Unit 2: Constitutional Foundations (Part II Government)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

33 Terms
confederation
form of government in which independent states maintain sovereignty & give just a few powers to a weak central government

Reason for Creation of Articles of Confederation
fear of abuse of power/tyranny by a central figure or government as experienced under British rule
republic
form of government in which people elect representatives to make decisions for them

Weakness of Articles of Confederation
states kept too much sovereignty; unable to unify the country, unable to get states to give them tax $ or soldiers for the military, could not regulate trade or force the states to use a uniform currency
Branches Missing Under Articles of Confederation
executive & judicial
Shays' Rebellion
Rebellion led by farmers in western Massachusetts in 1786-1787, protesting mortgage foreclosures. It highlighted the need for a strong national government just as the call for the Constitutional Convention went out.

Philadelphia Convention (1787)
(Constitutional) The meeting of state delegates in 1787 in Pennsylvania called to revise the Articles of Confederation. It instead designed a new plan of government, the US Constitution.

Congress
legislative branch that is bicameral & consists of 2 houses--House of Representatives & the Senate

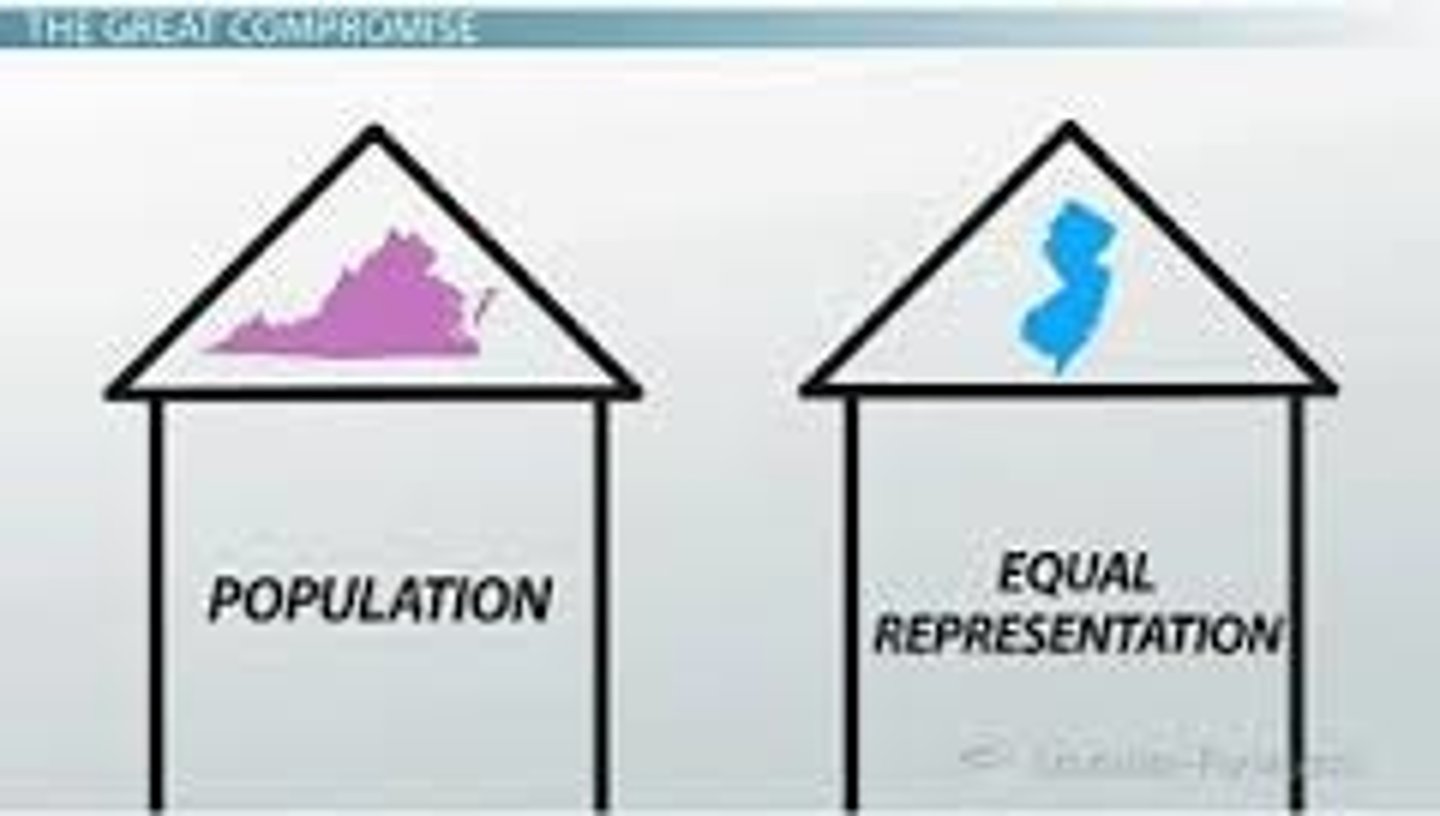
Great Compromise
created a bicameral Congress where the # of representatives in the House of Representatives is based on a state's population & each state has 2 Senators in the Senate
Three-Fifths Compromise
allowed southern states to count 3/5s of their slave population for the purpose of determining representation in the House of Representatives

