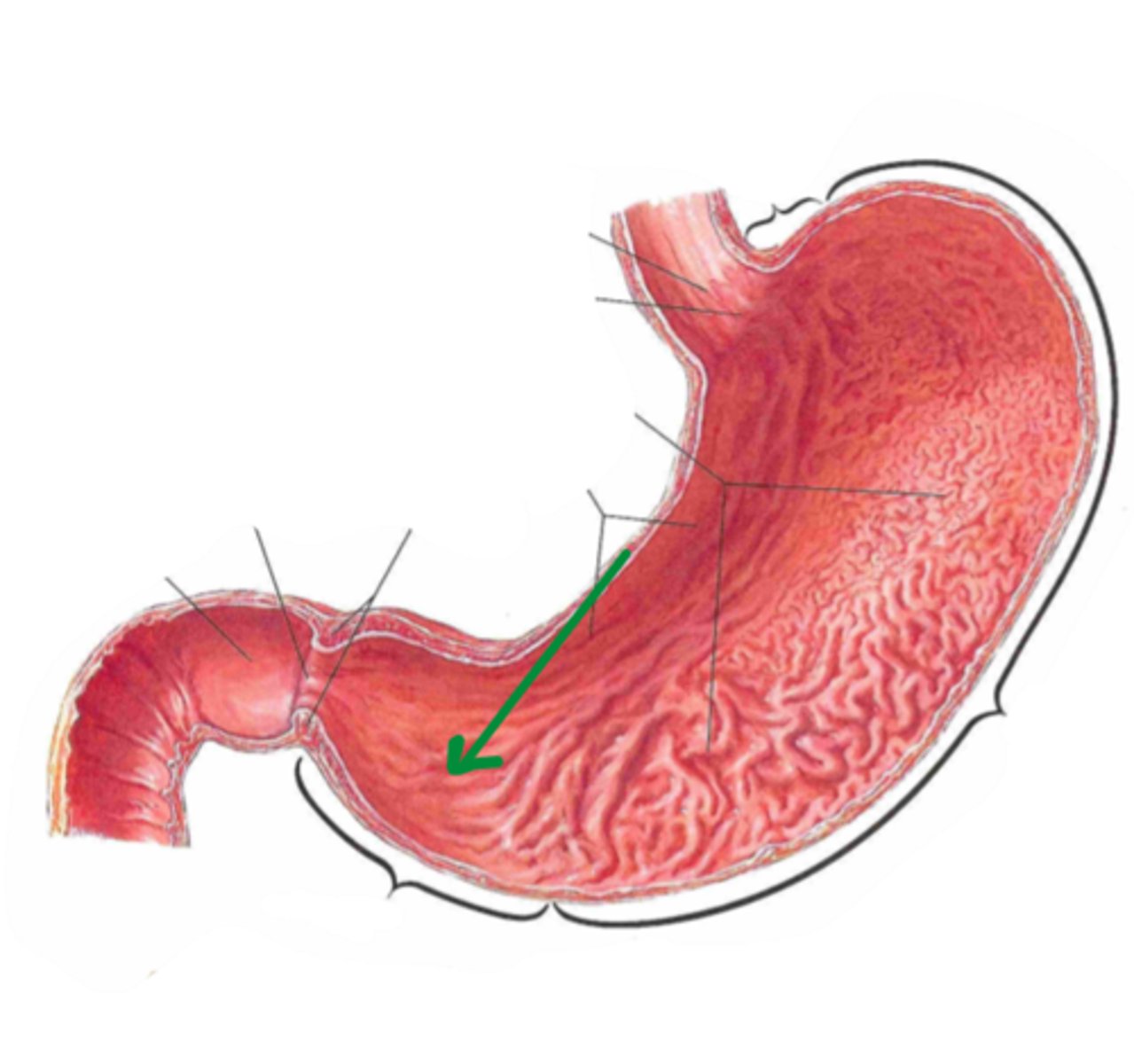
rugae
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
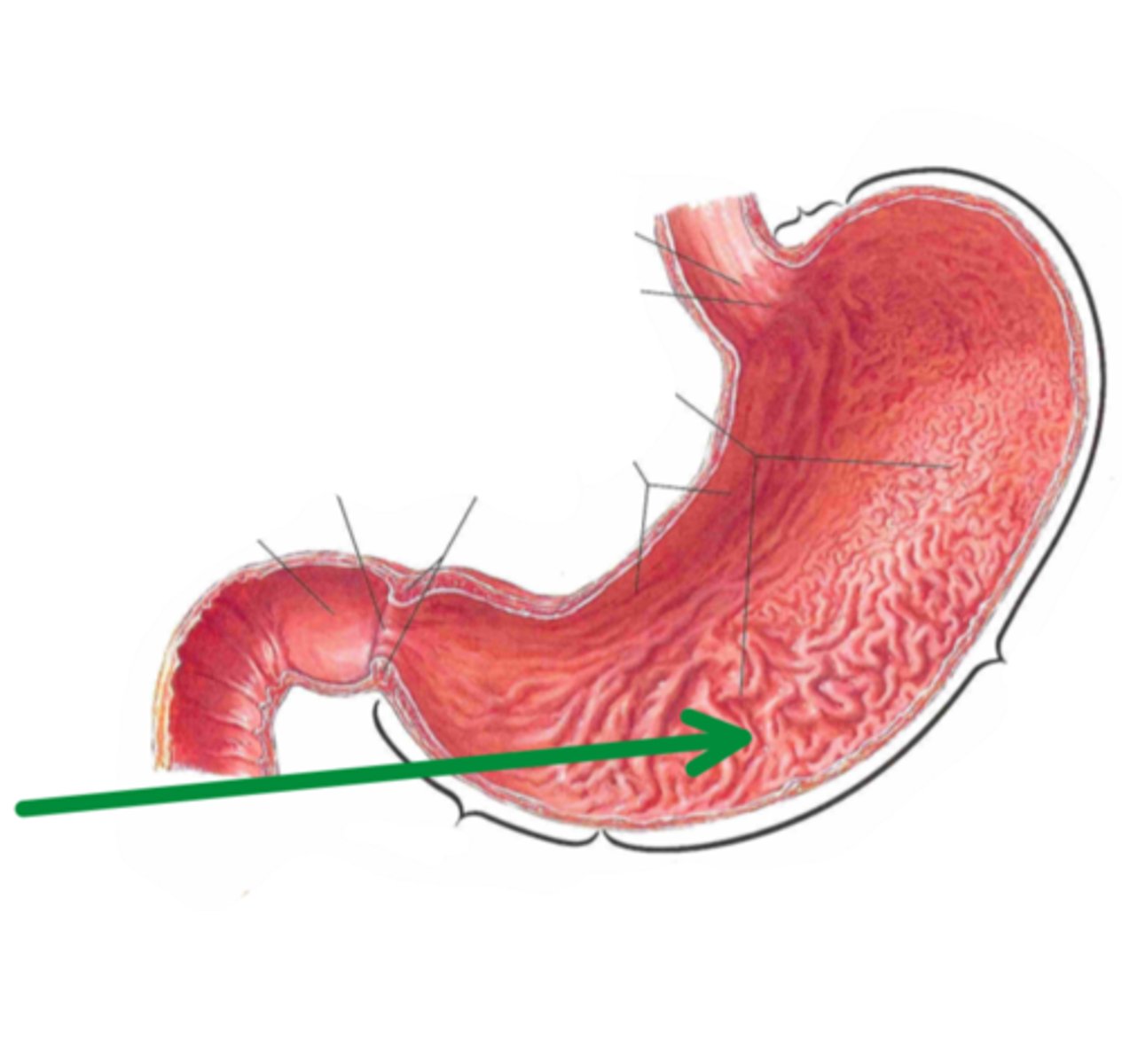
pyloric sphincter
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
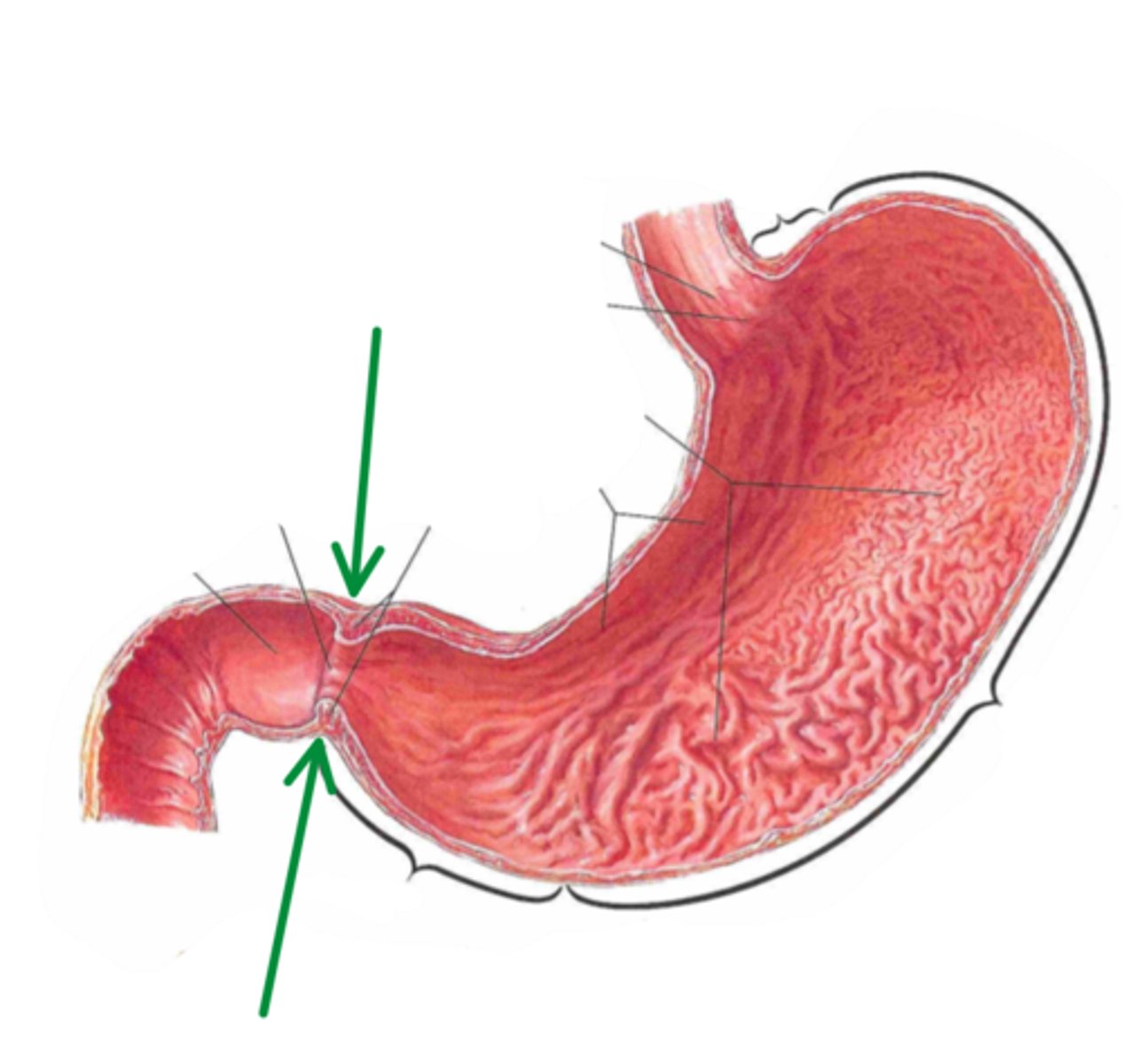
pepsin, gastrin, intrinsic factor
enzymes secreted by stomach
pepsin
enzyme involved in the digestion of proteins
gastrin
enzyme that simulates the production of HCl
intrinsic factor
enzyme that mediates the absorption of vitamin B12
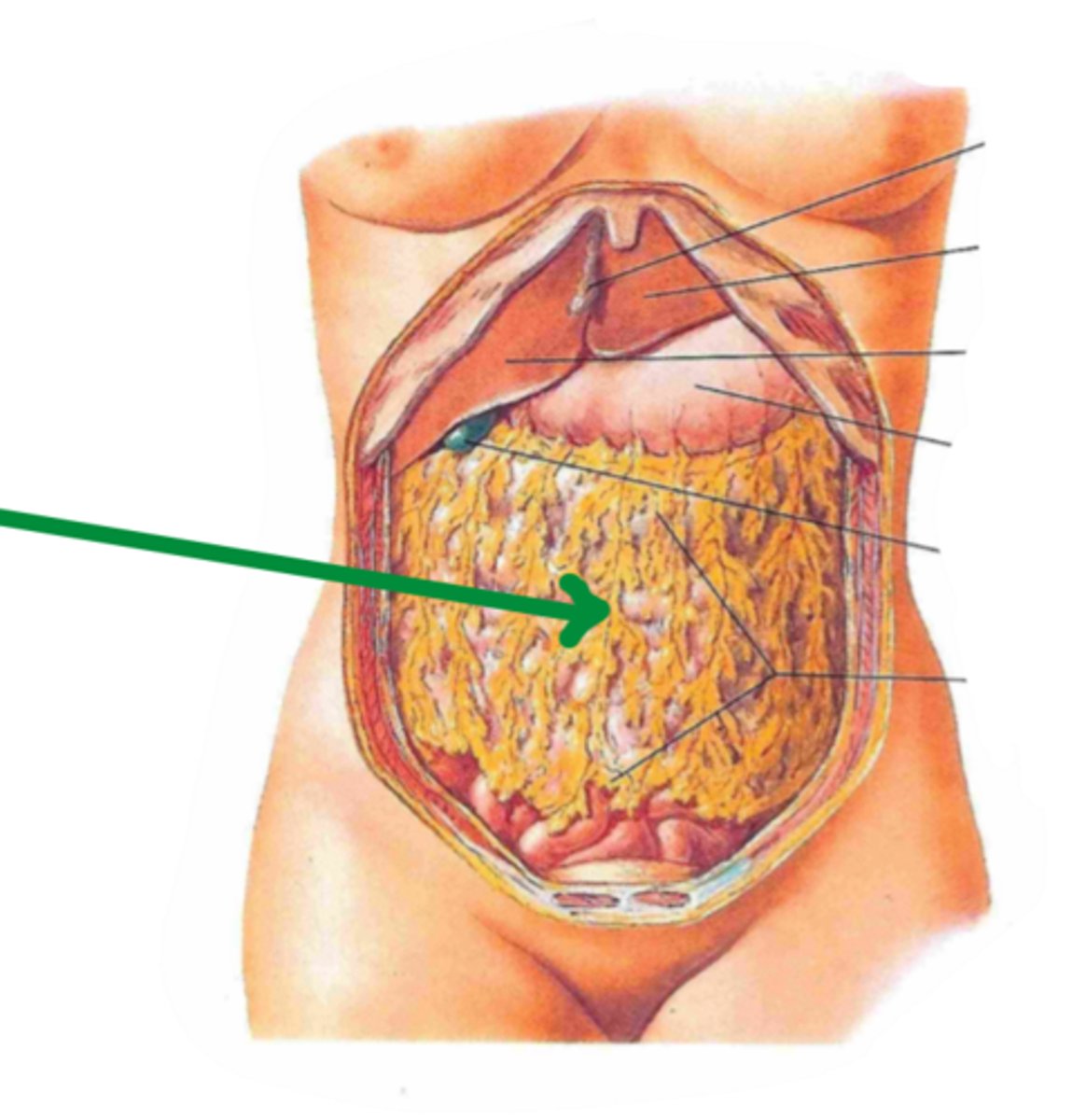
greater omentum
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
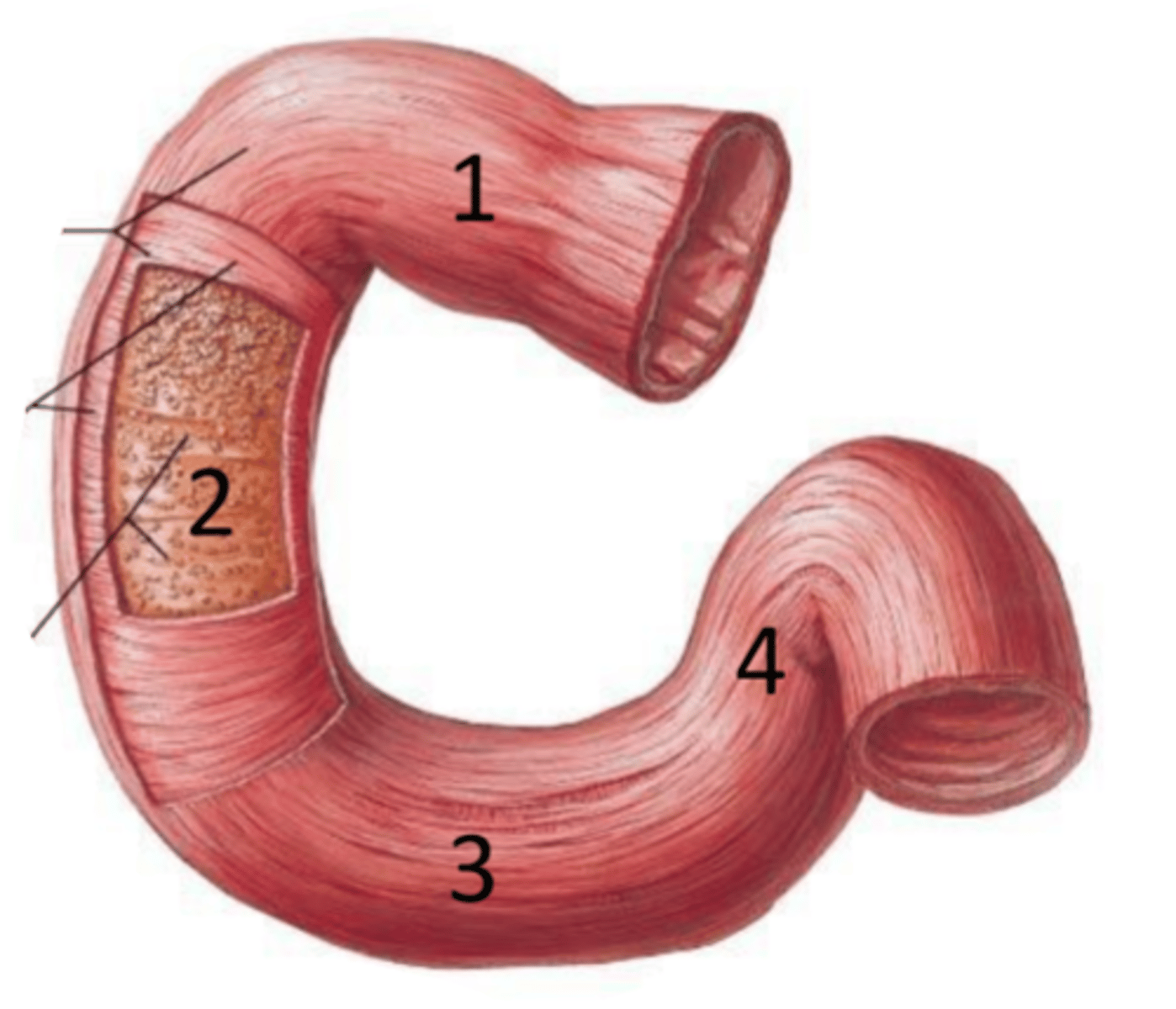
duodenum
identify the structure
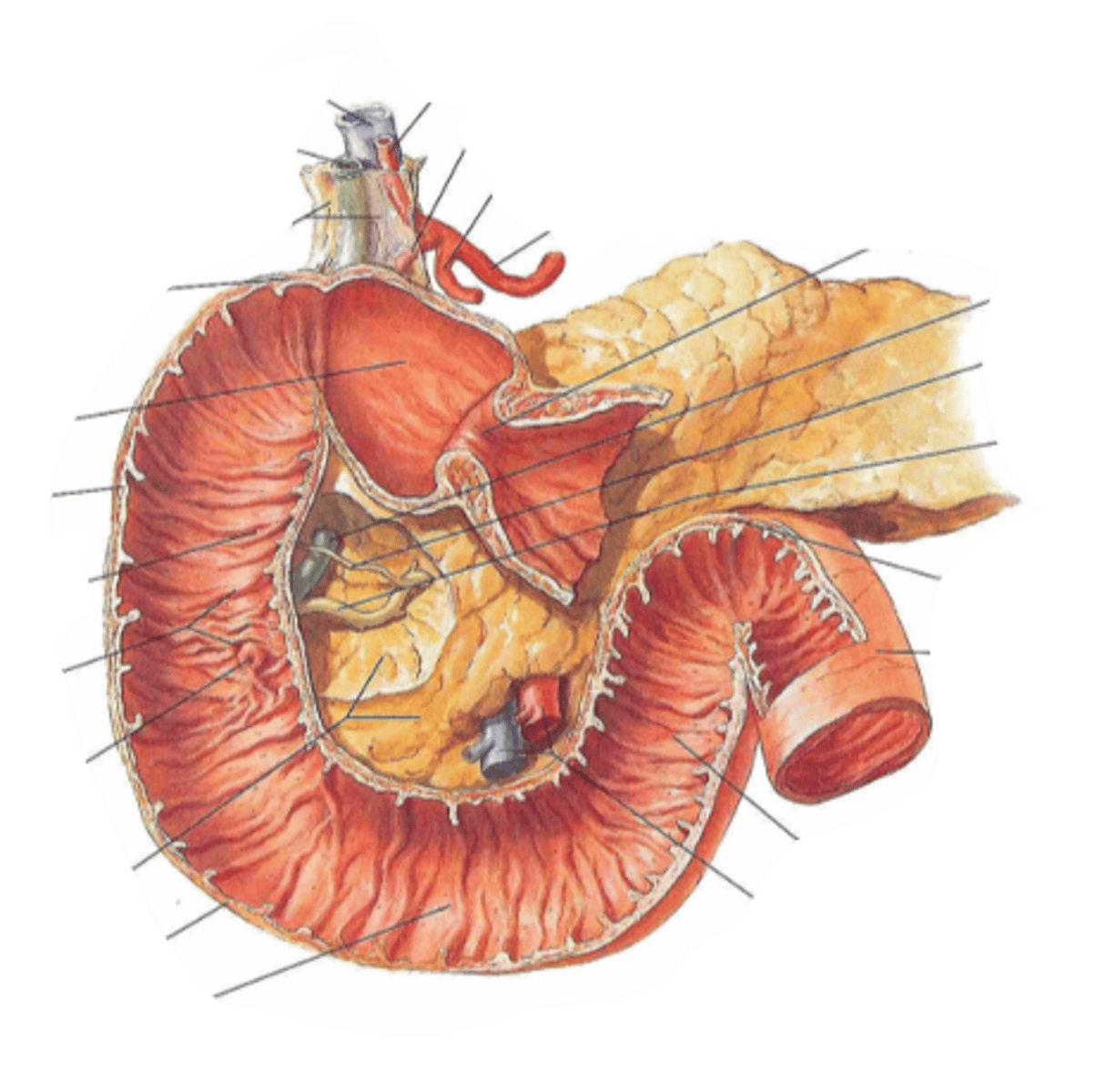
superior part (of duodenum)
identify the structure #1
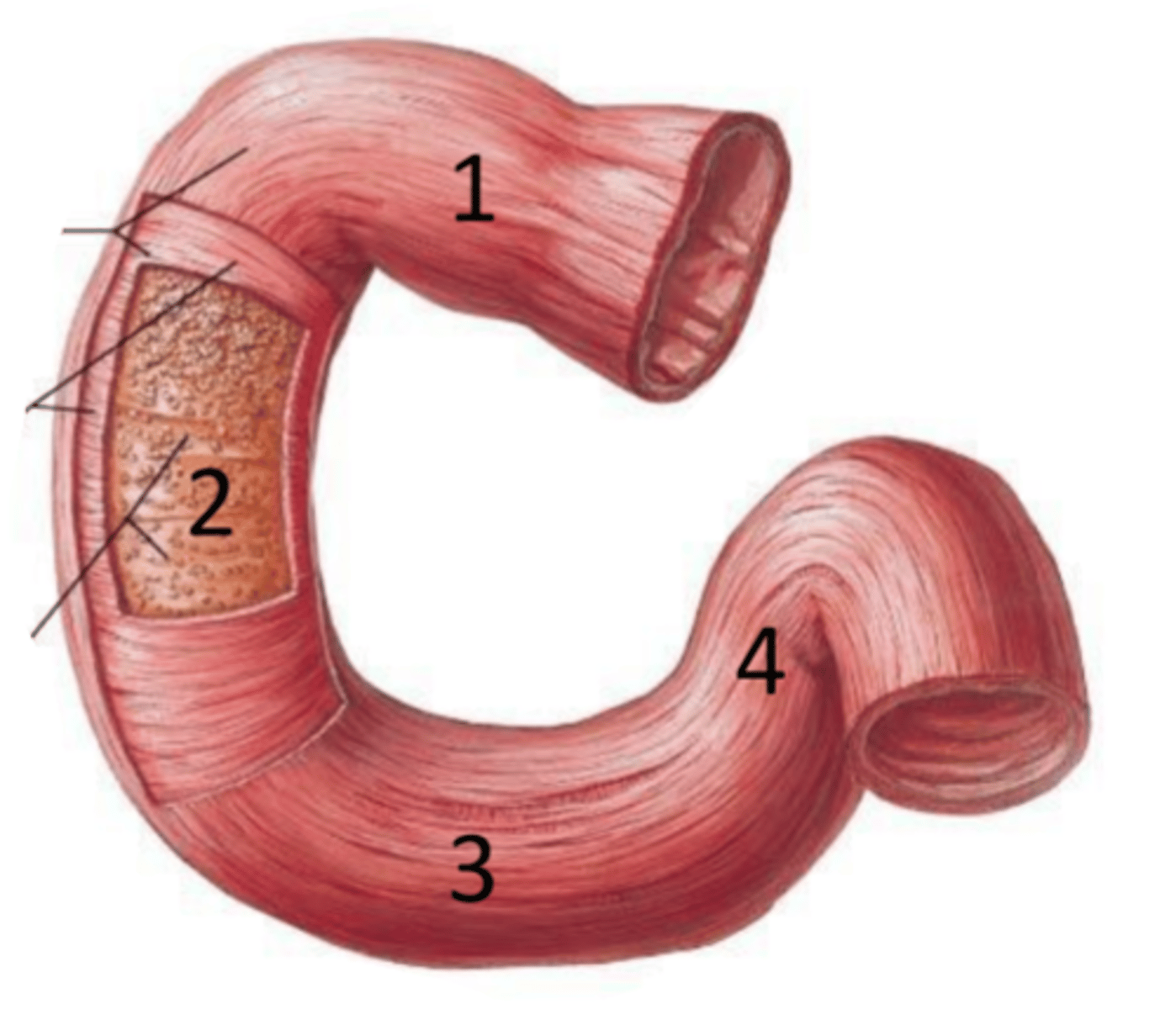
descending part (of duodenum)
identify the structure #2
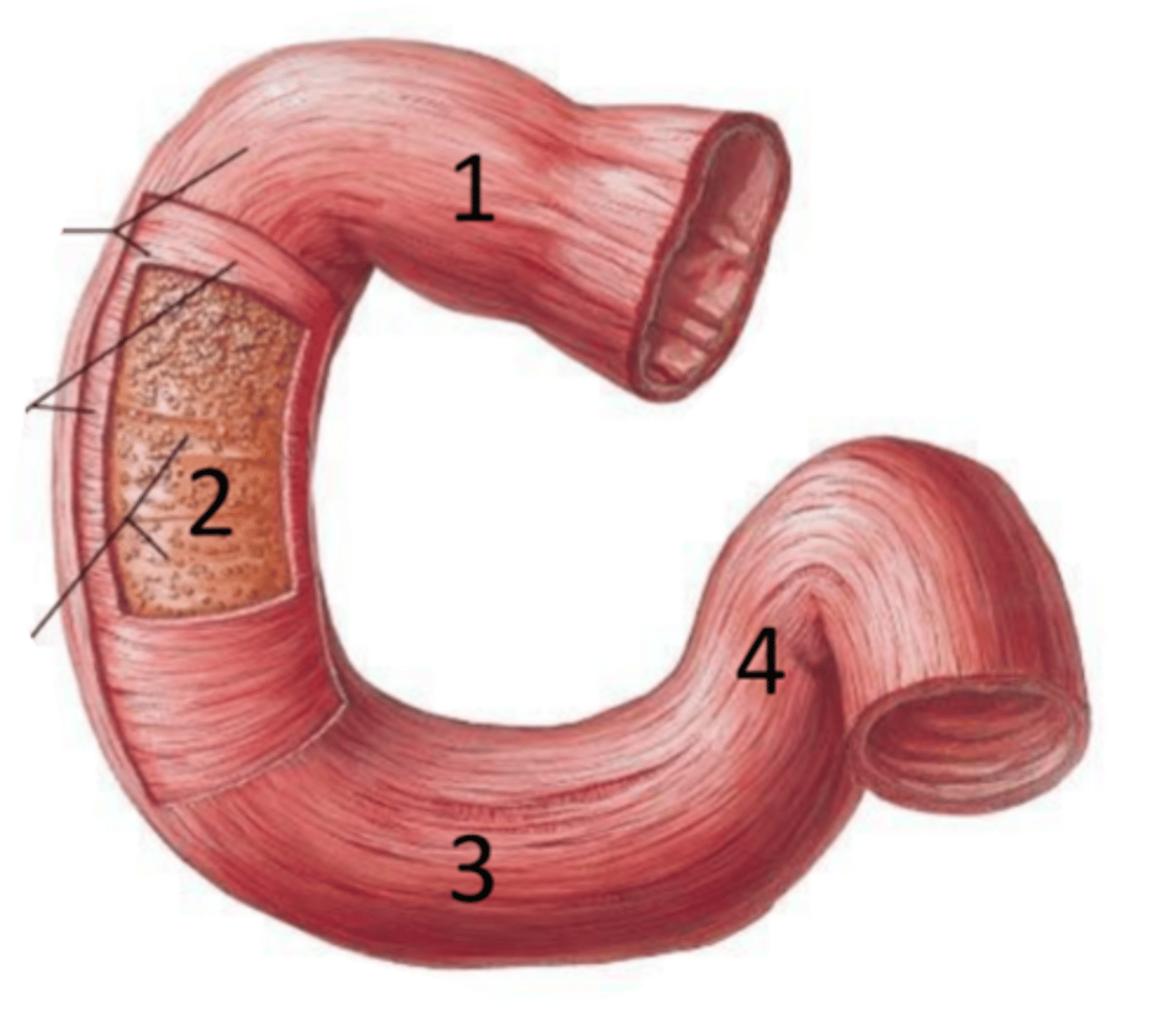
horizontal part (of duodenum)
identify the structure #3
