past paper questions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
State the Cosmological Principle.(2)
Universe is isotropic and homogeneous
Describe the important properties of the cosmic microwave background radiation and how the standard model of the Universe explains these properties. Explain their significance as evidence for the past evolution of the Universe. In your answer, you should make clear how your explanation links with the evidence.(5)
Uniform intensity in all directions / everywhere Structure in background intensity / ripples
Produced when matter and radiation decoupled
Originally gamma radiation (gamma) red-shifted to microwave / originally higher energy
Evidence that universe began with big bang
Temperature corresponds to 2.7 K / 3K / that predicted by big bang model
Explain why our understanding of the very earliest moments of the Universe is unreliable.(2)
No experimental evidence / no physical evidence
/ laws of physics unknown
The future of the Universe may be open, closed or flat. Explain the meaning of the terms in italics, using a graph to illustrate your answer. ‘size measure’ of Universe and age of Universe graph (4)
Open: Universe expands for all time
Flat: expands to a limit (but never reaches it)
Closed: Universe contracts / collapses back B1
Reference to role of gravity / critical density B1 Marks for
(a) can be gained on a labelled diagram
The mean density of the Universe, ρ0, is thought to be approximately 1 × 10–26 kg m–3 . Calculate a value for the Hubble constant H0.
Ho2 = (1 × 10-26 × 8 × π × 6.67 × 10–11) / 3
Ho = 2.36 × 10-18 s–1
State Hubble’s law and define any symbols used.(2)
the recessional velocity of a galaxy is proportional to its distance from earth
v α r / v = Ho × r
Describe Olbers’ paradox and explain how the work of Edwin Hubble provides an answer.(5)
infinite Universe (1)
all lines of sight end on star (1)
so night sky should be bright/ not dark
expanding Universe/light undergoes red shift (1)
more distant galaxies have greater red shift (1)
age of Universe is finite (1)
light from distant stars not yet reached Earth (1)
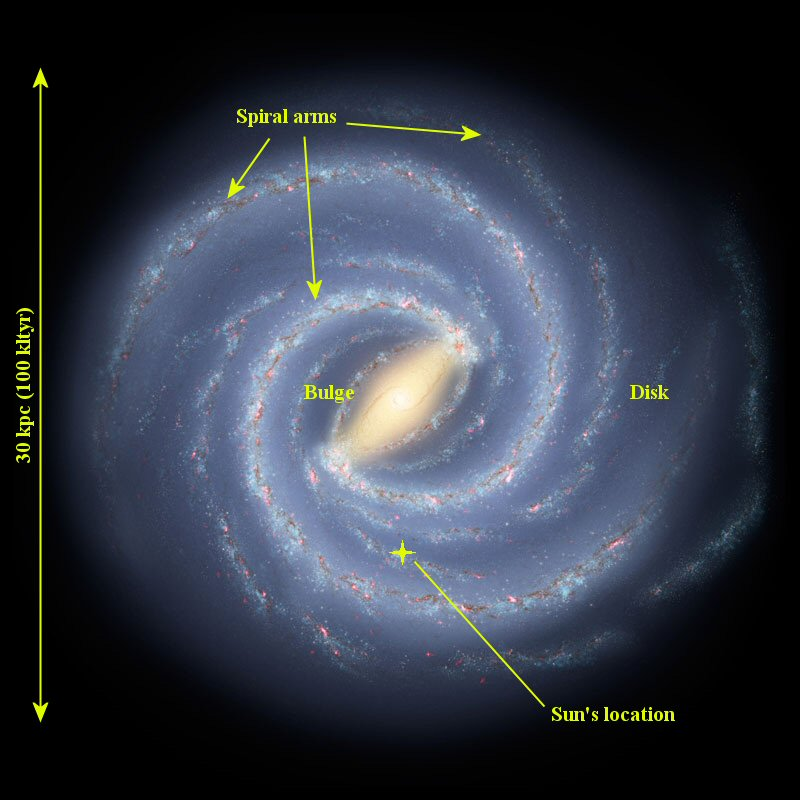
Describe the shape and structure of our galaxy. Illustrate your answer with a sketch. (2)
side: central bulge (1) galactic disc each side (1)
plan: accumulation of stars in centre. (1) spiral arms (minimum of 2 arms) (1)
correct position of Sun (accept 28000ly from centre) (1)
Some Cosmologists have estimated that as much as 90% of the total mass of a galaxy is made up of gas, referred to as dark matter. (i) Suggest the nature and origin of this gas. (2)
hydrogen / helium gas (1)
formed after big bang / remnants of supernovas (1)
The precise amount of dark matter in the Universe is unknown. Explain how the presence of dark matter affects the average density of the Universe and thus has a role in determining the ultimate fate of the Universe itself. (4)
critical density is condition for flat Universe. (1)
dark matter increases density of Universe. (1)
density greater than critical density. (1)
Universe will contract / big crunch. (1)
When a star ceases to be Main Sequence, it may evolve in several different ways. Explain the circumstances which will lead to the formation of a neutron star.(4)
end of H burning/red giant/supergiant (1)
onset of He fusion/fusion of heavier nuclei (1)
gravitational collapse of core (1)
supernova explosion/ star explodes (1)
suitable mass limit (chanderasekha limit 1.4M) (1)
