A2 Unit 4.2 Aromaticity
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
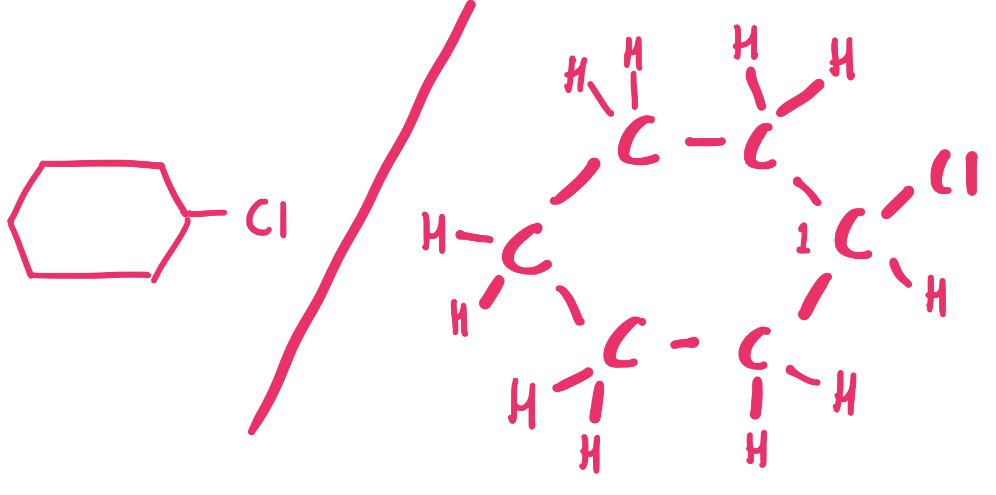
What does the structure of 1-chlorocyclohexane look like?
What are Alkanes, Alkenes & Alkynes?
Alkane - Hydrocarbon with only single bonds e.g Pentane
Alkene - Hydrocarbon with a double bond e.g Pentene
Alkyne - Hydrocarbon with a triple bond e.g Pentyne
What is an Arene?
Arenes are a type of hydrocarbon.
