Chap 6: Nucleic acids & protein synthesis
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
polynucleotide
a chain of nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bond
nucleotide structure
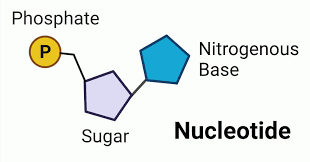
nucleic acids
made up of nucleotides monomers
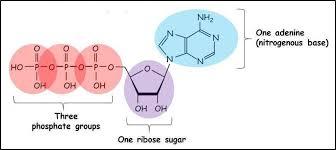
ATP structure
adenine + ribose = adenosine
3 phosphate = trisphosphate
ATP = adenosine triphosphate
purines
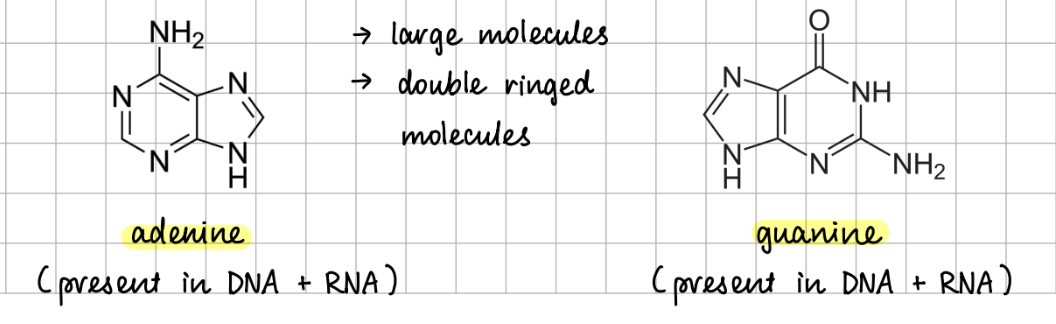
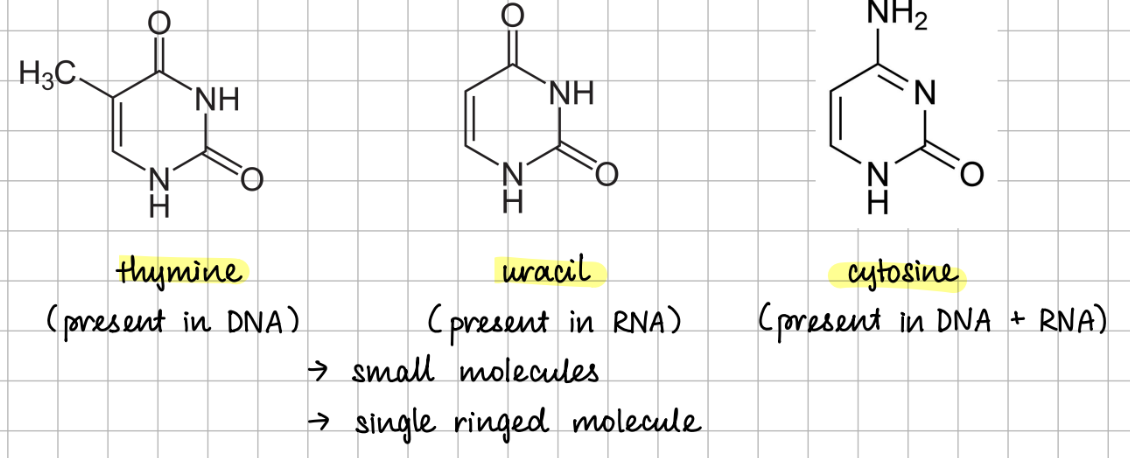
pyrimidines
complementary base pairing
A - T (2 H bonds)
C - G (3 H bonds)
→ In RNA, there are no T, therefore, A bonds with U
DNA nucleotide structure
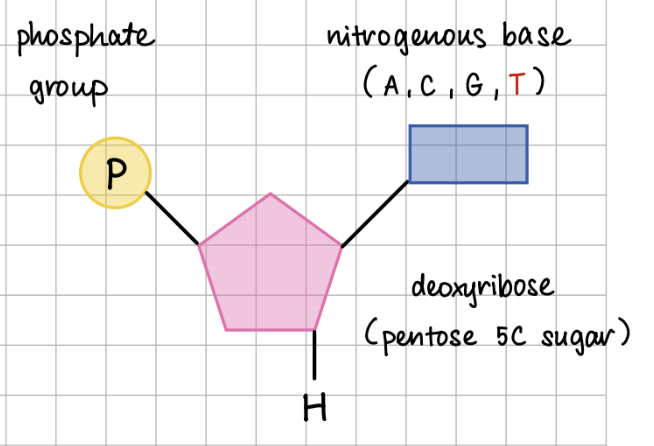
DNA structure (5)
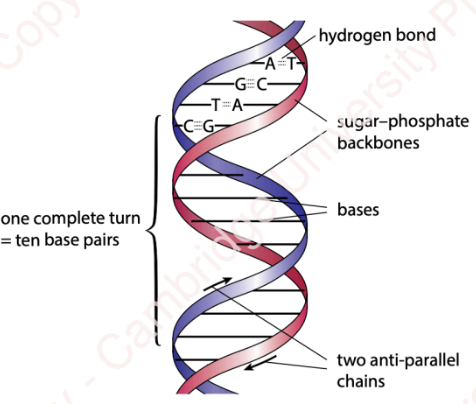
double helix
sugar-phosphate backbone
anti-parallel chains (one 5’ to 3’, one 3’ to 5’)
H bonds between complementary base pairs
nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester
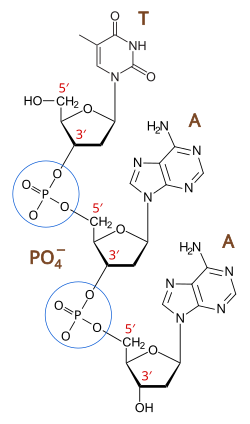
phosphodiester bond in DNA
phosphodiester bond alternating deoxyribose sugars and phosphate group
phosphodiester bonds link 5’ of one sugar to the 3’ of another sugar via a phosphate group
→ give DNA strand a direction of 5’ end or 3’ end
semi-convervative replication def
the method by which a DNA molecule is copied to form two identical molecules, each containing one strand from the original strand
describe DNA replication (7)
two strands of DNA are unwinded by breaking the H bonds
DNA polymerase attaches nucleotides to leading strands in the direction of 5’ to 3’