supported against gavity by neutron gas pressure/ ref to Fermi pressure (1)
internal structure protons and electrons combined/ very thin atmosphere/ metallic crust (1)
State how the density of a neutron star compares to that of materials commonly found on Earth.(2)
density (very) much greater than material on Earth (1)
quotes typical density on Earth 1 – 104 kg m-3 (1)
atomic structure collapsed / density same as atomic nucleus (1)
Explain how the Universe became transparent (3)
protons and electrons separate initially (1)
matter-radiation equilibrium/charge prevents passage of em waves (1)
proton-electron recombination /formation of atoms (1)
gamma/ em waves no longer absorbed (1)
Describe and explain two pieces of evidence which suggest that the Universe did in fact begin with a big bang.(5)
star-light shows red shift (1)
galaxies (stars) receding from Earth (1)
recessional velocity proportional to distance (1) cosmological microwave background radiation (CMBR) (1)
uniform intensity in all directions (1)
small ripple (1)
(black body temperature) 2.7 K (3K) (1)
High ratio of helium to hydrogen (1)
Indicates very high temperatures existed (1)
ratio too high to originate from stellar fusion (1)
The cosmic microwave background radiation is evidence for the way in which the Universe began. State a feature of the intensity of this microwave background radiation.(1)
uniform intensity detected in all directions/ isotropic
The first stars are thought to have formed many years after the Universe came into being. What are the similarities and differences between the composition of the Sun and that of the very first stars?(3)
Hydrogen and helium in early stars and sun
Sun has greater proportion of helium than early stars/ H changed to He by fusion in sun.
Virtually no higher elements in first stars/ sun contains traces of higher elements (accept specific examples up to iron)
In 1929 Edwin Hubble showed that the Universe was expanding by studying the light from stars and galaxies. Explain how. (5)
red shift data for galaxies (accept stars)
calculate velocity from red shift 1 galaxies/ stars receding from Earth
distance data for galaxies/ stars
velocity α distance / v/r = constant / v-r graph straight line
universe began at a single point
Describe how the fate of the Universe depends upon its mean density and explain why this ultimate fate is not yet known.(5)
critical density is that for flat universe
density > p0 universe closed/contracts/big crunch
density < p0 universe open/ expands forever
any 2 from fate unknown because size/mass/density universe uncertain
fate unknown because p0 / H0 not known
State Kepler’s laws of planetary motion.
Planets move in ellipses (Sun at one focus)
Planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
Period2 α radius3 / T2 / r3 = constant
Explain how a main sequence star can develop into a supernova. Discuss what may remain after the explosion.(6)
Nuclear/hydrogen burning ends (1) Mass > Chandrasekhar limit (1)
Expanding gas/planetary nebular/red giant (1) Gravitational collapse /ref. to burning He or higher metals (1)
Correct ref. to (Fermi) pressure/ radiation pressure (1) (must have ref. to pressure or force from radiation.)
Neutron star (neutron by itself, not enough) (1)
Correct reference to Schwarzschild radius/ allow mass> 3M/ allow ref. critical radius (1)
Black Hole (1)
Large distances in the Universe may be measured in parsecs. Explain what is meant by a parsec. (2)
correct reference to
AU (1) parallax of 1 arcsecond