General Organic Chemistry, Reaction Mechanisms
1/147
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mostly done, may add stuff later. Suitable for JEE and IAT and whatever. I'm making flashcards for all other chapters too check them out. Anyway, Question Mode: Flashcards only. Answer Mode: Answer with Definition. Enjoy!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
What are the two types of bond fission?
Homolytic fission
Heterolytic fission
What are usually the conditions for homolytic fission of a bond?
Both bond participants have almost the same electronegativity.
What can you add to a reaction to make C-H homolytic fission?
sunlight
What are the properties of the particle formed after homolytic fission? (2 things)
free radicals
electron deficient
What is usually the condition for heterolytic fission?
There is a large difference in electronegativities of the particles participating in the bond.
What are the two types of reagents in a reaction?
Electrophiles
Nucleophiles
What is the identifying property of an electrophile?
It is electon-deficient.
What is the identifying property of a nucleophile?
It is electron-rich.
Is H^+ a nucleophile or electrophile?
Electrophile
Is CCl_2 a nucleophile or electrophile?
Elecrophile, the central C atom has an incomplete octet.
Is CN^- a nucleophile or electrophile?
Nucleophile.
Is H_2O a nucleophile or electrophile?
Nucleophile.
What are the three types of reaction intermediates (for carbon) in organic reactions?
Carbocation
Carbon free radical
Carbanion
What is the hybridization of a carbocation?
sp²
What is the hybridization of a carbon free radical?
sp²
What is the hybridization of a carbanion?
sp³
What is the magnetic nature of a carbocation?
Diamagnetic
What is the magnetic nature of a carbon free radical?
Paramagnetic
What is the magnetic nature of a carbanion?
Diamagnetic
Label these as electron deficient or electron rich:
carbocation
carbon free radical
carbanion
carbocation — electron deficient
carbon free radical — electron deficient
carbanion — electron rich
Which carbon reaction intermediate is a Lewis acid?
Carbocation
Which carbon intermediate is a Lewis base?
Carbanion.
What are the four electron displacement effects?
Inductive effect
Electromeric effect
Mesomeric effect
Hyperconjugation
Which electrons are displaced by the Inductive effect, and is it permanent?
\sigma electrons are displaced, and it is permanent.
Which electrons are displaced by the electromeric effect, and is it permanent?
\pi electrons are displaced, and it is temporary.
Which electrons are displaced by the mesomeric effect, and is it permanent?
\pi electrons are displaced, and it is permanent.
Which electrons are displaced by Hyperconjugation, and is it permanent?
\sigma electrons are displaced, and it is permanent.
What is the main cause of Inductive effect?
Difference in electronegativity of attached groups.
order from most electronegative to lease electronegative
sp³, sp, sp²
sp>sp²>sp³
Till how many carbons in the chain is inductive effect significant?
applicable up to 3rd carbon, negligible from 4th carbon
What are the two types of inductive effect?
Electron releasing effect (+I)
Electron withdrawing effect (-I)
What sort of groups provide +I effect?
groups with less electronegativity compared to carbon
What sort of groups provide -I effect?
groups with more electronegativity
How do +I and +M groups affect stability of carbocations?
They help stability
How do -I and -M groups affect stability of carbocations?
They make less stable
is -CH_3 a +I group or -I group?
+I
How do +I and +M groups affect stability of carbon free radicals?
they help stability
How do -I and -M groups affect stability of carbon free radicals?
they make less stable
How do -I and -M groups affect stability of carbanions?
they make more stable
How do +I and +M groups affect stability of carbanions?
they make less stable
When does hydride shifting happen?
When it increases the stability of a first degree or second degree carbocation.
When does methyl shifting happen?
When there is a first degree carbocation attached to a carbon with no -H but a -CH_3 group.
Which degree of carbocation is most stable?
third degree
Which degree of carbanion is most stable?
first degree
How do -I and -M groups affect acidic strength of a molecule?
it increases the stability of the conjugate base so it increases acidic strength.
How do +I and +M groups affect acidic strength of a molecule?
It decreases the stability of the conjugate base so it decreases the acidic strength.
How do -I groups affect basic strength of a molecule?
It decreases the negative charge (tendency to accept H^+) so it decreases the basic strength.
How do +I groups affect basic strength of a molecule?
It increases the negative charge (tendency to accept H^+) so it increases the basic strength.
What is the main cause of Electromeric Effect?
Presence of a Reagent. (Van der Waals’ forces)
What type of reagent causes positive Electromeric Effect? (+E)?
Electrophiles
What type of reagent causes negative Electromeric Effect? (-E)?
Nucleophiles
What sort of charge on the adjacent carbon does Positive Electromeric Effect (+E) create?
Positive
What sort of charge on the adjacent carbon does Negative Electromeric Effect (-E) create?
Negative
What is the characteristic of Electrophilic addition reaction?
Electrophile attacks first
What is the characteristic of Nucleophilic addition reaction?
