PLTW IED Unit 3: Measurement and Statistics
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
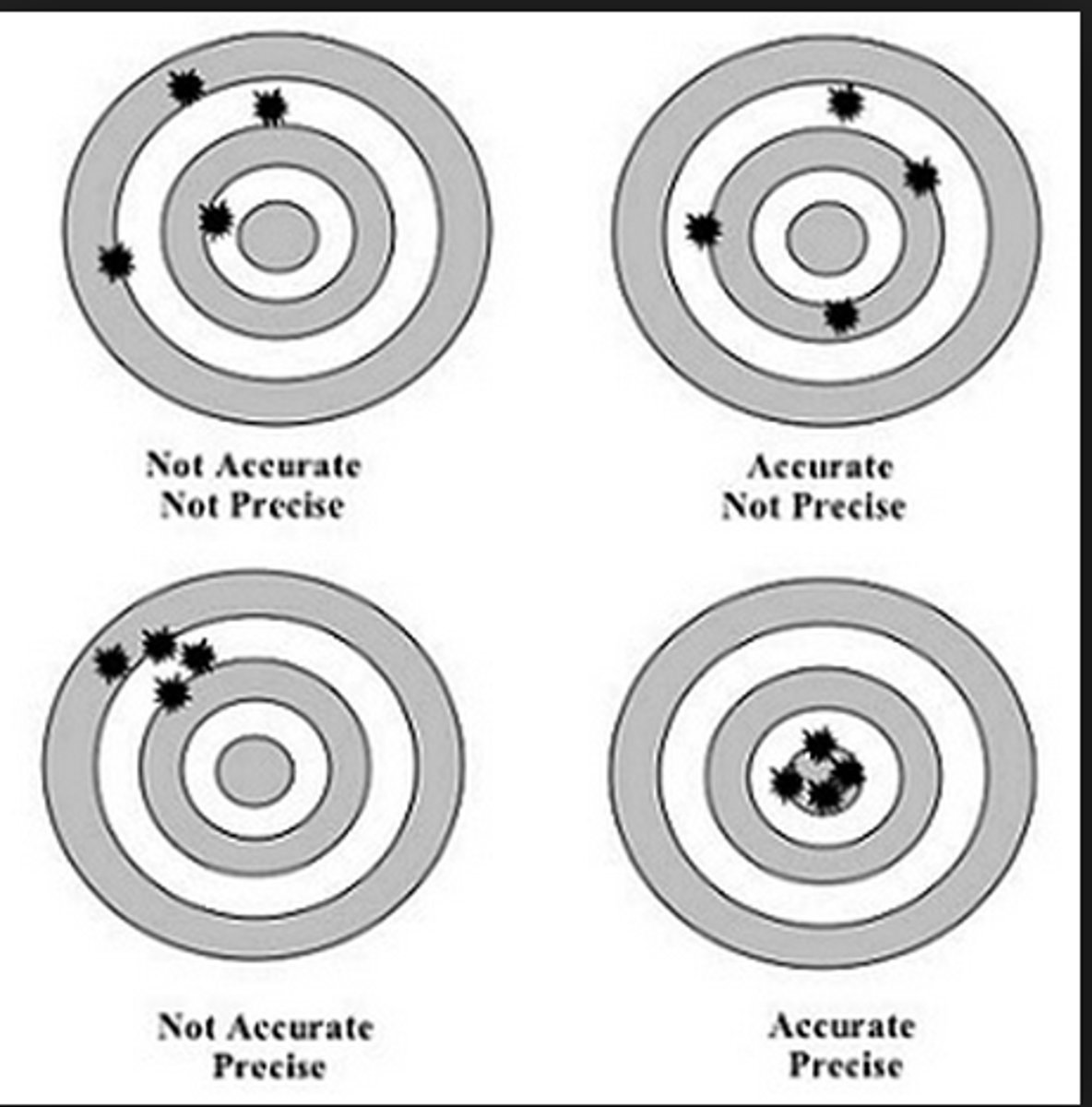
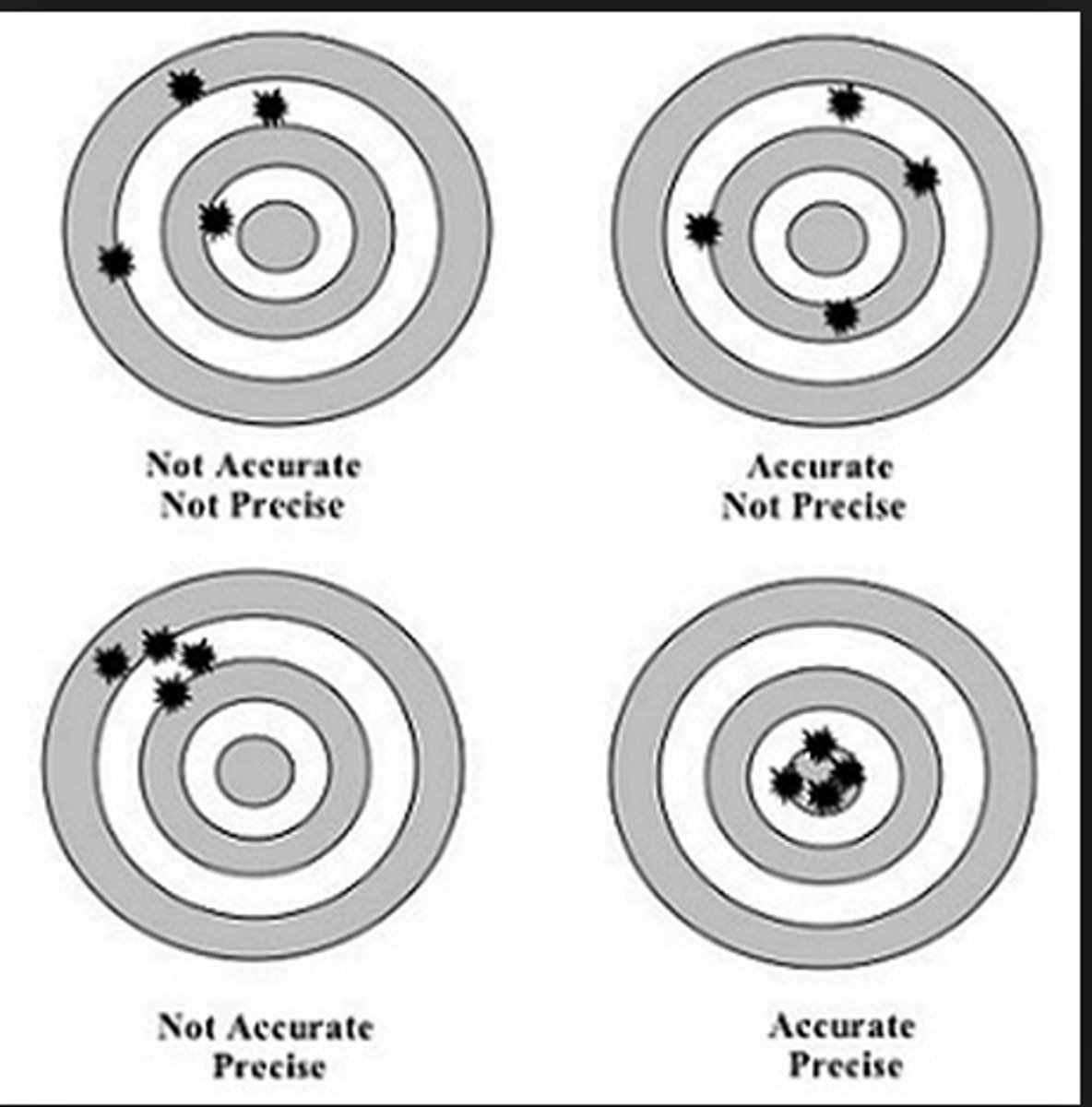
Accuracy
The degree of closeness of measurements of a quantity to the actual (or accepted) value.
- dependent on calibration to a standard
Arrowheads
Arrowheads are used to indicate the end of a dimension line or leader.
Caliper
A measuring instrument having two adjustable jaws typically used to measure diameter or thickness.
Class Interval
A group of values that is used to analyze the distribution of data.
Convert
To change money, stocks, or units in which a quantity is expressed into others of a different kind.
Data
Facts and statistics used for reference or analysis.