Arene - Any organic compound with a benzene ring attached (Aromatic) e.g 3-phenyl pentane
What is an Aliphatic hydrocarbon?
Aliphatic - Any organic compound without a benzene ring attached to it, but could be cyclic e.g hexane, cyclohexane, hexene or cyclohexene (straight chain)
What is an Aryl?
Aryl - An adjective used to describe an organic compound with a functional group attached directly to a benzene ring e.g Aryl chloride

What is an Alkyl?
Alkyl - An adjective used to describe a functional group not directly joined to a benzene ring e.g 1-chloro-2-phenyl ethane
Benzene side chain = Phenyl
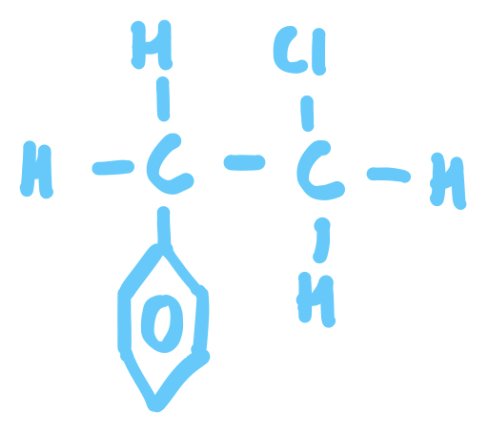
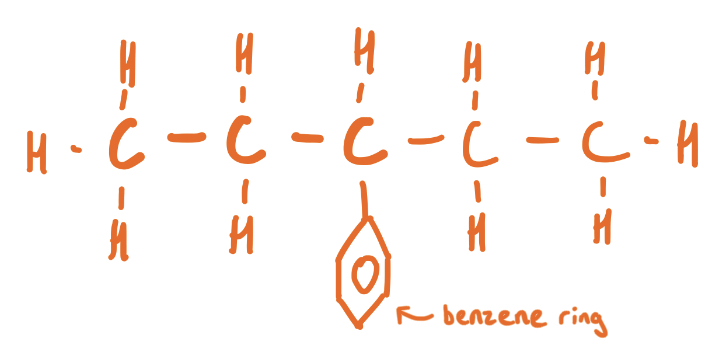
Naming Carbonyl Organic Compounds - Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic acids

Naming Esters

