Ch 6, Part 3: Chr. MT's: Variation in #/arrangement (OCT 1st)
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part III: How do major changes in chromosomal structure take place, and what are the implications of such changes?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Why would chromosomes vary in structure and content”
what is the natural and catastrophic means
when is it most visible
Breakage and Fusion
Natural means:
-breakage and fusion mechanisms of recombination in meiosis I
-DNA repair mechanisms
Catastrophic:
-spontaneous breakage due to radiation, free radicals followed by
attempted repair
Most visible in metaphase I homologous mispairing
Describe deletion
A piece of a chromosome breaks off and is not replicated
-only portions that retain the centromere tend to be replicated
Describe terminal deletion
When one end is lost
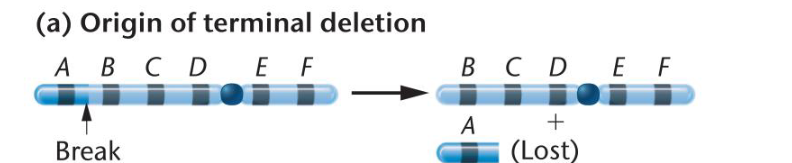
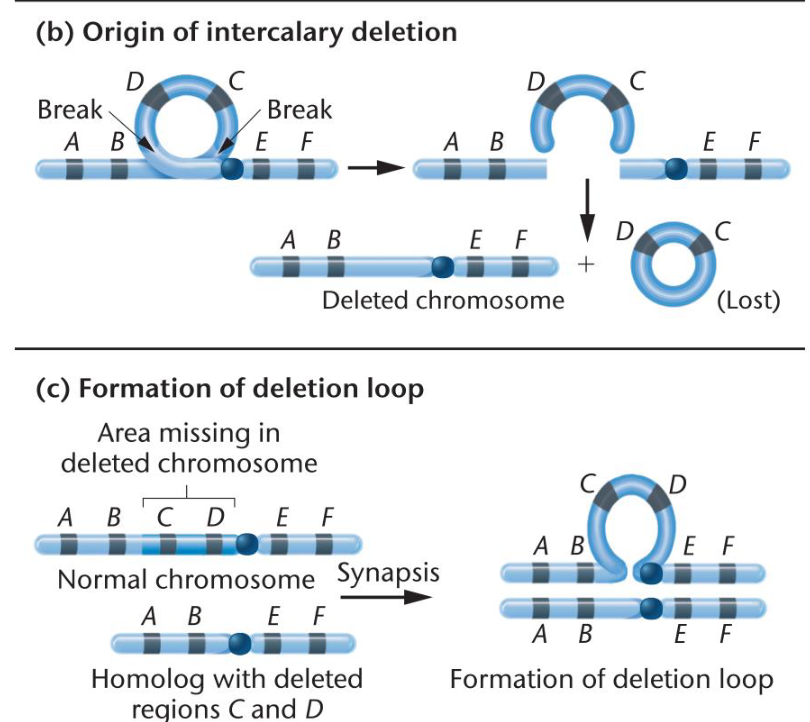
Describe intercalary deletion
When internal segment is lost
-intercalary deletion results in deletion loop in metaphase I
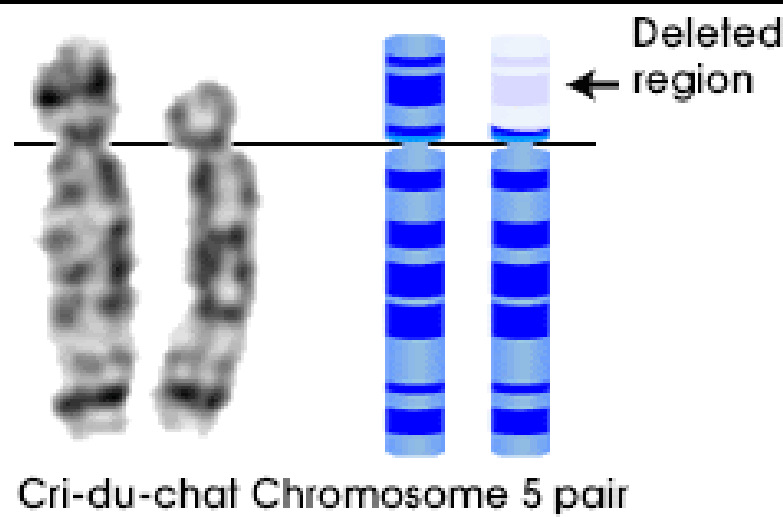
Describe Cri du Chat syndrome
(deletion mutation)
-Partial deletion of short arm on chromosome 5
-Not inherited; deletion occurs in gametes
-Dominant
-1 in 20,000–50,000 live births
-Severity of syndrome varies with length of deletion.