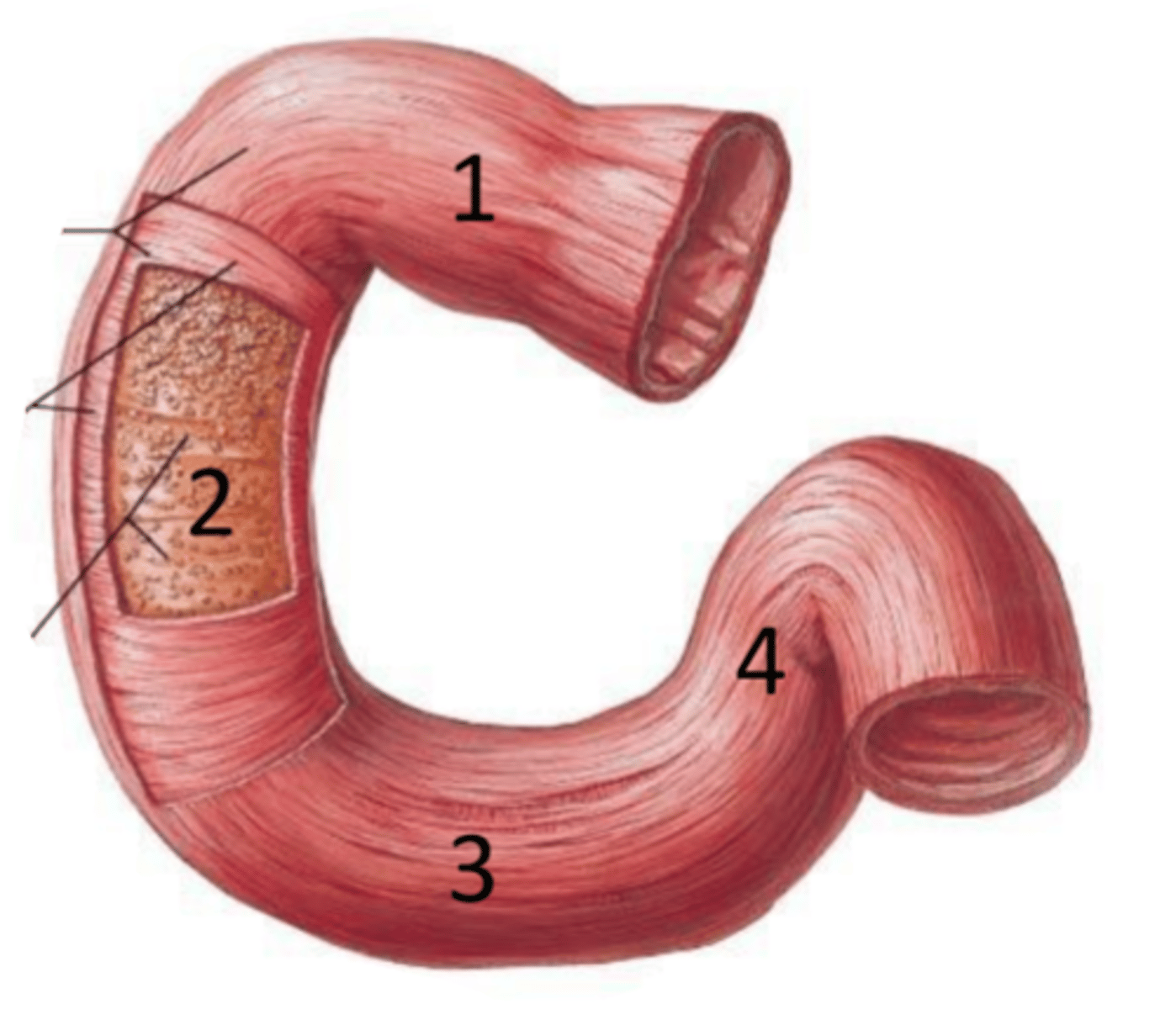
ascending part (of duodenum)
identify the structure #4
small intestine
identify the structure
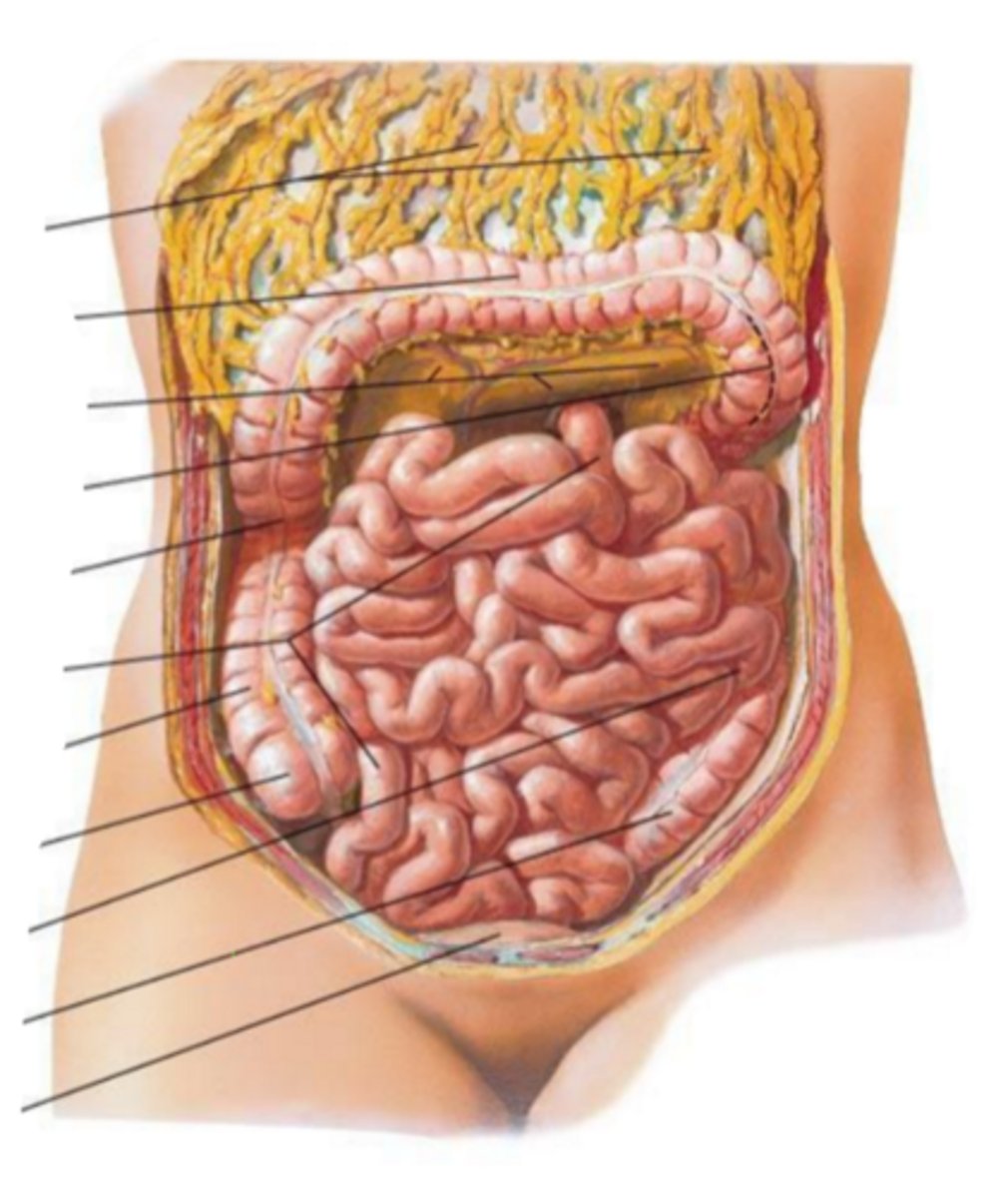
jejunum
proximal 2/5th of the small intestine
ileum
distal 3/5th of small intestine
enterokinase
activates pancreatic enzymes
cholecystokinin
stimulates gallbladder contraction and hepatic secretion of bicarbonate
secretin
Stimulates
secretion of the pancreatic
enzymes trypsin and
chymotrypsin
ileocecal junction
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
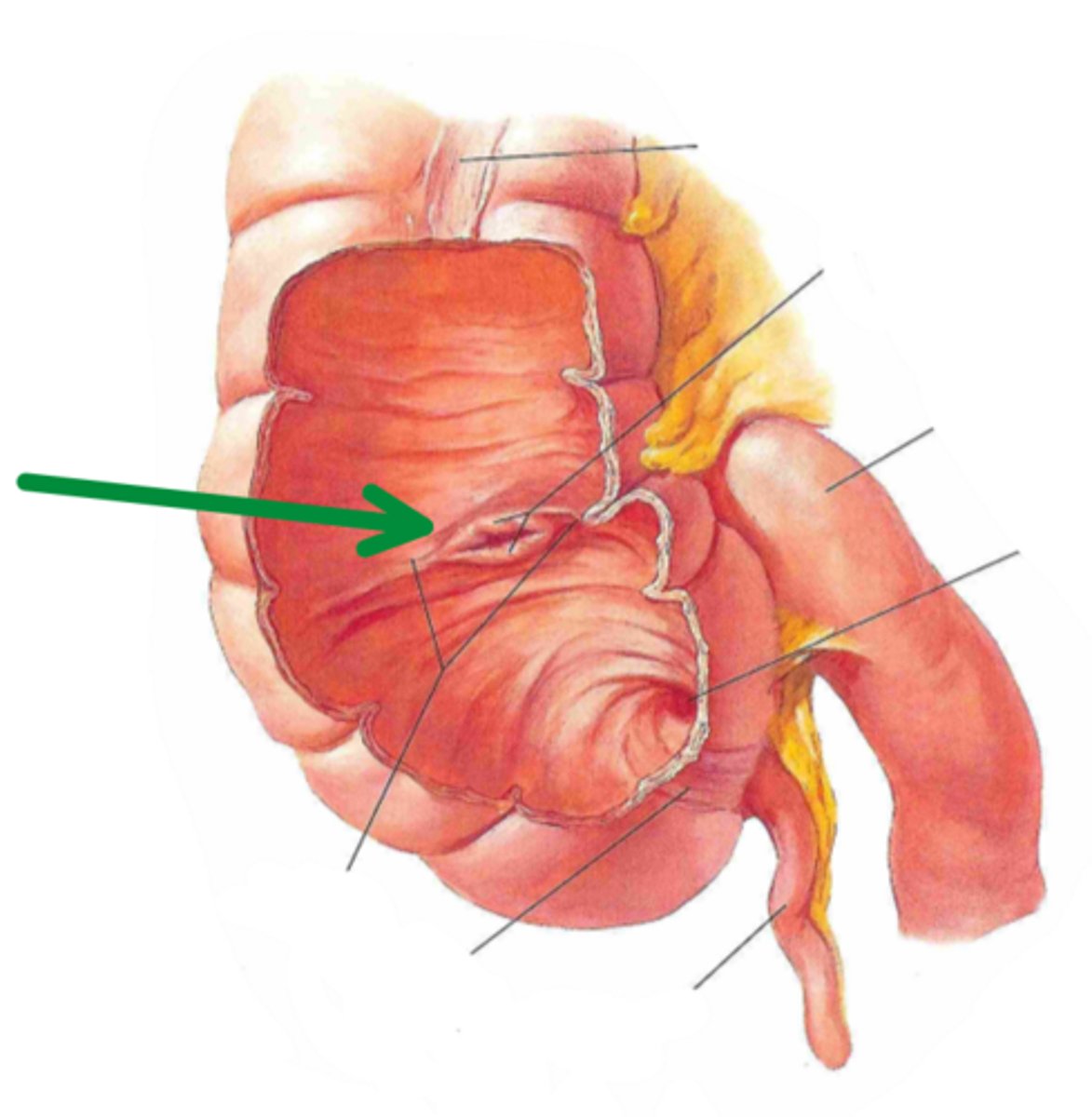
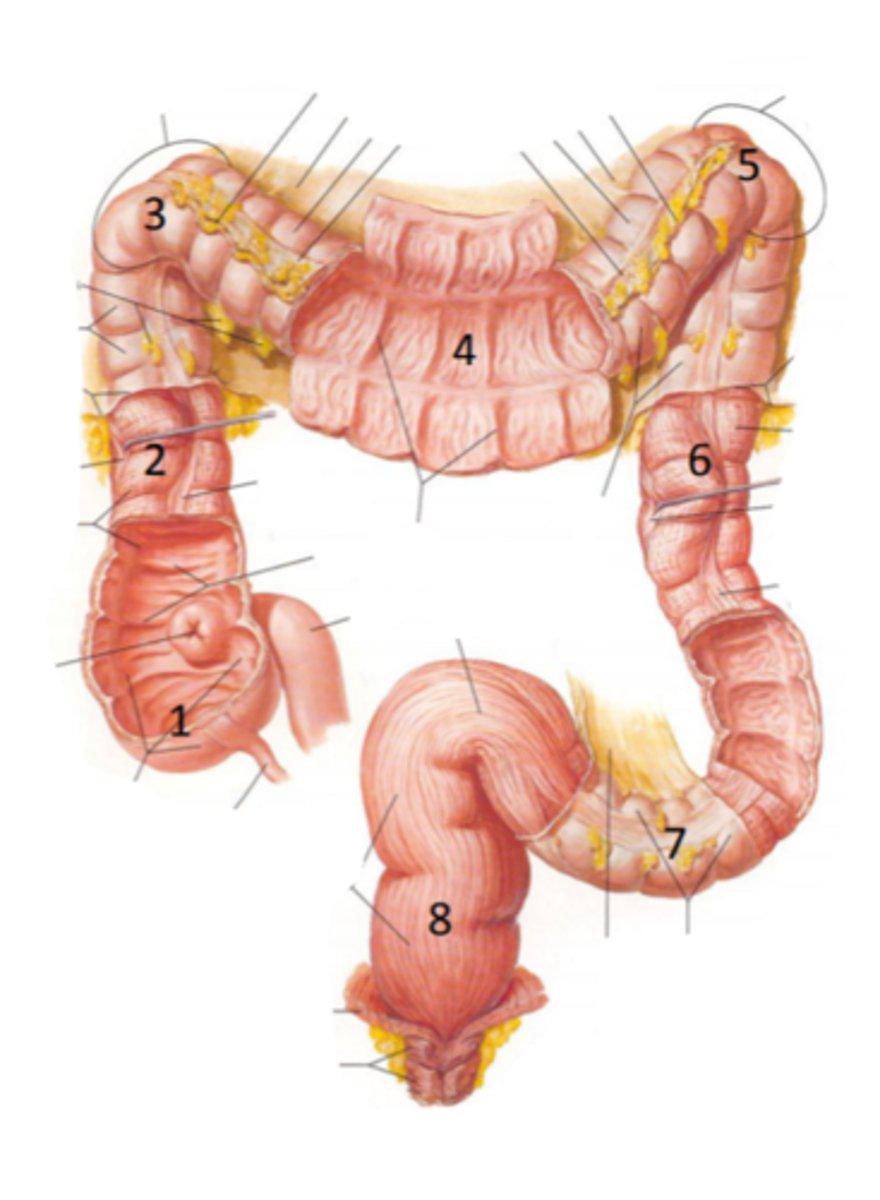
cecum
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
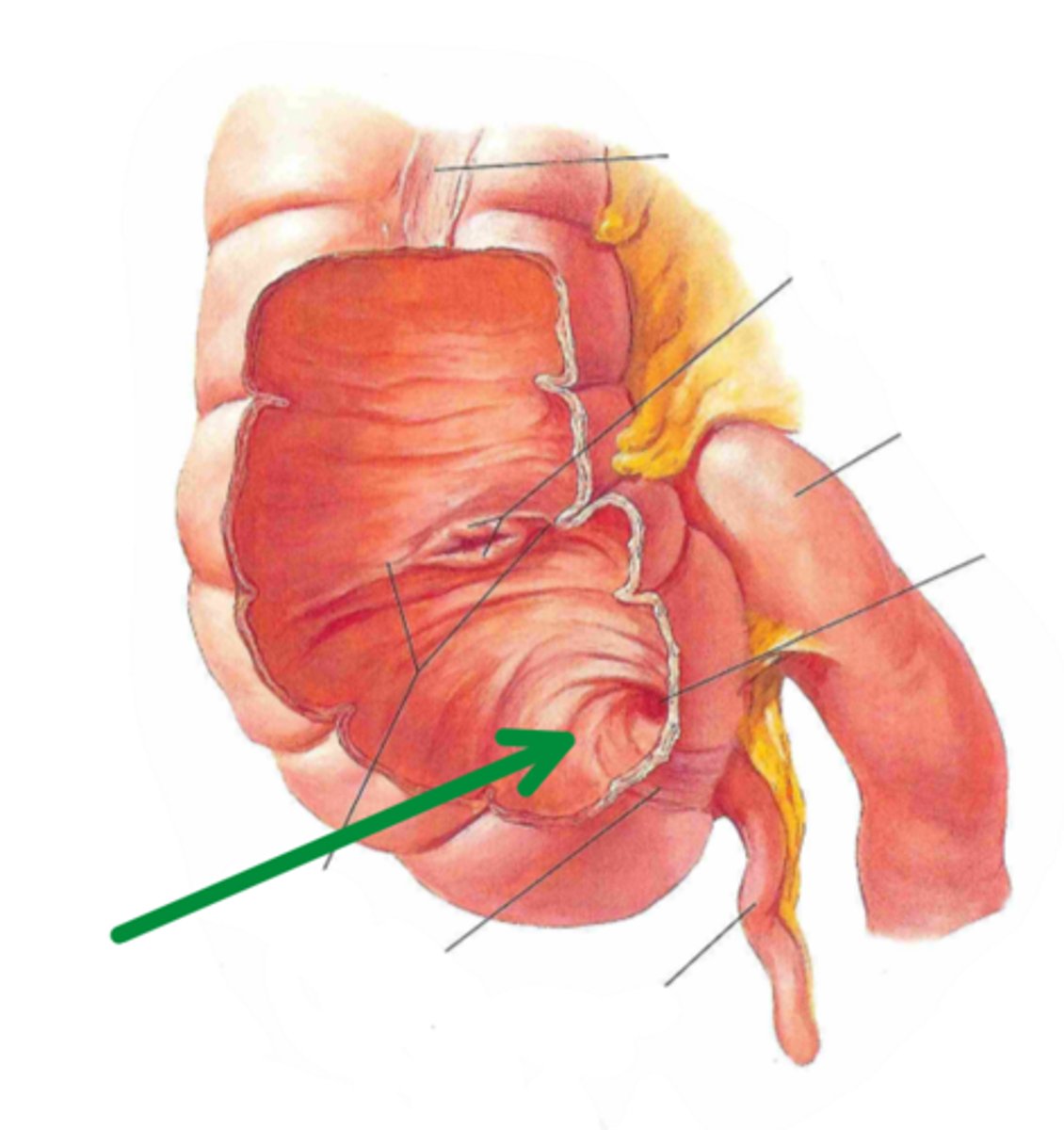
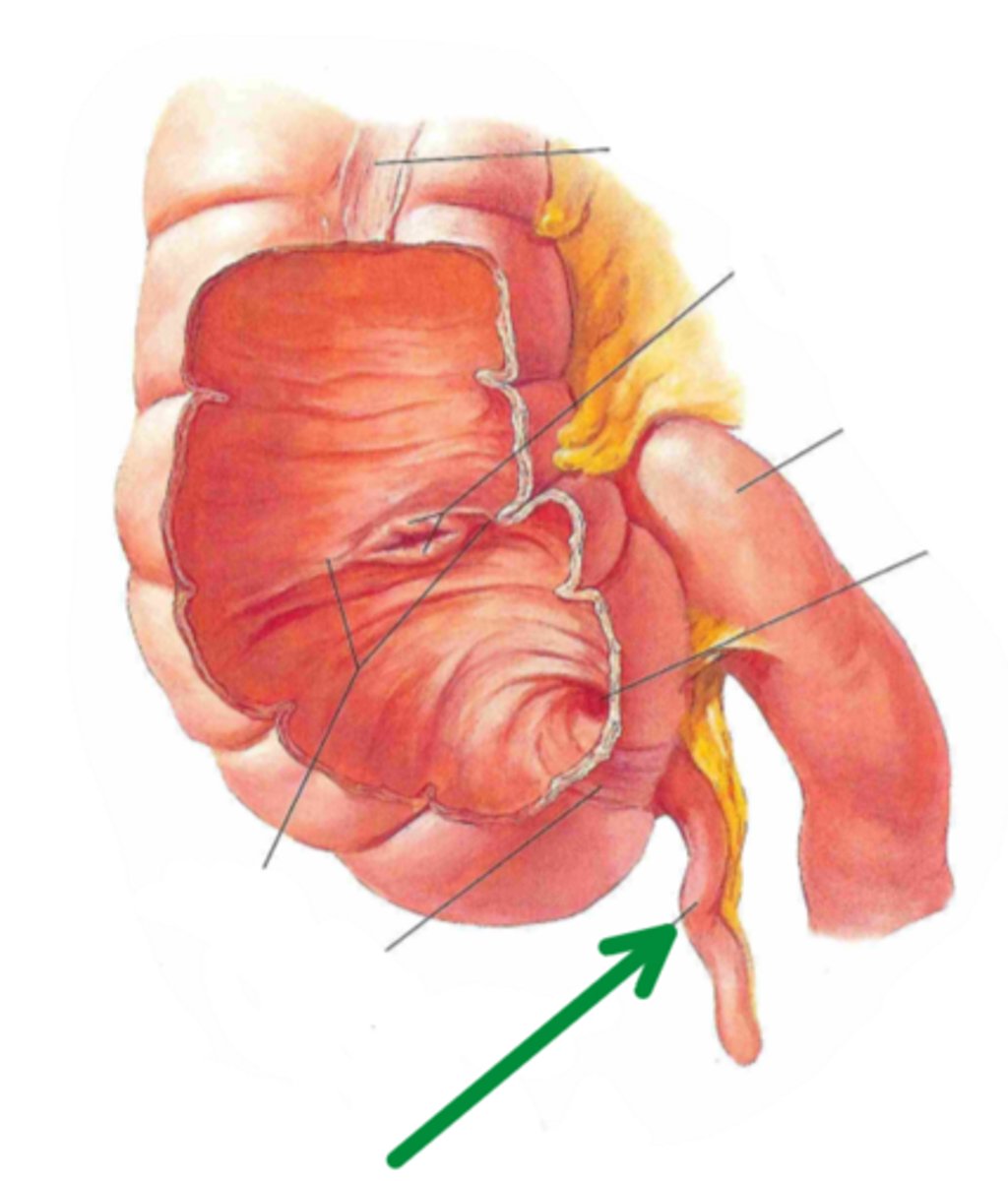
vermiform appendix
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
cecum
identify the structure #1
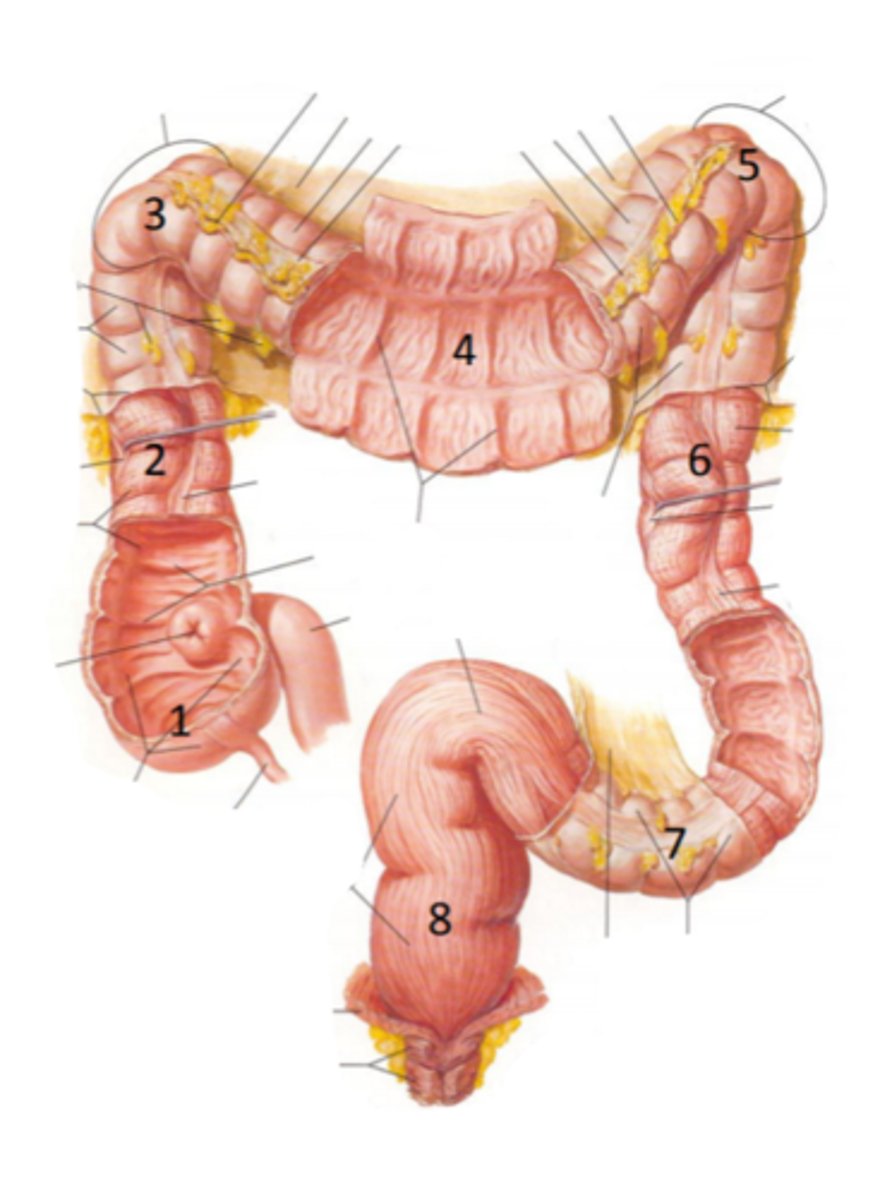
ascending colon
identify the structure #2