Acyl chloride
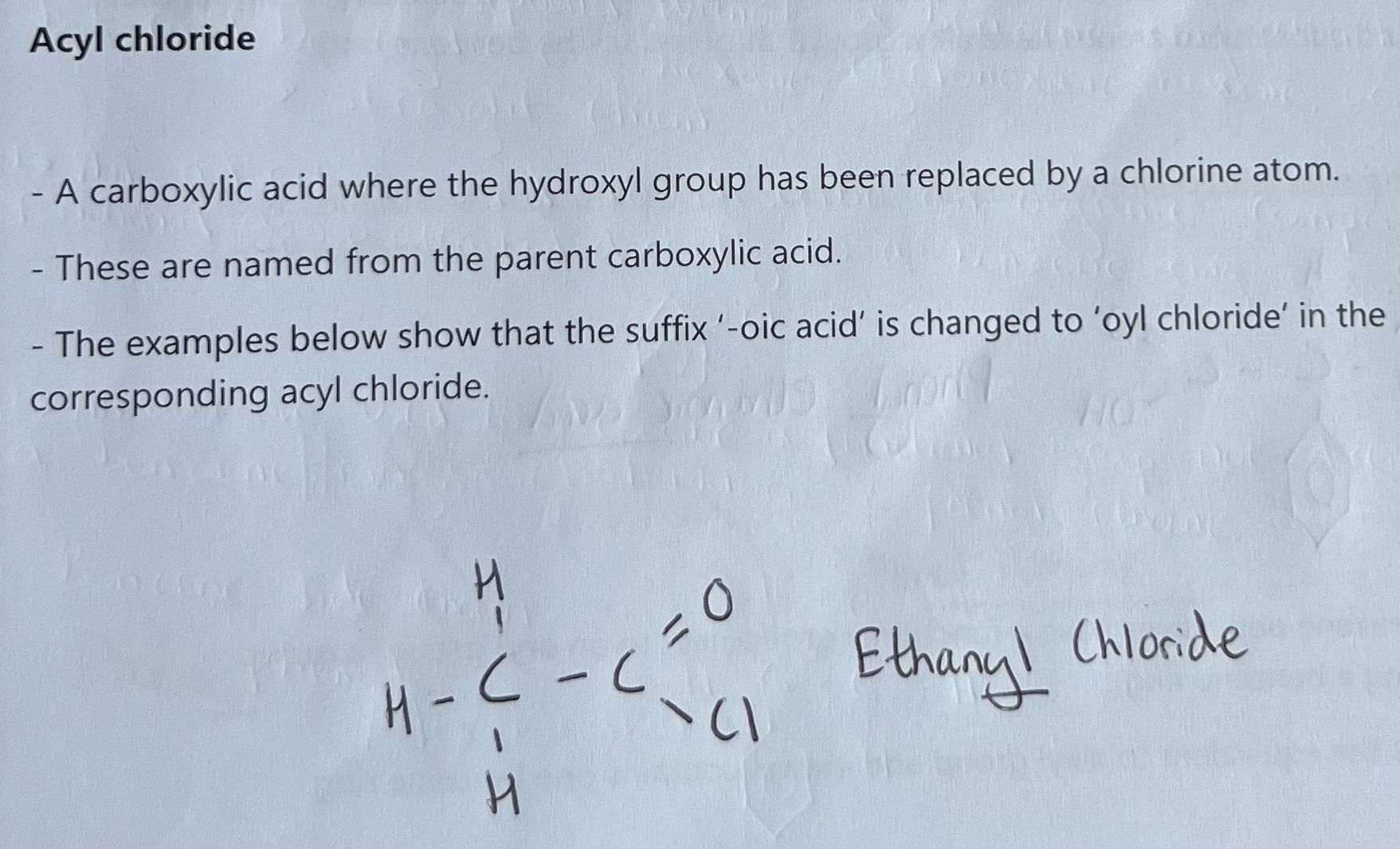
Aromatic Organic Compounds - Benzene
An aryl group is often represented as Ar-
The simplest aryl group is the phenyl group, C6H5, derived from benzene, C6H6
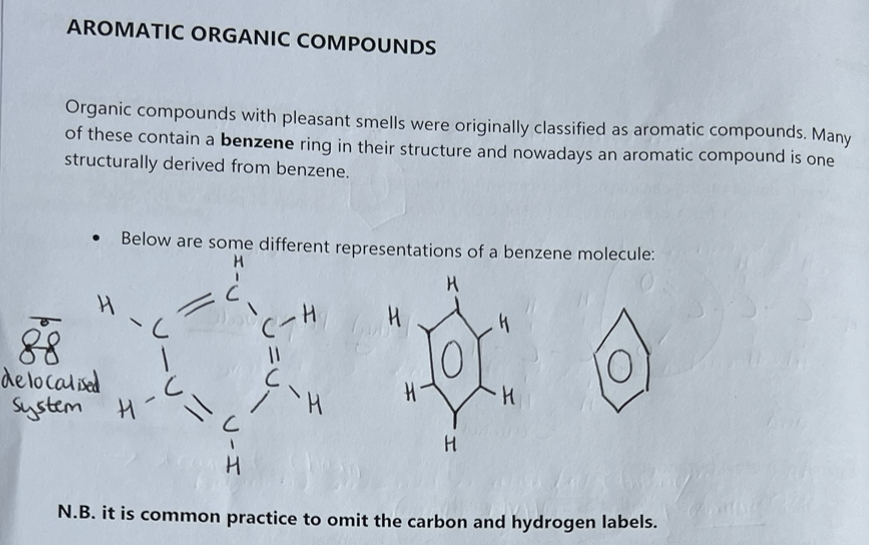
Arenes
An aryl group is often represented as Ar-
The simplest aryl group is the phenyl group, C6H5, derived from benzene, C6H6

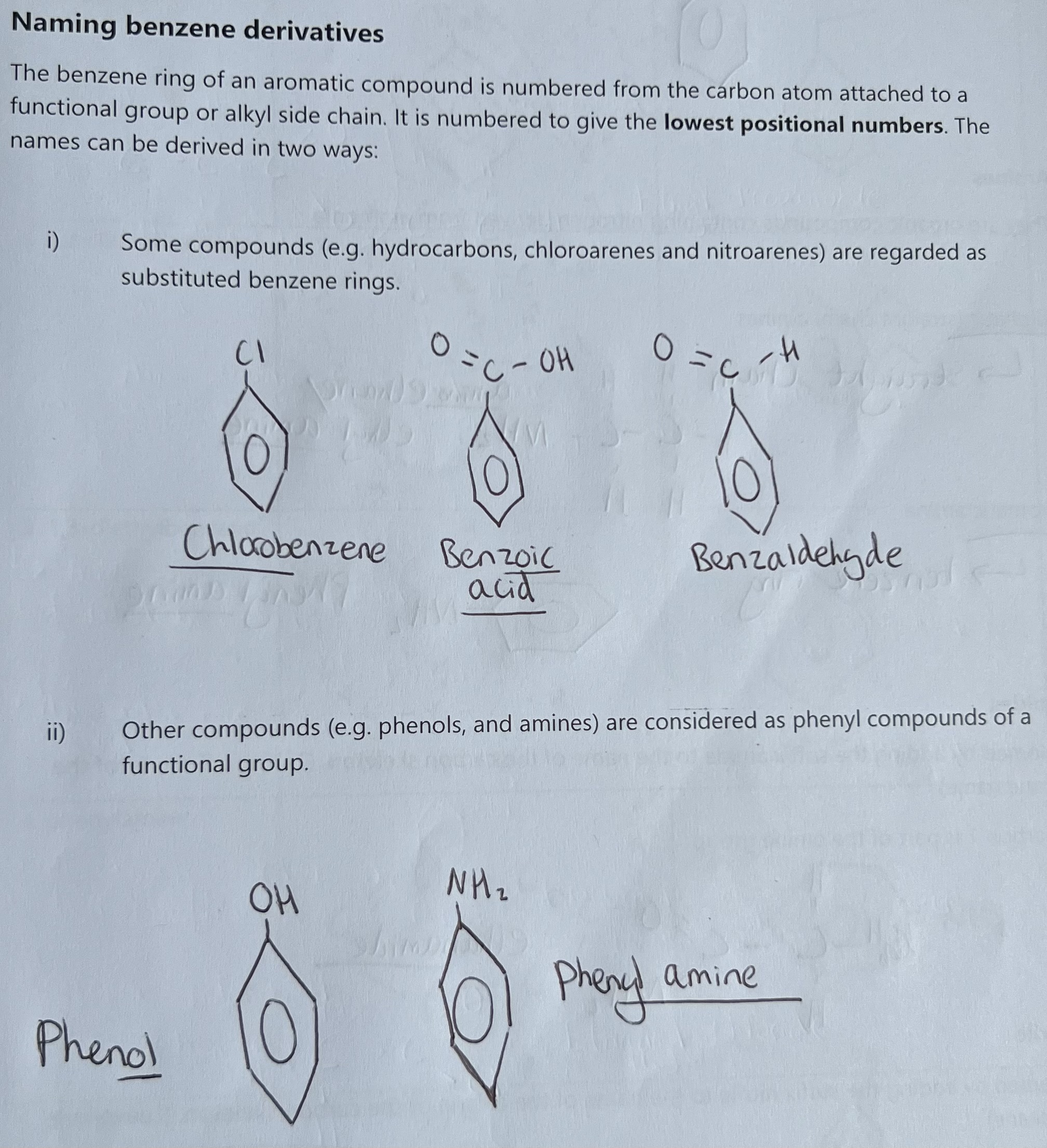
