Personal finance SUCKS bruh so annoying
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
budget deficit
spending more than you take in (debt)
budget surplus
the government cullects more money than it spends
shriking economy
high unemployment, low GDP, low CPI
expanding economy
low unemployment, high GDP, high CPI
ecomonmic growth/ GDP ideal rate
2.5 - 3.5%
unemployment ideal rate
3.5 - 4.5%
Consumer Price Index/ CPI ideal rate
2%
expansionary policy
dececrease percentages, decrease unemployment
contractionary policy
increase percentages, increase unemployment
3 purposes of the Fed
Regulate payment system, regulate banks, set monetary policy
what is the FOMC
fed. open market committee - implements monetary policy. made up of 7 BOG, new york bank president, and 4 other bank presidents
San Francisco
Regional bank #12
BOG
7 board of governers, 14 yr terms
Who appoints the BOG?
Appointed by president, approved by senate
4 ways monetary policy is implemented
adjust the resrve requirement, adjust discount rate, OMO, adjust intrest rate
What is OMO
The Fed buys/sells govt. securities (like bonds)
What is the Federal Reserve?
the US central bank/ lender of last resort
3 parts of the Fed
7 BOG, 12 banks, FOMC
What does GDP stand for
Gross Domestic Product
Jerome Powell
current fed. chairman

Janet Yellen
current secretary of treasury

what is fiscal policy
governments policies to influence the economy
CPI meaning
consumer price index (measure of inflation)
Who’s the father of macroeconics
John Maynard Keynes
What is bank #2
New York, New York
What is M1
the narrowest measure of money supply
what is the federal funds rate
the rate banks charge each other (CANNOT be directly influenced by Fed. reserve)
when was the fed. reserve created
1913 (federal reserve act)
2 goals of monetary policy
limit employment & control inflation
what is money supply
the total amount of currency & liquid assets in circulation at a specific time
what is the MAIN way the FOMC implements monetary policy
adjusts the IROB & RRP to raise/lower the FFR target range
the Fed dual mandate
Maximum employment & price stability
what interest rates are raised/lowered by the Fed?
IORB, ON RRP, Discount rate (in turn affects the FFR)
what is arbitrage
the act of buying and selling simultaneously for profit
what is reservation rate
the lowest rate a buyer would accept
money multiplier equation
1 divided by Reserve requirement
what is reserve requirement
the amount of $ a bank must have in supply
Inflation is…
…too much money chasing too few goods
official name for US dollar
Federal Reserve Note
what manufactures coins
The US Mint
what prints dollar bills
The Bureau of Engraving & Printing
what is the majority of US revenue from
Individual Income Taxes
3 categories of expenditures
Mandatory, Discretionary, Interest
Nominal GDP vs real GDP
nominal is w/o adjustments, real gdp adjusts for inflation
Business cycle
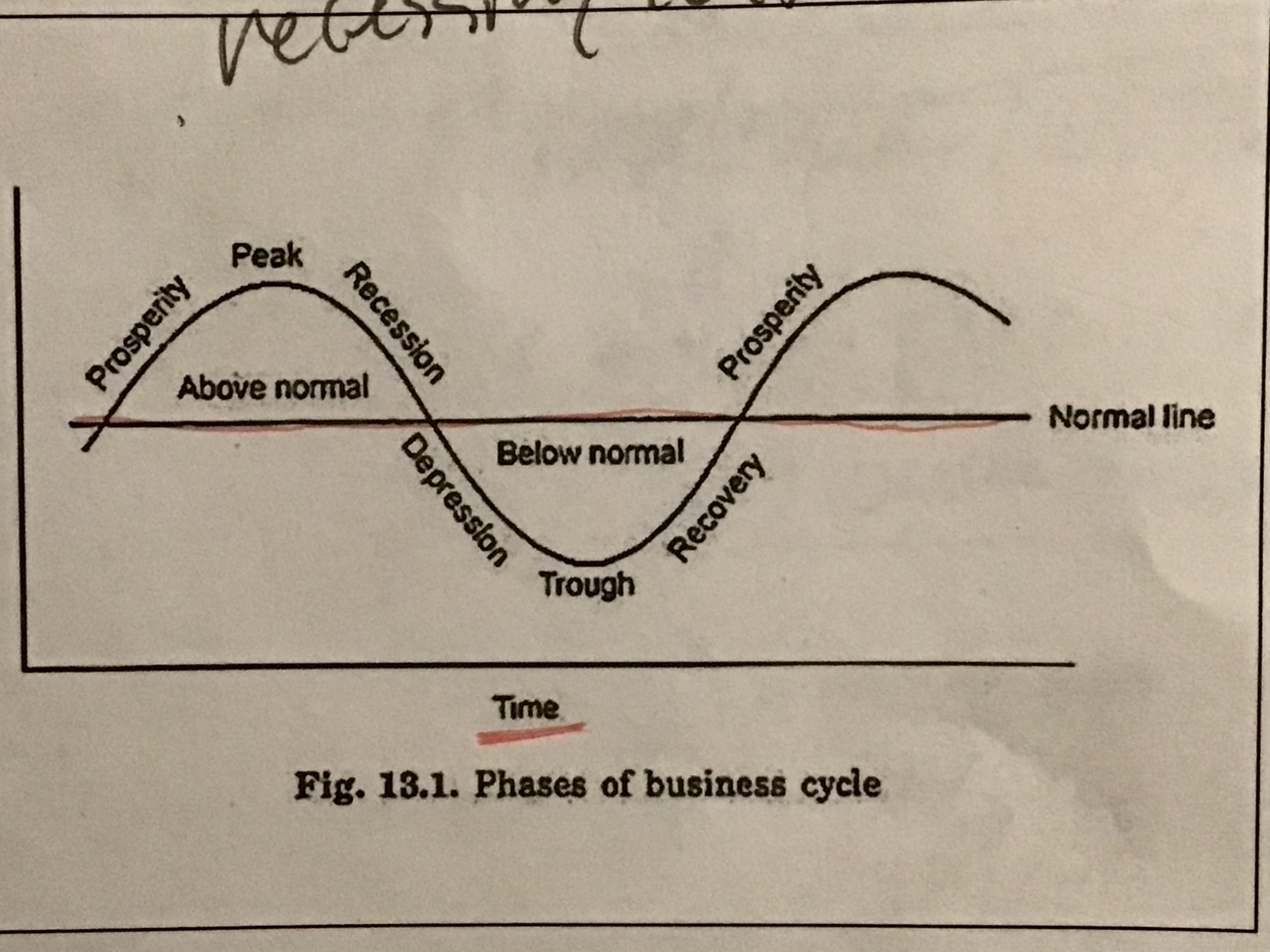
money is 3 things…
medium of exchange, unit of account, a store of value
6 characteristics of money
Divisible, Portable, Acceptable, Scarce, Durable, Stable
what is fractional reserve banking?
when the bank keeps a portion of each deposit then loans out the rest
what is FIAT money?
money backed by the people’s confidence. not by gold/silver
what is legal tender?
any currency declared legal by a government
how does the FFR influence us consumers?
it influences interest rates and borrowing