Slave Trade Compromise
Congress could not outlaw the importation of slaves before 1808

Fugitive Slave Clause
Allowed runaway slaves or free blacks in the North to be captured and returned to the South, part of the Compromise of 1850

Electoral College
method of selecting the President; winner must win a majority of the Electoral College votes (270/538)

federalism
division of power between the central (also known as national or federal) government & the states

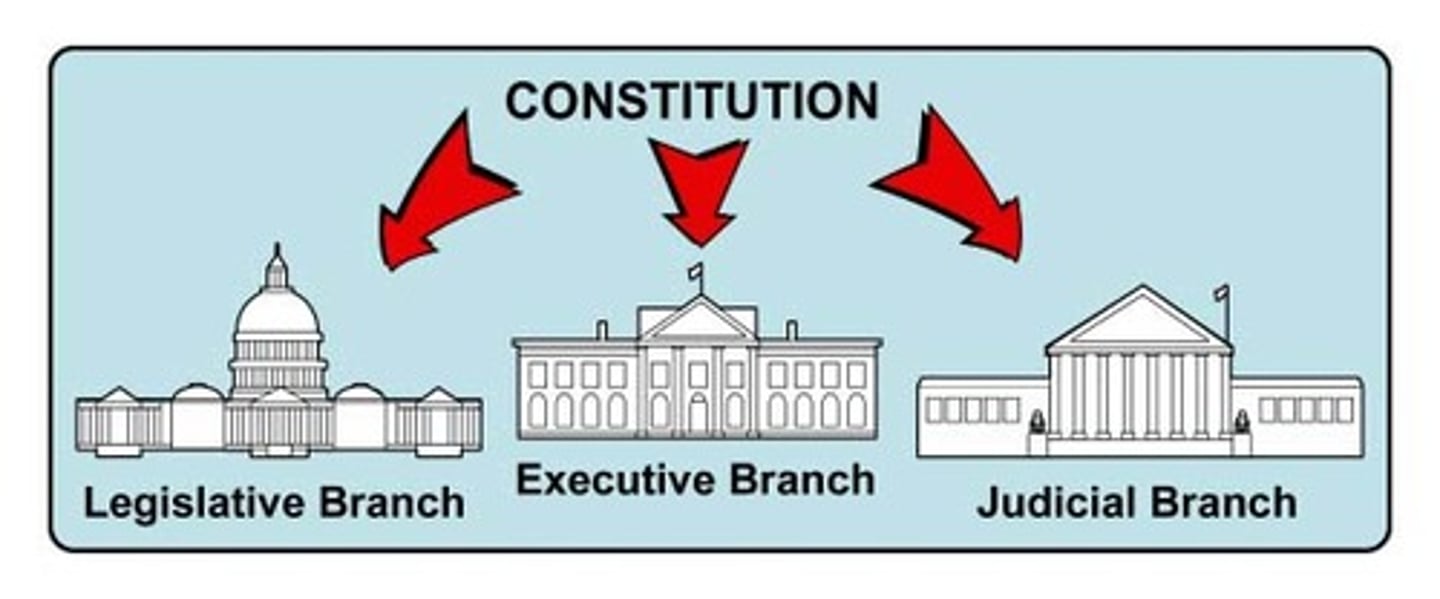
separation of powers
division of power between the legislative, executive, & judicial branches
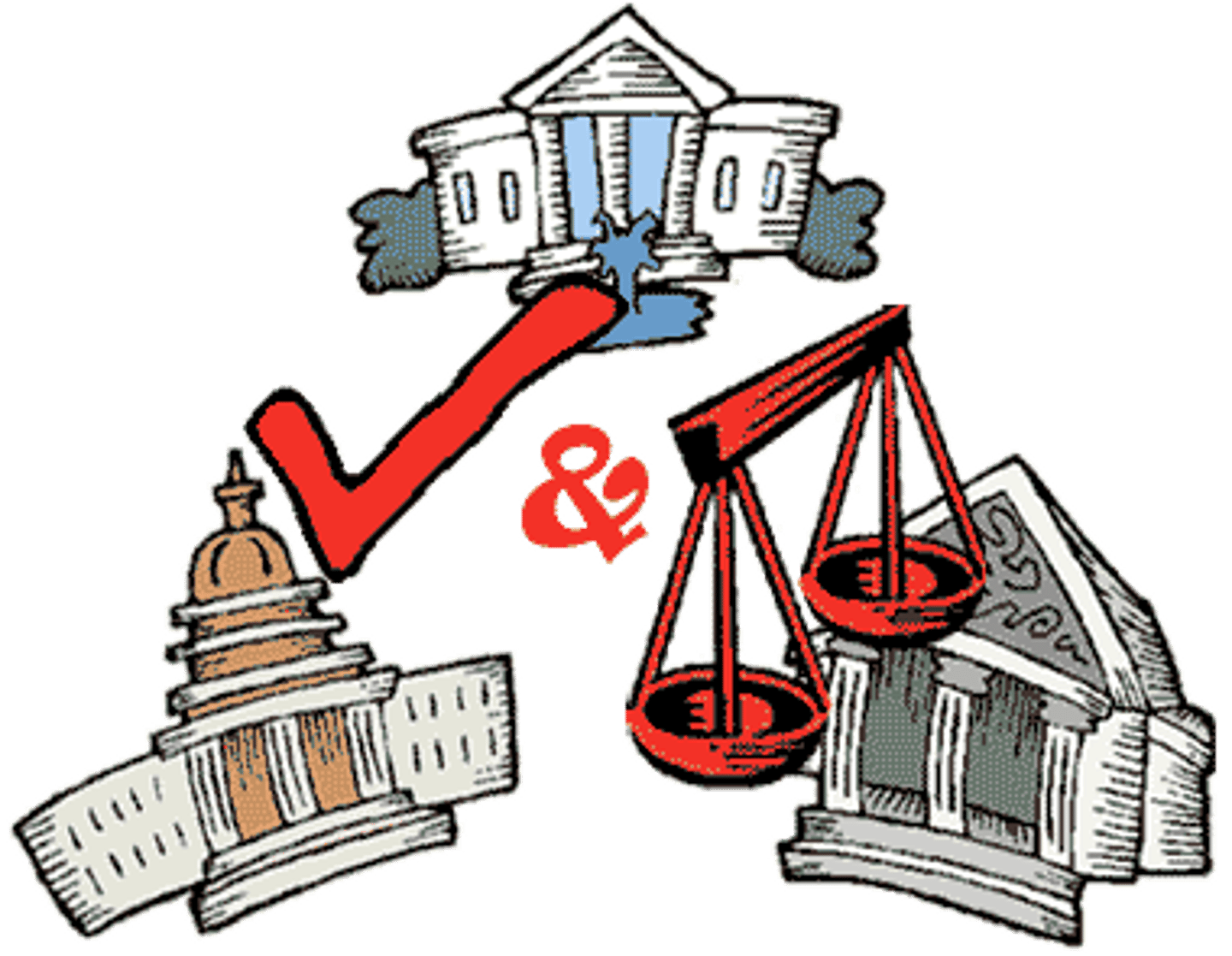
checks & balances
giving each branch of government tools to stop the abuse of power by the others
popular sovereignty
power rests with the people; consent of the governed; "We the People" in Preamble & achieved with election of the House of Representatives

Federalists
wrote the Federalist Papers to push for ratification of the Constitution; felt Constitution did a good job limiting possible power abuse; wanted a stronger central government

Anti-Federalists
opposed ratification of the Constitution; preferred power in the states & insisted on addition of the Bill of Rights
delegated powers
powers granted to the national government in the Constitution

implied powers
Powers inferred from the express powers that allow Congress to carry out its functions.
reserved powers
powers not granted to the national government are set aside for the state governments (confirmed in the 10th Amendment; example = control education)

Amendment Process
2/3 of both houses of Congress to propose them & 3/4 of the state legislatures to ratify (goes to states because power rests with people)

Supremacy Clause
makes the Constitution, national laws, & treaties the supreme law of the land

1st Amendment
freedom of speech, press, religion, assembly, petition

4th Amendment
protection against unreasonable search & seizure; created in response to writs of assistance under British

census
population count every 10 years; used to determine # representatives per state in the House

due process
set procedures that must be followed by the government when accusing someone of breaking a law

Marbury v. Madison (1803)
Established judicial review; "midnight judges;" John Marshall; power of the Supreme Court.

McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)
the Supreme Court upheld the power of the national government and denied the right of a state to tax the federal bank using the Constitution's supremacy clause. The Court's broad interpretation of the necessary and proper clause paved the way for later rulings upholding expansive federal powers

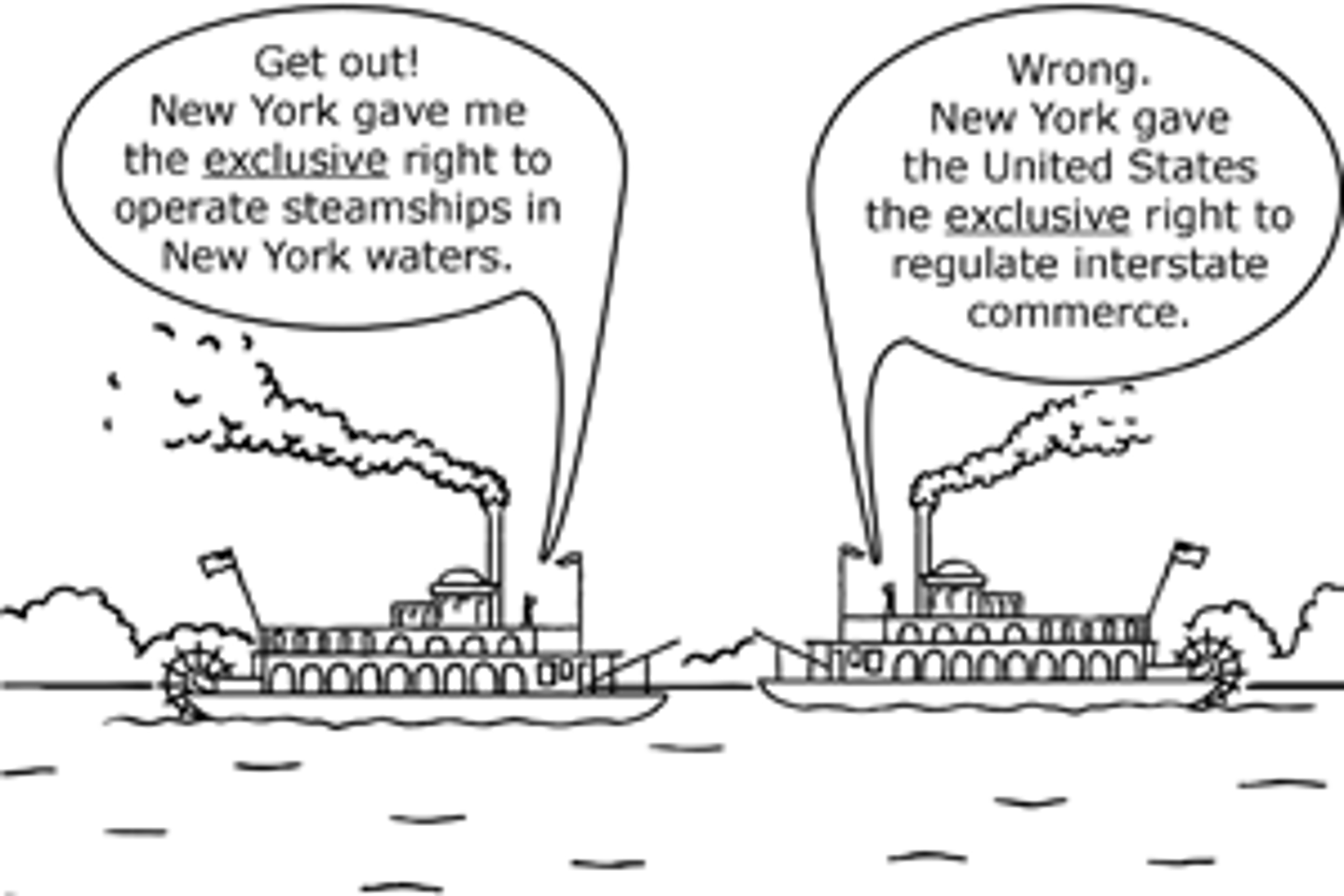
Gibbons v. Ogden (1824)
Affirmed federal control of interstate commerce under commerce clause of the Constitution.
Federalist Papers
A collection of 85 articles written by Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, and James Madison under the name "Publius" to defend the Constitution in detail.
Anti-Federalist Papers
a series of essays written to oppose and defeat the proposed U.S. Constitution