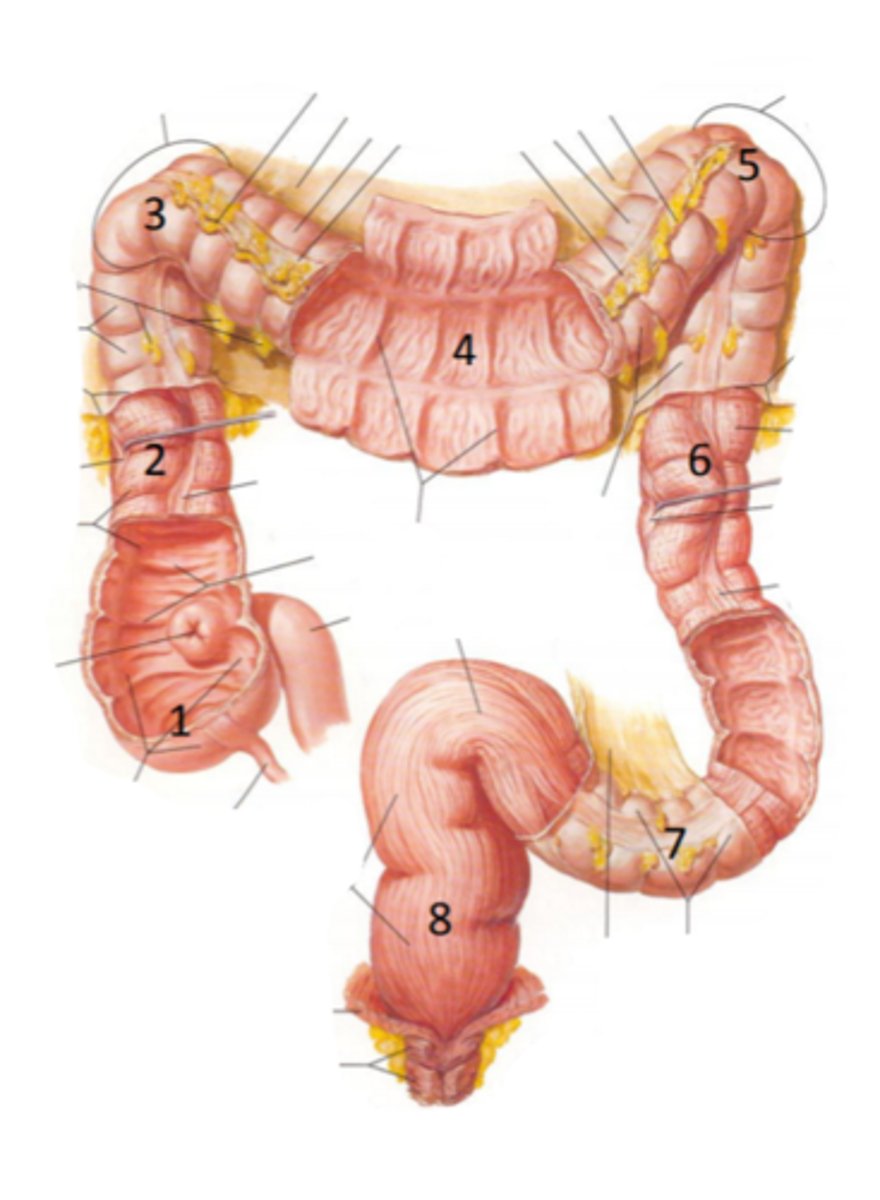
hepatic flexure
identify the structure #3
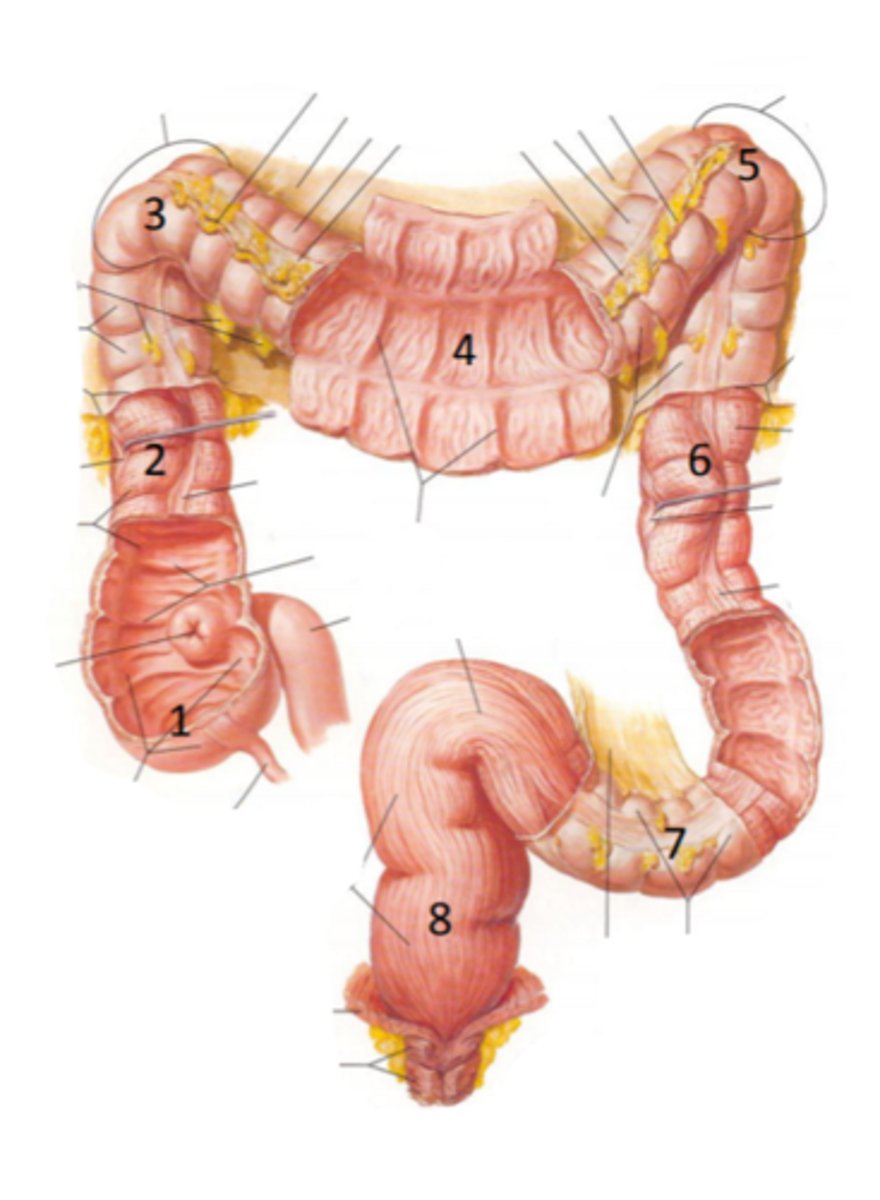
transverse colon
identify the structure #4
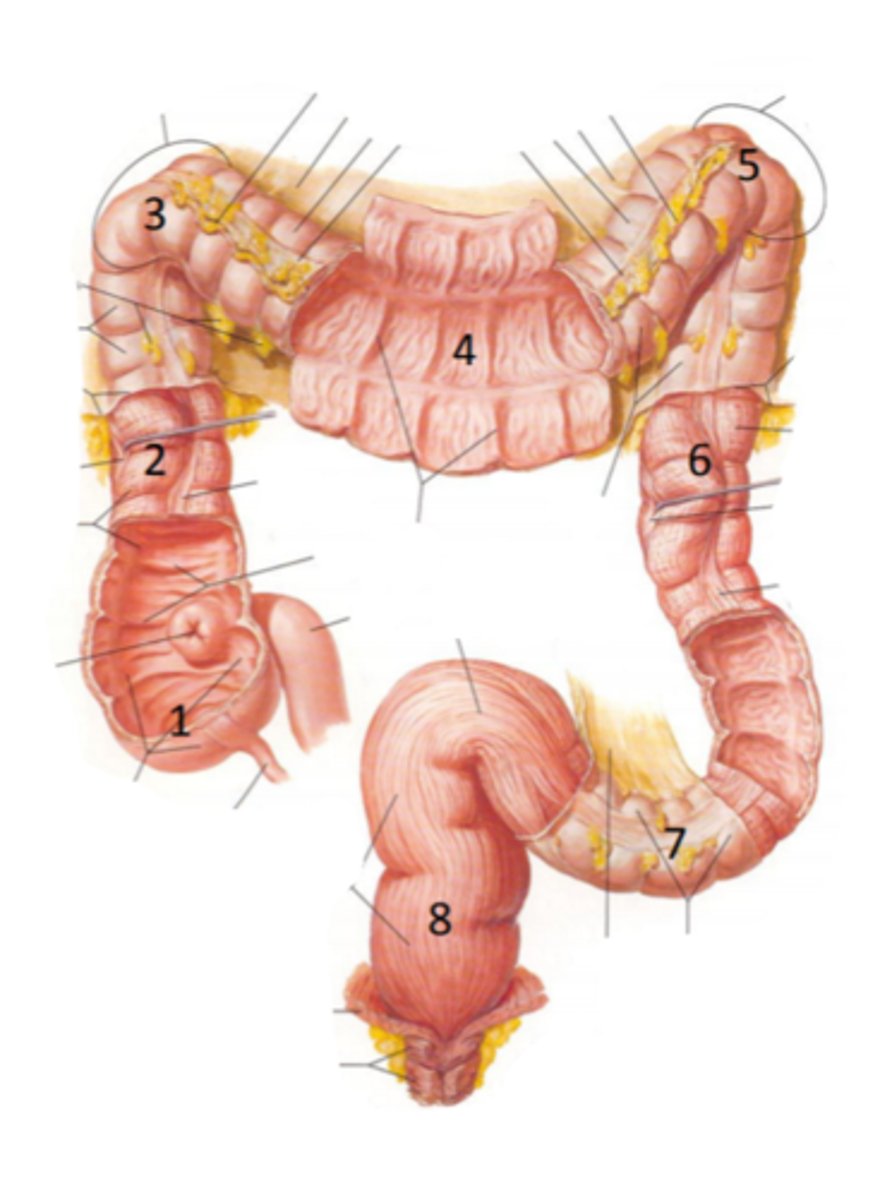
splenic flexure
identify the structure #5
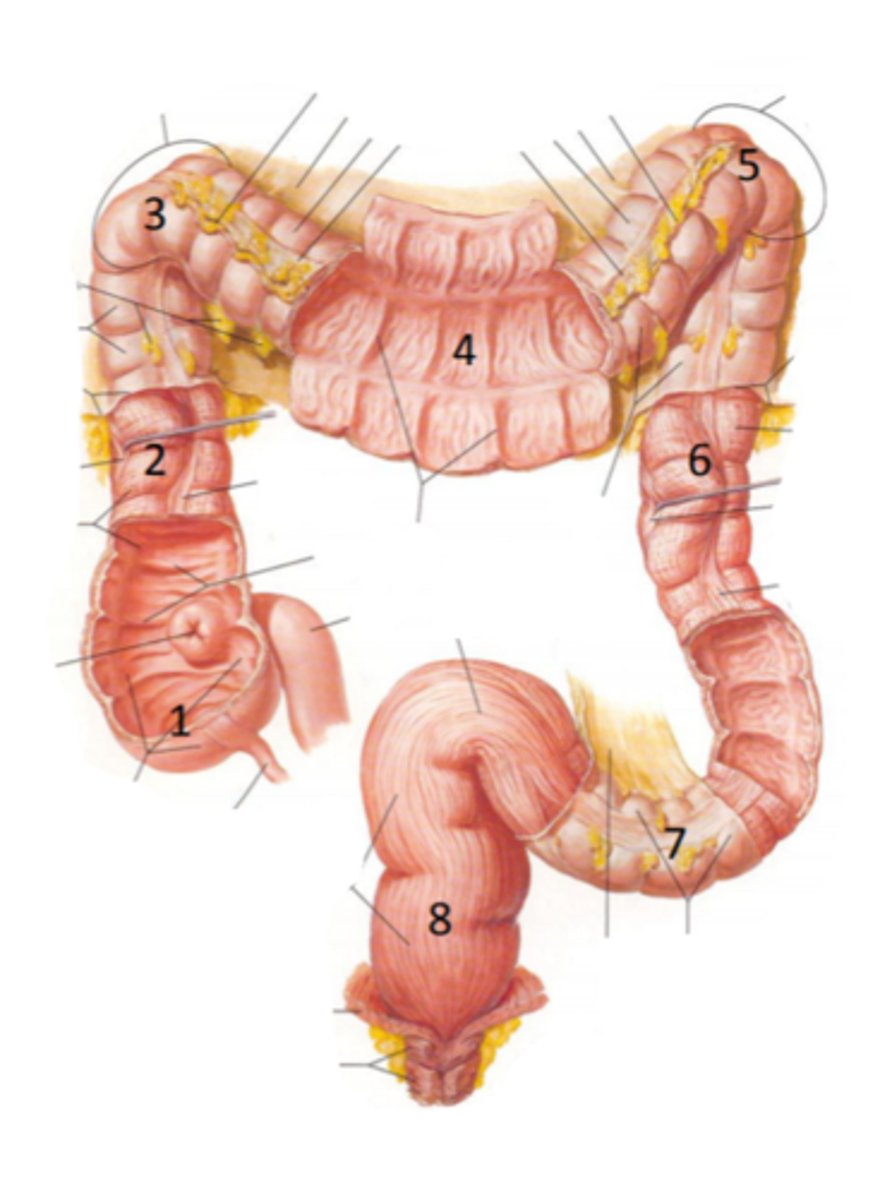
descending colon
identify the structure #6
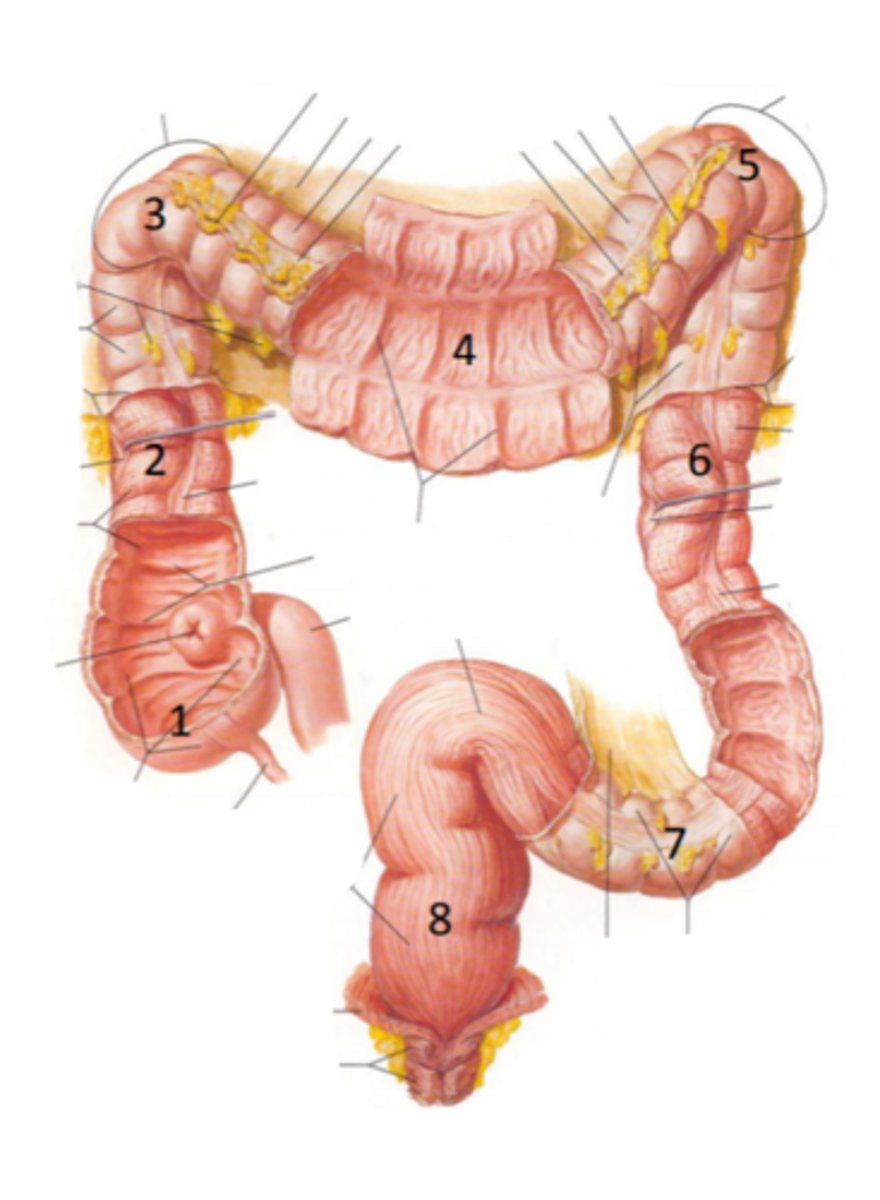
sigmoid colon
identify the structure #7
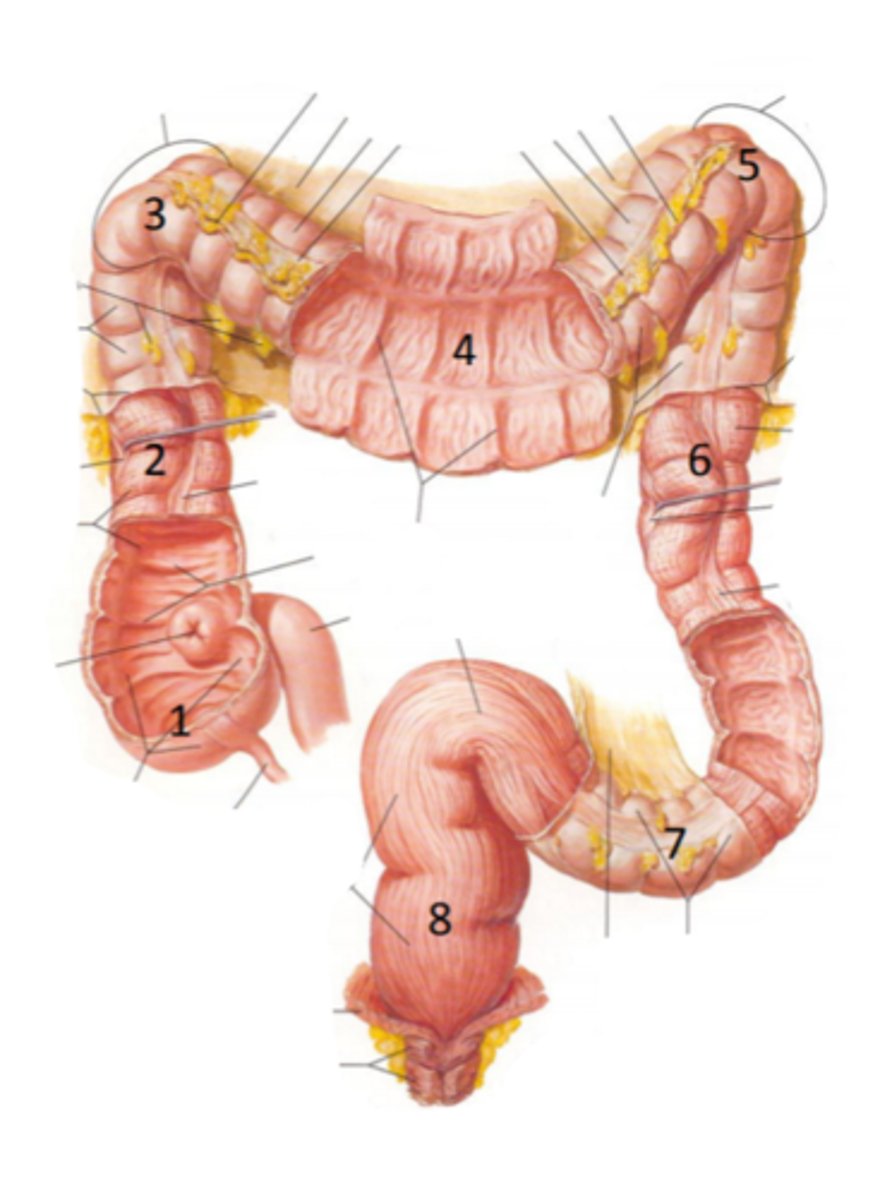
rectum
identify the structure #8
mesentery
small intestine is suspended by
mesocolon
large intestine is suspended by
peritoneum
connective tissue which
lines the abdominal cavity
parietal peritoneum
lining the
abdominal wall
visceral peritoneum
lining the
surface of organs
peritoneal cavity
space between peritoneal layers
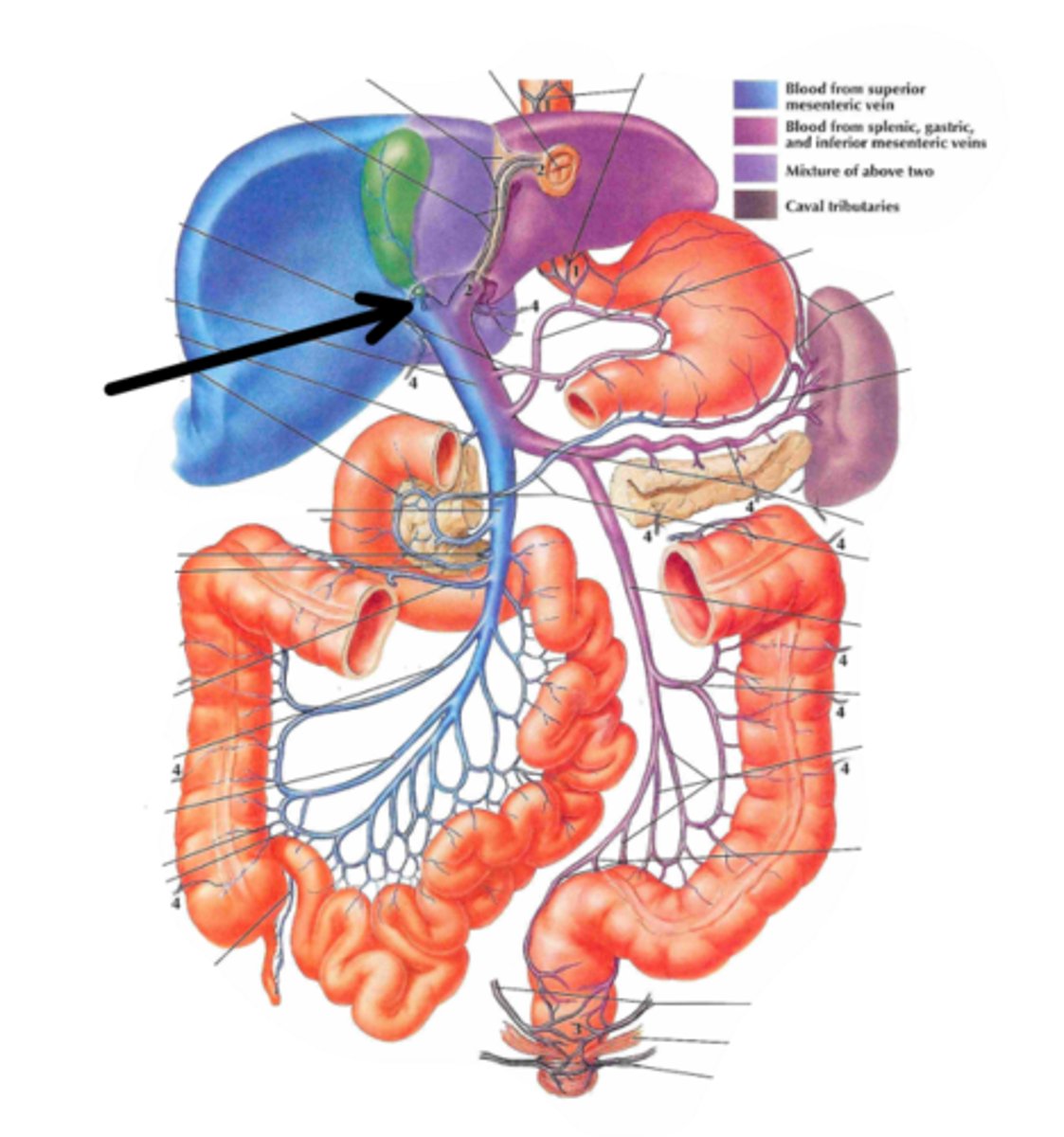
hepatic portal vein
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
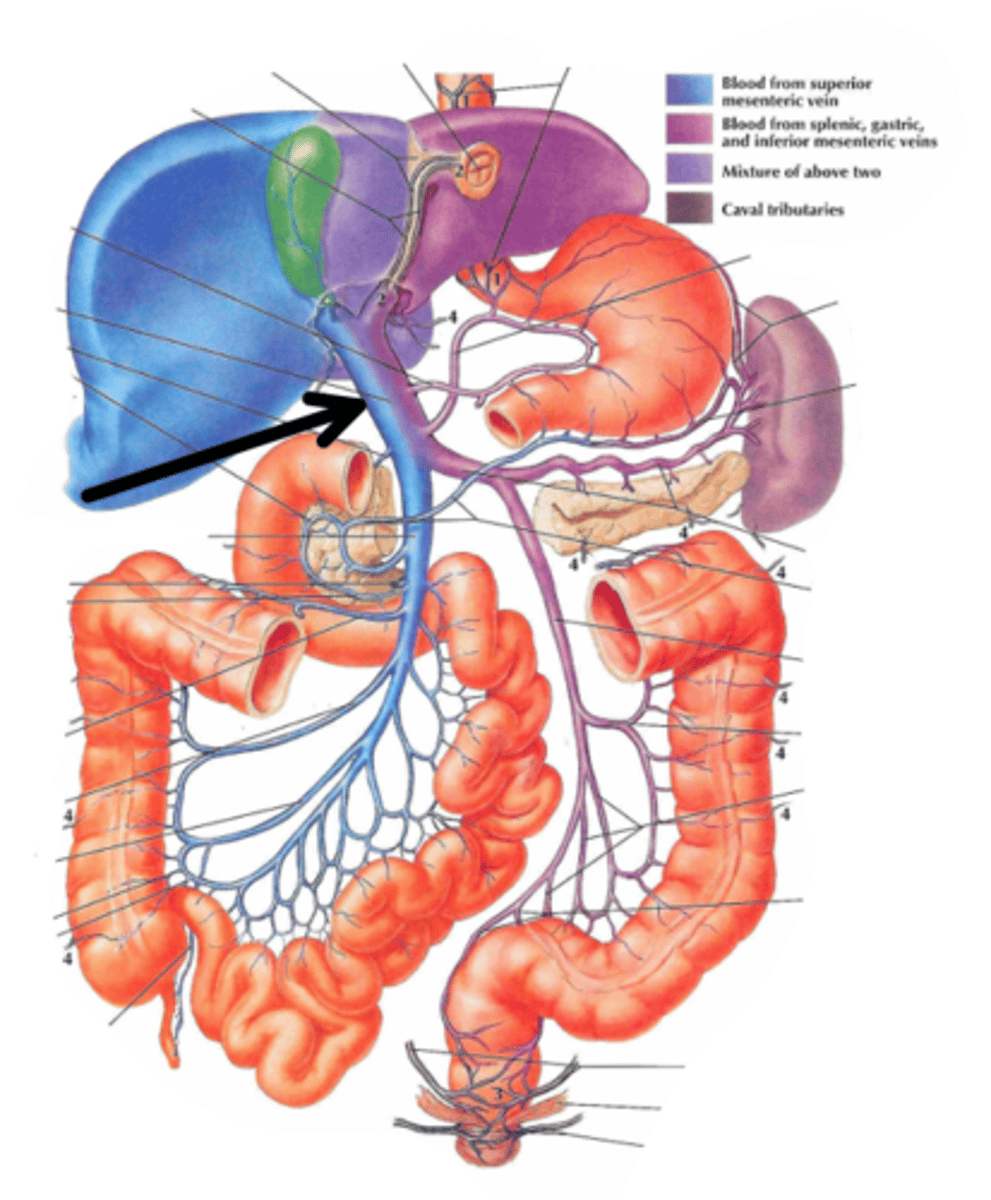
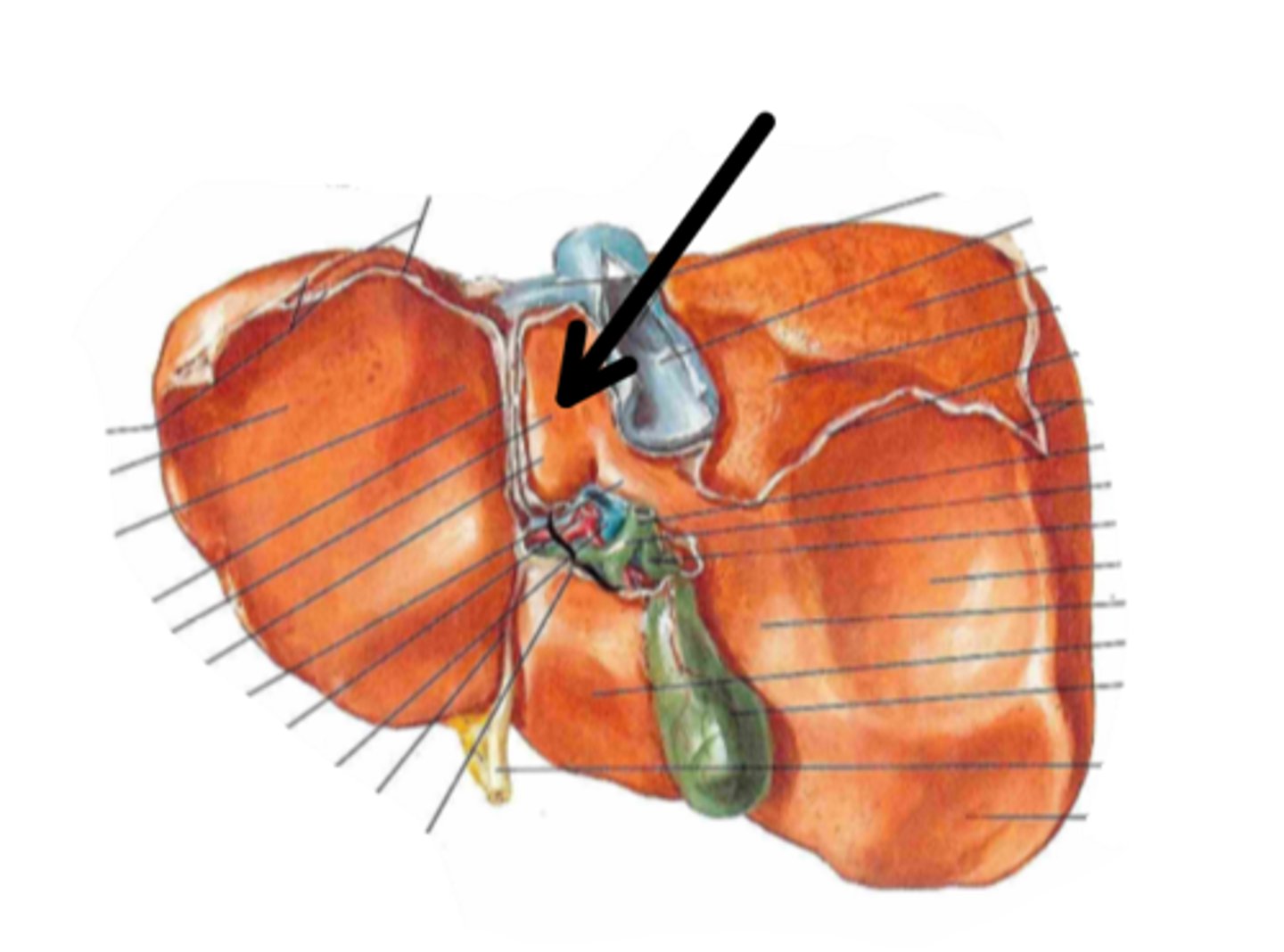
porta hepatis