what are the symptoms of Cri du Chat syndrome
Abnormalities in glottis and larynx
Cry similar to cat’s meowing.
Intellectual disability
Delayed development
Small head size
Describe duplication mutation…
where is duplication loop
It’s the unequal crossing over in meiosis results in one chromosome with duplicated segment and one chromosome with intercalary deletion
-duplication loop in heterozygote
why can duplications be selectively favored mutations
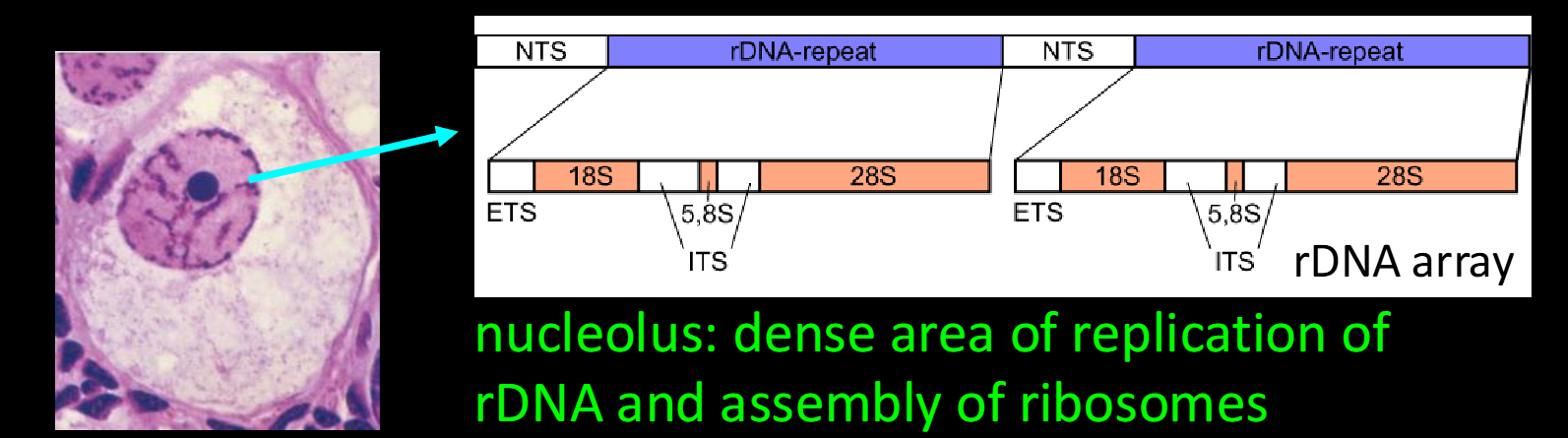
define nucleolus
Duplications as selectively favored mutations: essential structural genes may exist in MANY copies so that enough expression products can be produced.
