4. hemostasis
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Hemostasis
“arrest of bleeding”
Process of blood clotting, followed by dissolution of the clot once the injured
tissue is repaired
4 coordinated events in response to loss of vascular integrity (steps of hemostasis)
1. Vascular constriction
2. Platelet activation, adhesion, and aggregation → temporary, loose platelet plug
3. Coagulation → fibrin synthesis and formation of thrombus (clot)
4. Dissolution of the clot following tissue repair
Endothelial cells normally inhibit clot formation by Endothelial secretion of:
Prostacyclin (PGI2) + Nitric oxide (NO)
Prostacyclin (PGI2)
inhibitor of platelet function
Nitric oxide (NO)
vasodilator and inhibitor of platelet activation and aggregation
Endothelial cells normally inhibit clot formation by Expression of:
Heparin sulfate (HS)
Thrombomodulin (TM)
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI)
Heparin sulfate (HS)
activates antithrombin III
Thrombomodulin (TM)
changes the affinity of thrombin from procoagulation factors toward anticoagulation factors
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI)
inhibits TF-VIIa/Xa complex
primary vs secondary hemostasis
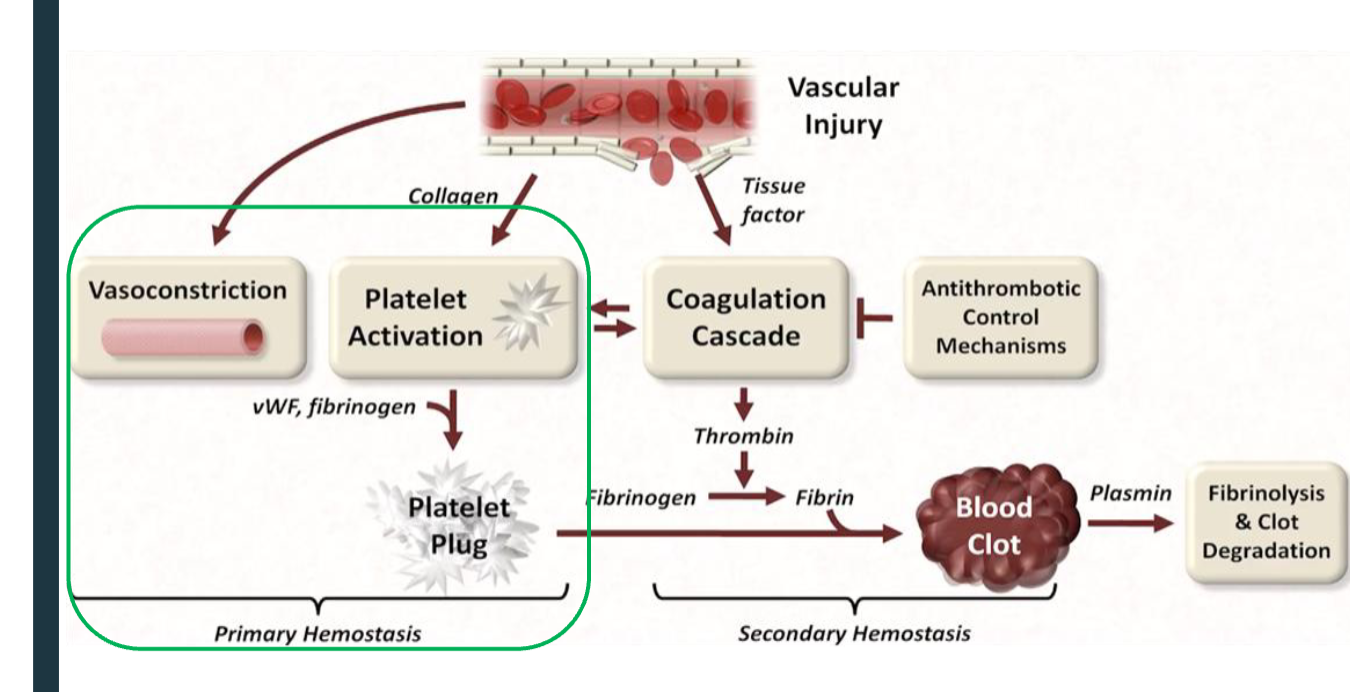
primary hemostasis: Vascular constriction
Immediate reduced blood flow to the injured area
Mediated by the local secretion of endothelin
Transient effect → bleeding resumes if clot is not formed
endothelin
potent endothelium-derived vasoconstrictor
Megakaryocytes
large cells produced in the bone marrow by endomitosis → single voluminous, polyploid cells
precursor of platelets
endomitosis
nuclear division without cytoplasmic division
how many platelets bud off from a single mature megakaryocytes + what stimulates this process
Approx. 4000
Stimulated by thrombopoietin
Platelets (thrombocytes) + life span
anuclear, lack most organelles, but have a complex cytoskeleton to maintain shape
Lifespan ~ 10 days
types of platelet cytoplasmic granules
dense
alpha
lysosomal
Dense platelet cytoplasmic graules
Ca2+, ATP/ADP, serotonin
Alpha platelet cytoplasmic granules contain
fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor (vWF), factor V
Lysosomal platelet cytoplasmic granules contain
hydrolytic enzymes
platelet membrane glycoprotein receptors:
GPIb
GPIa/IIa
GPIIb/IIIa
platelet membrane glycoprotein receptors: GPIb
binds to vWF immobilized on subendothelial collagen
platelet membrane glycoprotein receptors: GPIa/IIa
binds to collagen
platelet membrane glycoprotein receptors: GPIIb/IIIa
binds to free fibrinogen and vWF
von Willebrand factor
Large glycoprotein secreted by platelets (a-granules) and endothelial cells
Heterogeneous multimers linked by disulfide bonds
when are von Willebrand factors released + what occurs
Released from endothelial cells in response to damage
Forms a bridge between a glycoprotein complex on the surface of
platelets and exposed collagen fibrils
what do von Willebrand factors have binding sites for
Collagen
GPIb, GPIIb/IIIa
Factor VIII → transport and survival
Inherited deficiencies: von Willebrand disease
Most common inherited bleeding disorder (patient history before tooth extraction!!!)