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
liver
identify the structure
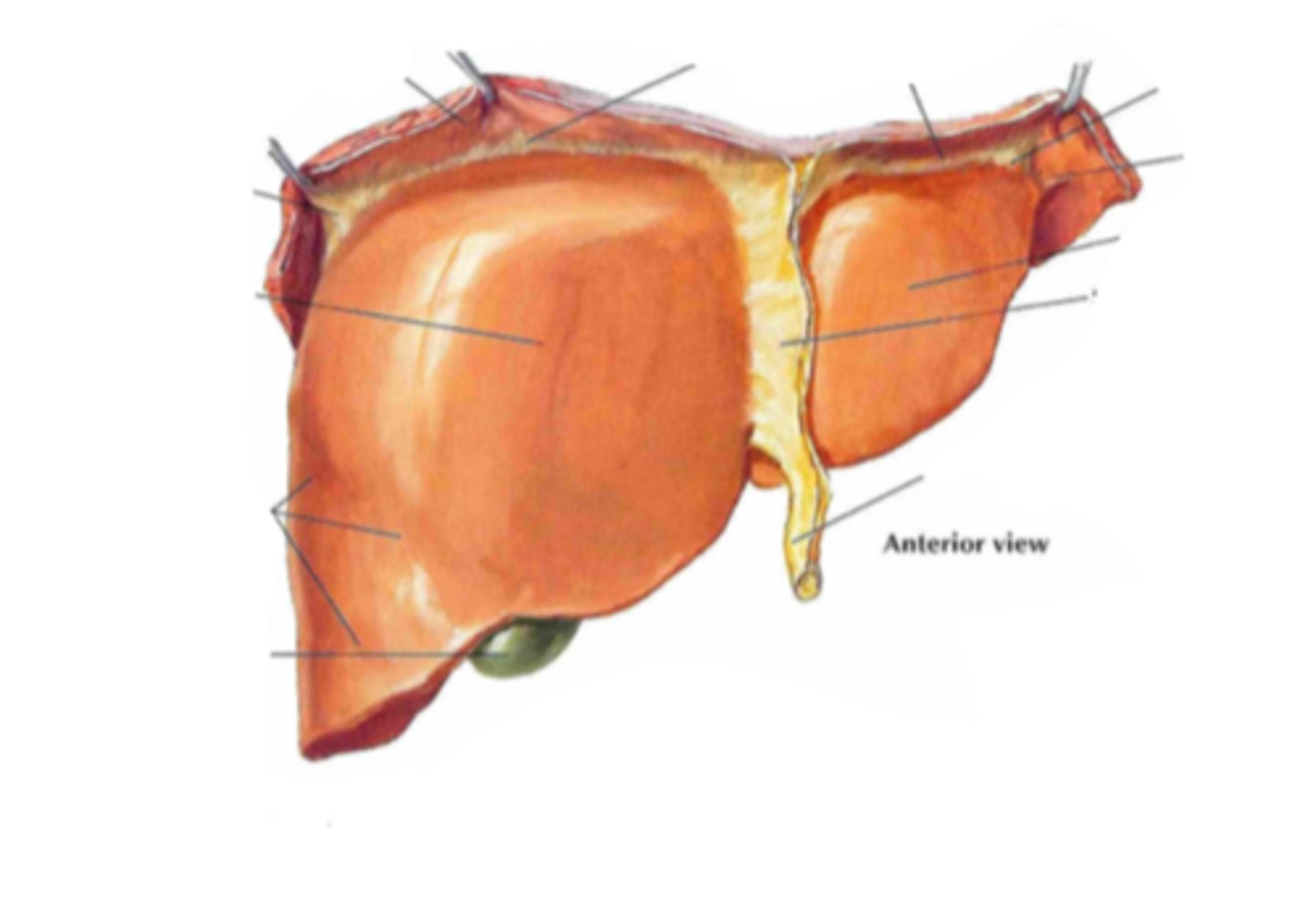
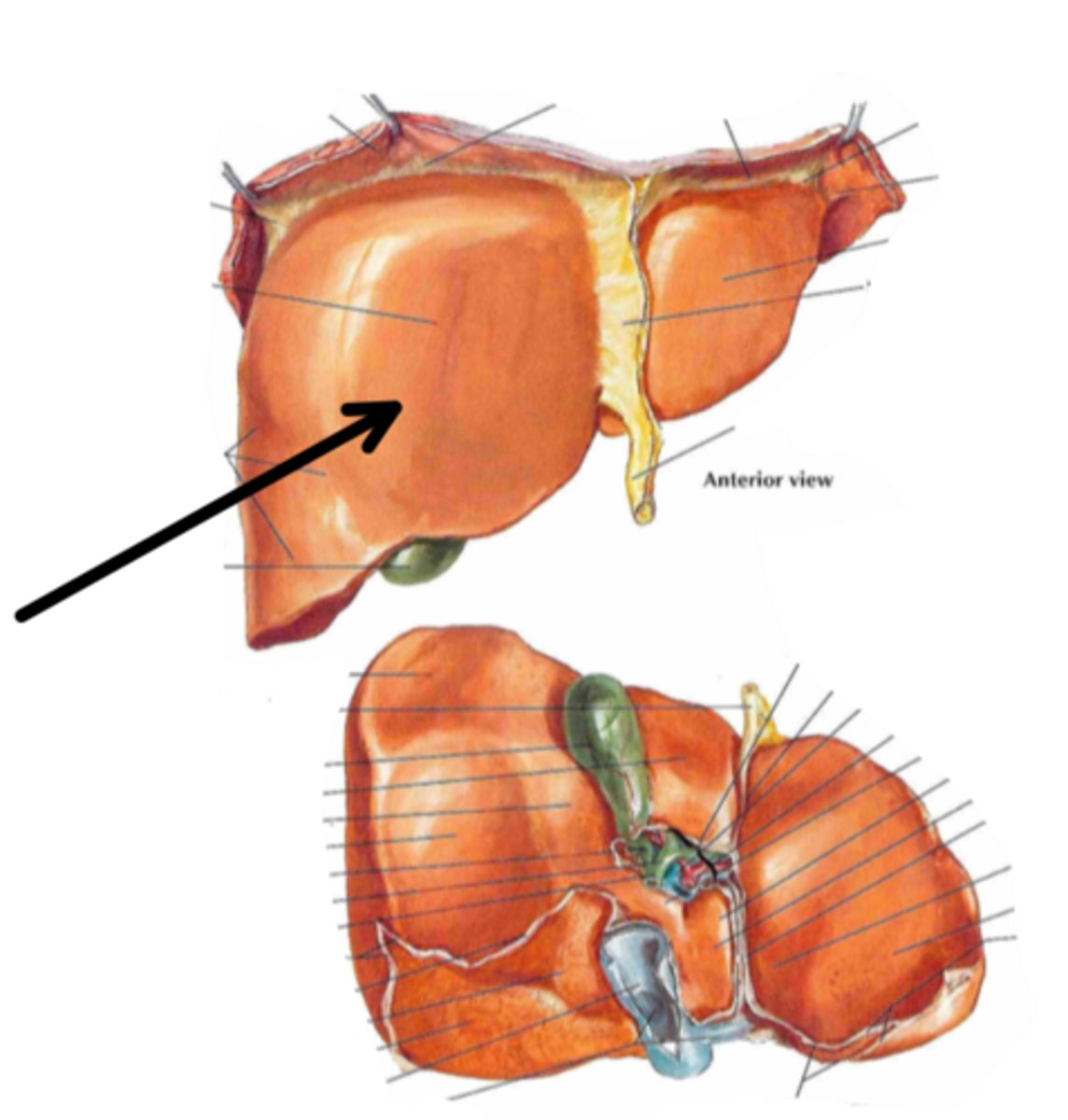
right lobe
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
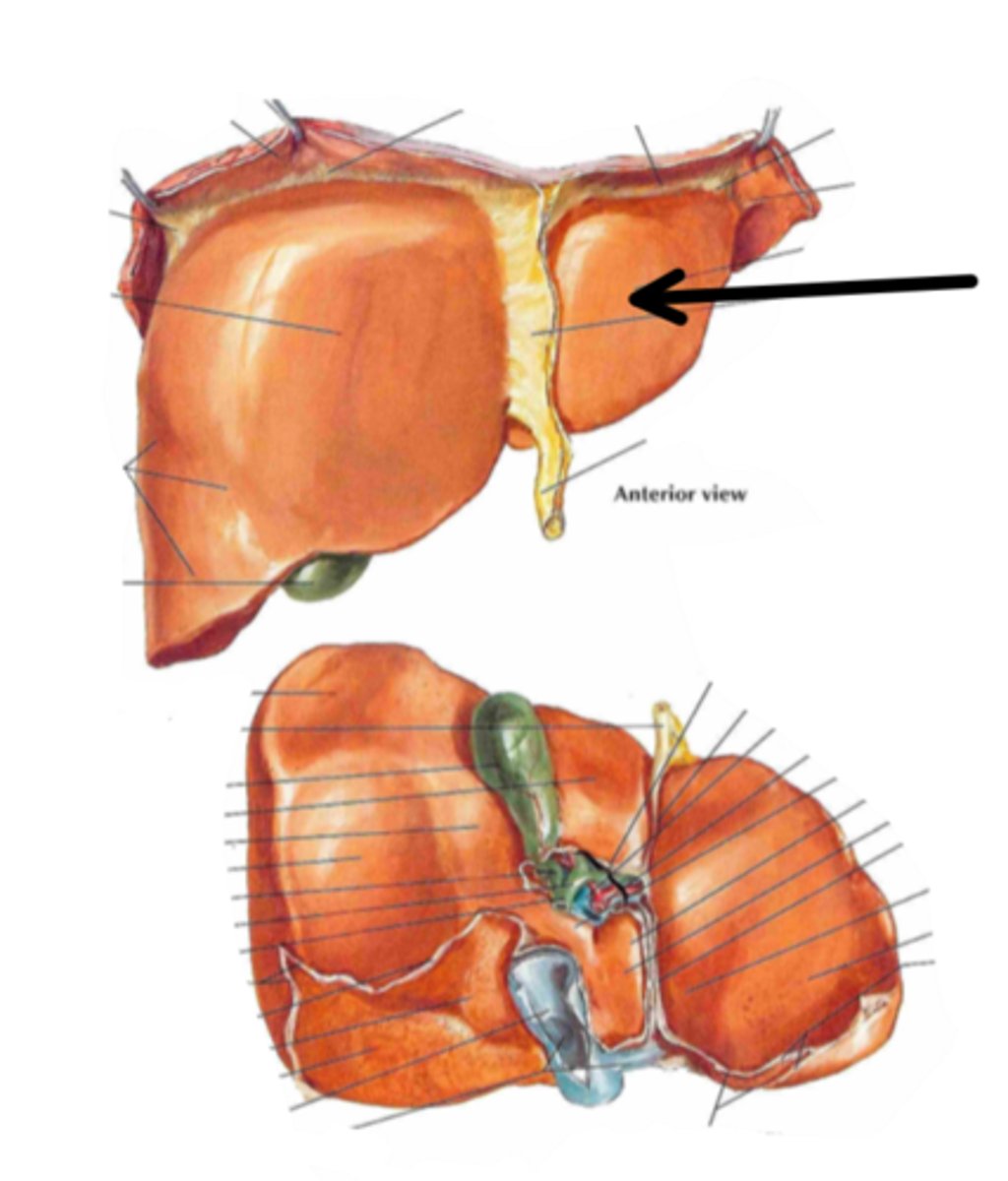
left lobe
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
caudate lobe
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
quadrate lobe
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
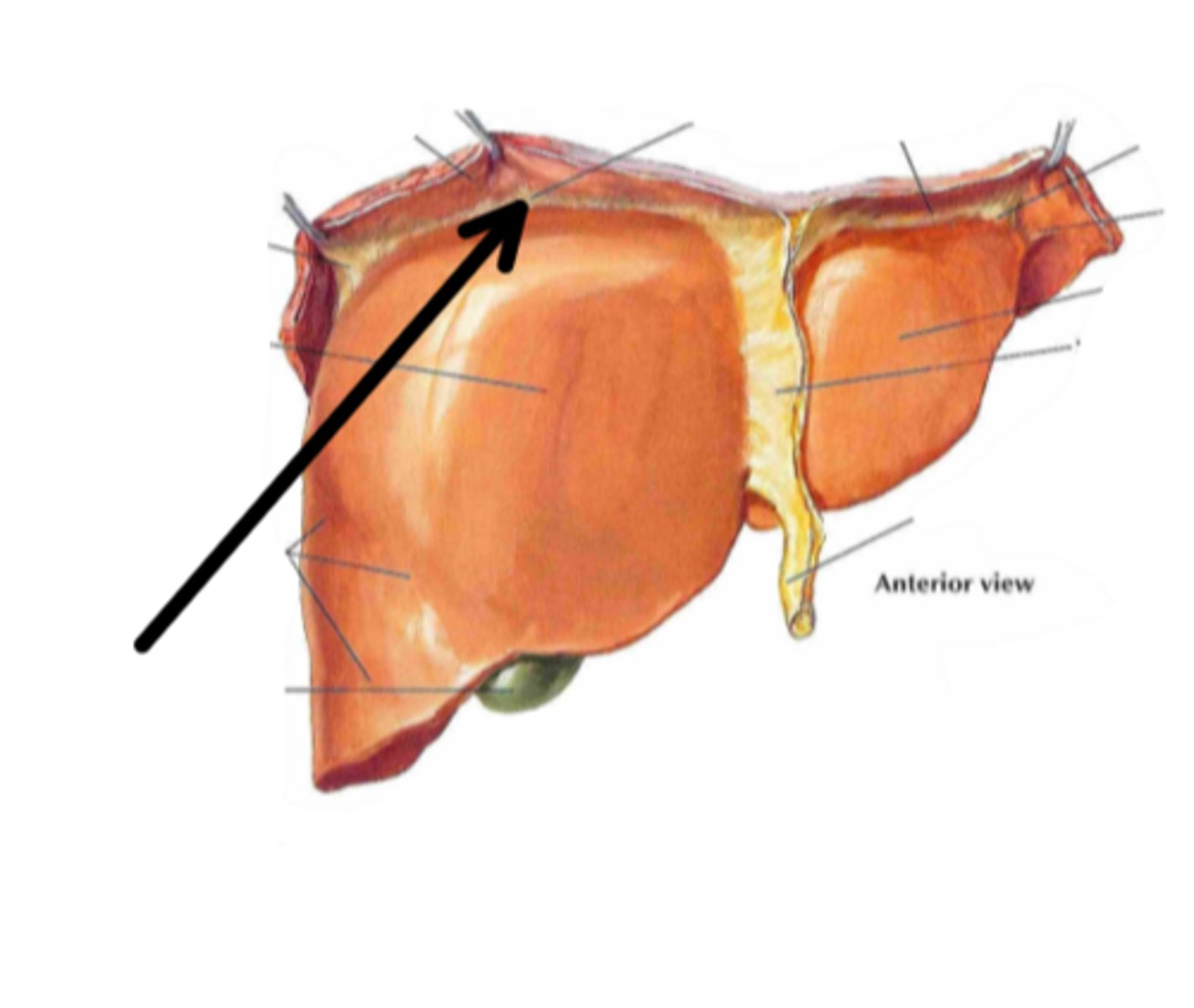
coronary ligament
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
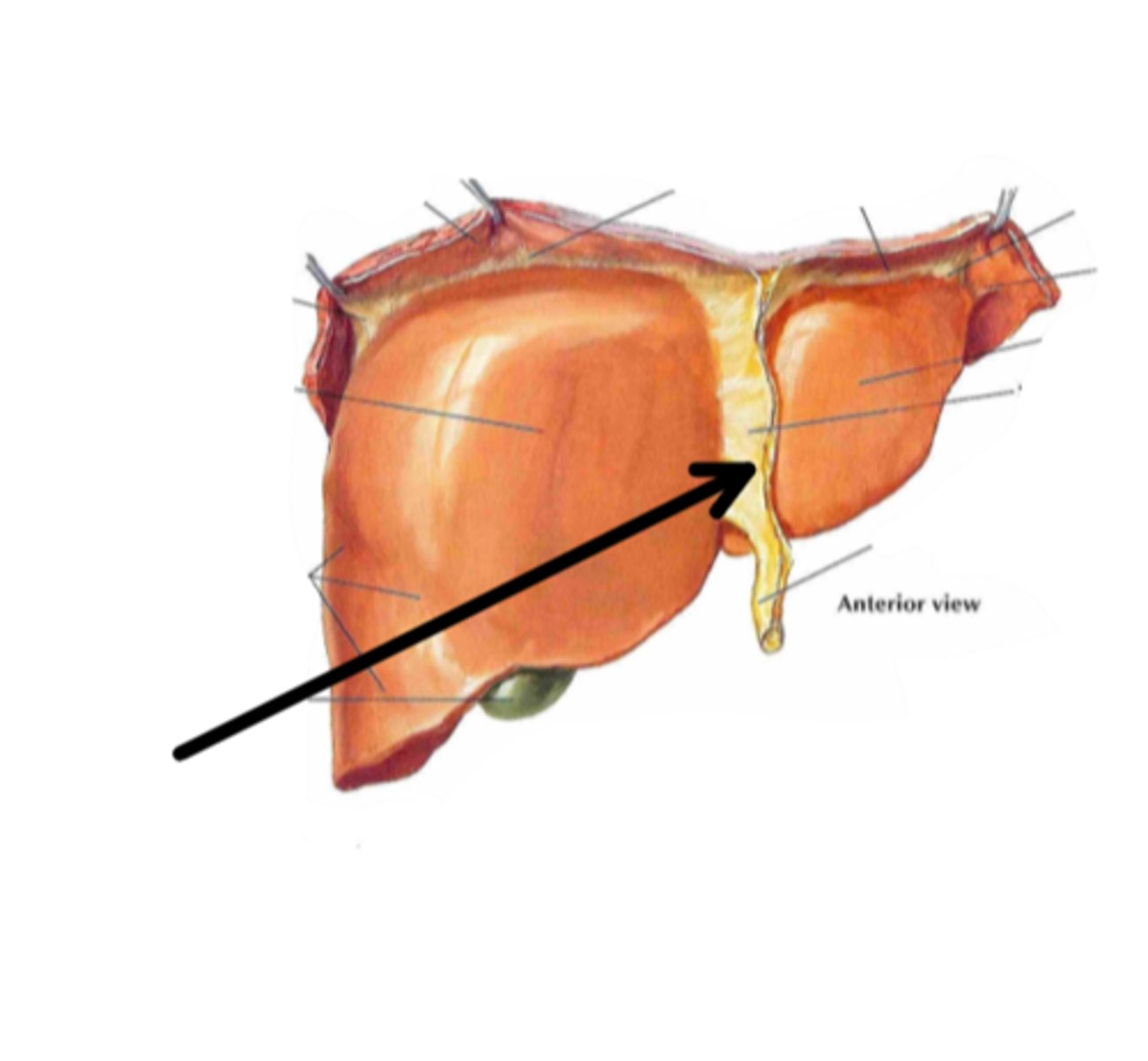
falciform ligament
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
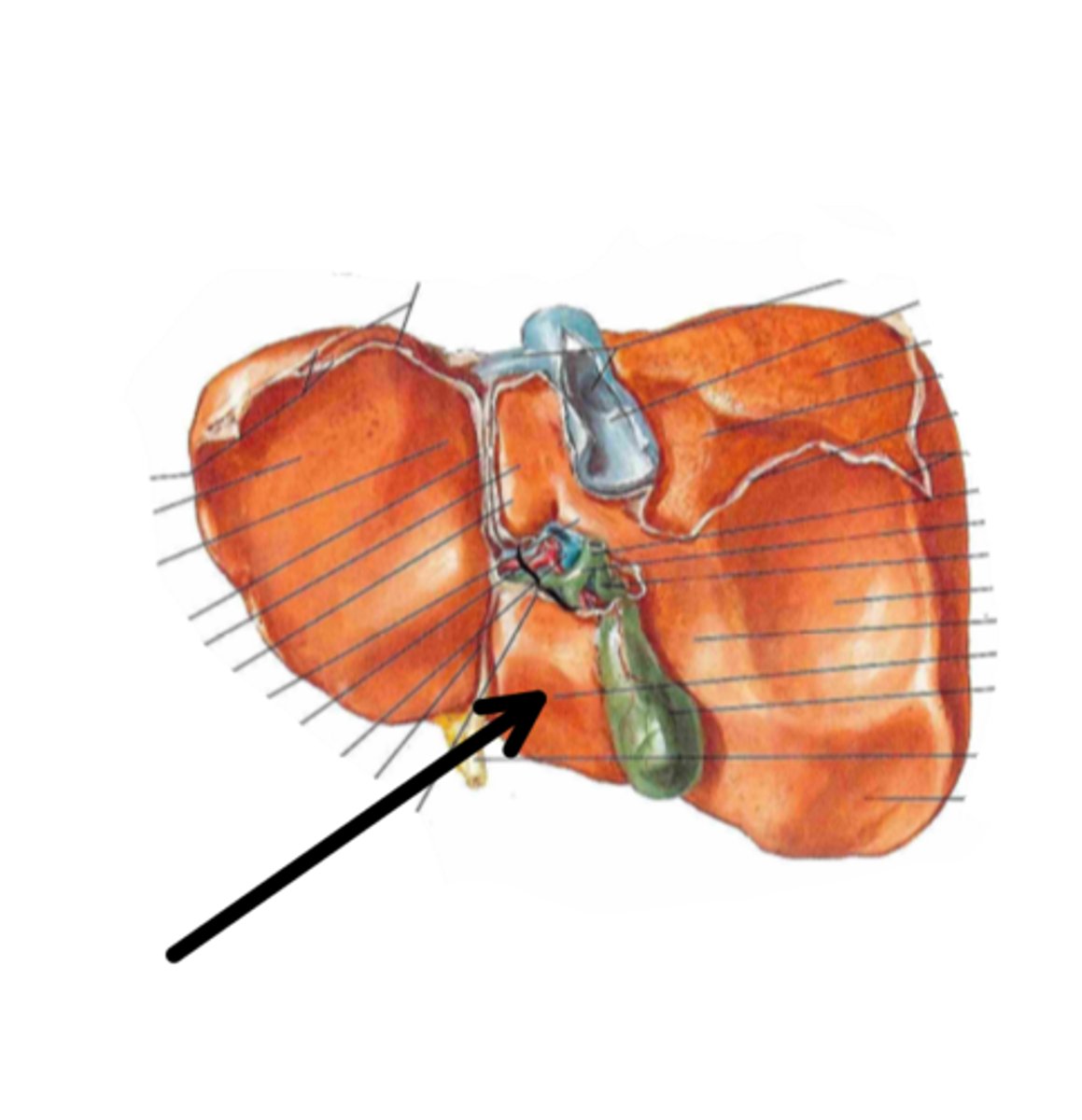
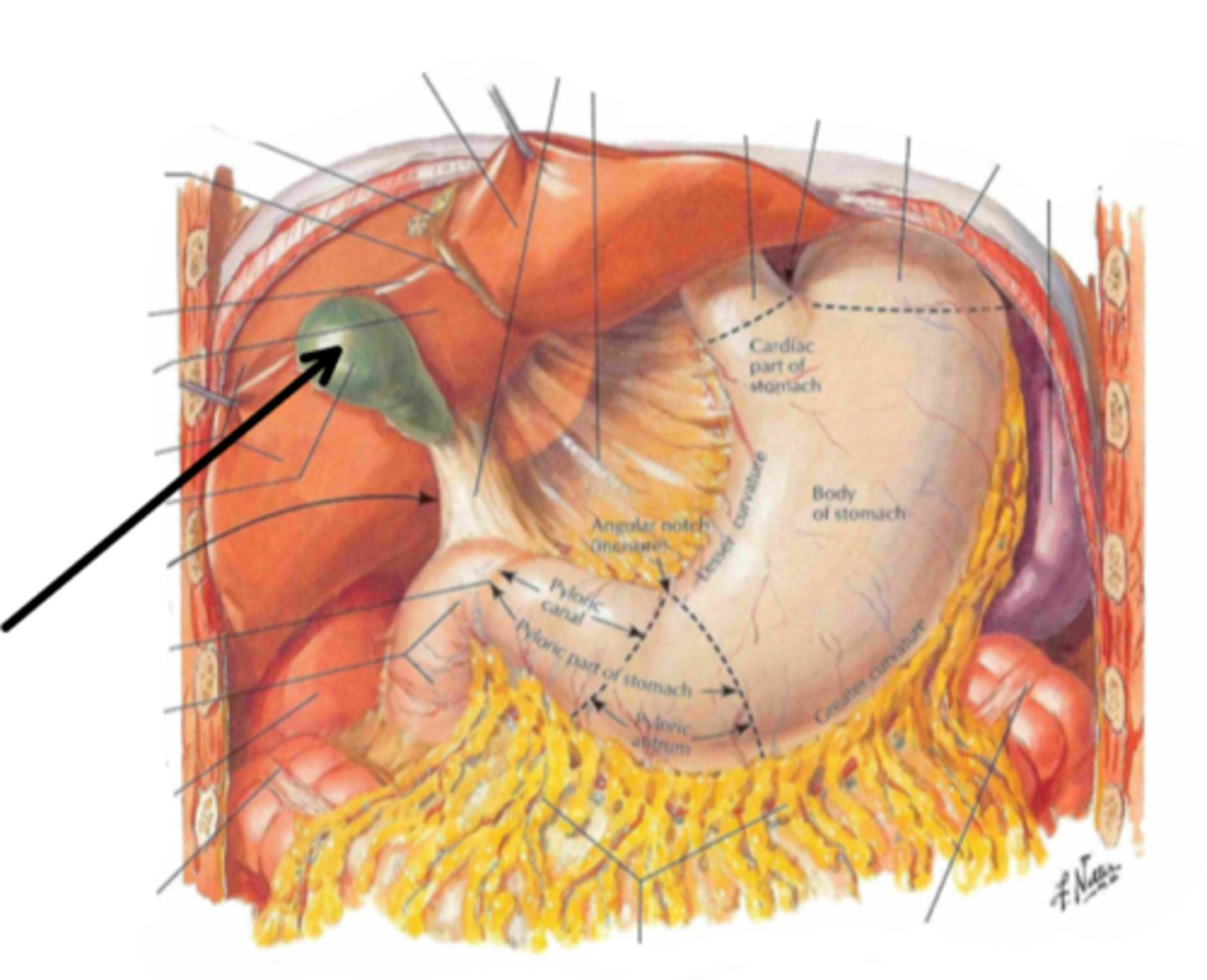
gallbladder
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
digestion and absorption of
fats and vitamins A, D, E, K
Bile is responsible for
head (of pancreas)