DNA polymerase can only runs in 5’ to 3’ direction
the nucleotides are attaches by complementary base pairing
the lagging strand is synthesised in Okazaki fragments
the Okazaki fragments are hold to the original strand by H bonds between bases
the DNA ligase connect the Okazaki bonds by phosphodiester bond
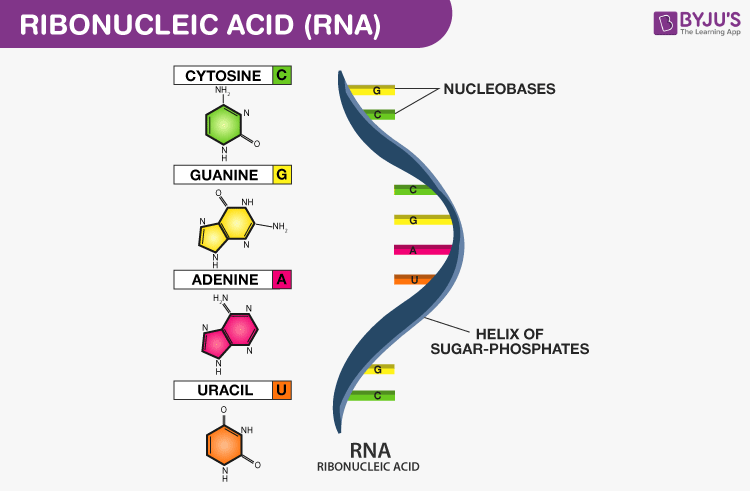
RNA nucleotide
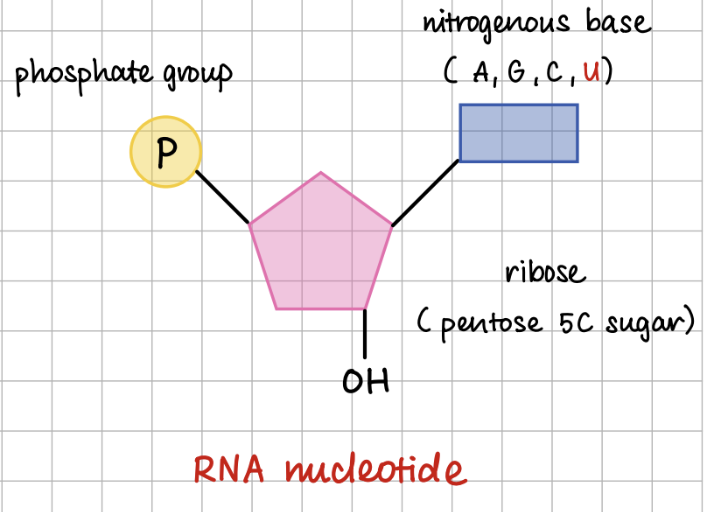
RNA structure (4)
single strand
ACGU bases
ribose sugar
no H bonds as there are no complementary base pairing
gene
sequences of DNA nucleotides that codes for a polypeptide
polypeptide
is coded for by a gene
triplet
3 bases of DNA (e.g: ACT)
functions of triplets (3)
1) start codon: where transcription begins
2) stop codon: where transcription ends
3) code for a specific amino acid
genetic code is non-ambiguous
1 codon will code for 1 amino acid, but 1 amino acid can be coded by many codons
codons that code for amino acids are…
the same across all organisms
transcription
from DNA to RNA
translation
from RNA to polypeptide
codon
a sequence of 3 adjacent nucleotides in mRNA that codes for one amino acid
DNA triplets → RNA codons
describe transcription process (5)
1) RNA polymerase unwinds DNA by breaking H bonds → expose the gene to be transcribed
2) free (activated) nucleotides complementary pair up with the template strand by H bonds
3) RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotide until stop codon
4) when mRNA is complete → the H bonds are broken
5) mRNA leaves nucleus through nuclear pores