Naming benzene derivatives
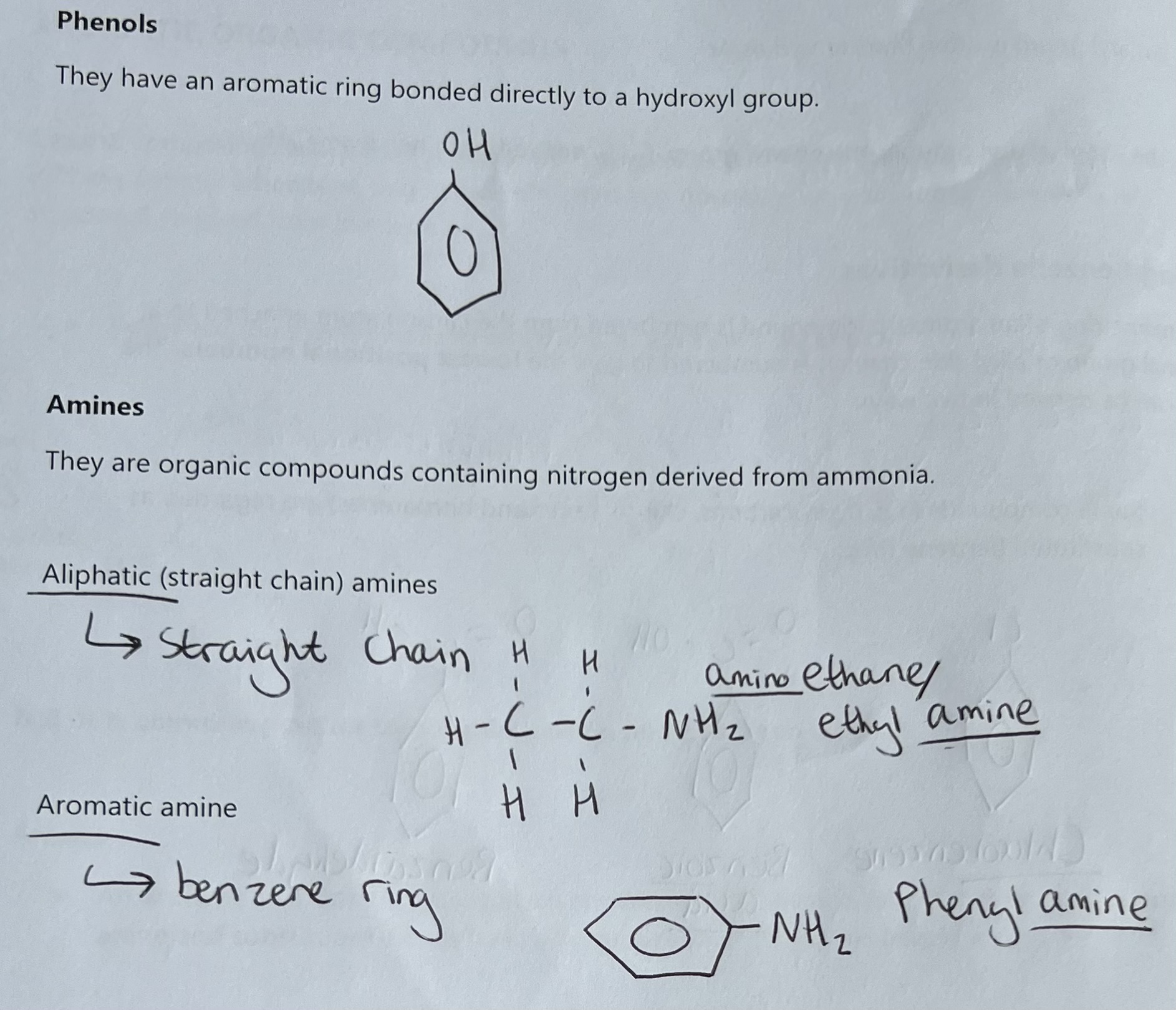
Phenols and Amines
Amides and Nitriles

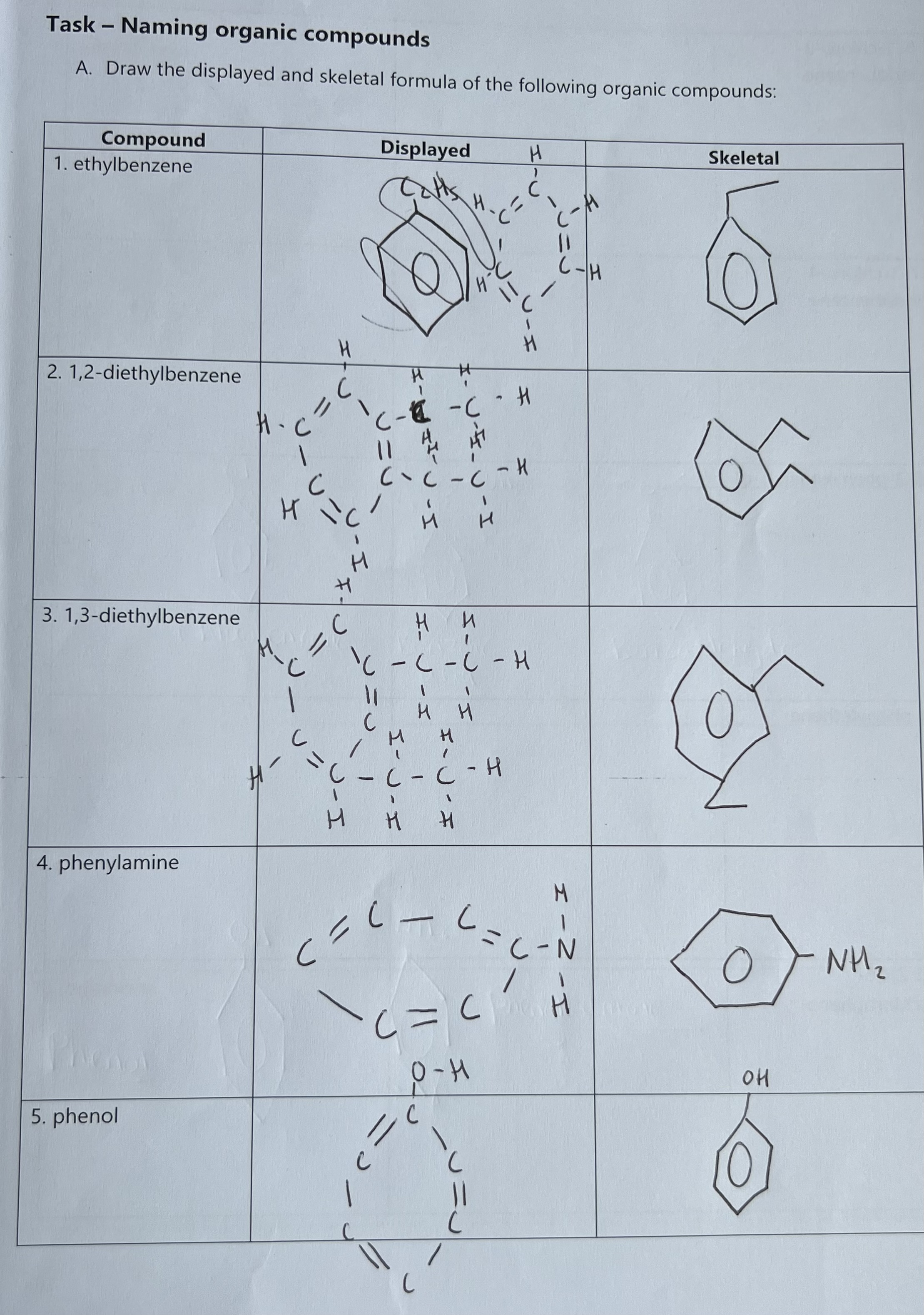
Examples of Naming Organic Compounds
(Practice questions on pg. 9-14)
Kekule Structure
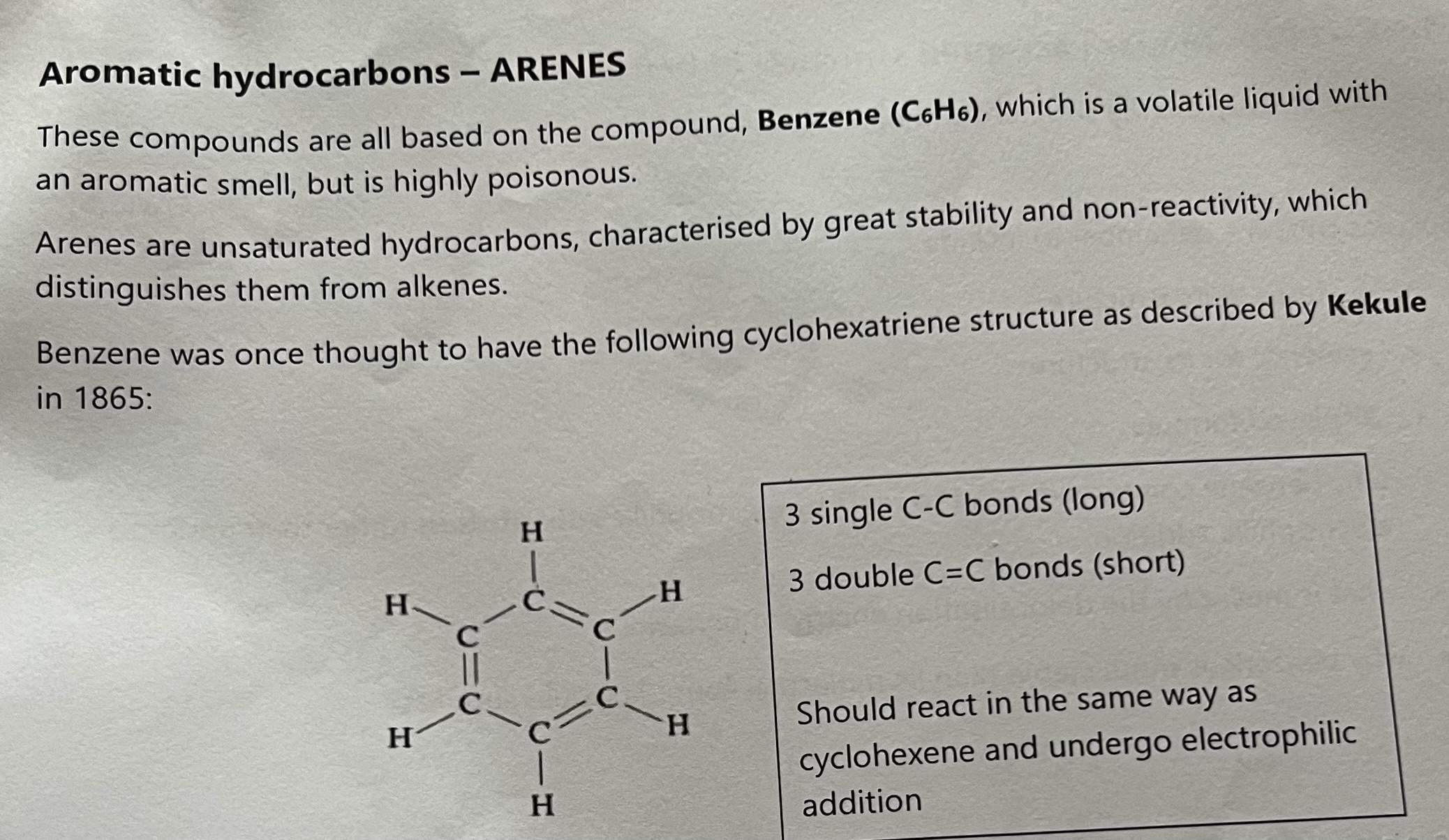
Describe how the currently accepted structure and bonding in benzene differ from the Kekule structure