nucleolus: dense area of replication of rDNA and assembly of ribosomes
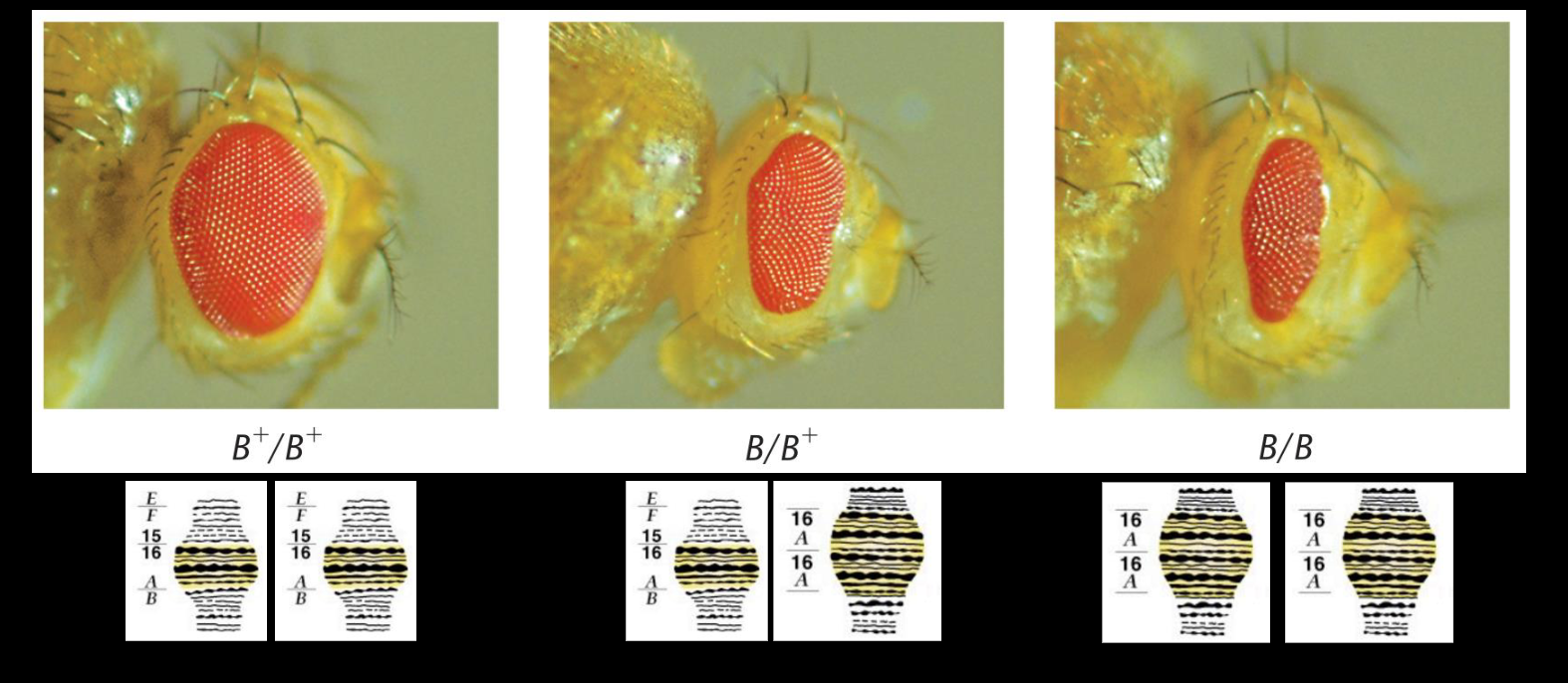
Describe bar-eye phenotype, duplication mutation
-Bar-eyes: narrow, slit-like eyes
-X-linked, incomplete dominant mutation from duplication
-Double-bar: double duplication
duplication and diversity
how do new genes arise?