location of transcription
nucleus
location of translation
cytoplasm
describe translation process
1) mRNA attches to a ribosome, 2 codons exposed to ribosome at a time
2) tRNA attaches to specific amino acid → brings to mRNA on ribosome
3) the anticodon complementary pair with base of mRNA
4) 2nd tRNA brings another amino acid next to first amino acid → peptide bond between 2 amino acids
5) the ribosome moves along the mRNA to read the next codon
6) 1st tRNA (w/o amino acid) leaves ribosome → another one enter
7) repeat until stop codon
non-transcribed strand
the other strand that is not used in transcription
transcribed/template strand
the strand that is used in transcription
primary transcript
the RNA nucleotides synthesised after transcription that contains introns and exons
introns
non coding sequence so they do not code for an amino acid
exons
coding sequence so they code for an amino acid
DNA splicing
occurs after transcription, modification of primary transcript, remove introns and join exons tgt
→ functional mRNA will be formed
gene mutation
a change in the sequence of base pairs in the DNA molecule that may result in an altered polypeptide
deletion/insertion mutation
=> cause frameshift mutation
may introduce stop codon → alter primary structure → shorter polypeptide → tertiary structure altered → non-functional polypeptide
substitution mutation
=> may/may not change the polypeptide formed
may lead to stop codon
may cause silent mutation: base is changed, amino acid produced is the same so no effects on polypeptide