L2 - the Big Bang
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is Obler’s Paradox?
There was no explanation for why it is dark at night
The black background between stars suggested either the universe is finite or that the light emitted from stars is intercepted by dark matter
Who came up with the ‘cosmic egg’ theory? When?
Georges Lemaître
1920s
What was the ‘cosmic egg’ theory?
Lemaître envisioned that there was a concentrated entity
It exploded and thew matter away from each other and into an expanding universe
The force of the explosion prevents the gravitational pull from drawing the matter towards the centre of the universe
What did Hubble observe?
Hubble reported a shift towards the red spectra of light reaching us from distant galaxies
Meant the galaxies were speeding away from ours at incredible speeds
This observation provided evidence for the expanding universe theory.
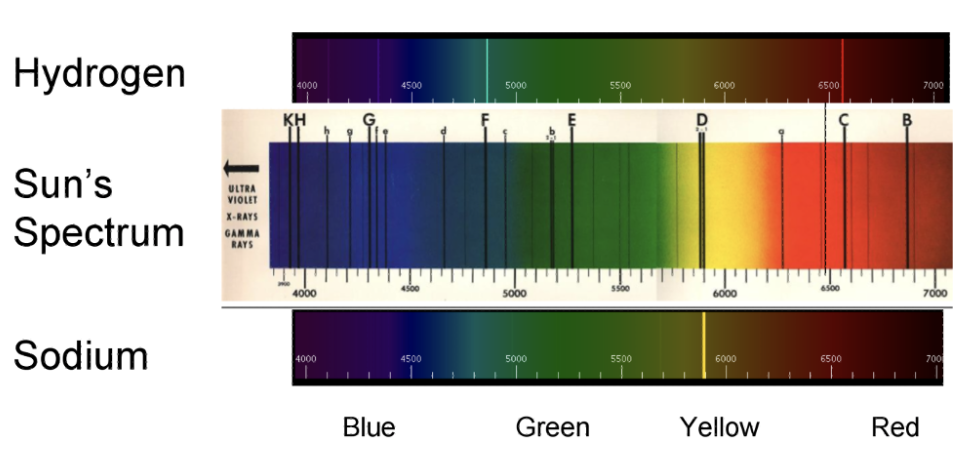
What do the missing wavelengths mean in this image?
The missing wavelengths indicate that certain elements are being absorbed by the gas in the atmosphere of the star or galaxy, which can reveal information about its composition and movement.
Explain ‘red shift’
The further away things are, the closer to red they become
The light is being stretched out because the light source is moving away from us - resulting in stars and galaxies appearing red.
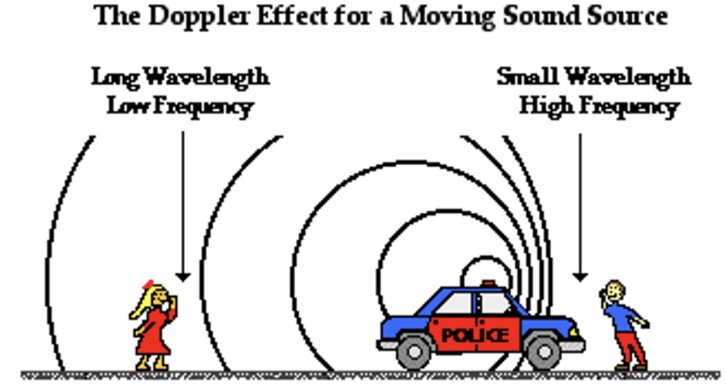
Explain the Doppler Effect in relation to a police car
As the police car moves towards you, the sound waves compress and the frequency increases, raising the pitch.
As the police care moves away, that stretches the sound waves, increasing wavelengths and lowering pitch
Who discovered Cepheid stars?
Henrietta Levitt
What are Cepheid stars?
Henrietta Levitt noticed stars vary in brightness
Different stars ‘pulse’ at different rates but the rate of pulsation correlated with how bright the star was.
How can Cepheid stars be used to calculate the distance of stars?
From the blinking rate, the luminosity of a star can be estimated
By comparing the luminosity with the intensity of light seen from earth, the distance of a star could be determined
How can Cepheid stars be used to calculate the distance of distant galaxies?
The distant galaxy appears only slightly larger than a nearby star, so no pulsing stars can be identified.
Most galaxies are found in clusters
Galaxies in very distant clusters have a similar spectrum of sizes and brightness as the ones in closer clusters
Therefore, can use the same method to measure the distance of distant galaxies.
What is blackbody radiation?
All objects above absolute zero emit radiation that is diagnostic of their temperature
This radiation can be used to estimate the temperature of distant objects.
The wavelength of emitted radiation decreases as the temperature increases.
How does temperature influence blackbody radiation?
At very low temperatures, the radiation is not visible
But, as temperature gets above a few hundred degrees C, the wavelengths start to enter the visible range, and the object glows a dull red.
Describe how blackbody radiation works in hot temperatures
If an object is heated up, it will absorb some of that energy and reradiate that energy in the visible spectrum of red light (i.e. ‘red hot’)
As that object gets hotter, there will be more of the visible spectrum of light emitted, so that the object will appear to be flowing white (i.e., ‘white hot’)
How was blackbody radiation discovered?
An experiment on radio waves detected a signal which corresponds to a blackbody radiation/temperature of 2.73 kelvin.
Initially thought it was noise.
Later realised the detected radiation was a background signal/echo from the Big Bang
How does the presence of Hydrogen and Helium provide further support for the Big Bang?
The universe matter immediately after the Big Bang consisted almost entirely of only 2 elements: H and He
The calculated 10:1 distribution is consistent with theoretical calculations of the Big Bang event and creations of matter
Why was dark energy hypothesised?
1990s Hubble telescope launched
Scientists found the universe is still expanding and that expansion is speeding up
The contracting universe theory emerged following this.
Things are moving apart, and the rate at which they do is accelerating: no one really knows why.
Dark energy was hypothesised following this
What is dark energy (theoretically)?
There has to be some sort of energy source that is strong enough to overcome the forces of gravitational attraction, which should be slowing down the expansion of the universe
Dark energy, in theory, explains why the universe is still expanding at an increasing rate.