-Gene duplication
-Initial change in dosage
-One performs essential function; other free to mutate
-Change in expression pattern or function is a source of novel variation
-Origin of gene families
Define HOX genes (duplication and diversity)
HOX genes encode regulation factors that set of expression cascades that have resulted in segmentation and tagmatization
define tagmatization
the evolutionary process in animals where repeated body segments fuse to form specialized functional regions called tagmata
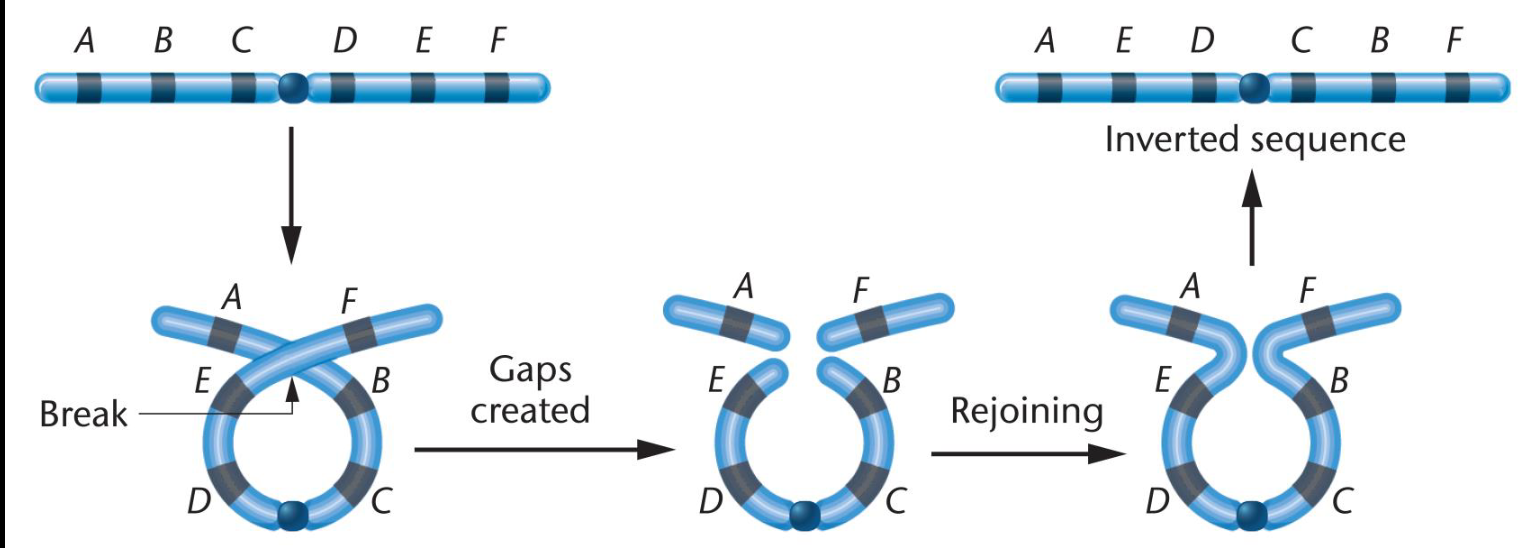
how do inversion mutations alter gene order?
-Segment of chromosome turned 180° within chromosome.
-Loop, two breaks, and repair
-Rearrangement of linear gene sequence.