Data Set
A group of individual values or bits of information that are related in some way or have some common characteristic or attribute.
Dimension
A measurable extent, such as the three principal dimensions of an object as in width, height, and depth.
Dimension Lines
A line which represents distance.
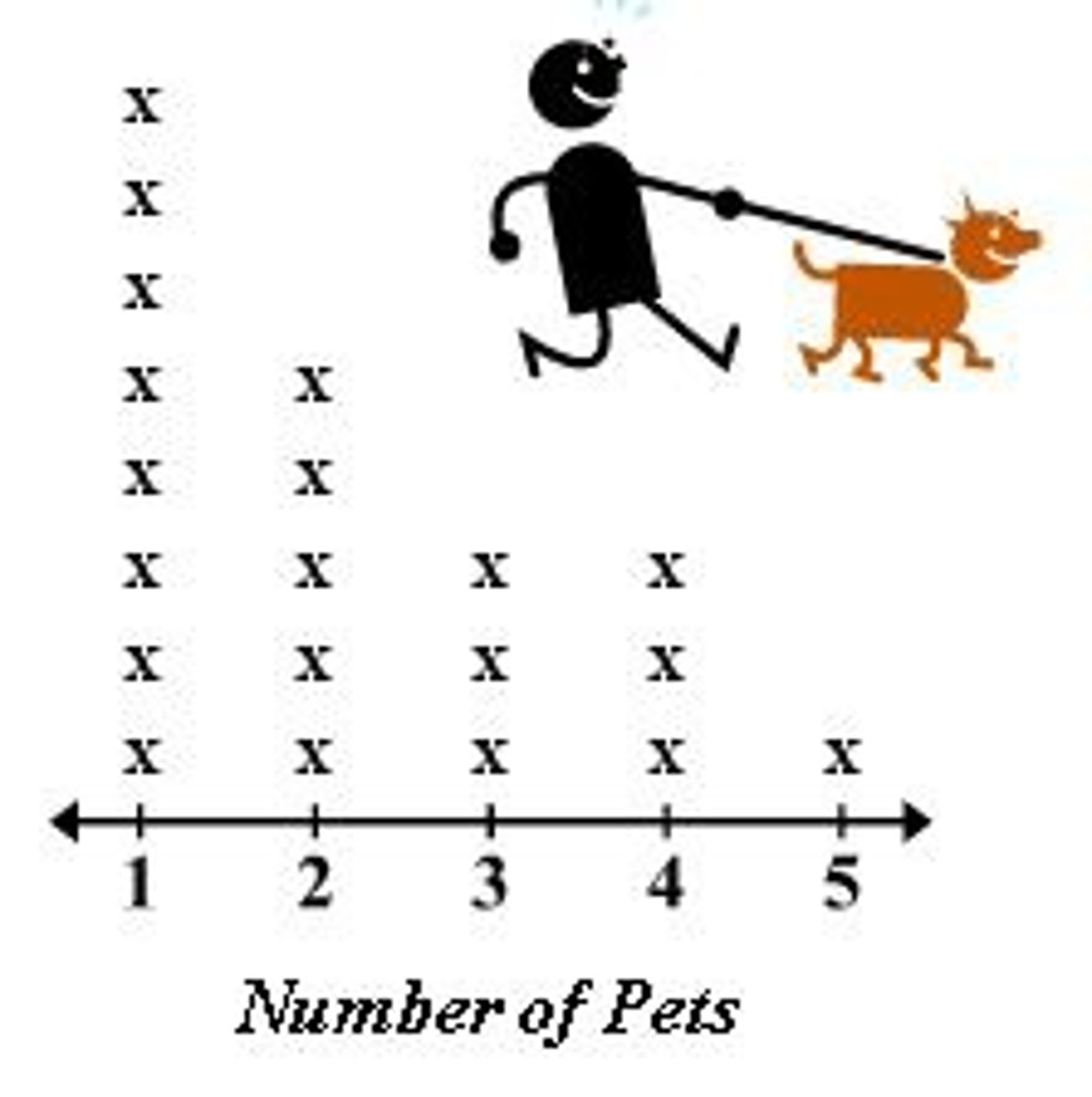
Dot Plot
A method of visually displaying a distribution of data values where each data value is shown as a dot or mark above a number line. Also known as a line plot.