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
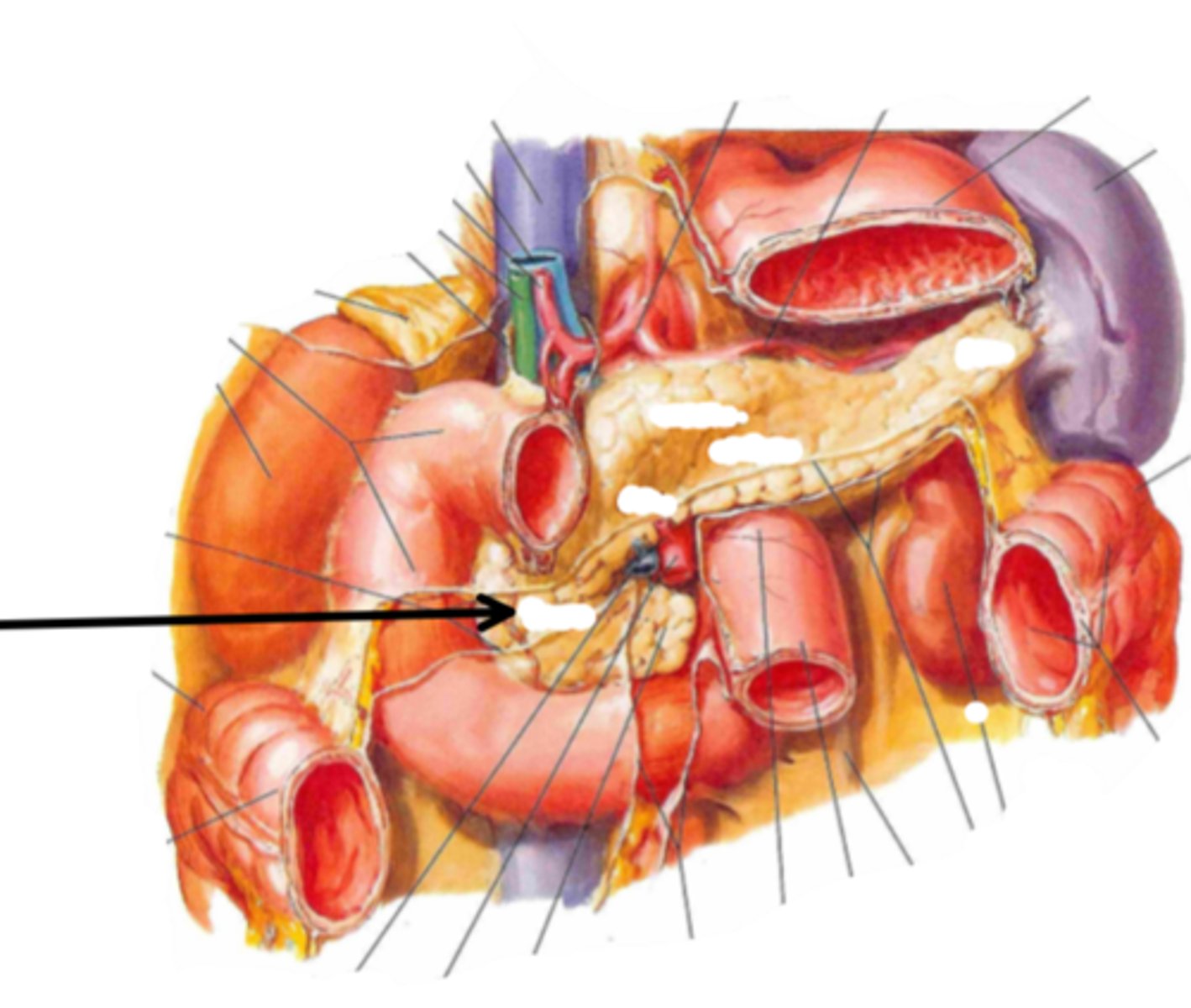
body (of pancreas)
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
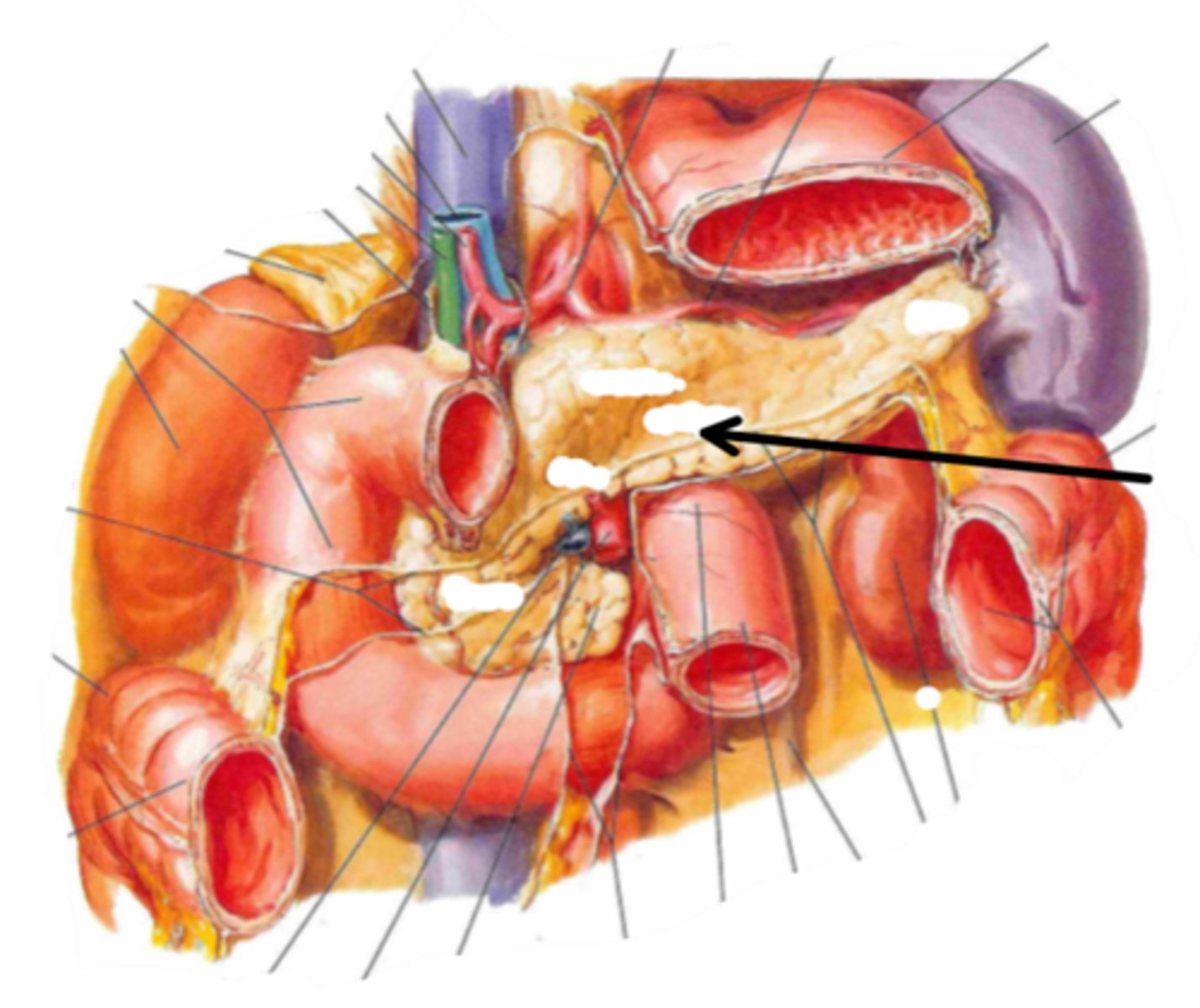
tail (of pancreas)
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
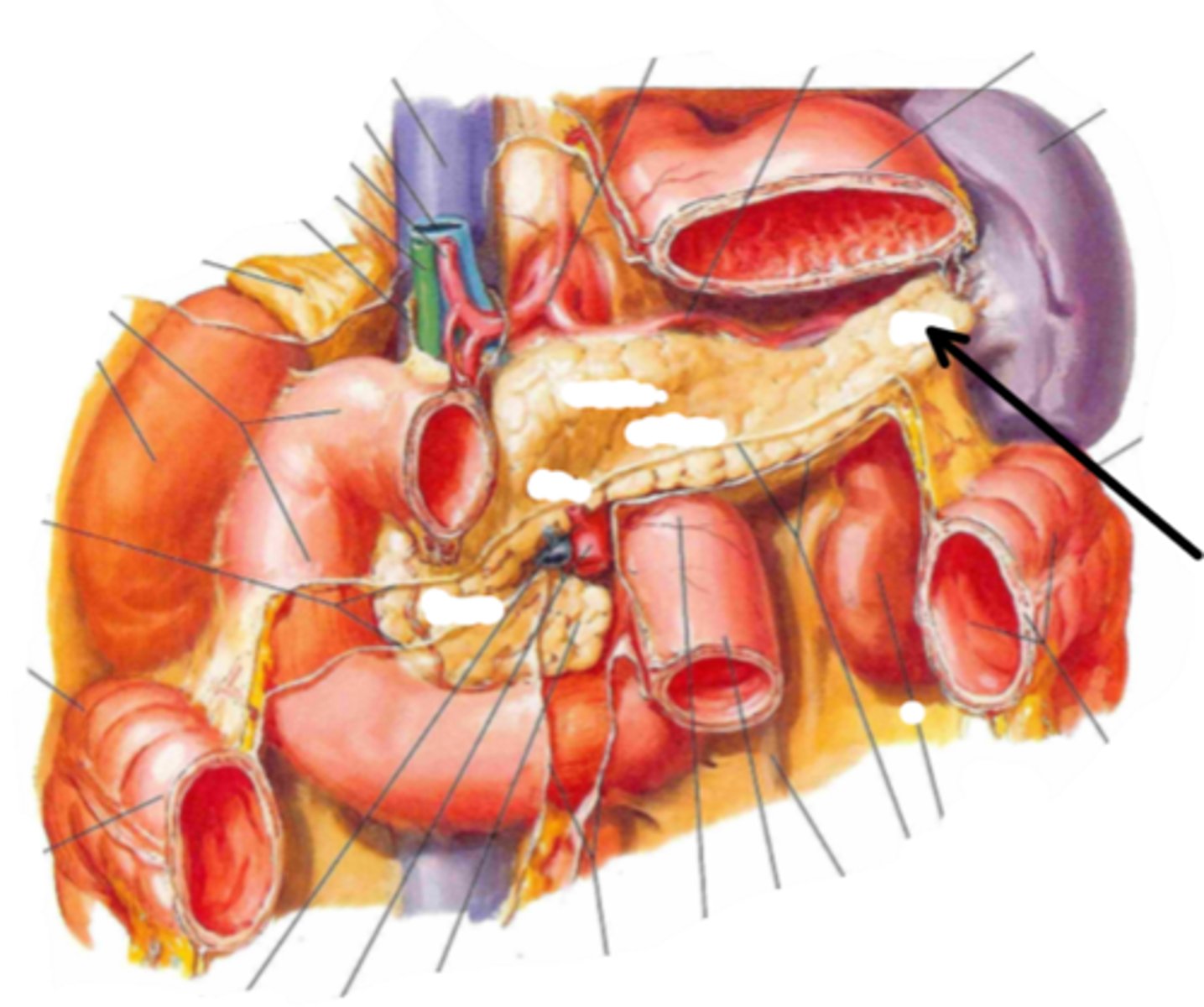
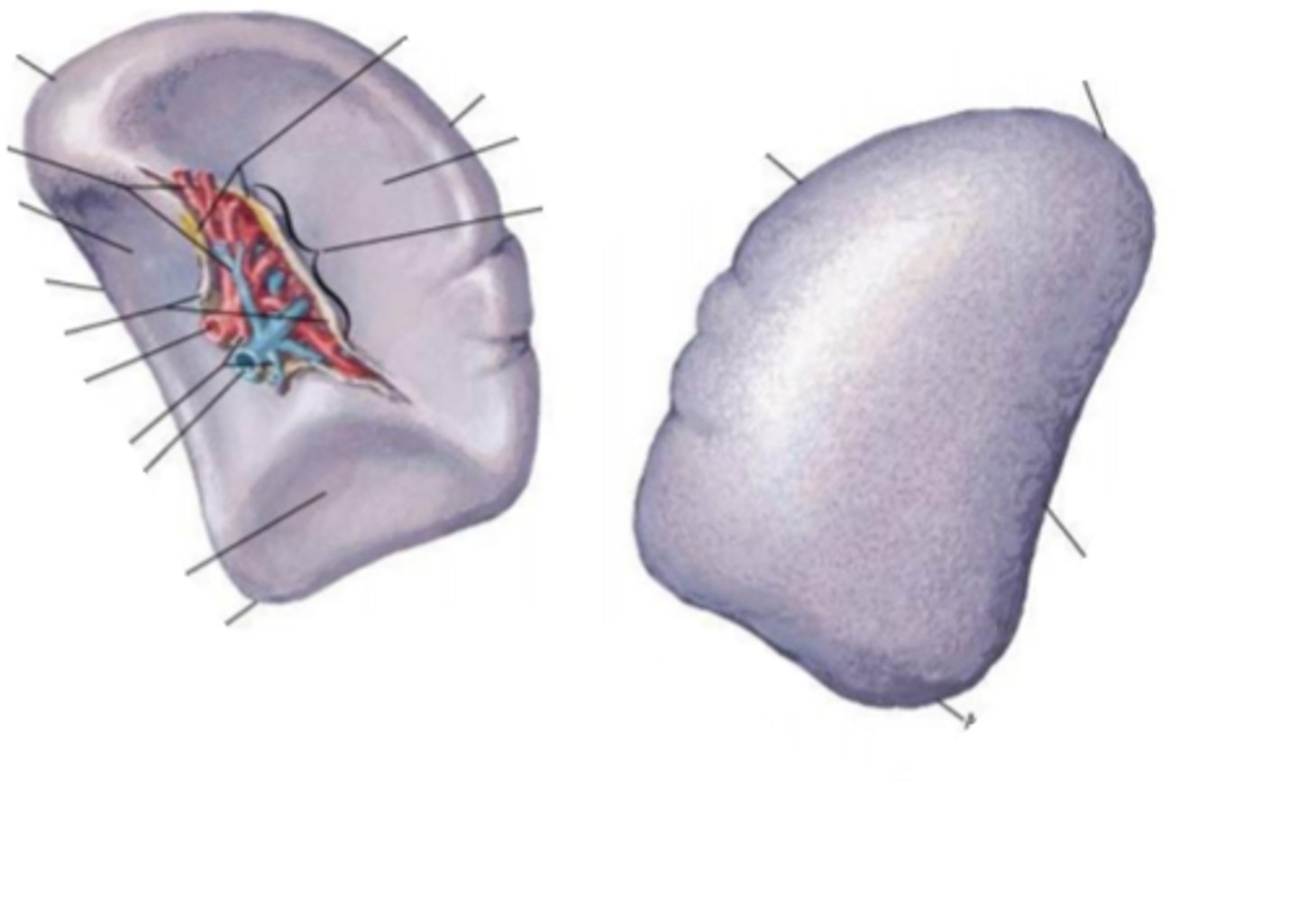
spleen
identify the structure
right hepatic duct
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
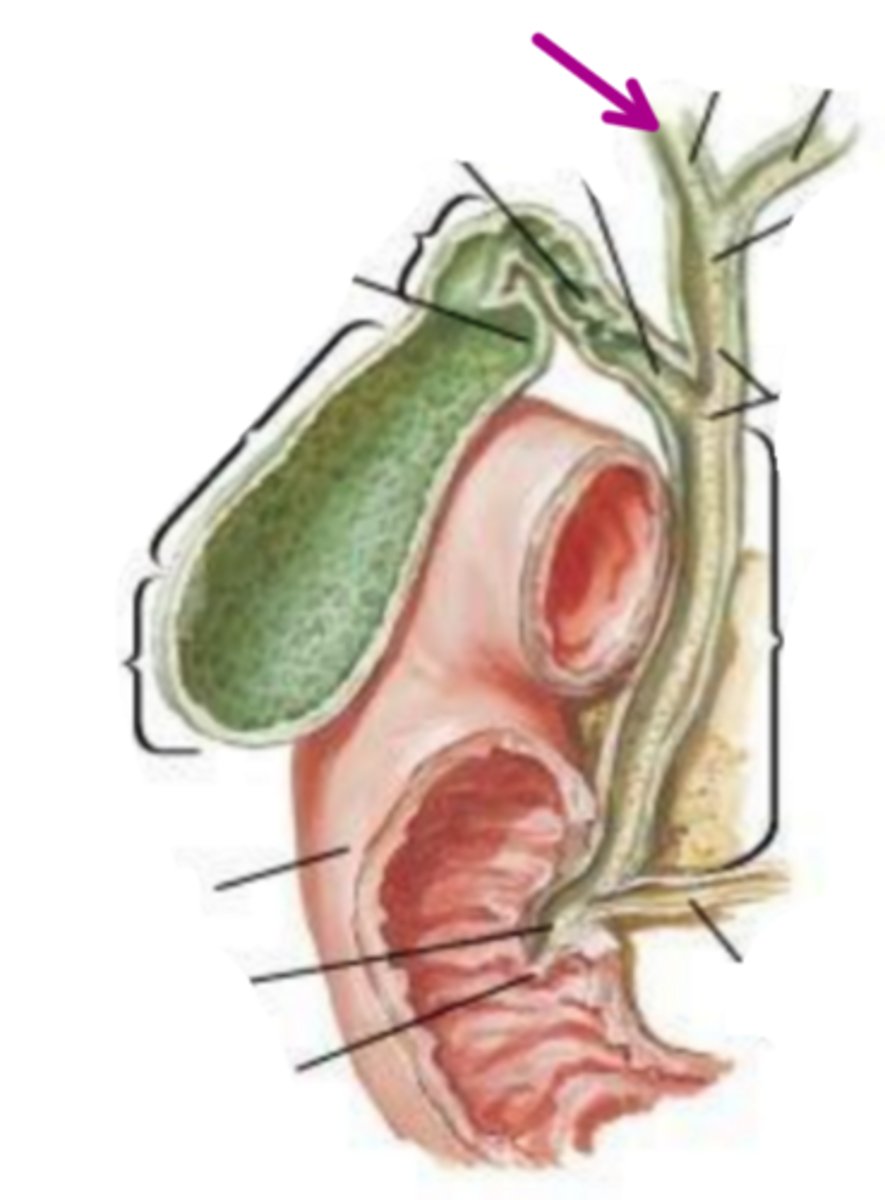
left hepatic duct
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
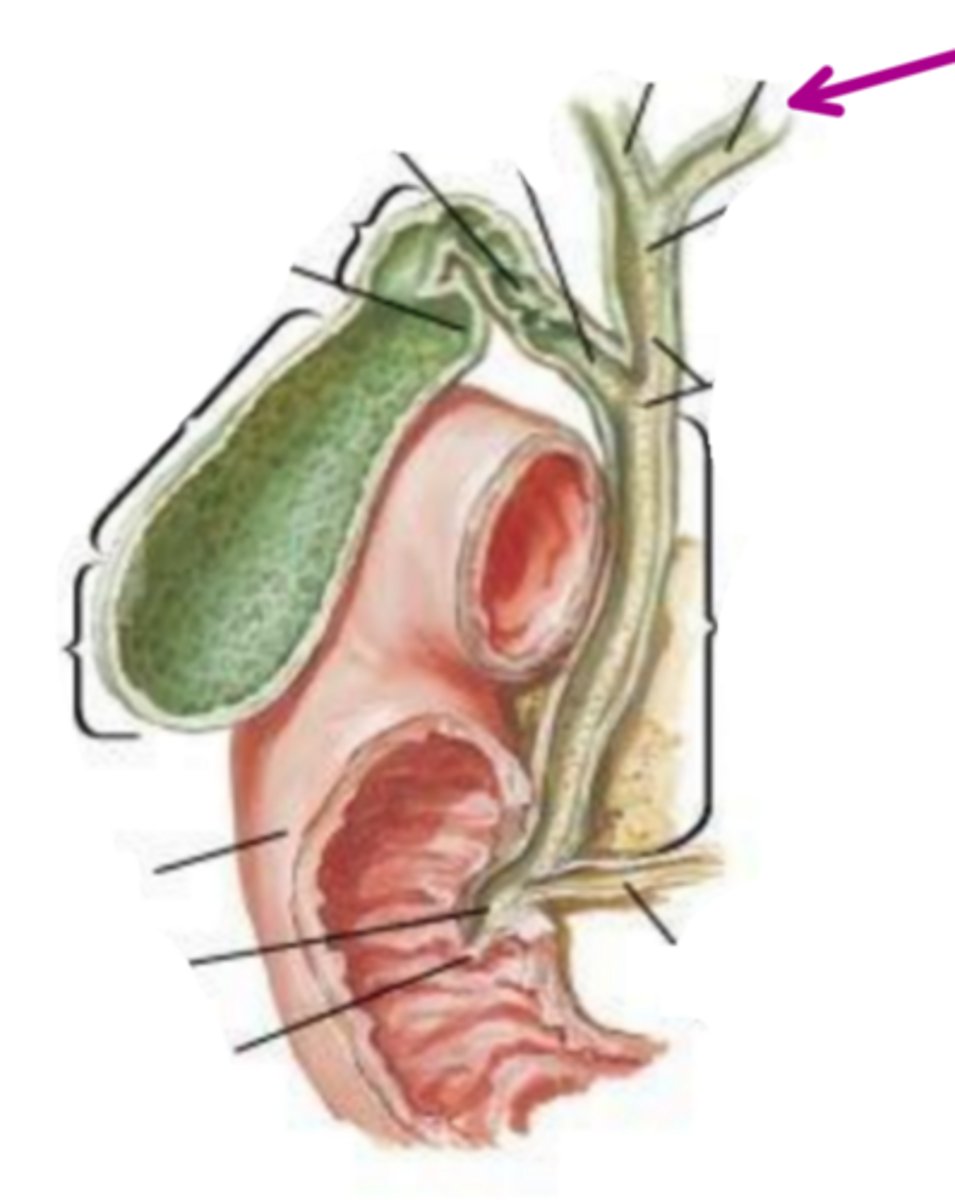
common hepatic duct
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
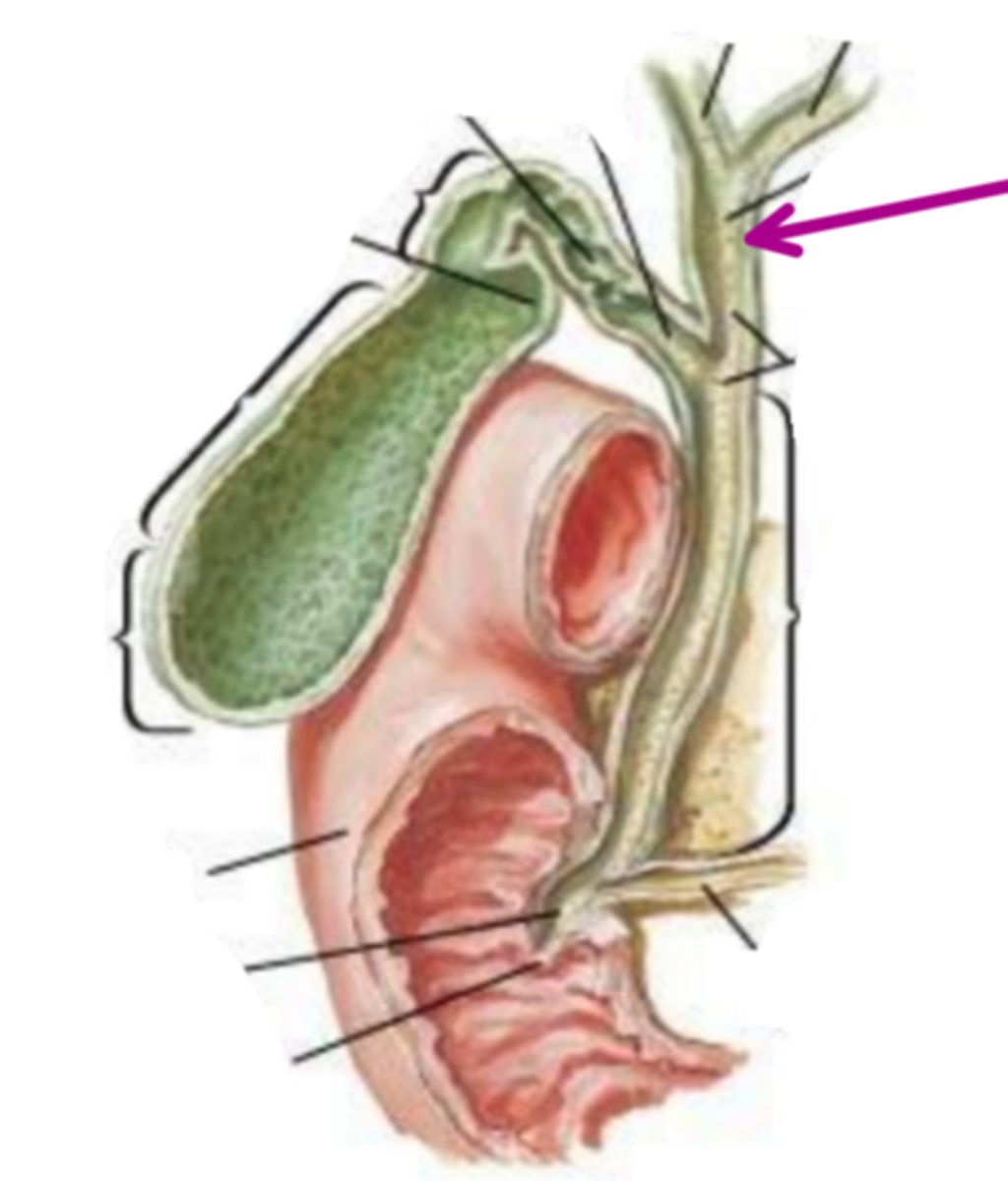
cystic duct
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
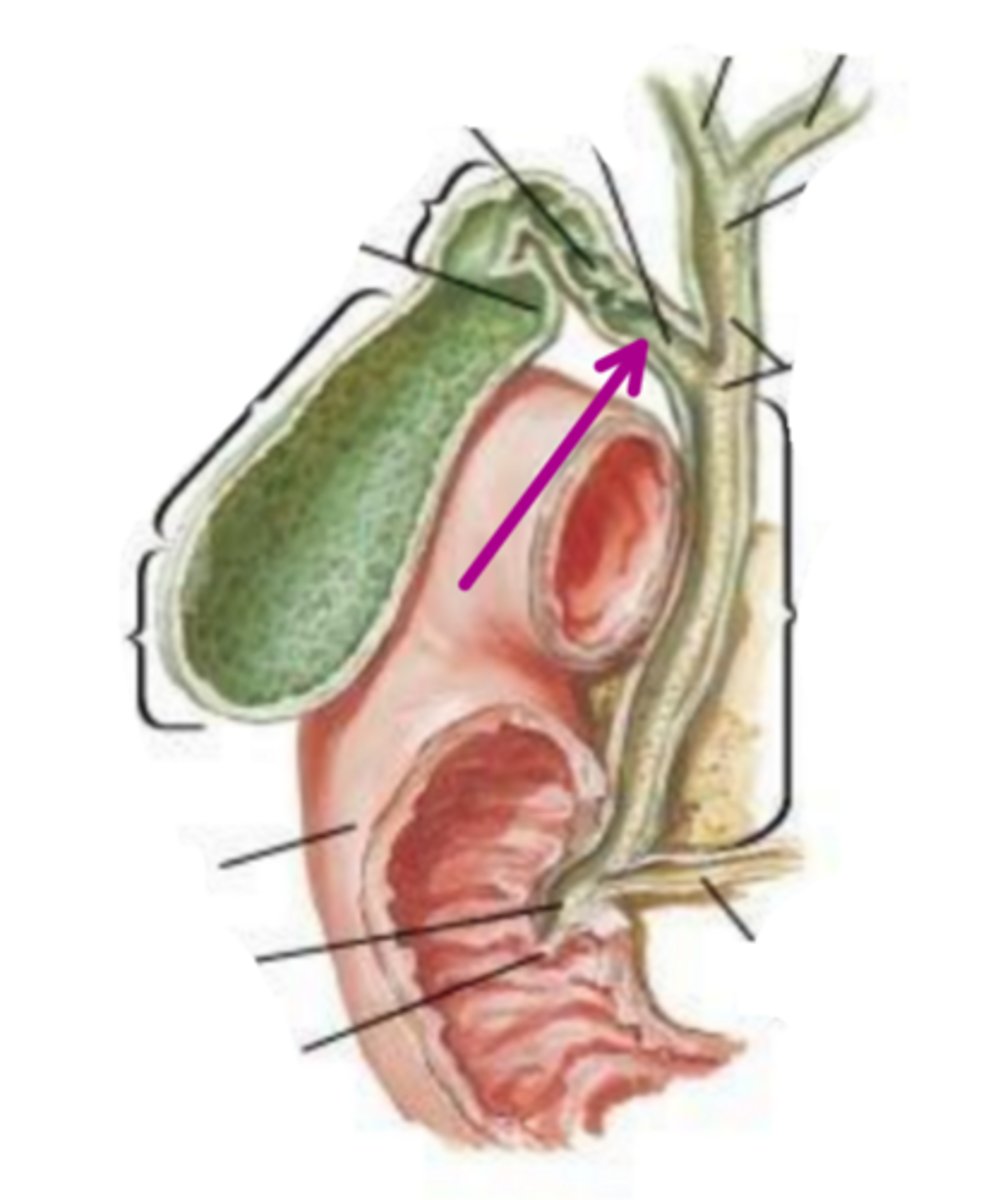
common bile duct
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
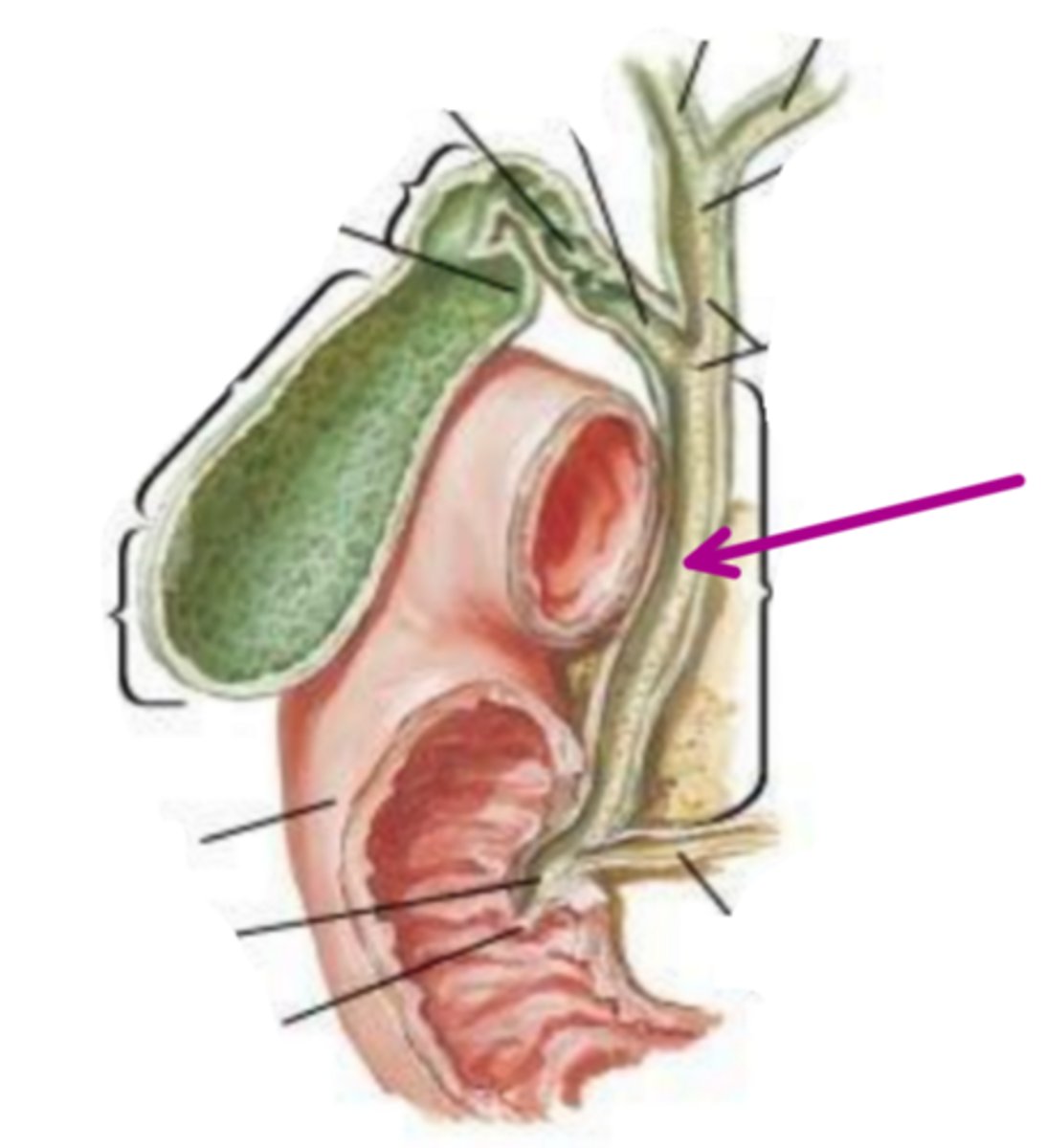
pancreatic duct