Modern accepted structure of Benzene - 6 QER

Chemical Reactions of Benzene

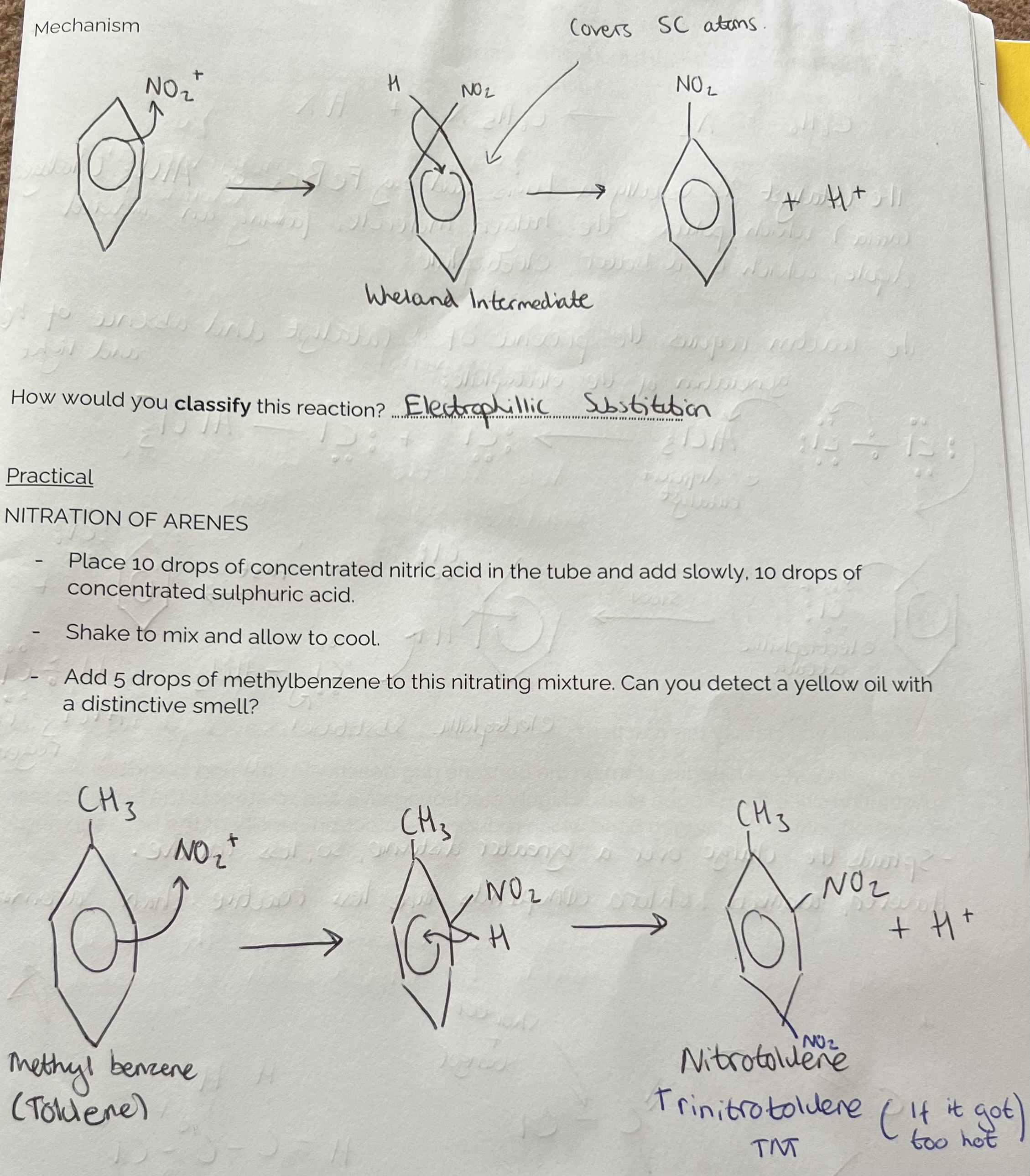
Nitration of Benzene (electrophilic substitution) Mechanism
Include + in circle of wheland intermediate
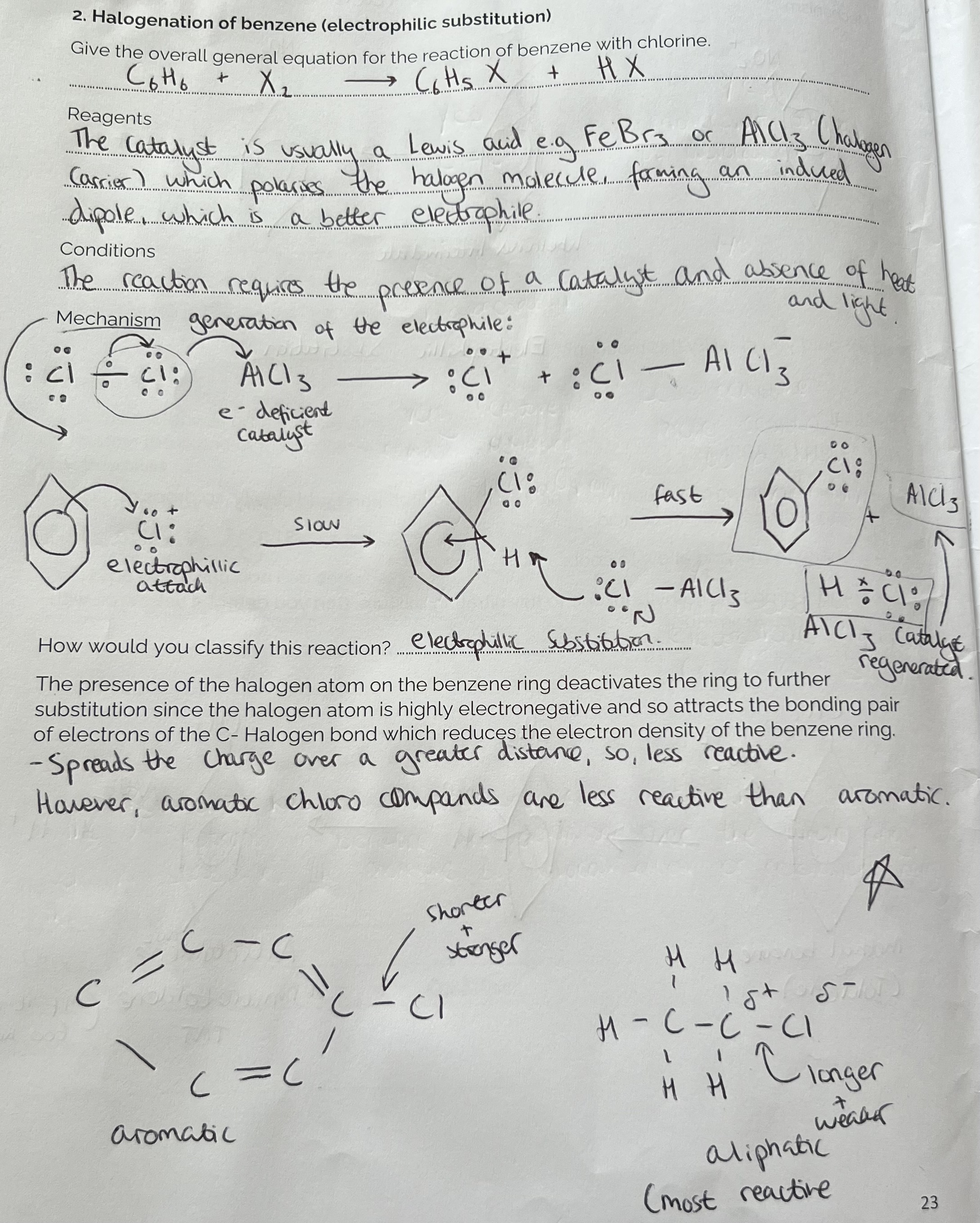
Halogenation of benzene (electrophilic substitution)
Reagents - Halogen Molecule e.g Chlorine/ CL2 + C6H6 (in the absence of UV light)
AlCl3/ FeCl3 Catalyst (as a halogen carrier)