Frequency
The rate at which something occurs over a particular period or in a given sample.
Graph
A diagram showing the relation between variable quantities, typically of two variables measured along a pair of lines at right angles.
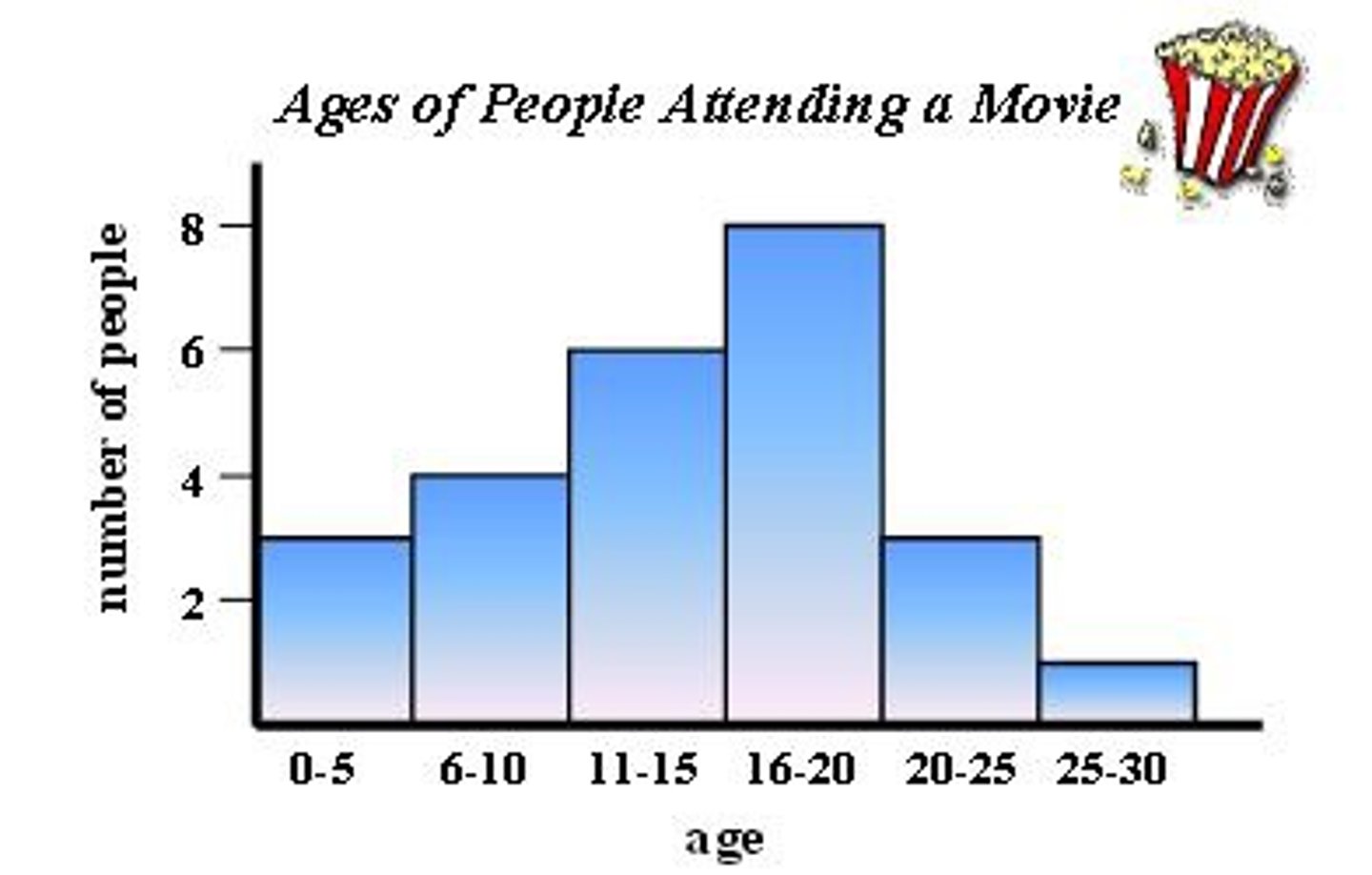
Histogram
A graph of vertical bars representing the frequency distribution of a set of data.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
A non-governmental global organization whose principal activity is the development of technical standards through consensus.
