Macromolecules
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Carbon atoms have [ ] electrons but [ ] valence electrons that can form strong _______ bonds.
6; 4; covalent
Carbon can bond to _____________ making unlimited chains with ________, _________, or ___________ bonds.
other carbon atoms; single; double; triple
Cells build (most) macromolecules by taking small molecules and putting them in long chains called ___________.
polymers
Monomers form polymers by _________ bonds. This is called ___________.
covalent; polymerization
Function of carbohydrates
Main source of short term energy. It is also the main energy source for the body.
Carbohydrate Elements
1 Carbon, 2 Hydrogen, 1 Oxygen
Carbohydrate Monomers
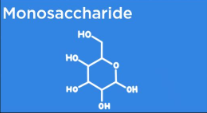
Monosaccharides (single sugars)
Carbohydrate Polymers
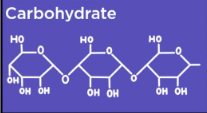
Polysaccharides (3 or more monosaccharides put together)
Examples of carbohydrates
Cellulose (plants), glycogen (animals), bread, potatoes, corn, pasta

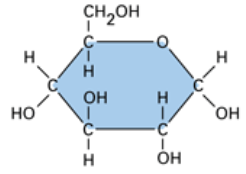
Carbohydrate structure
Ring form or linear form (but most commonly ring form, where it looks like either a hexagon or a pentagon)
Lipid function
Long term energy storage, protection, insulation, buoyancy
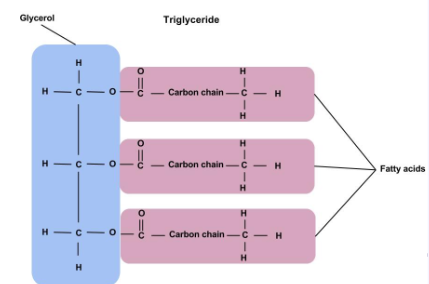
Lipid monomers
Fatty acids and glycerol (but not a true monomer because they lack a single repeating unit that forms the basis of their structure)
Lipid polymers
NONE- we just call them lipid monomers
Lipid Elements
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (although the phosphate head of a phospholipid is an exception, as it has nitrogen and phosphorus in it)
Examples of lipids
Cholestrol, hormones, phospholipids, steroids, waxes, oil, butter

Saturated fatty acids
Usually solid at room temperature (think butter), usually found in animal products like meat and dairy, has SINGLE BONDS
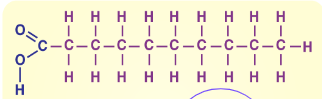
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Usually liquid at room temperature, found in plant products like nuts, oils, and fish, has DOUBLE bonds that usually depicted as BENT
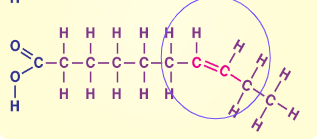
Lipid structure
Looks like a letter “E” (when the phosphate head is not included in the diagram).
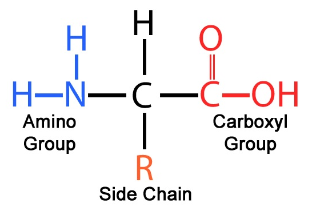
Protein functions
Control reactions, regulate cell function, form bones and muscles, fight/prevent diseases, transport substances
Protein elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen (CHON)
Protein Monomers
Amino acids (joined by peptide bonds)
Protein polymers
Polypeptides
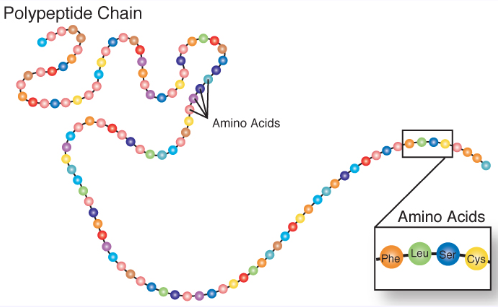
Protein examples
Enzymes, hemoglobin, antibiotics, hormones, eggs, tofu, nuts, beans, meat, fish

Nucleic acid function
Stores genetic information and protein synthesis
Nucleic acid elements
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus (CHONP)
Nucleic acid monomers
Nucleotides
Nucleic acid polymers
Nucleic acids
Examples of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
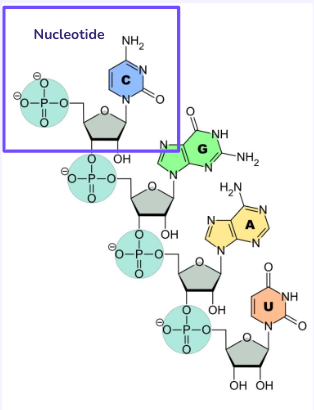
Nucleic acid structure
Has phosphorus, a nitrogenous base, and deoxyribose or ribose sugars
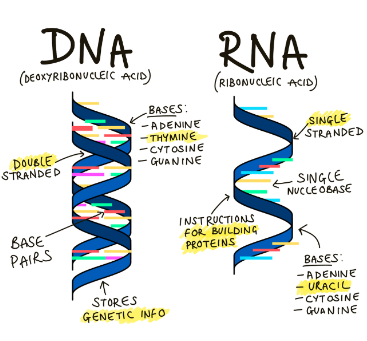
Differences between DNA and RNA
DNA is double stranded and has the nitrogenous bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. RNA is single stranded and has the nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, and cytosine, but instead of thymine, has uracil.
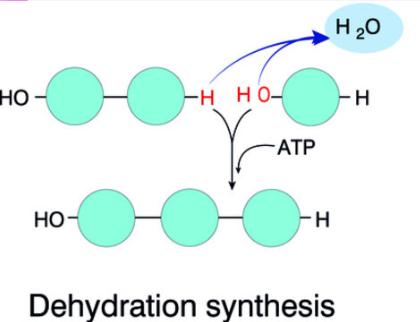
How polymers form
Dehydration synthesis: An H+ and OH- are removed to form polymers and water (the water is like a product)
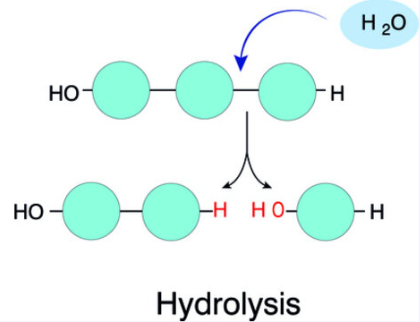
How polymers break apart
Water is ADDED to break polymers. Hydro = water. Lysis = break.