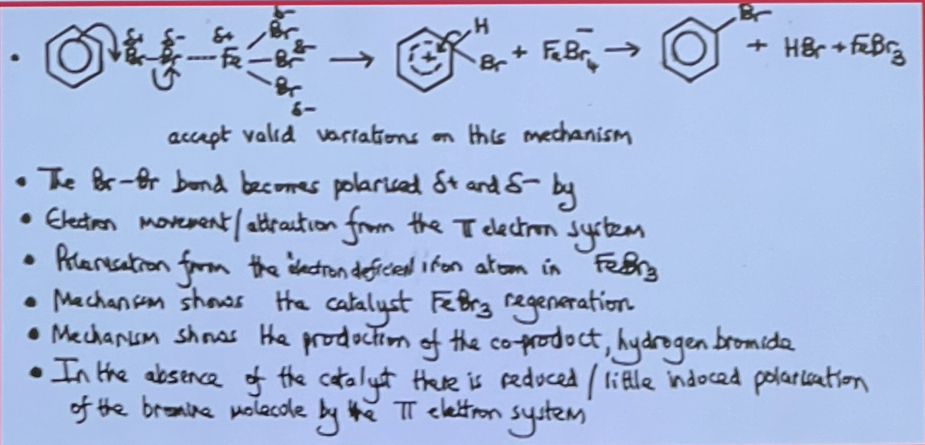
Halogenation of benzene with bromine [6 QER]
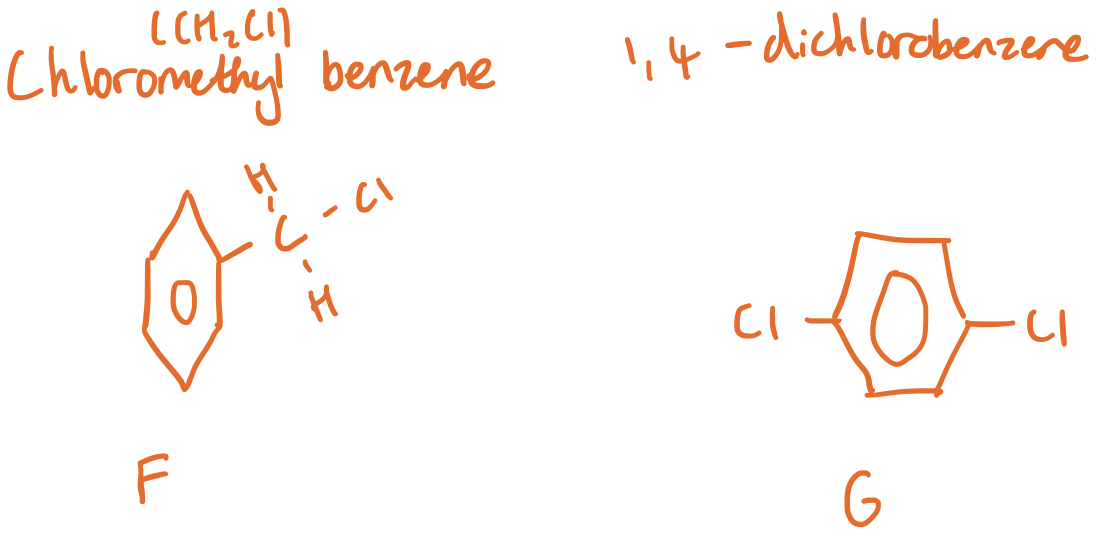
Chemical Tests to distinguish between Compounds F & G
Longer, weaker bonds in Chloromethyl benzene. Shorter stronger bond in 1,4-dichlorobenzene

Friedel-Crafts alkylation of Benzene
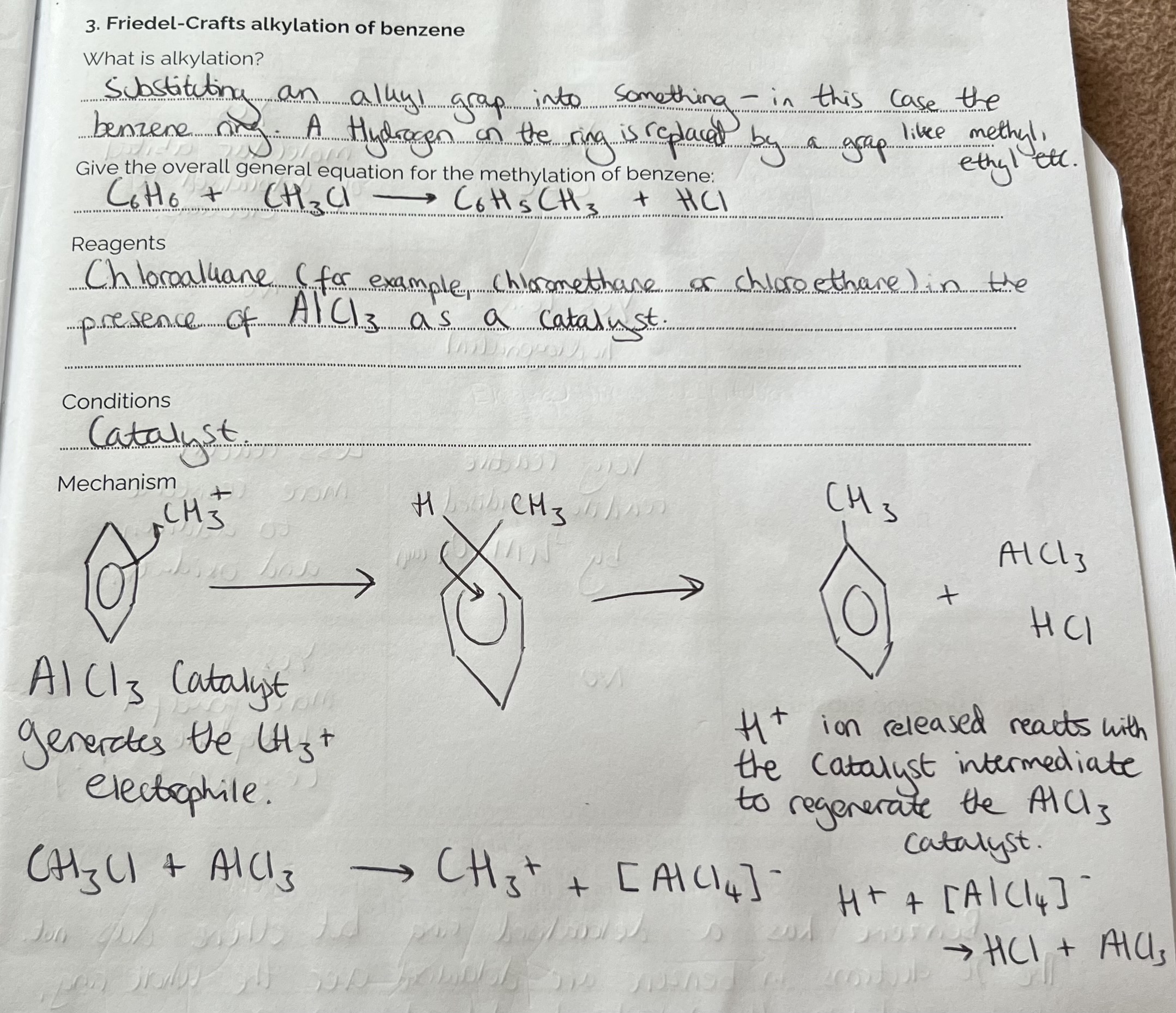
Ethene v Benzene
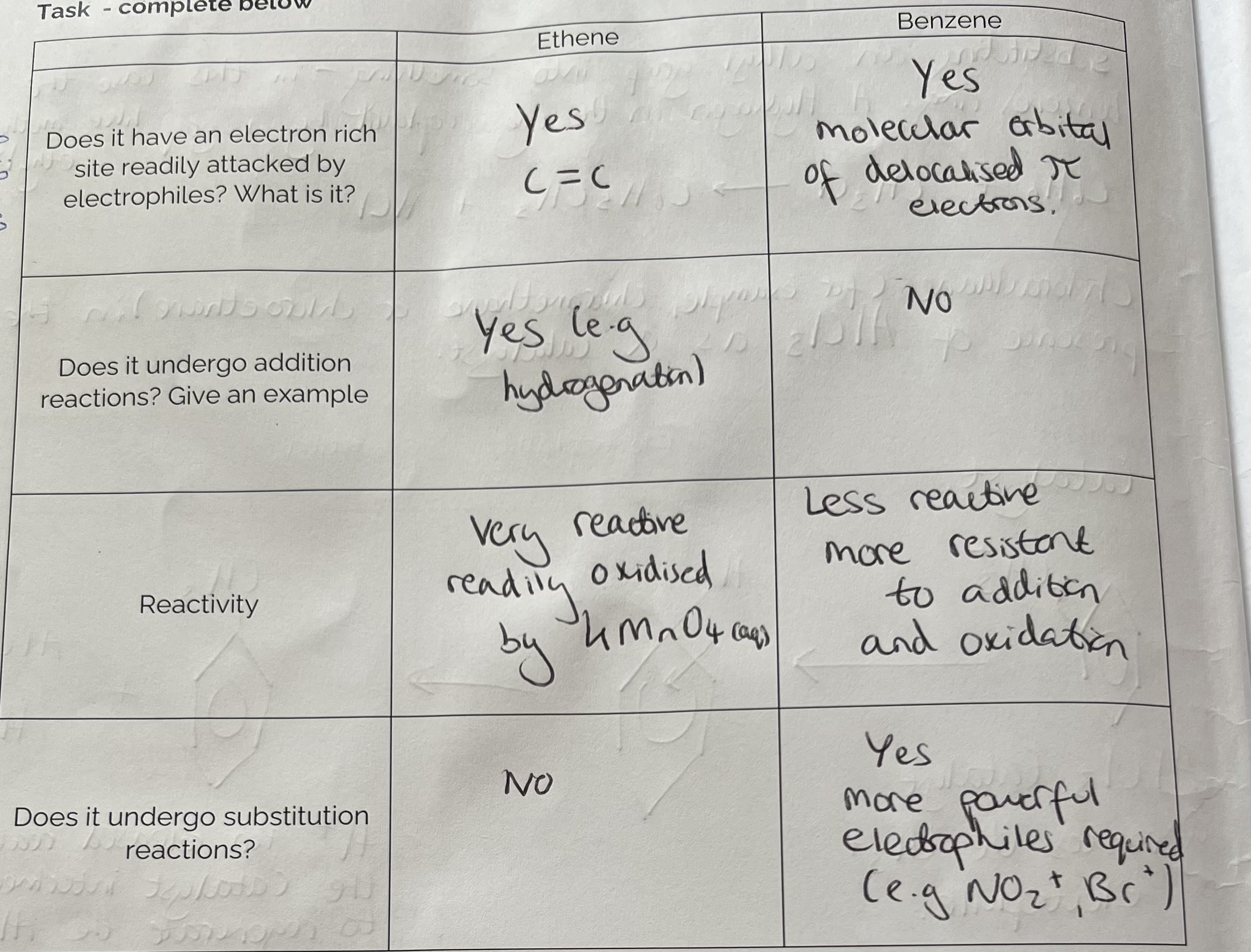