Nucleophile attacks first
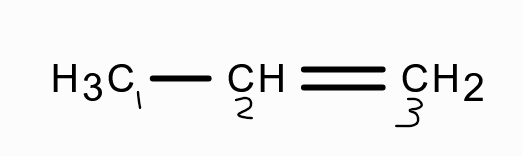
In the presence of a reagent, the \pi electrons in the double bond shift towards one carbon. Which carbon do they shift to?
third carbon
What is the main cause of resonance effect?
To increase stability of the compound (the hybrid structure is more stable than the resonating structures).
What are the conditions for resonance to occur in a compound? (2 things)
planarity: molecule must be planar, all atoms must be either sp² or sp hybridised
conjugation: molecule must have a conjugated system
What is +M effect?
Electron Releasing Effect due to Resonance
What is -M effect?
Electron Withdrawing Effect due to Resonance
When considering the stability of an organic structure, what should you consider and in which order? (3 things)
Resonance
Hyperconjugation
Inductive effect
What is the structure of triplet carbene?
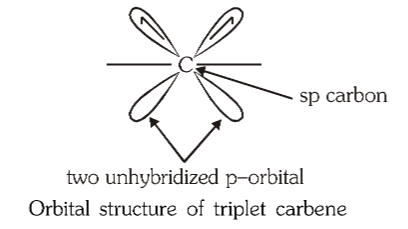
Would carbene be a nucleophilic reagent or electrophilic reagent?
electrophilic reagent
What is the hybridisation of triplet carbene?
sp
What is the structure of singlet carbene?
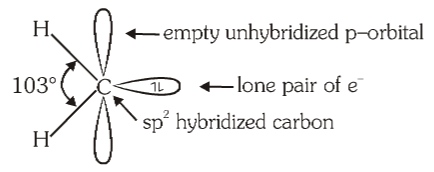
What is the hybridisation of singlet carbene?
sp²
Singlet carbene is ________
Triplet carbene is ________
(paramagnetic, diamagnetic)
Singlet carbene is diamagnetic.
Triplet carbene is paramagnetic.
What is the general structure of nitrene?

A Lewis acid is a _________
(nucleophile, electrophile)
electrophile
A Lewis base is a _________
(nucleophile, electrophile)
nucleophile
A species that possesses an empty orbital is a _______
(nucleophile, electrophile)
electrophile
A species that possesses a lone pair that is loosely held is a ________
(nucleophile, electrophile)
nucleophile
A species that attacks the points of high electron density is __________
(nucleophile, electrophile)
electrophile
A species that attacks the points of low electron density is _________
(nucleophile, electrophile)
nucleophile
What is resonance energy really?
The difference between the experimental and calculated energies (heat of hydrogenation) of resonating compounds
Why is aniline less basic than ammonia?
Because aniline is stabilized by resonance and negative charges / electron pairs stabilized by resonance mean decreases basicity
At which positions does a -I or +I effect act from on benzene?
ortho, meta, para
At which positions does a -M or +M effect act from on benzene?
ortho and para
At which positions does a +H or -H effect act from on benzene?
ortho and para
Which resonating structures are more stable, polar or non-polar?
non-polar
In polar resonating structures, which is more stable, complete octet or incomplete octet?
complete octet
What really is hyperconjugation effect?
delocalization of sigma electrons
What are the conditions for hyperconjugation? (structure)
The sigma bonds (usually C-H or C-C) must be in conjugation with a couple bond, carbocation, or carbon free radical.
How does H effect affect the stabiltity of a carbocation or carbon free radical?
increases the stability
How does H effect affect the stability of a carbanion?
decreases the stability
How does H effect affect the stability of a double bond?
increases the stability.

remember the difference between geminal and viscinal, trans and cis, okay?
okay c:
What is the characteristic reaction of alkanes?
Free radical substitution
What is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes?
Electrophilic addition reaction
What is the characteristic reaction of alkyl halides?
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
What is the characteristic reaction of aldehydes and ketones?
Nucleophilic addition reaction
What is the characteristic reaction of carboxylic acid and derivatives?
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
What is the characteristic reaction of aromatic compounds?
Electrophilic substitution.
In positive Electromeric effect, which carbon do the \pi bonds shift towards?
The carbon where the reagent attacks
In negative Electromeric effect, which carbon do the \pi bonds shift towards?
The carbon where the reagent does not attack (so generally the carbon adjacent to that)
What are the three steps of the mechanism of Free Radical Substitution Reactions?
Chain initiation step
Chain propagation step
Chain termination step
What happens in the Chain initiation step of free radical substitution reactions?
Homolytic fission of some of the the reagent / reactants
What happens in the Chain Propagation step of free radical substitution reactions?
Sort of like that.
The free radicals formed thus react with other non-fissioned reactant molecules in simple substitution reactions, leaving still free radicals at the end
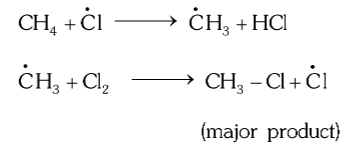
What happens in Chain Termination step of free radical substitution reactions?
All remainin free radicals react with each other to form complete compounds and thus no intermediates (free radicals) are left at the end of it
What are the steps of the mechanism of Electrophilic Substitution reactions? (there are 3)
Formation of Electrophile
Attack of Electrophile
Removal of positive group (usually H^+)