-No loss of genetic information
Define (remember inversion mutations alter gene order)
-Paracentric inversion
-Pericentric inversion
-Paracentric inversion: does not include centromere
-Pericentric inversion: includes the centromere
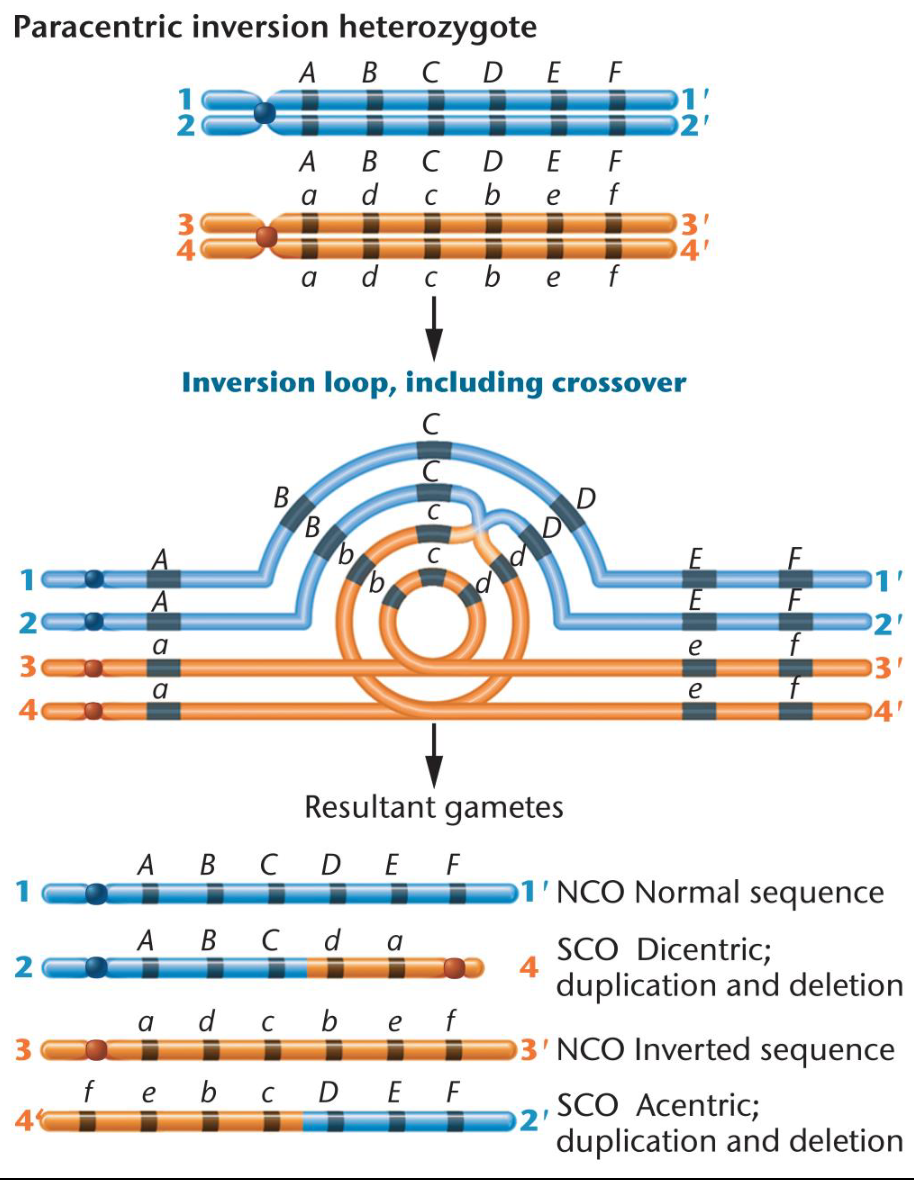
Inverstion mutations produce meiotic error