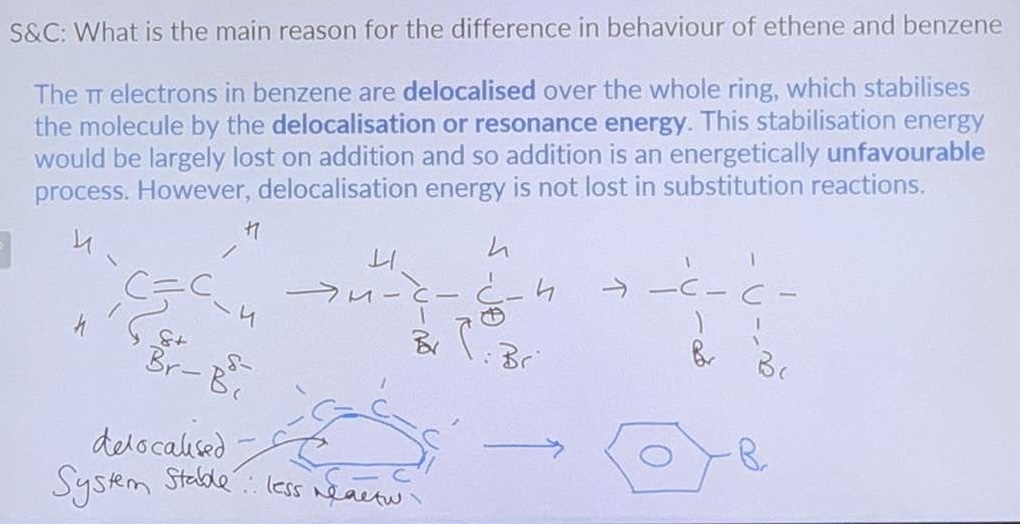
What is the main reason for the difference in behaviour of ethene and benzene?
Alkaline Hydrolysis of Chloroalkanes v Chlorobenzene

Alkaline Hydrolysis of Chloeobenzene



Why does benzene not undergo addition reactions?
Addition reaction would involve breaking the delocalises system which is not energetically favourable.


(answer questions on pg. 27)