International System of Units (SI)
An international system of units of measurement consisting of seven base units.

Line Plot
A method of visually displaying a distribution of data values where each data value is shown as a dot or mark above a number line. Also known as a dot plot.
Mean
A measure of center in a set of numerical data, computed by adding the values in a list and then dividing by the number of values in the list.
Measure
To determine the size, amount, or degree of an object by comparison with a standard unit.
Median
A measure of center in a set of numerical data. The median of a list of values is the value appearing at the center of a sorted version of the list - or the mean of the two central values if the list contains an even number of values.
Mode
The value that occurs most frequently in a given data set.
Normal Distribution
A function that represents the distribution of variables as a symmetrical bell-shaped graph.
Numeric Constraint
A number value or algebraic equation that is used to control the size or location of a geometric figure.
Precision (repeatability)
The degree to which repeated measurements show the same result.
- dependent on the characteristics and/or capabilities of the measuring device and its use
Scale
1. A straight-edged strip of rigid material marked at regular intervals and used to measure distances. 2. A proportion between two sets of dimensions used in developing accurate, larger or smaller prototypes, or models of design ideas.
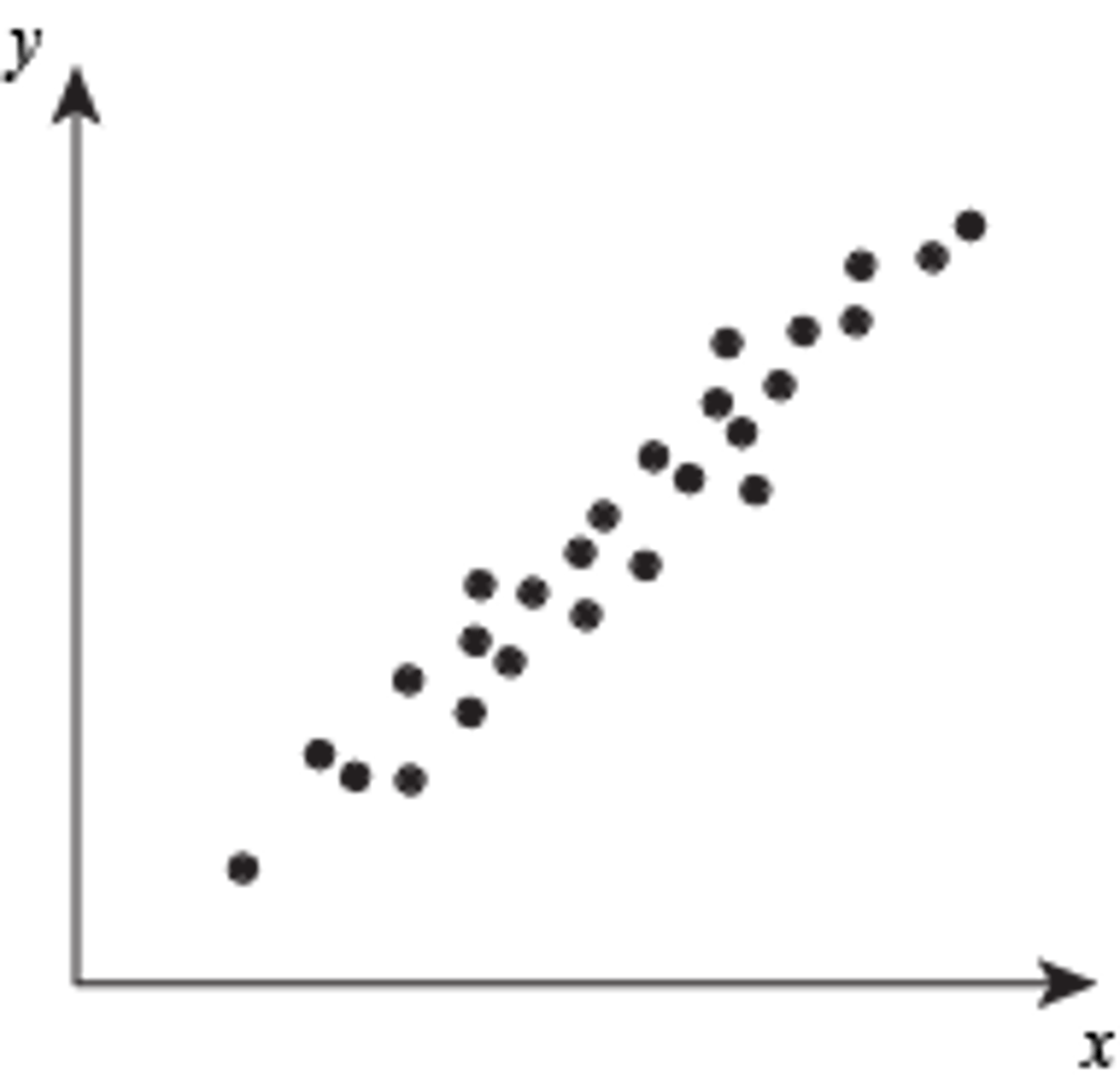
Scatter Plot
A graph in the coordinate plane representing a set of bivariate data.