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
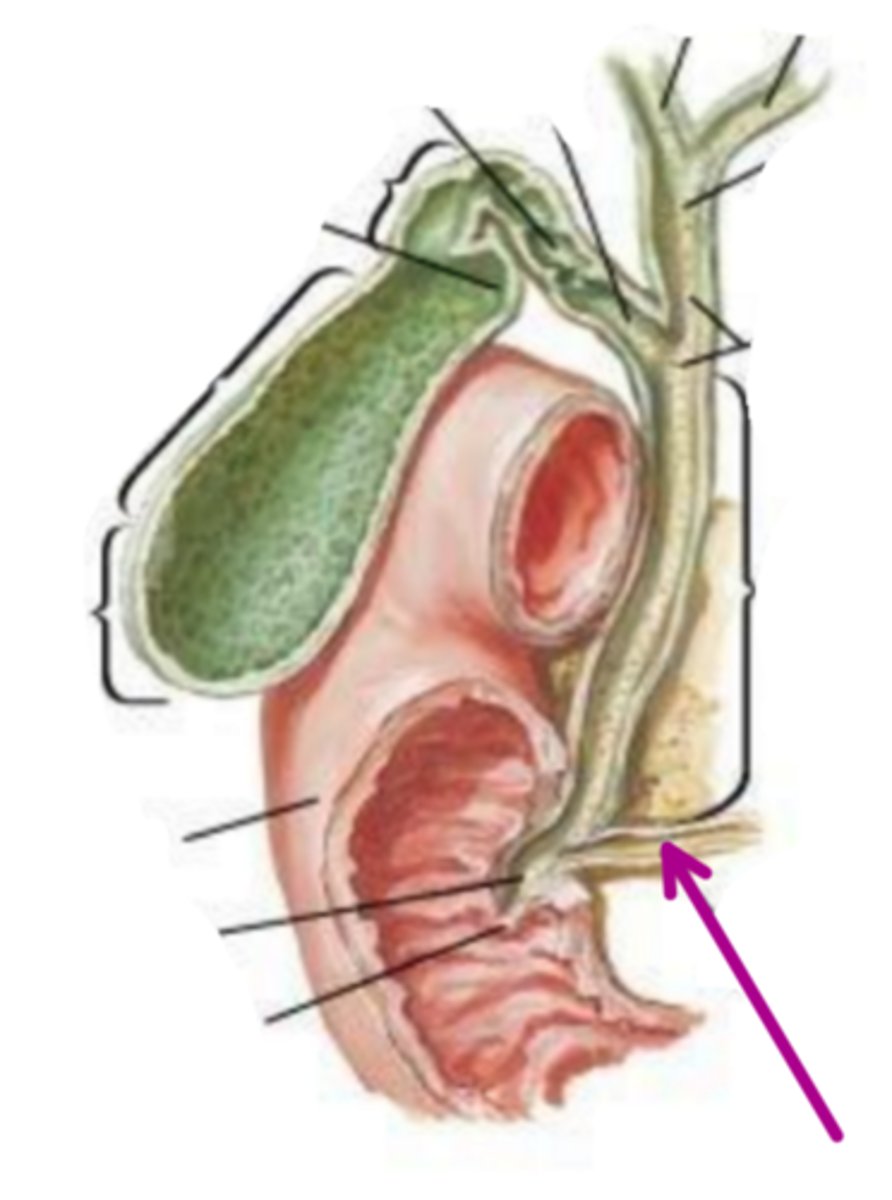
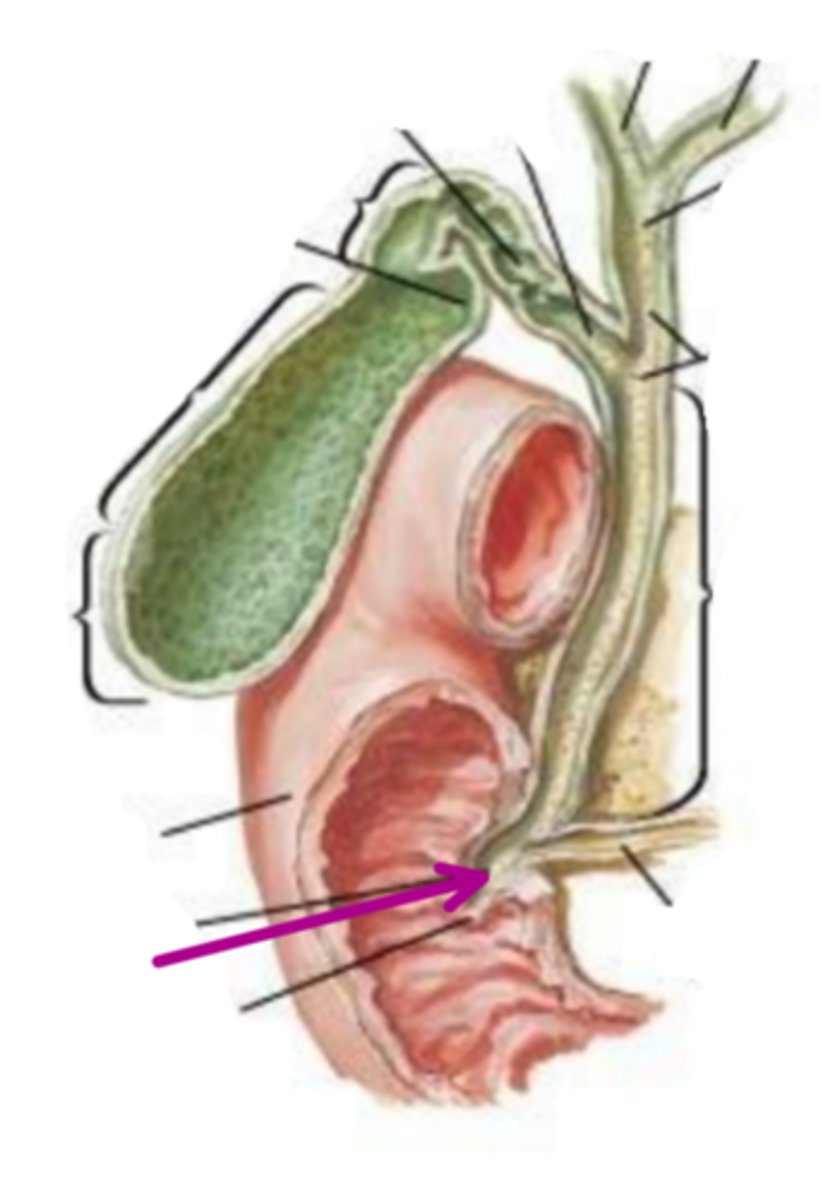
hepatopancreatic ampulla of vater
identify the structure indicated by the arrow
pharynx
structures 1, 2, & 3 form the
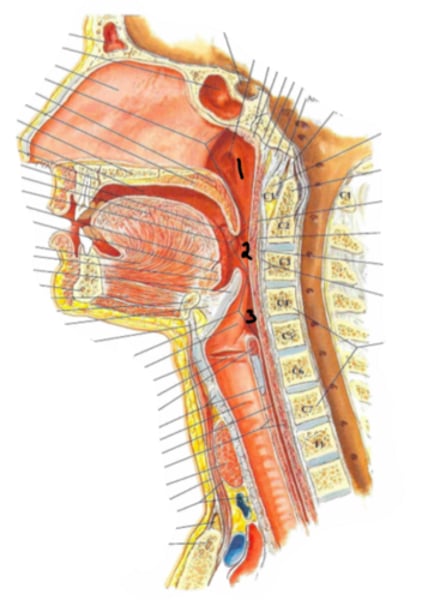
nasopharynx
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
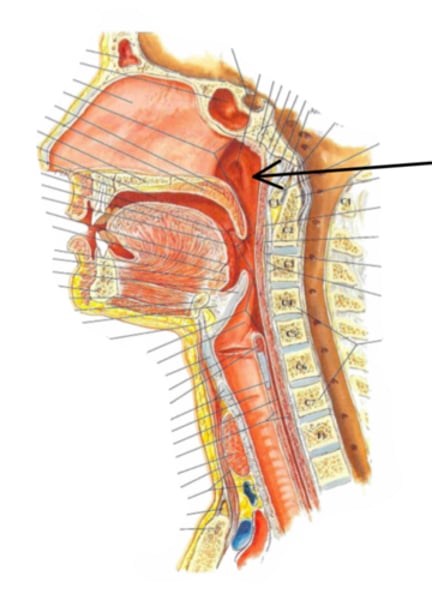
Eustachian tube
nasopharynx contains the opening for the
oropharynx
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
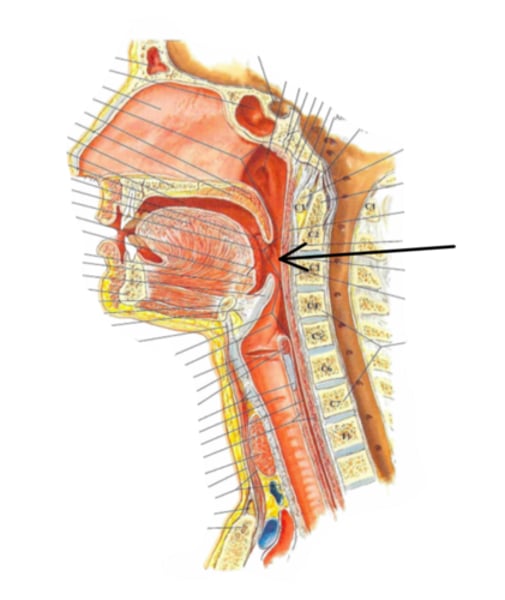
uvula
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
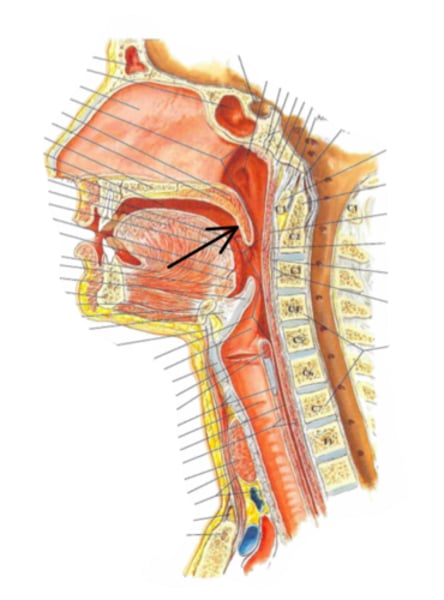
laryngopharynx
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
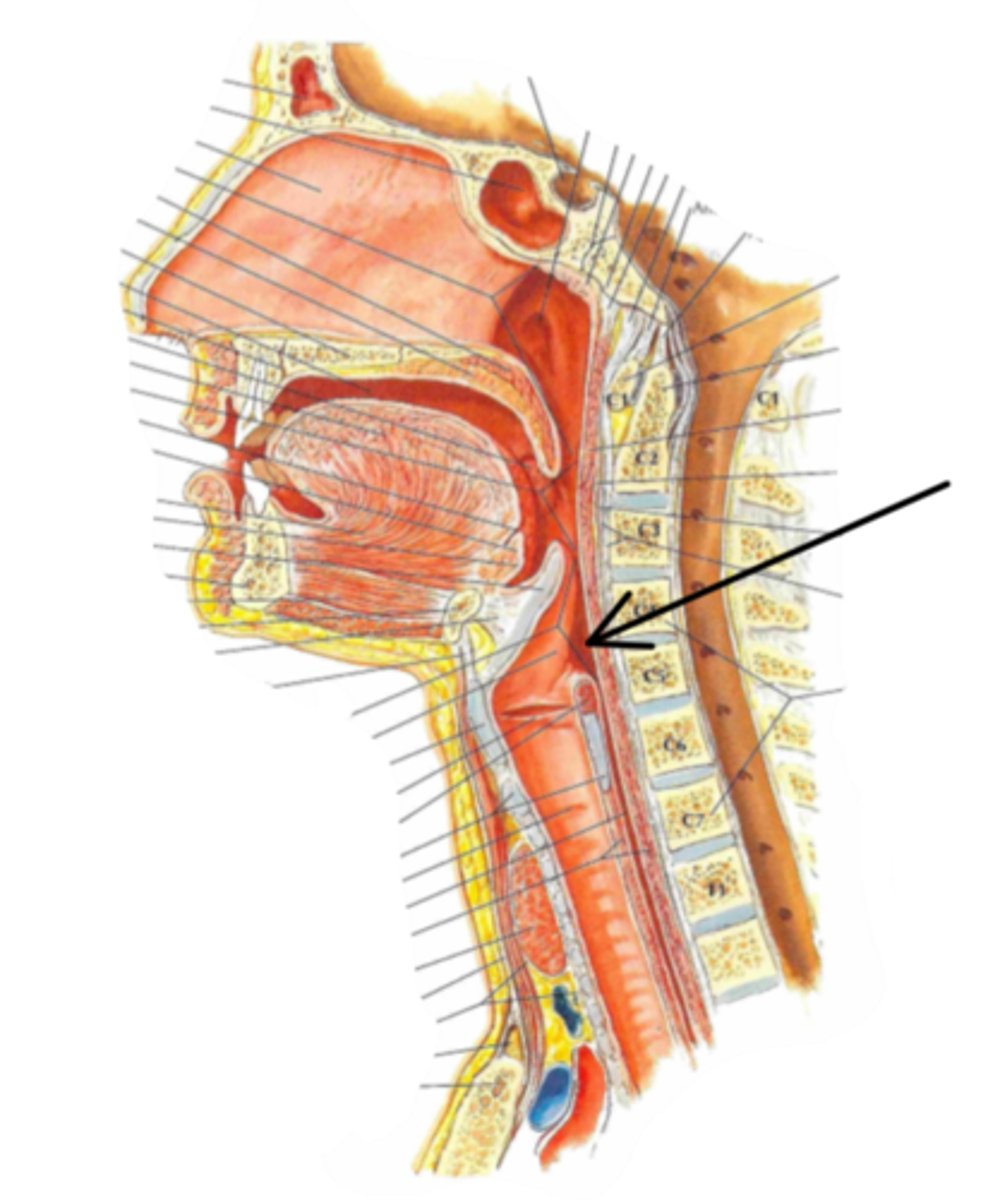
larynx
Identify the structure
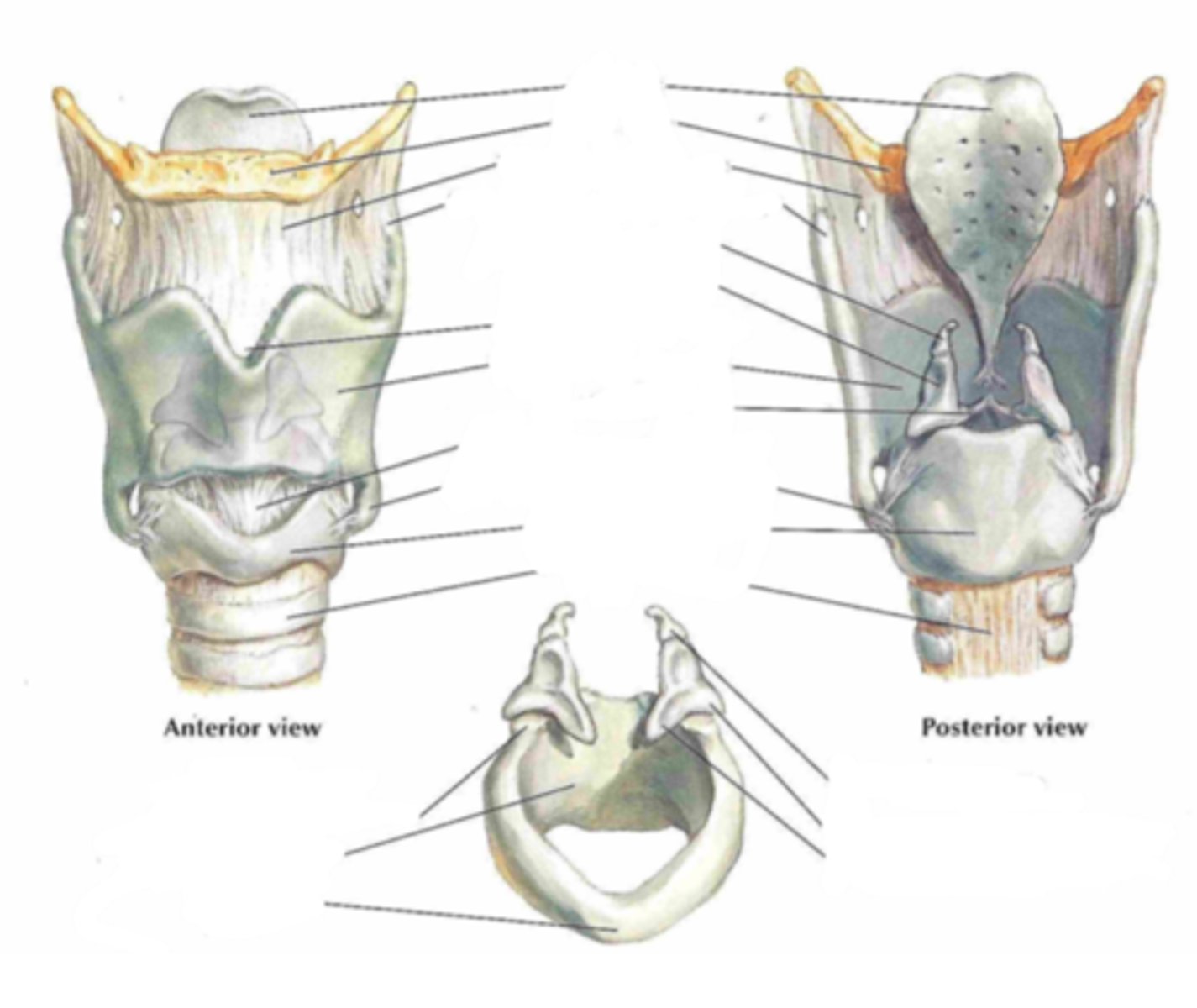
thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, epiglottic cartilage
what types of cartilage make up the larynx