Inversion heterozygotes
-Organisms with one inverted chromosome and one noninverted homolog
-Pairing between these two chromosomes requires inversion loop
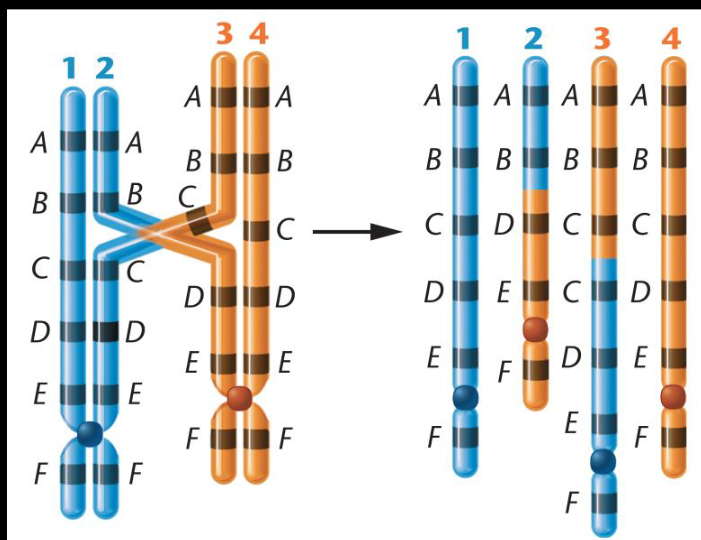
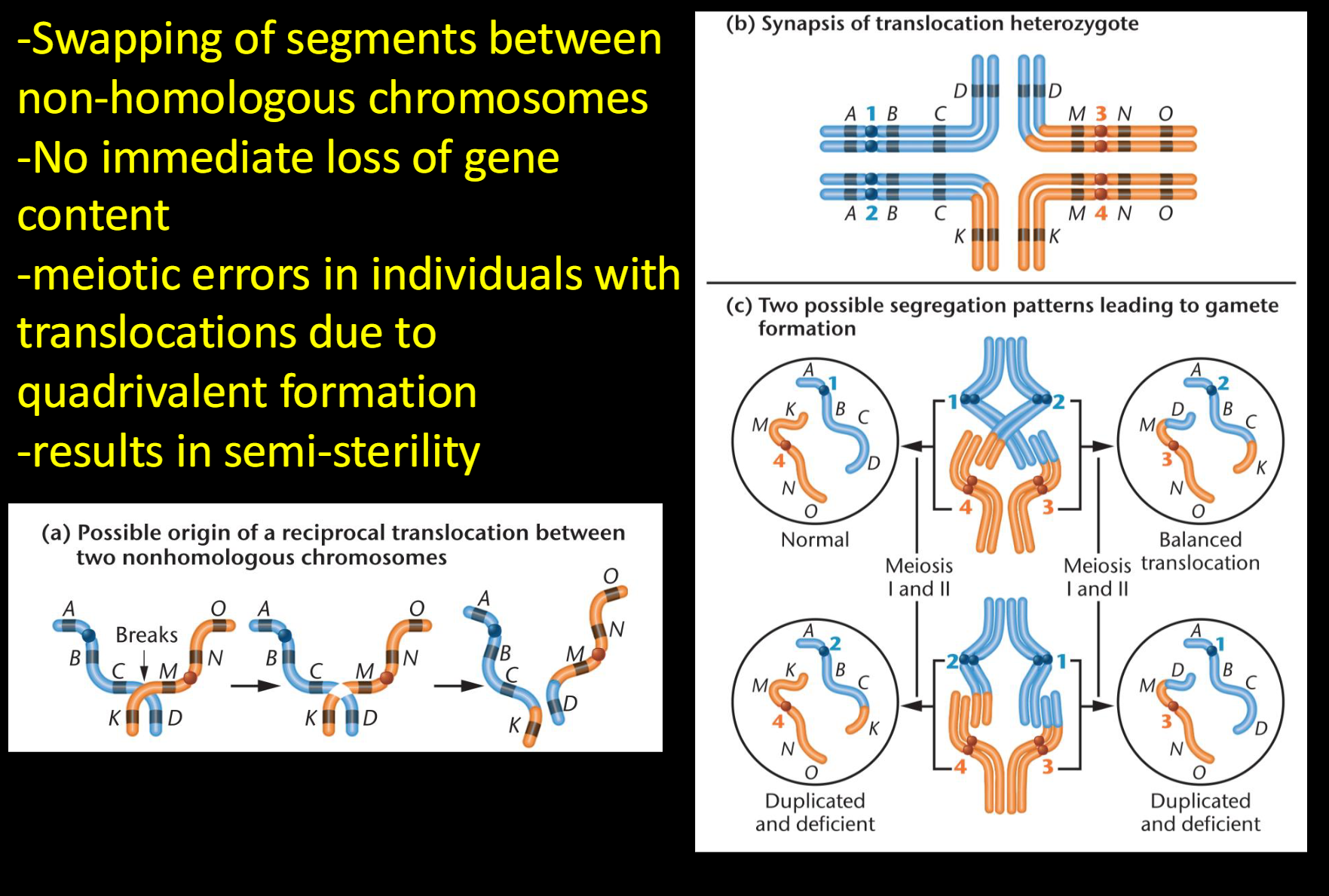
Define reciprocal translocation