Significant Digits
The digits in a decimal number that carry meaning contributing to the precision or accuracy of the quantity.
- All digits you record for a measurement are considered significant
- Include all certain digits in a measurement and one uncertain or estimated digit
Standard Deviation
The distance of a value in a population (or sample) from the mean value of the population (or sample).
Statistics
Collection of methods for planning experiments, obtaining data, organizing, summarizing, presenting, analyzing, interpreting, and drawing conclusions based on data.
Unit
A standard quantity in terms of which other quantities may be expressed.
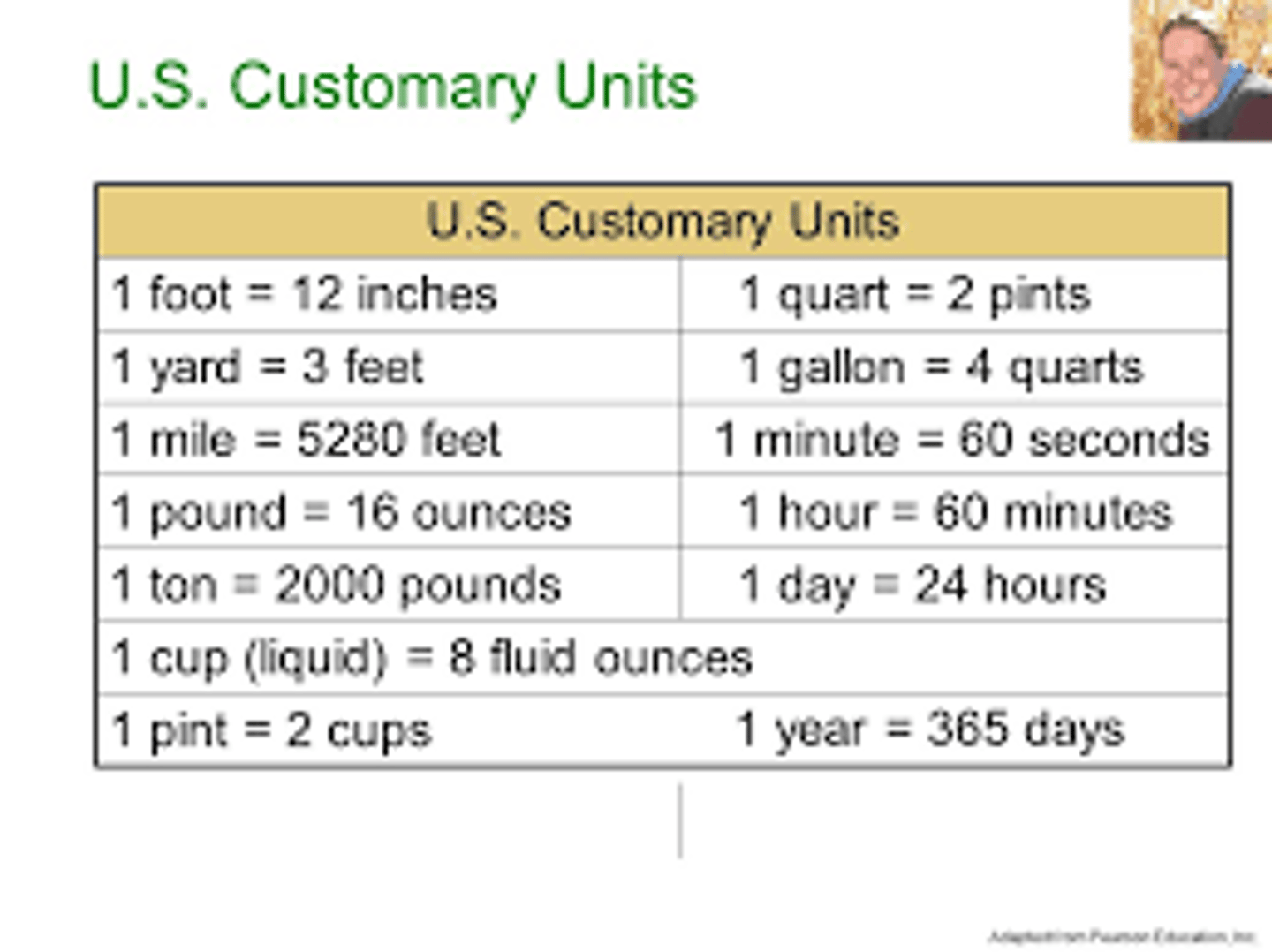
US Customary Measurement System
System of measurement used in the United States.
Variation
A change or slight difference in condition, amount, or level.
General Rules of Significant Digits
Digital Instruments - Read and record all digits, including zeros after the decimal point, exactly as displayed
Decimal Scaled Instruments - Record all digits that you can certainly determine from the scale markings and estimate one more digit
Metric Scale
A typical metric scale often includes a 30+ centimeter graduated scale
- Each centimeter is graduated into 10 millimeters
Millimeter
the smallest increment found on a typical metric scale; one thousandth of a meter
- the next larger marking on a metric scale shows 5 millimeters
Fractional Length Measurement
A typical ruler provides:
- A 12 inch graduated scale in US Customary units
- Each inch is graduated into smaller divisions, typically 1/16" increments
Dial Caliper Measurements
-outside diameter of object thickness
-inside diameter or space within
-step distance
-hole depth
Section View
- Provides a view of an object as if it were cut by a saw
- Location is indicated by a cutting plane line on another view
Cutting Plane Line
- Indicates location of the cut
- Thick and broken line
- Arrows indicate direction of view
- Labeled with a letter for identification on drawing
Section Lines
- Section lines
