3.3.1 Labour Markets part 2
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Factors of Demand for Labour
1. total d__ in e__
> economic b__ = more d__ for labour (as consumers want more)
demand, economy, boom, demand
Factors of Demand for Labour
2. P__ of labour
productivity
Factors of Demand for Labour
3. Change in non-w__ employment costs e.g. sick leave
> as if these increase, D for labour __
wage, decreases
Factors of Demand for Labour
4. C__ of labour
cost
Factors of Demand for Labour
5. Cost of labour compared to m__
as tech improvements = c__ to use capital machinery instead of labour
machinery, cheaper
Factors of Demand for Labour
6. P_ change
pop
Supply of labour consists of
people of working age & both willing & able to work
Factors of Supply of Labour
1. change in pop/d__
> more pop = more S of labour
demographic
Factors of Supply of Labour
2. change in b__ of occupation
> lack of prospects, less h__ = less S of labour
benefits, holidays
Factors of Supply of Labour
3. change in p__ of e__
> if schools stopped teaching acct, = less accountants
provision, education
Factors of Supply of Labour
4. Change in s__ leaving a__
> higher = less S of labour
school, age
Factors of Supply of Labour
5. change in r__ age
higher = more S of workers
retirement
Define labour force.
portion of the working age pop that is either employed or unemployed
Minimum Wage
define national minimum wage.
legal min firms can pay employees
Why min wages?
> e__ wage rate < $$ workers need to meet basic n__
> stops e__ of workers
> reduce income i__
equilibrium, needs, exploitation, inequality
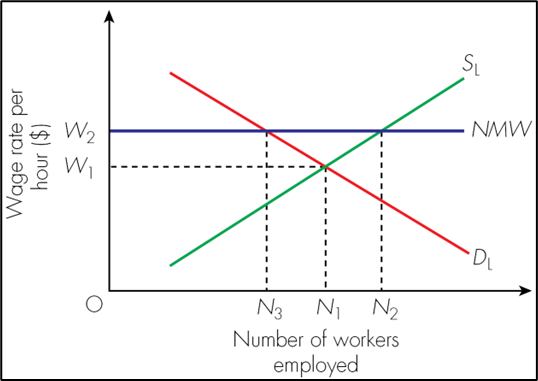
What is happening at NMW?
S > D, = unemployment
Effect of Min. Wages
> u__ people have greater incentive to work
> low i__ workers can spend more
>>> more D in economy = compensates for job l__
> firms choose c__ intensive production over labour
> more c__ for firms = __ prices for consumers
unemployed, income, losses, capital, cost, higher
Define Living Wage
hrly wage worker needs to pay for necessities of life & participate as active citizen in community
Role of Govt in Labour Markets
1. O__ & regulate practices of powerful t__ u__/businesses
> powerful employers can set __ wages bc they employ a lot of the pop. with those skills
> powerful trade unions with lots of S of workers can inrc w_ without incr in productivity
outlaw, trade union, low, wages
Role of Govt in Labour Markets
2. outlaw d__
discrimination
Role of Govt in Labour Markets
3. reduce u__ via s__ for training
unemployment, subsidies