-Swapping of segments between non-homologous chromosomes
-No immediate loss of gene content
-meiotic errors in individuals with translocations due to quadrivalent formation
-results in semi-sterility
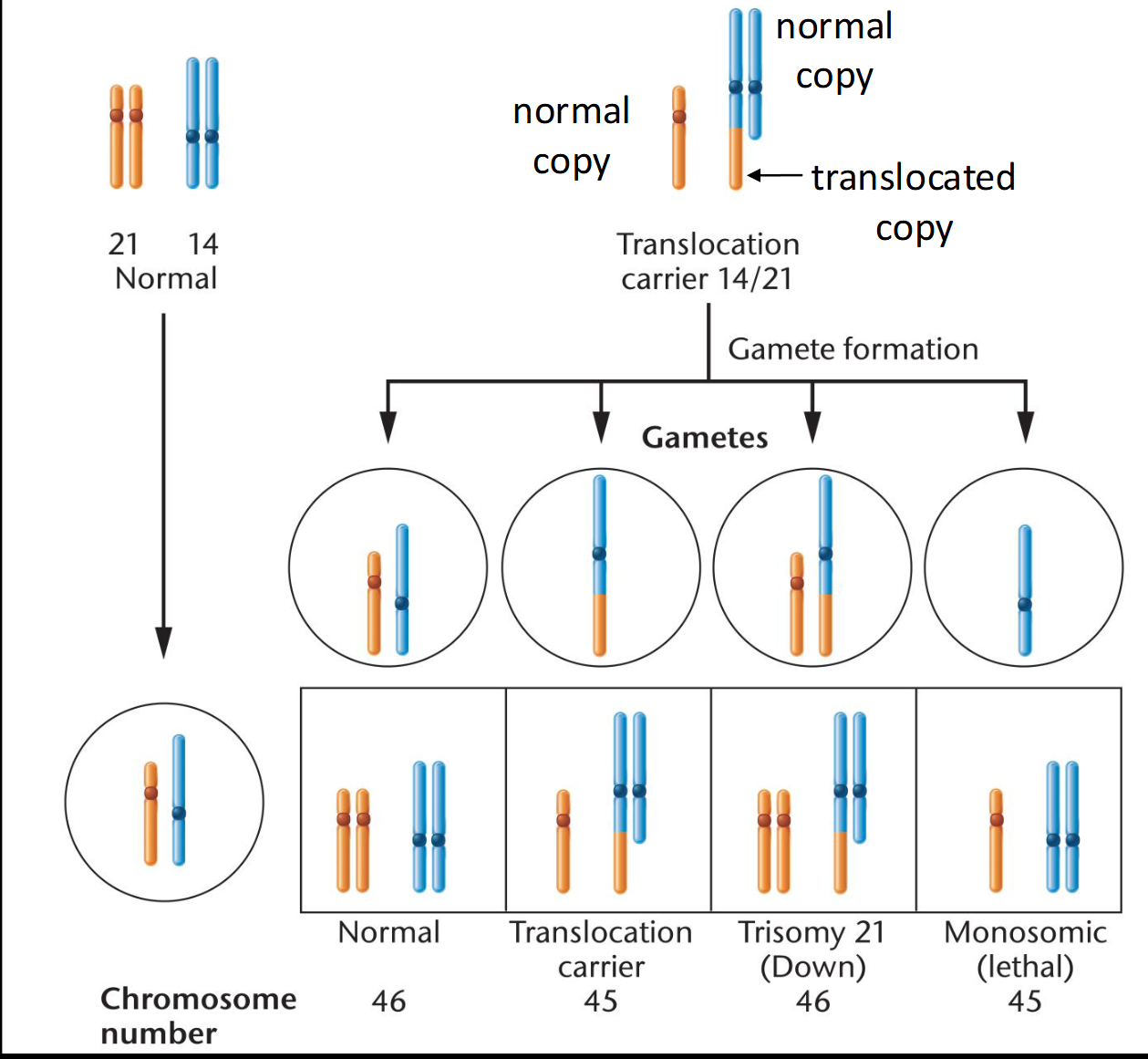
Define Robertsonian Translocation
-Non-homologous acrocentric chromosomes swap arms.