- Hatch lines that indicate material that was "cut" at the cutting plane line
- Thin lines
Dimensioning Guidelines
1. Dimensions should reflect actual size of the object, not the scaled size.
2. Include overall dimension in the three principle directions - width, height, and depth. (Overall dimensions should be placed the greatest distance away from the object so that intermediate dimensions can nest closer to the object.)
3. Include all dimensions necessary to produce or inspect the part.
4. Do not include unnecessary dimensions. (Dimensions should NOT be duplicated or the same information given in two different ways.)
5. Dimensions should be attached to the view that best shows the contour of the feature to be dimensioned.
6. A dimension should be attached to only one view; for example, extension lines should not connect two views.
7. Whenever possible, locate dimensions between adjacent views.
8. Avoid dimensioning to hidden lines.
9. Do not place dimensions on the object unless it is absolutely necessary.
10. Do not cross a dimension line with another dimension line or with an extension line.
11. Avoid crossing dimension or extension lines with leader lines.
12. Leader lines point toward the center of the feature and should not occur horizontally or vertically.
13. Dimension numbers should be centered between arrowheads, except when using stacked dimensions, and then the numbers should be staggered.
14. In general, a circle is dimensioned by its diameter and an arc by its radius.
15. Holes should be located and sized in the view that shows the feature as a circle.
16. Holes are located by their centerlines, which may be extended and used as extension lines.
Central Tendency
The center of a distribution: mean, median or mode
Variation (statistics)
Spread of values around the center
- Range, standard deviation, interquartile range
Distribution
Summary of the frequency of values
- Frequency tables, histograms, normal distribution
Rounding in Statistics
-Don't round until the final answer
-Mean and Standard Deviation round to one more decimal place than the original data