Affects both platelet adherence and coagulation cascade (FVIII)
primary hemostasis: platelet actiation overview steps
platelets triggered
adhesion
secretion
shape change
aggregation
platelet plug formation
Platelet activation Triggers
Exposed subendothelial collagen
ADP – from platelet degranulation
TXA2 – secreted by activated platelets
Thrombin – from coagulation cascade
Adhesion
refers to the platelet-subendothelial interaction at the site of injury
GPIb binds to vWF immobilized on exposed collagen
GPIa/IIa bind to directly to collagen → conformational change to expose GPIIb/IIIa to bind more vWF and free fibrinogen
Secretion
degranulation of dense and alpha-granules
Release of ADP (potent platelet activator), vWF, serotonin (vasoconstrictor), Ca2+
Shape change
from discoidal to irregular with long pseudopods
Increased surface → increased ability to bind to other platelets
Expression of phosphatidylserine (PS)
Aggregation
recruitment of other platelets
Exposed GPIIb/IIIa bind to fibrinogen and vWF to form bridges with neighboring platelets
Platelet plug formation
3-5min
1. Platelet adhesion to exposed subendothelial collagen directly (GPIa/IIa) or mediated by vWF (bridge btw collagen and GPIb)
2. Adhesion followed by shape change and release of various procoagulants (ADP, TXA2, fibrinogen)
3. Secreted procoagulants aid in recruitment of additional platelets and promote their aggregation → primary loose hemostatic plug
secondary hemostasis: Coagulation
Series of amplifying enzymatic reactions that lead to the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot
coagulation factors
Major components are glycoproteins secreted primarily by the liver (except TF and Ca2+)
Most factors are synthesized in zymogen form and become active by proteolysis
Non-proteolytic factors (accessory proteins) are activated by conformational change
zymogen
inactive form that becomes active by proteolysis
accessory proteins are activated by
conformational change
Complex assembly
Negatively charged phospholipid phosphatidylserine (PS) on activated platelets and injured endothelial membrane
Ca2+ binds to g-carboxylated glutamate residues in factors II,
VII, IX, and X
g-carboxylation of glutamic acid
posttranslational modification of 9-12 glutamate residues (N-term)
Vit. K coenzyme needed
hydroquinone (functional vit K) is oxidized to vit K epoxide, which is reduced to regenerate hydroquinone by Vit K epoxide reductase (VKOR)
Warfarin
anticoagulant
synthetic Vitamin K analog inhibits VKOR
Vitamin K
dietary fat-soluble
2 forms: Phyloquinone (K1) + Menaquinone (K2)
Vitamin K: Phyloquinone (K1)
in green vegetables
Vitamin K: Menaquinone (K2)
produced from K1 by gut bacteria
Coagulation cascade
initiation
amplification
propagation
Coagulation cascade: 1. initiation
extrinsic/ TF-pathway
Tissue factor is available when injury occurs
binds to circulating FVII, which is activated (TF-FVIIa)
TF-FVIIa activates FX to FXa
Initiation of signal by injury, but insufficient Xa production
Where is tissue factor (TF) produced?
in vascular adventitia
Coagulation cascade: 2. amplification
intrinsic/ contact activation pathway
Thrombin activates FV, FVII, FVIII, FXI, FXII
FIXa complexes with FVIIIa (bound to vWF to increase its half-life) to
activate FXFXa triggers an explosion of thrombin generation (4000x amplification of signal)
Coagulation cascade: 3. propagation
common pathway
FXa activates prothrombin to thrombin (FIIa)
Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin
Fibrinogen
3 pairs of polypeptides (Aa, Bb, g2) covalently linked at the N-termini by disulfide bonds
how is fibrin formed
Thrombin cleaves fibrinopeptides A and B from fibrongen → monomers of
abg2 (fibrin)
weak fibrin mesh
Fibrin spontaneously aggregates in a regular array
insoluble fibrin clot formation
Thrombin activates FXIII to FXIIIa
FXIIIa = transglutaminase that forms cross-links between fibrin monomers → insoluble fibrin clot
overview of hemostasis
1. Release of clotting factors from damaged endothelial cells and activated platelets at the injury site → temporary platelet plug
2. Cascade of chemical reactions → formation of thrombin
3. Formation of fibrin and trapping of blood cells → insoluble blood clot
Clot propagation termination 2 mechanisms:
Antithrombin (antithrombin III)
Protein C pathway
Clot propagation termination mechanisms: Antithrombin (antithrombin III)
Serine protease inhibitor (Serpin) which inactivates thrombin, VIIa, IXa, Xa, and XIa
Activated by heparin
Clot propagation termination mechanisms: Protein C pathway
Endothelial thrombomodulin induces conformational change in thrombin
Altered thrombin is incapable of activating platelets or converting fibrinogen to fibrin, but can activate protein C
Activated protein C + cofactor protein S inactivates Va and VIIIa
Fibrinolysis
process of clot dissolution
Plasminogen is activated by conversion to plasmin by t-PA (tissue plasminogen activator) secreted from vascular endothelial cells and u-PA (urokinase) secreted by a variety of cells
Plasmin cleaves fibrin (and other clotting factors) at multiple sites, releasing fibrin fragments (D-dimers)
Inhibitors of fibrinolysis include:
Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1)–inhibits t-PA
α2-Antiplasmin (α2AP) = plasma protein -rapidly inhibits free plasmin