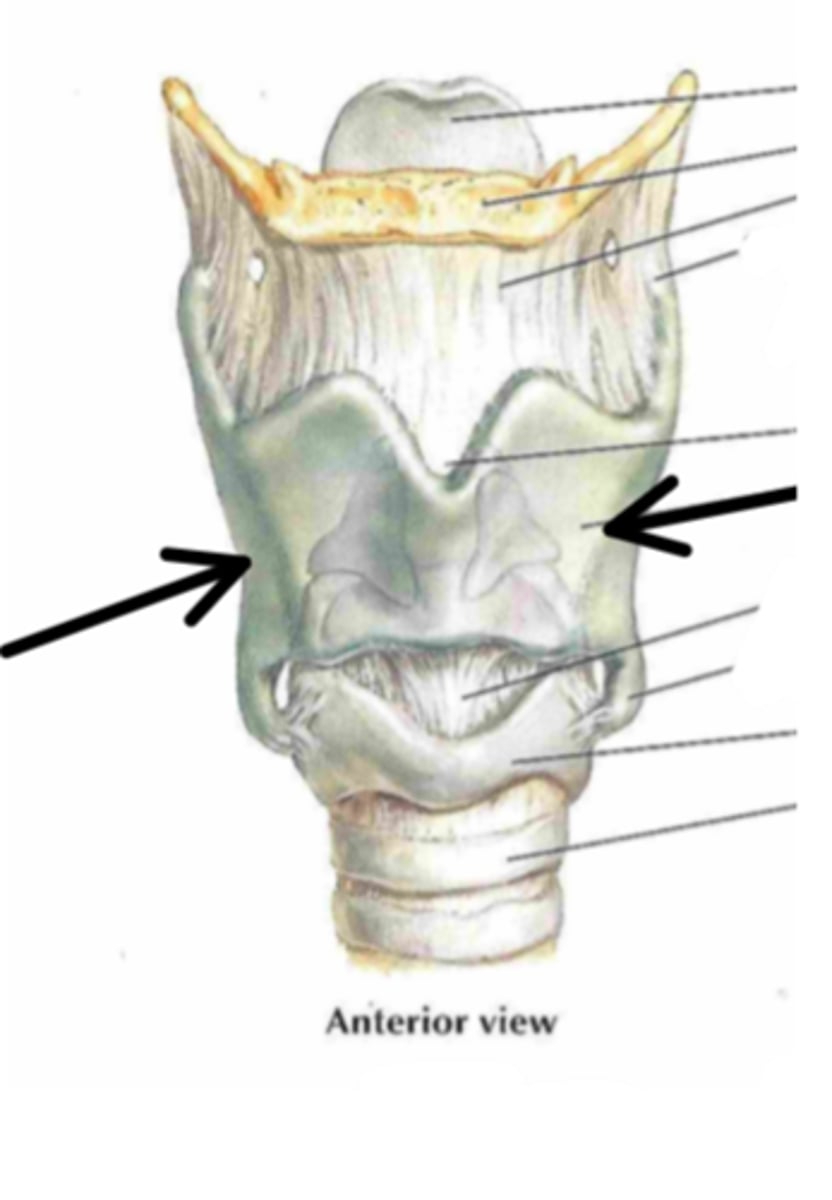
thyroid cartilage
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
cricoid cartilage
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
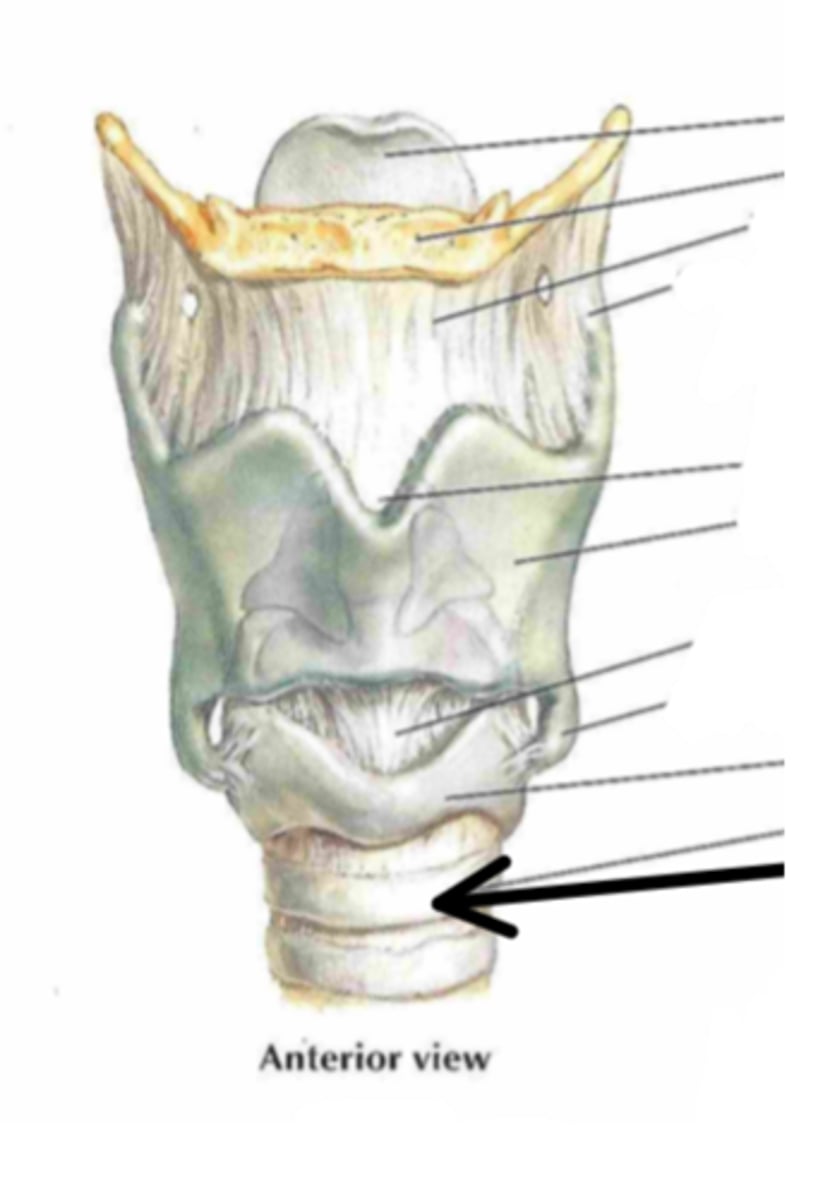
trachea
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
epiglottis
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
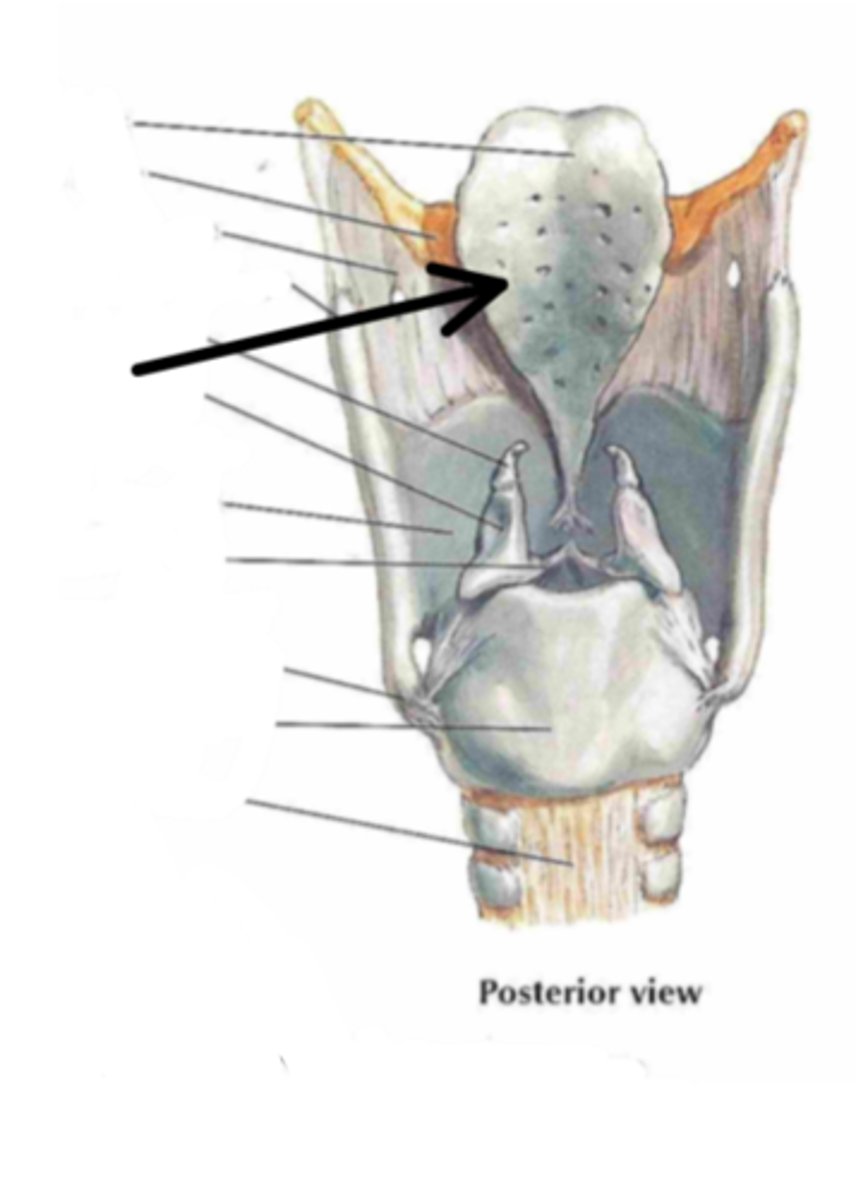
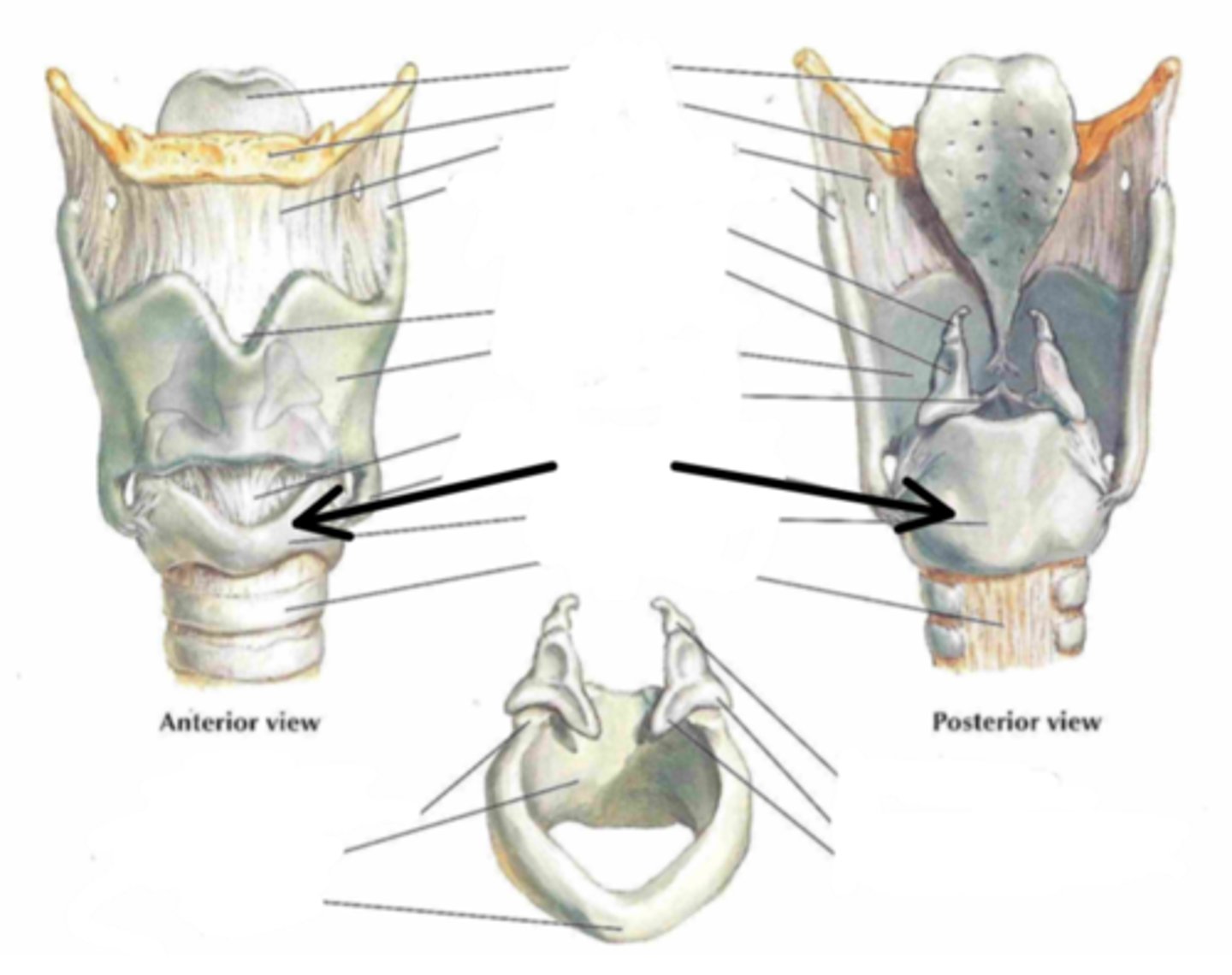
stalk of petiolus
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
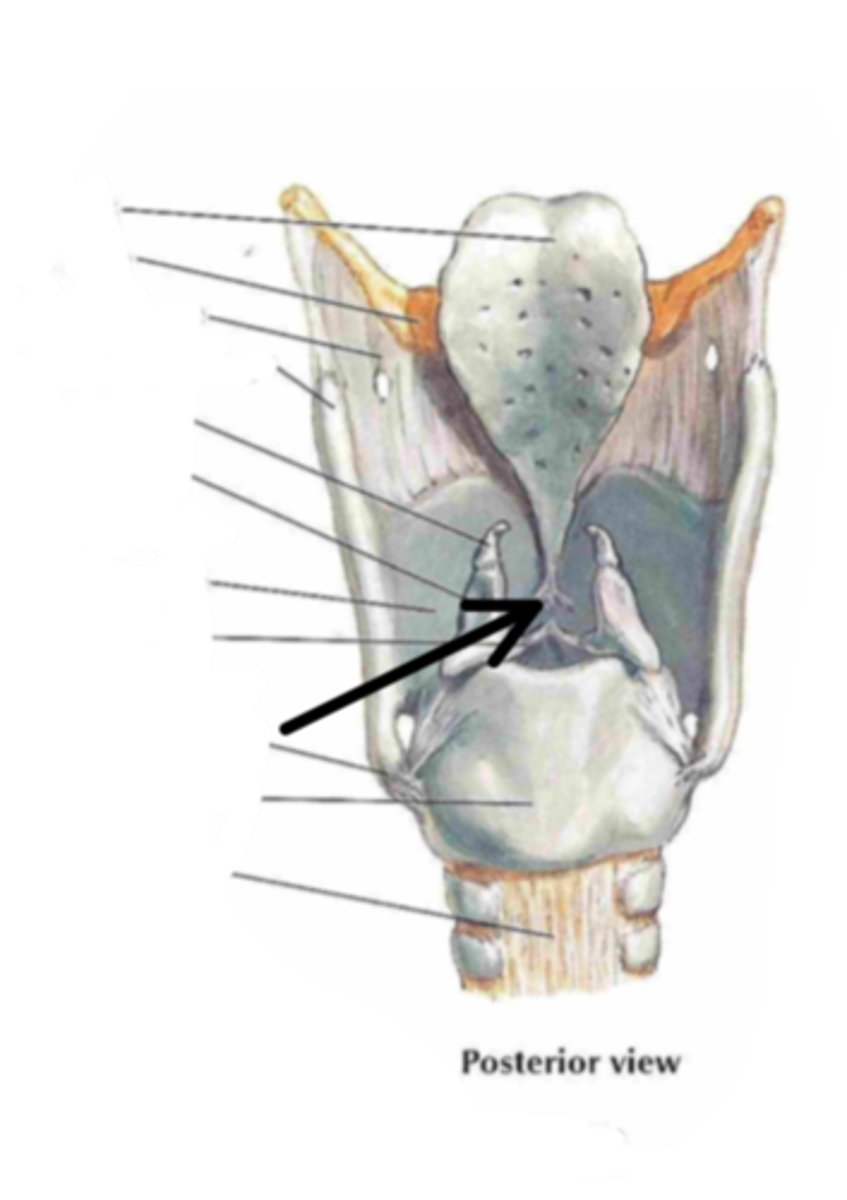
vestibular folds (false vocal cords)
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
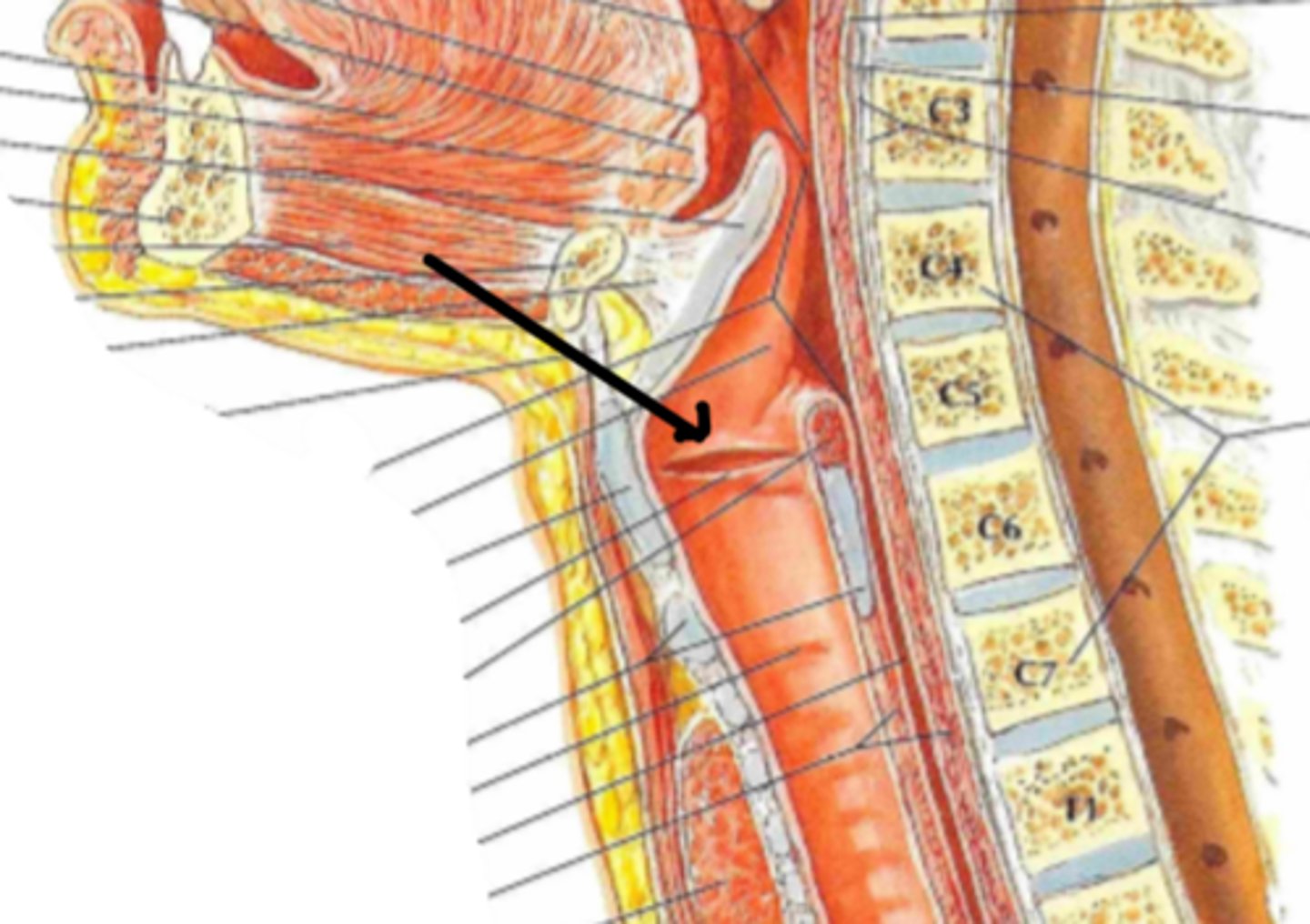
Ventricular vocal folds (true vocal cords)
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
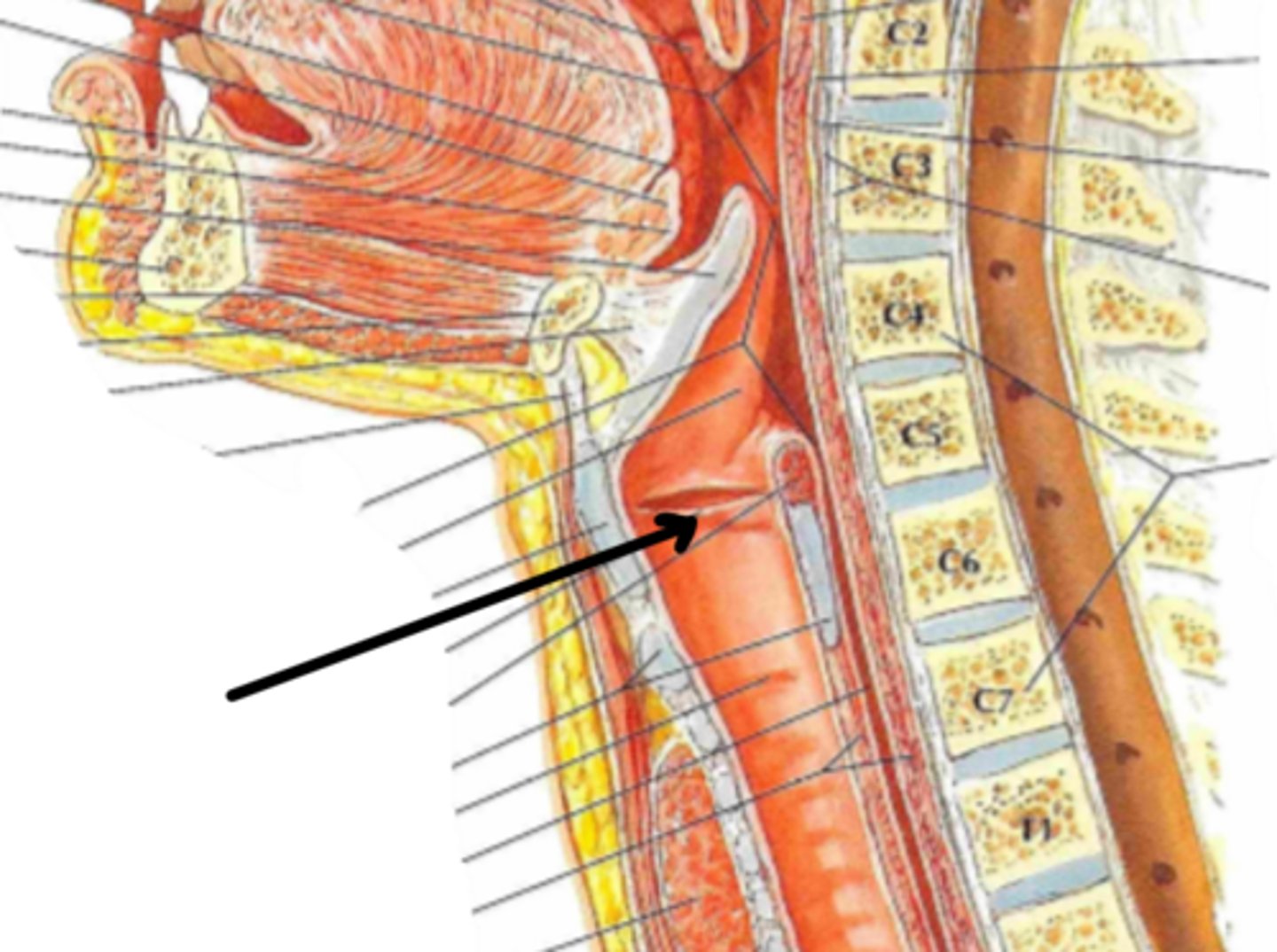
trachea
Identify the structure
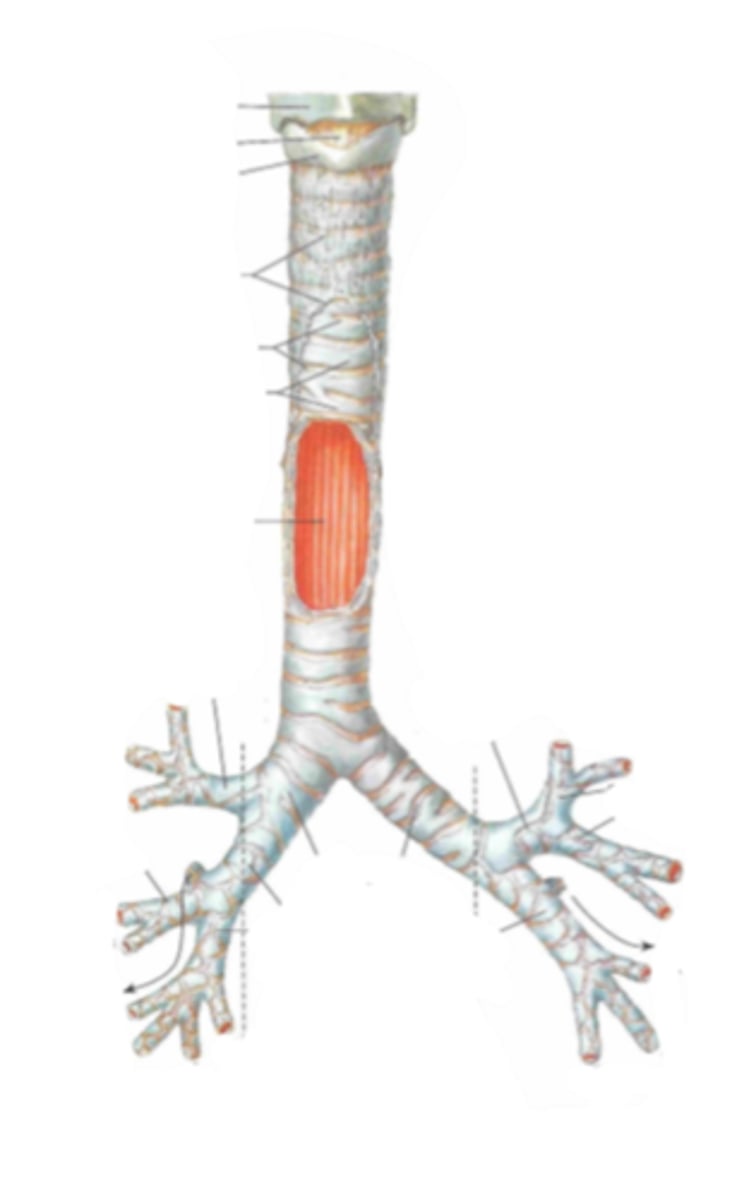
esophagus
Identify the structure
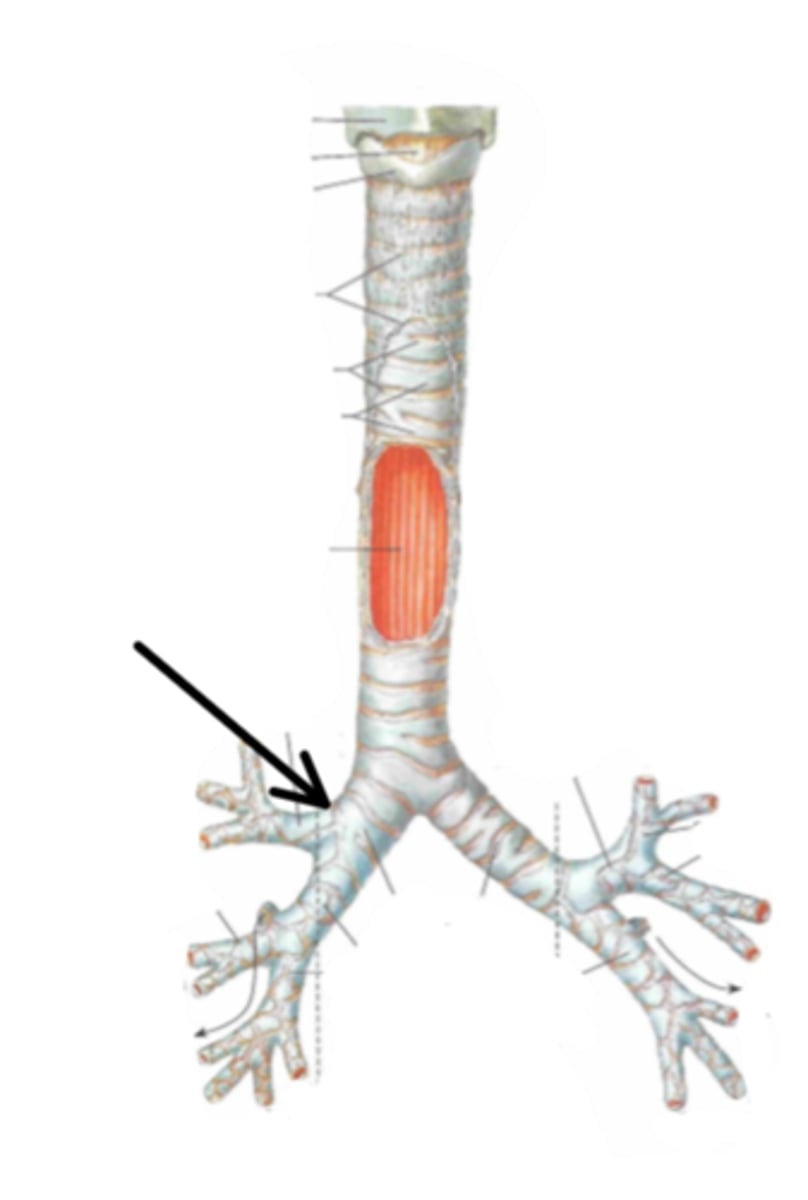
right primary bronchus