-One chromosome with two long arms and one chromosome with
two short arms.
-High chance for short chromosome to have no centromere, and
hence fragment is lost
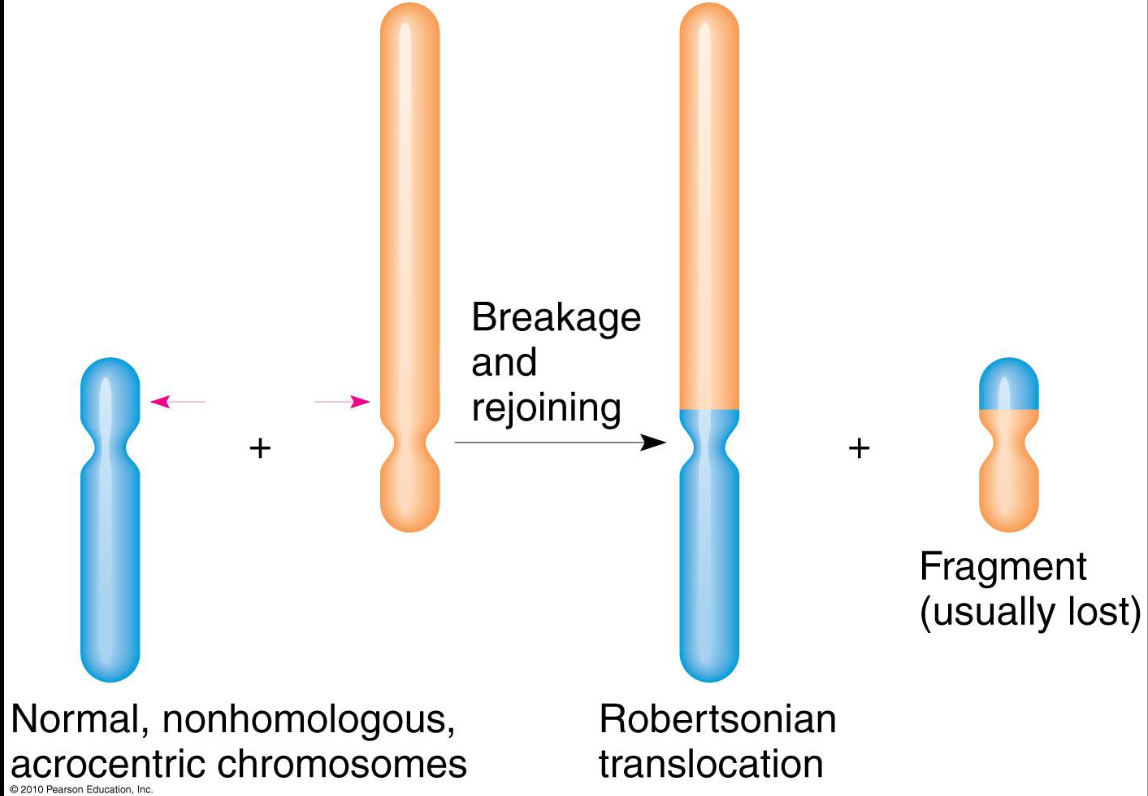
Draw
Robertsonian Translocation: Familial Down Syndrome