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
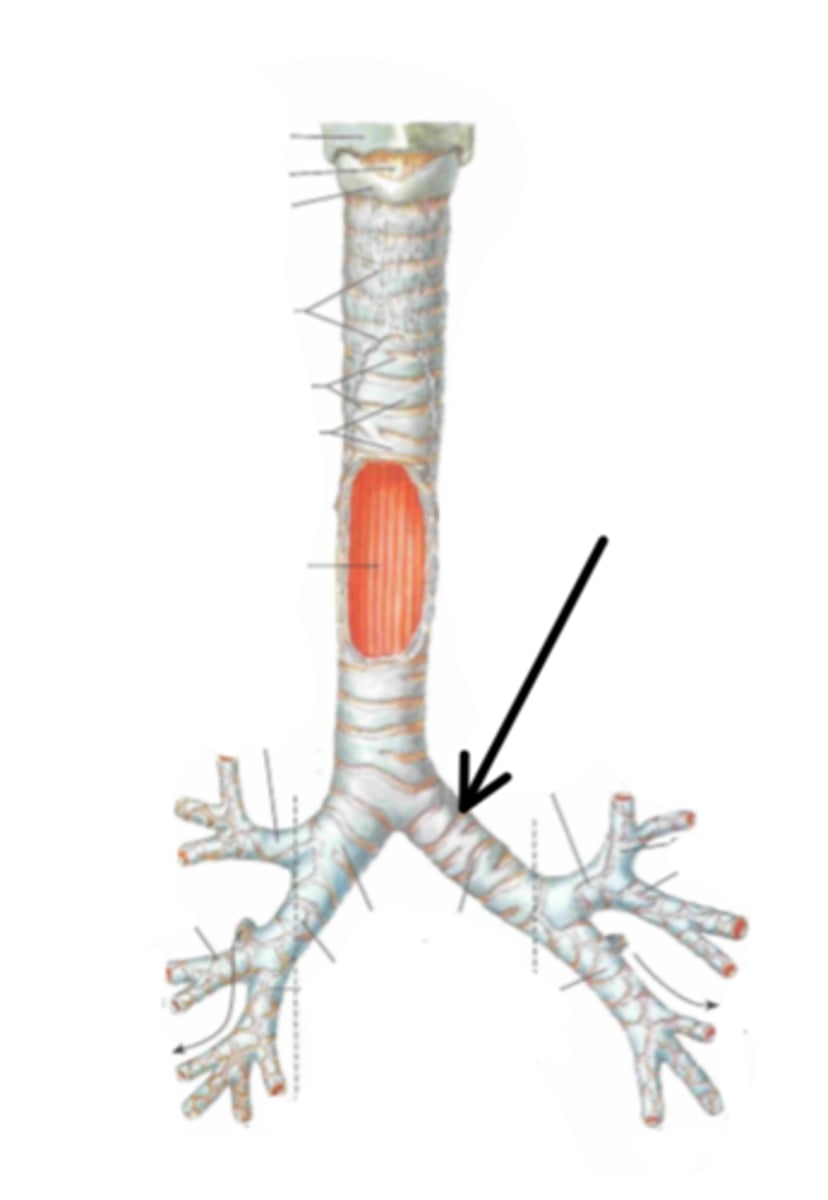
left primary bronchus
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
secondary bronchi
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
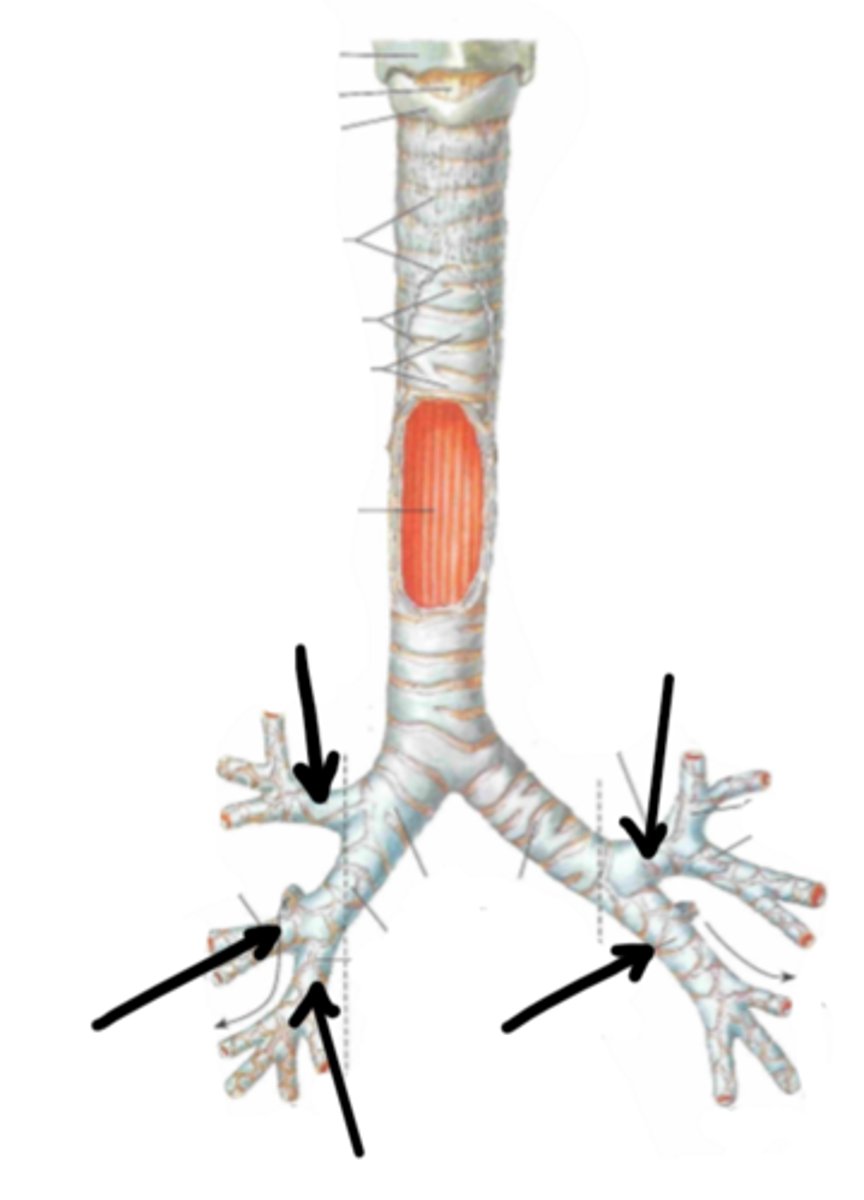
3
how many secondary bronchi does the right primary bronchus divide into?
2
how many secondary bronchi does the left primary bronchus divide into?
tertiary bronchi
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
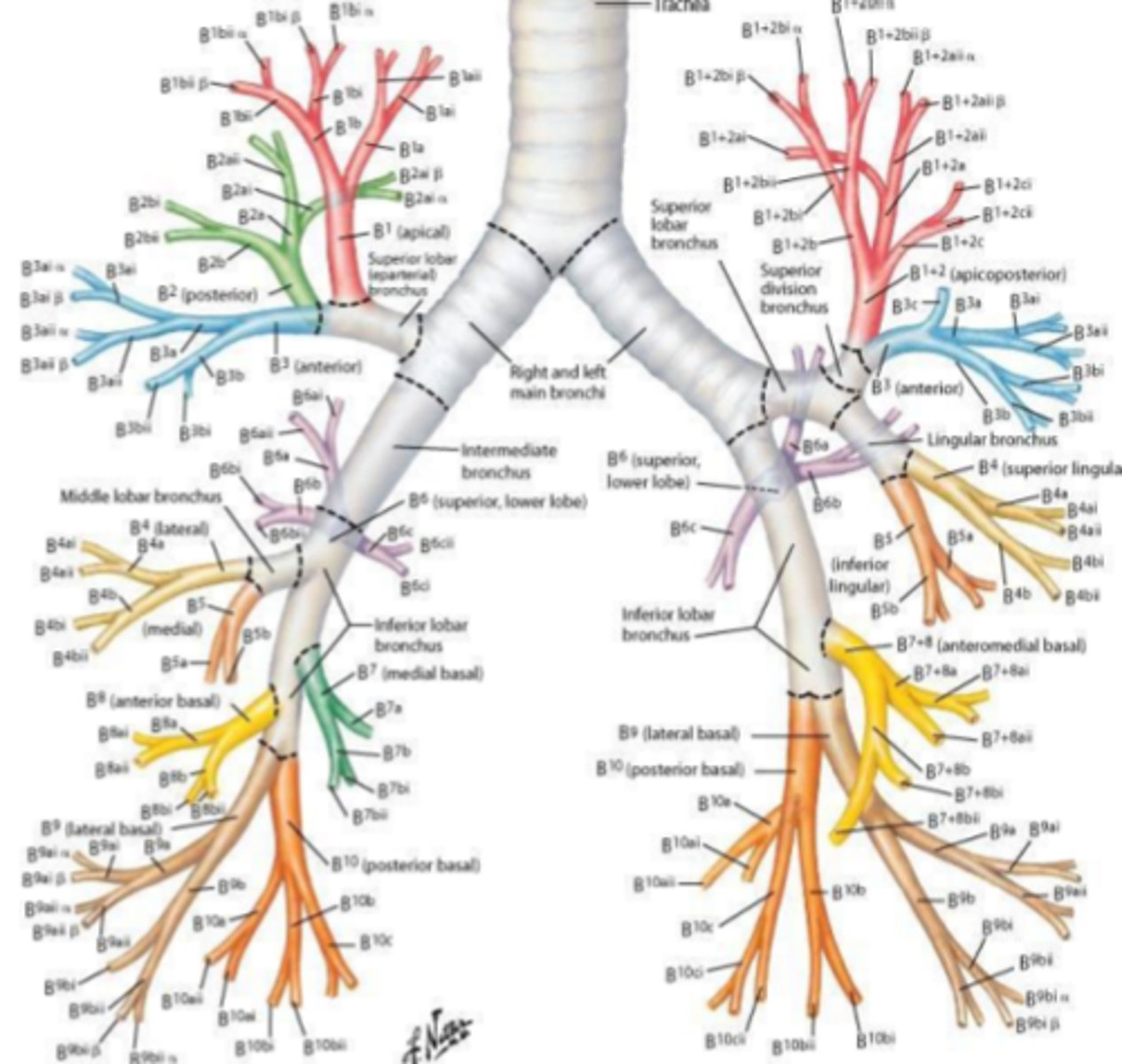
bronchopulmonary segments
tertiary bronchi supply
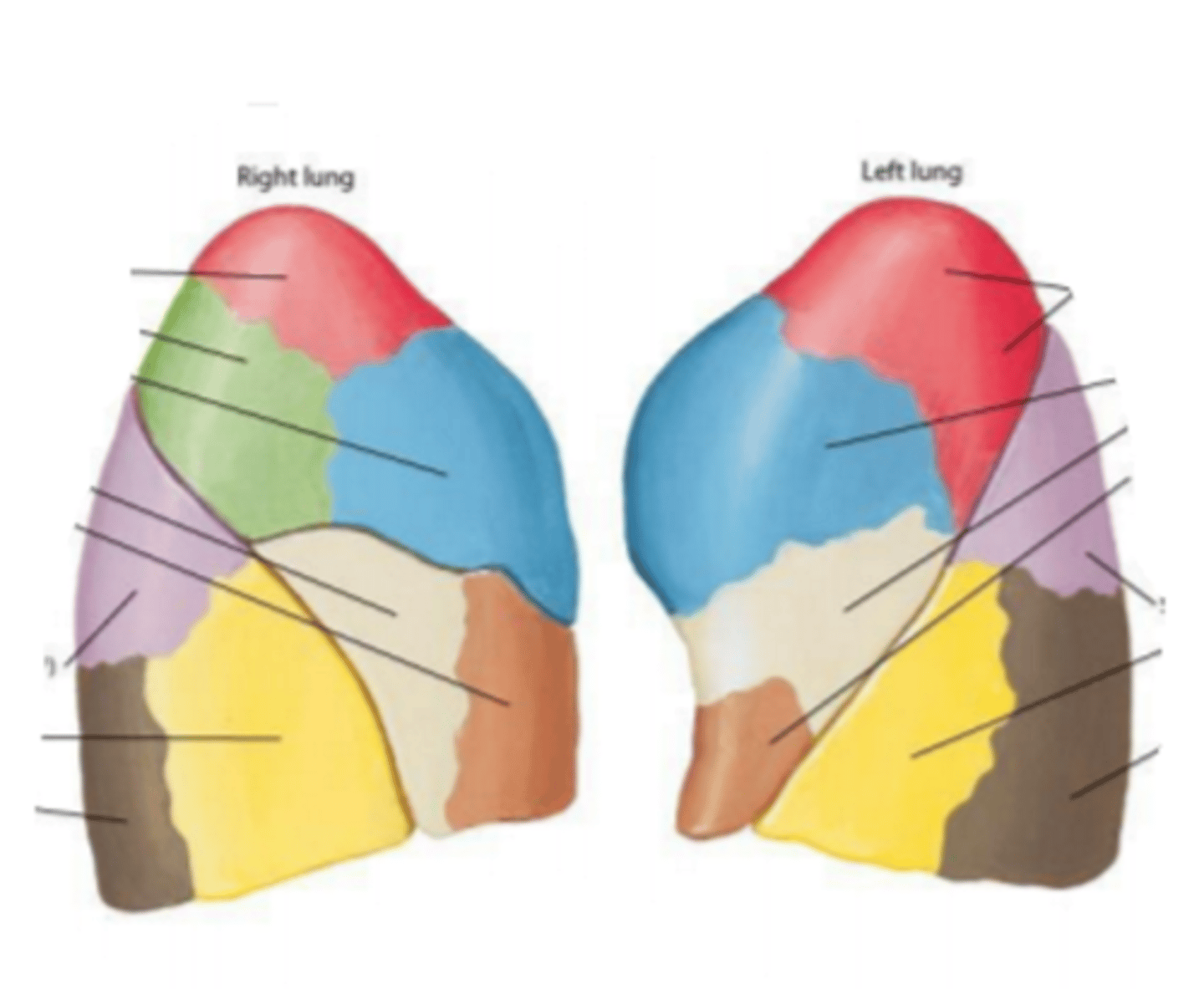
bronchopulmonary segments
Identify the structures
bronchioles
tertiary bronchi further divide into
respiratory bronchioles
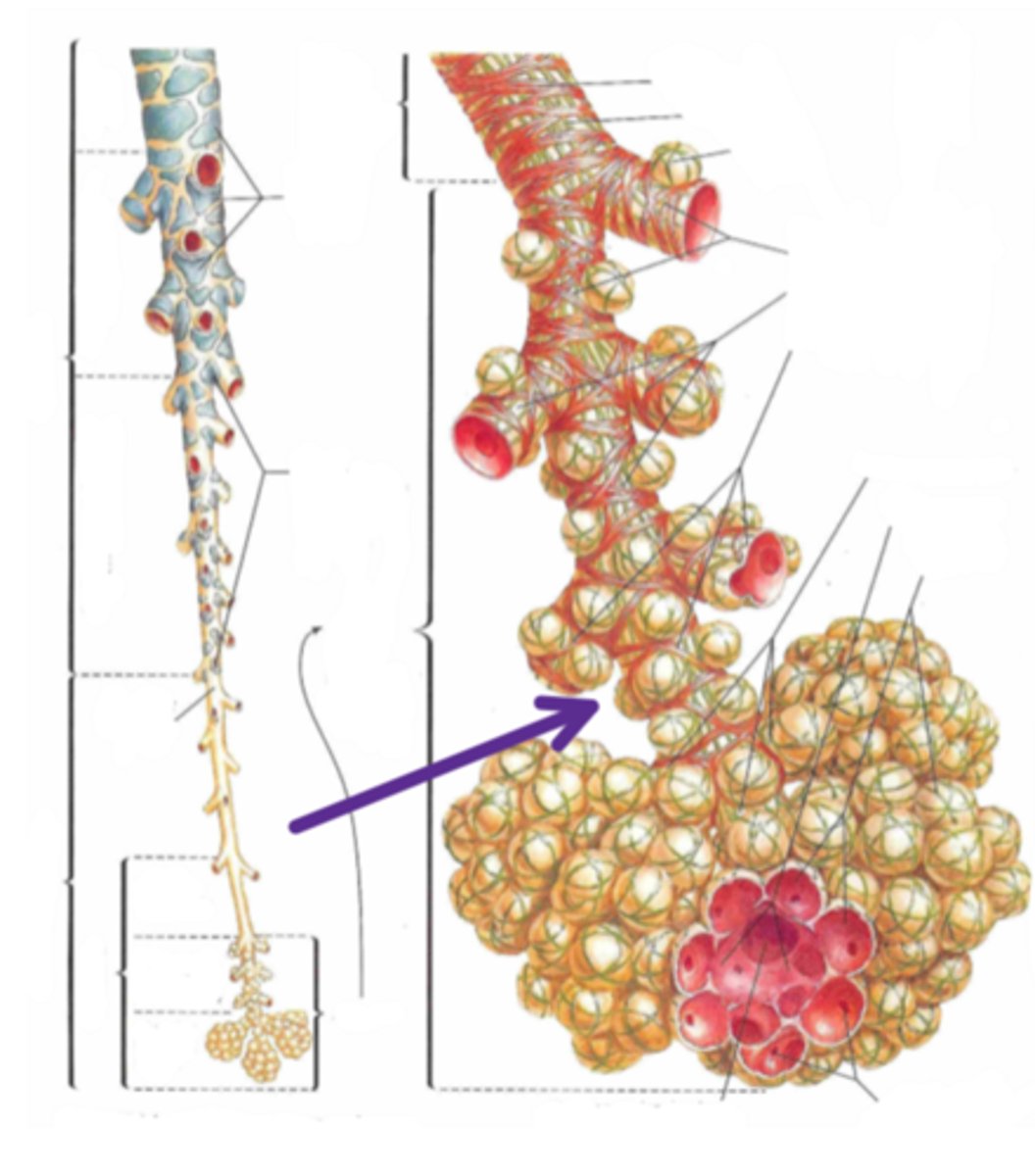
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow
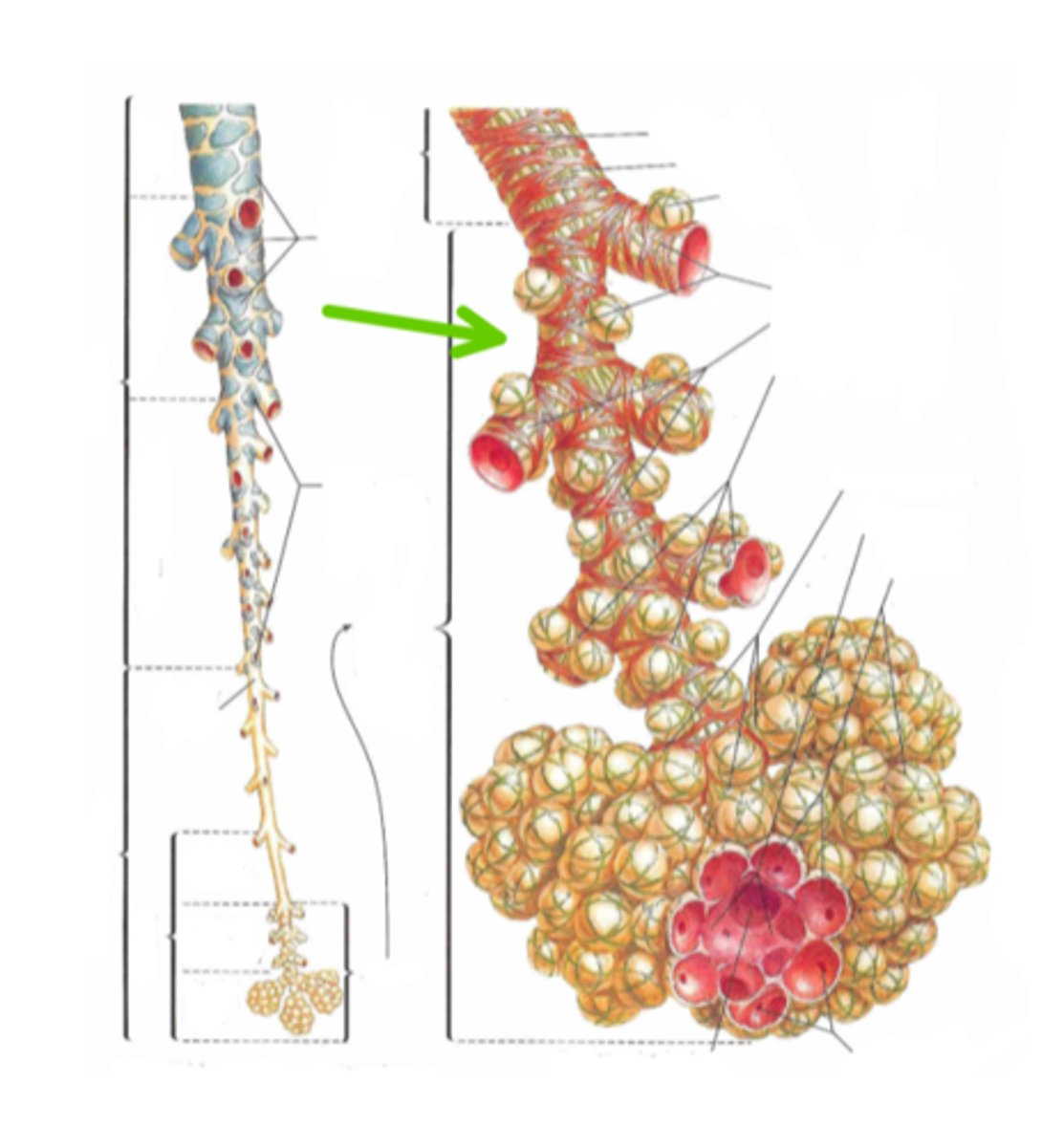
Alveoar ducts
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow