AP Macroeconomics Final Exam Cram Set (Read Description)
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Economics
Term that describes behavior science concerned with how scarce resources are allocated among unlimited needs, wants, and desires
Factors of Production
Term that defines land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship
Opportunity Cost
Term describing the highest value, foregone alternative to any decision made
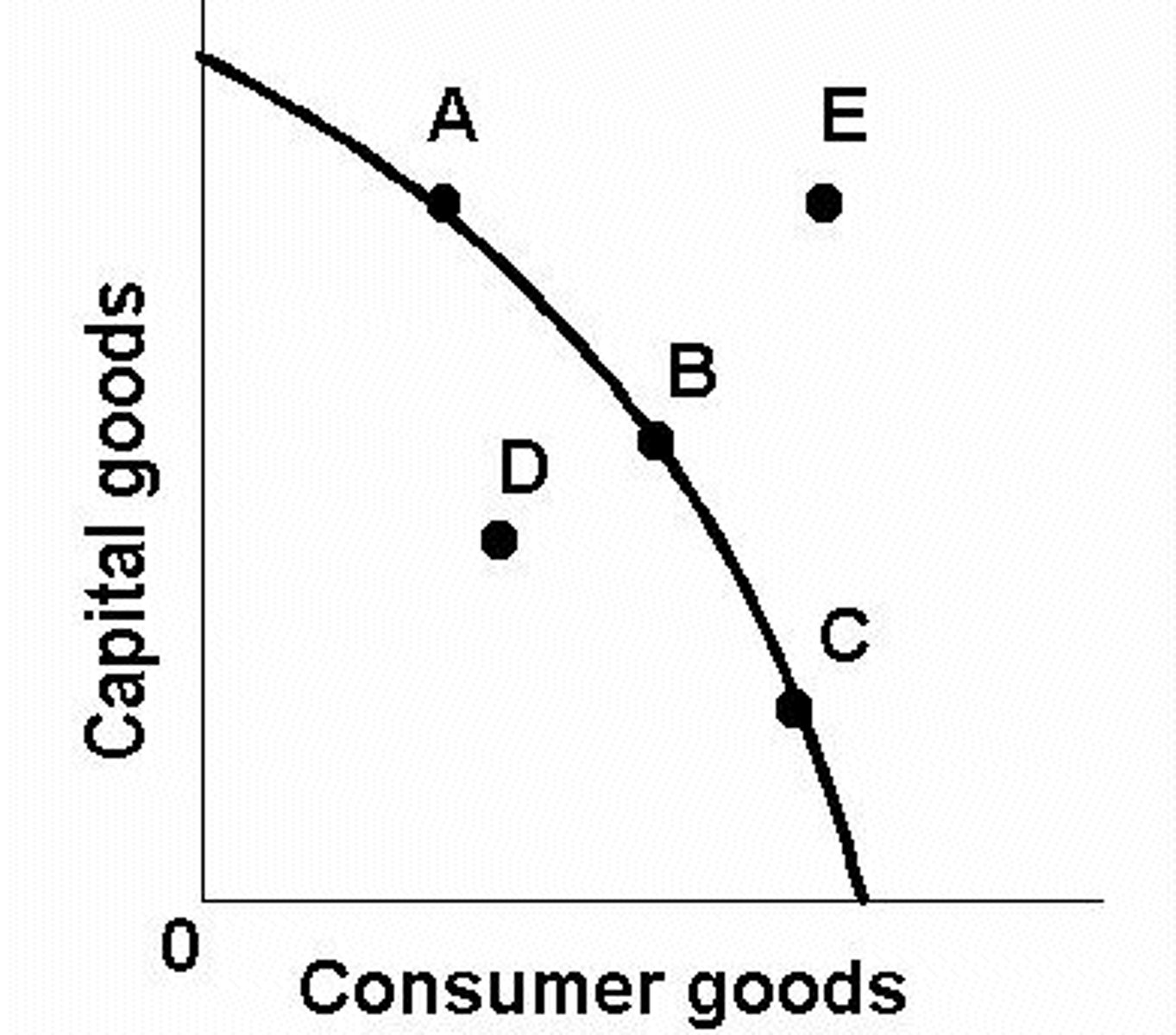
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
Graph describing a simplified model and economy producing only two goods or two categories of goods
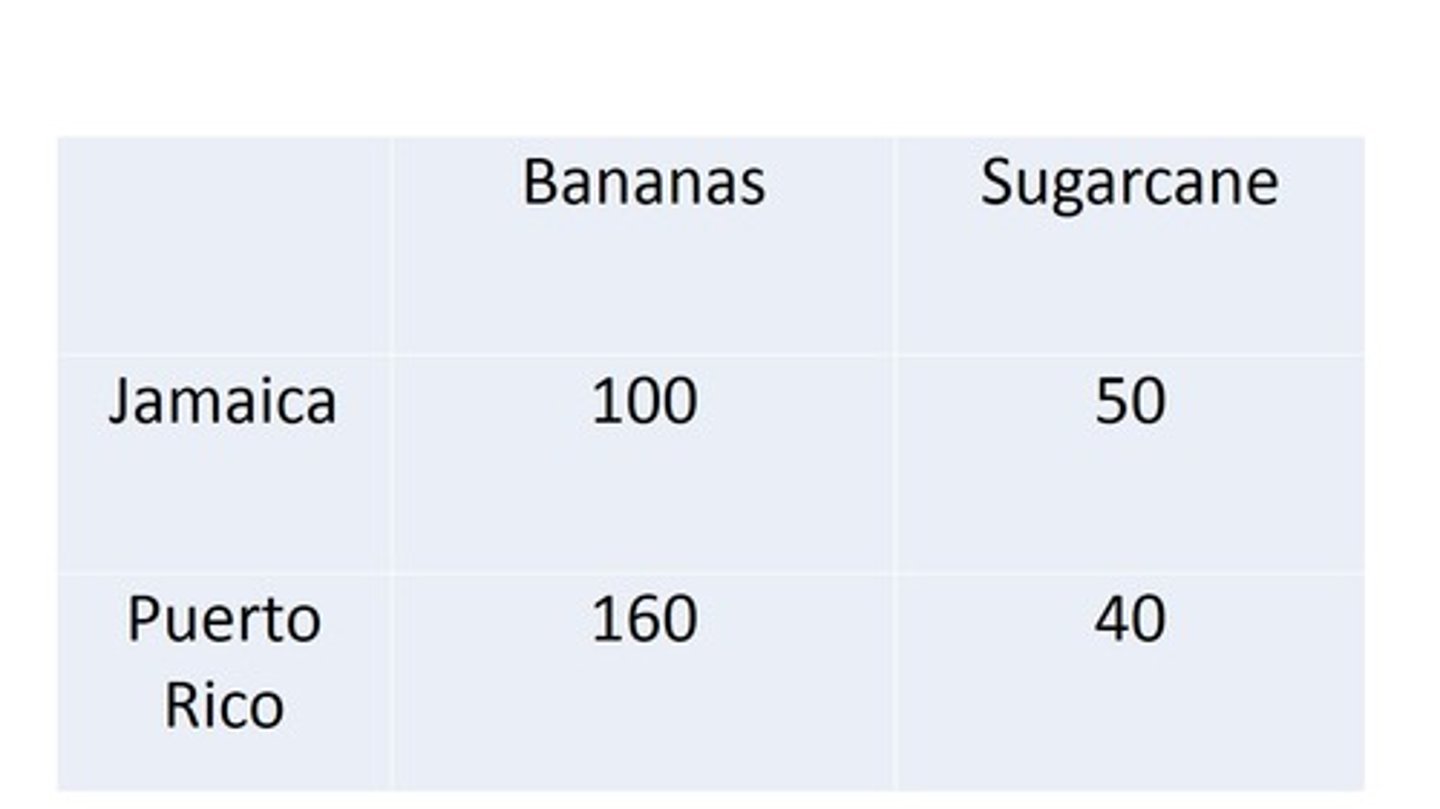
Absolute Advantage
Term for an advantage realized by the producer able to generate greater output with a given amount of time or resource
Comparative Advantage
Term for an advantage realized by the producer able to generate a given output at a lower opportunity cost
Jamaica
Who has absolute advantage in sugarcane?
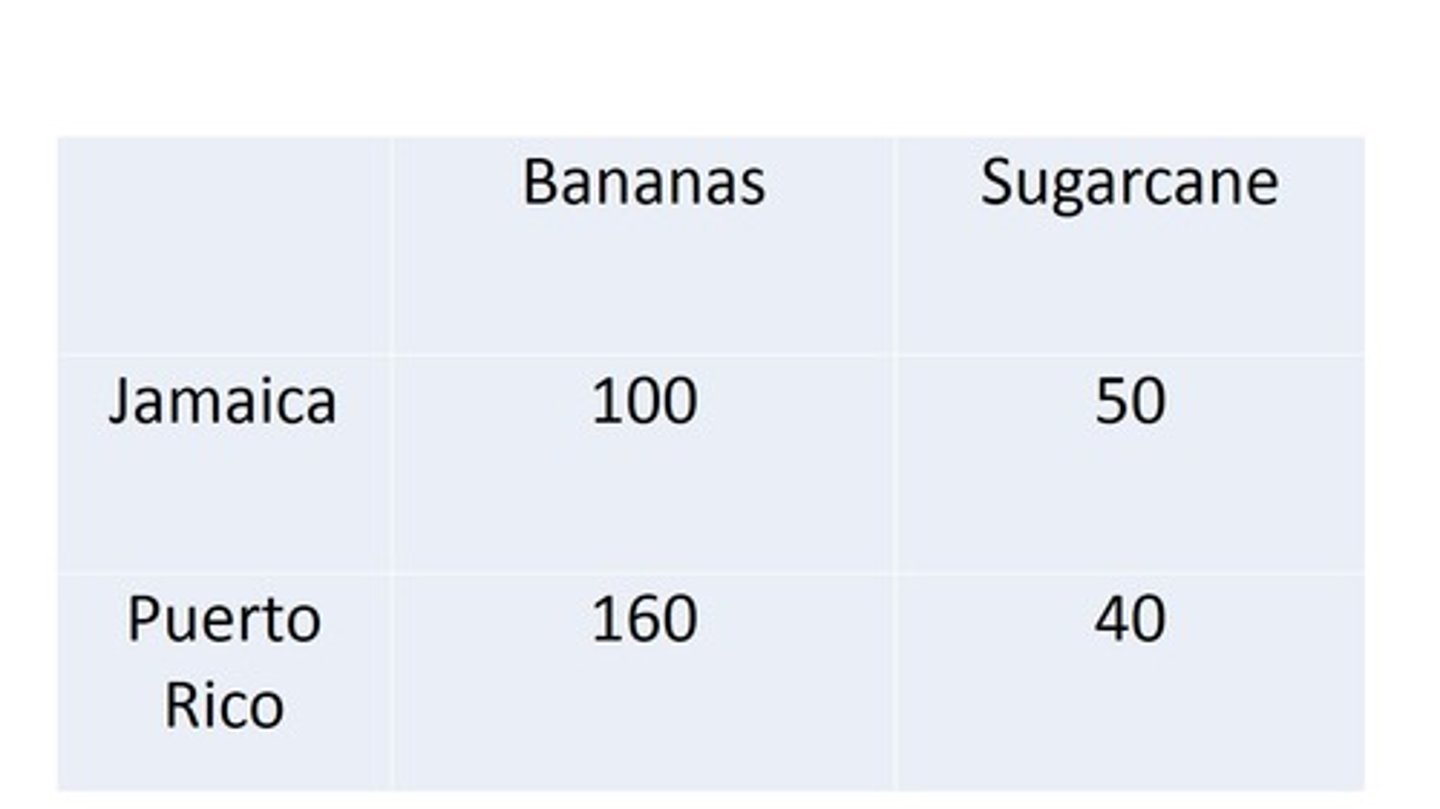
Puerto Rico
Who has comparative advantage in bananas?
Terms of Trade
Term describing an agreed upon exchange rate of two goods between 2 producers
Competitive Market
Term for a market in which there are many buyers and sellers at the same good or service, none of whom can influence the price at which the good or service is sold
Law of Demand
Other things being equal, as the price increases the corresponding quantity demanded decreases
Demand Curve
Term describing a graphical representation of demand in the competitive market which shows the relationship between quantity demanded and price
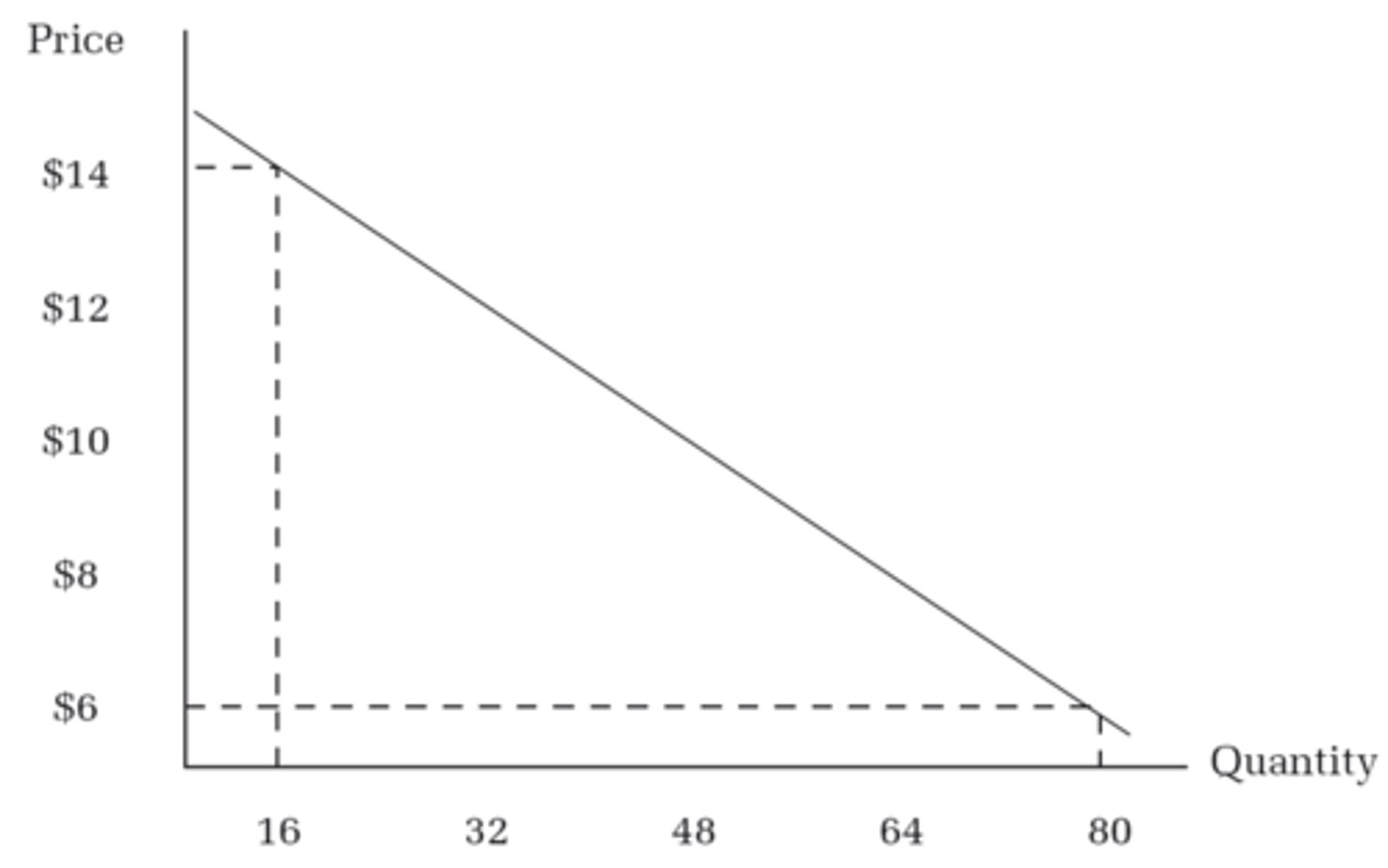
Things that affect demand
Market size, expectations, related prices, income, and tastes are all...
The Income Effect
Term describing that: if real income increases then demand increases if real income decreases then demand decreases
Substitution Effect
Effect that states that if prices change for a substitute of a specific product then it will affect demand for that specific product
Elastic Demand
Demand in which changes in price have large effects on the amount demanded
Inelastic Demand
Demand in which changes in price have little or no effect on the amount demanded
Things that affect supply
Technology, related prices, input prices, competition, and expectations are all...
Law of Supply
Other things being equal, the price and quantity supplied of a good are positively related (the higher the price, the more will be supplied)
Supply Curve
Term describing a graphical representation of supply in a competitive market, which shows the relationship between quantity supplied and price
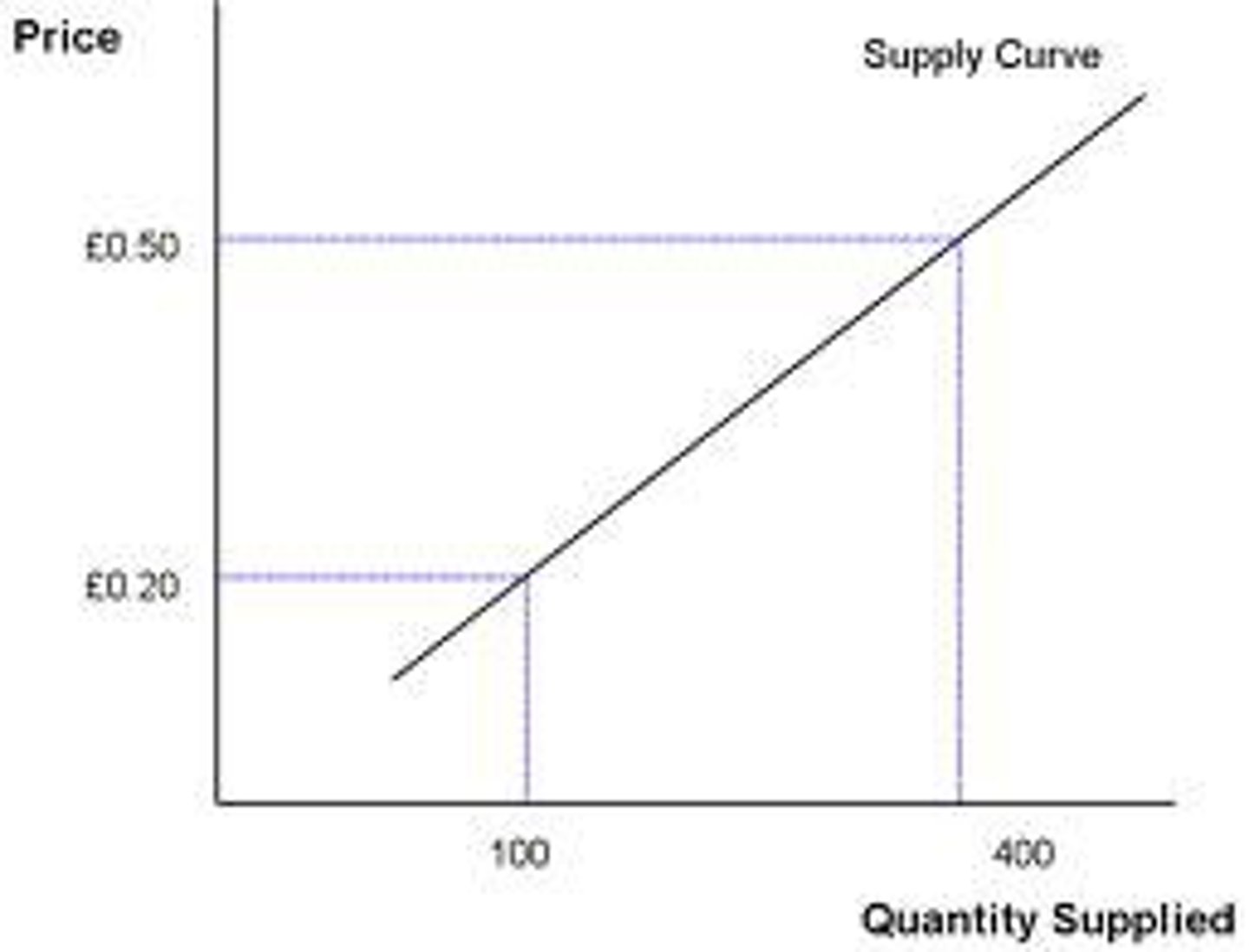
Surplus
Term describing what occurs when the price is above the equilibrium level
Price floor
A minimum price for a good or service
Shortage
Term describing what occurs when the price is below the equilibrium level
Price ceiling
Term describing a maximum price that can be legally charged for a good or service
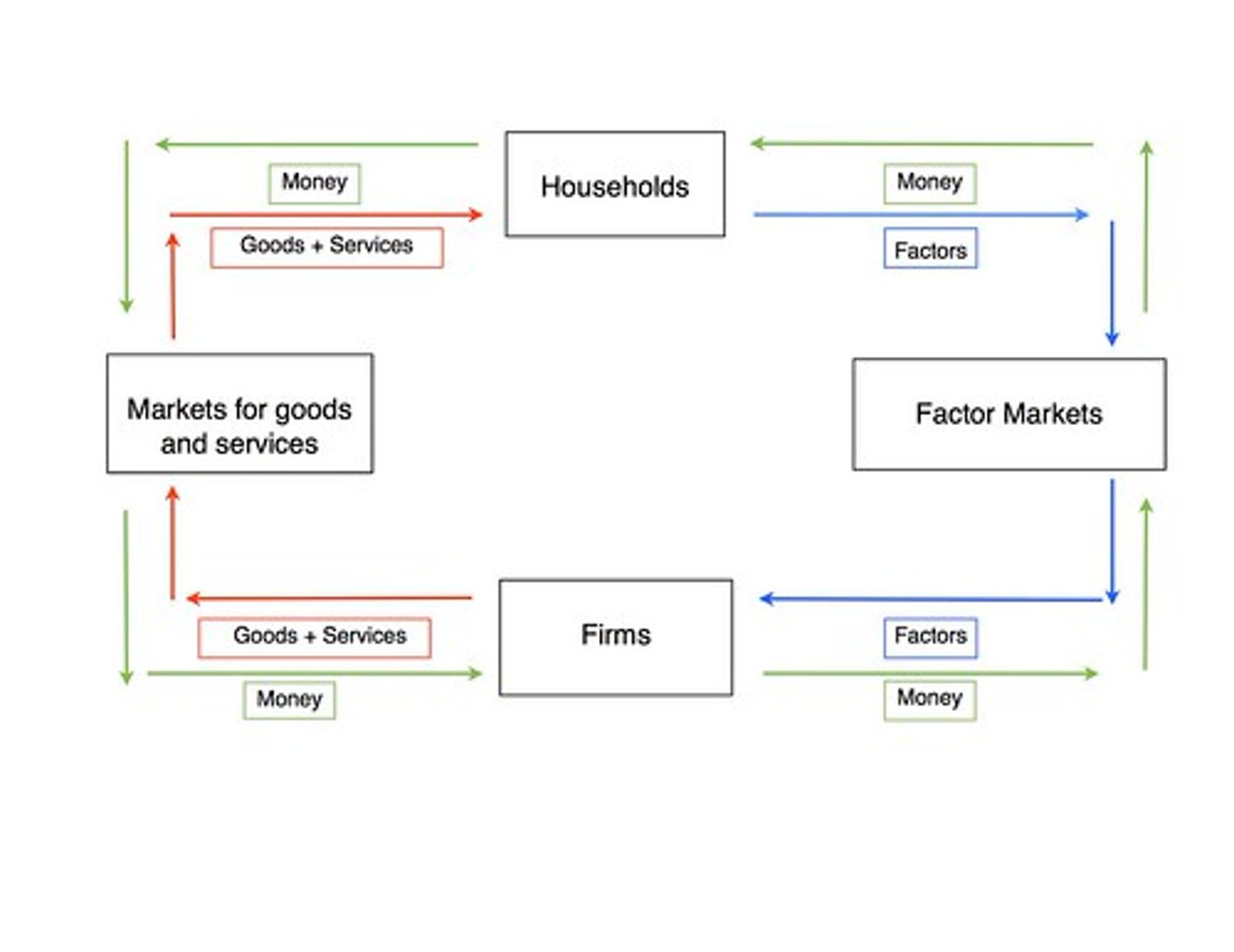
Circular Flow Diagram
Diagram describing how money flows through the economy
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Term describing the total market value of all final goods and services produced within the country in one year
Not included in GDP
Used or secondhand products, purely financial transactions, services provided for no money, intermediate goods and services, and foreign-produced goods and services are all...
Purely Financial Transactions
Term that describes transfer payments, such as social security, and stocks and bonds
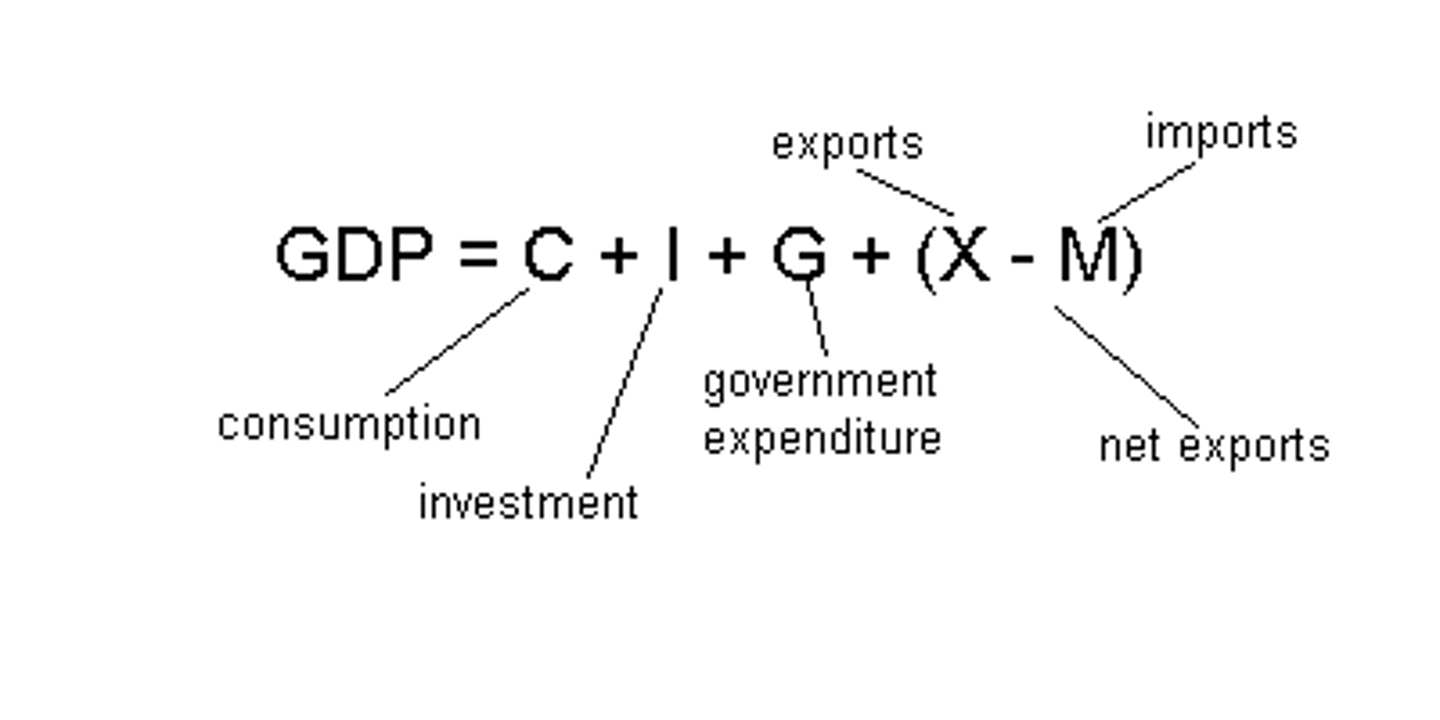
Expenditure approach of GDP
C + I + G + Xn
Employed
Term describing people who are currently holding a job in the economy, either full-time or part-time
Unemployed
Term describing people who are not working and looking for work
Labor Force
Term describing the sum of the employed and the unemployed - people who are currently working and people who are currently looking for work
Labor force participation rate
The percentage of the population, aged 16 and older, that is in the labor force
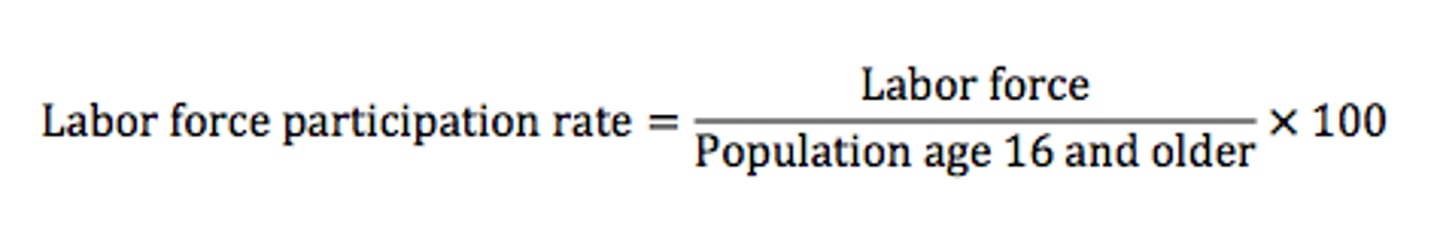
Unemployment rate
The percentage of the total number of people in the labor force who are unemployed

Discouraged workers
Term describing non-working people who are capable of working but have given up looking for a job due to the state of the job market, not included in the labor force nor the unemployment rate
Marginally attached workers
Term describing people who would like to be employed and have looked for a job in the recent past but are not currently looking for work, not included in the labor force nor the unemployment rate
Underemployed workers
People who work part-time because they cannot find full-time jobs
Frictional unemployment
Term describing unemployment due to the time workers spend in job search
Structural unemployment
Term for unemployment that occurs when workers' skills do not match the jobs that are available
Cyclical unemployment
Term describing unemployment caused by a business cycle recession
Natural Rate of Unemployment (NRU)
Frictional unemployment plus structural unemployment
Actual rate of unemployment
Natural rate of unemployment plus cyclical unemployment
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Term describing a measure of the average change over time in the price is paid by consumers for a fixed "market basket" of goods and services
Market Basket
Term that refers to the goods and services purchased by consumers
Consumer Price Index (CPI) formula
(Current Cost of Market Basket / Base Year Cost of Market Basket) x 100
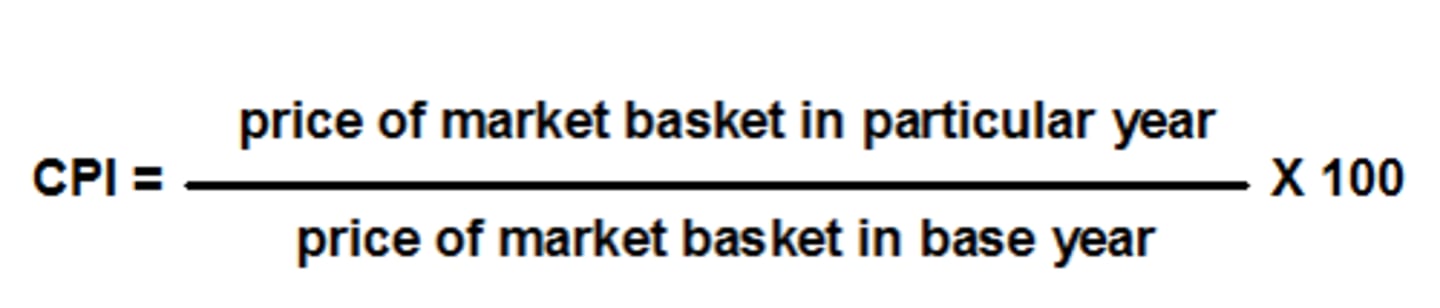
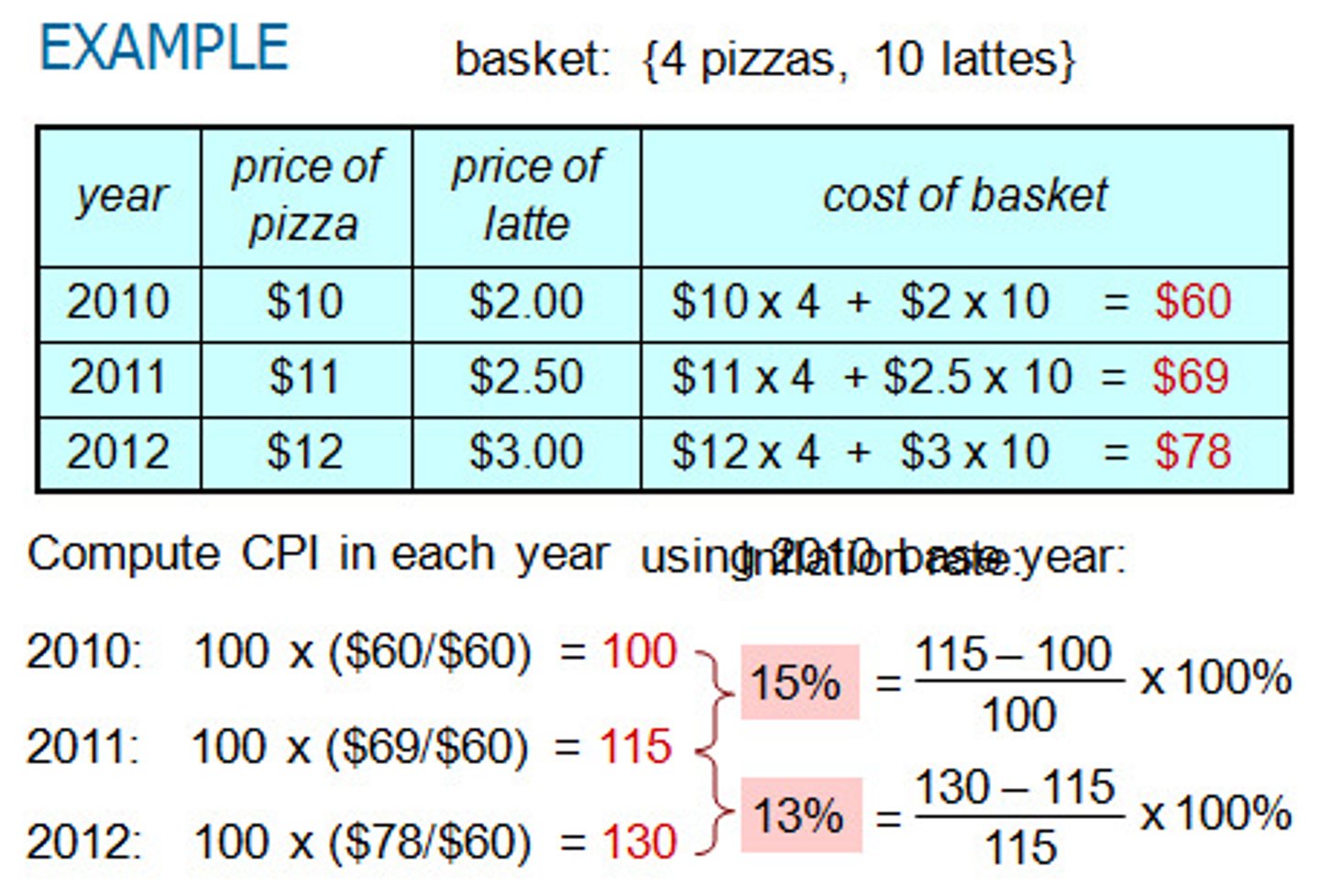
Sample Problem for CPI
Sample Problem for CPI
Nominal
Term describing variables that have NOT been adjusted for inflation
Real
Term describing variables that HAVE been adjusted for inflation
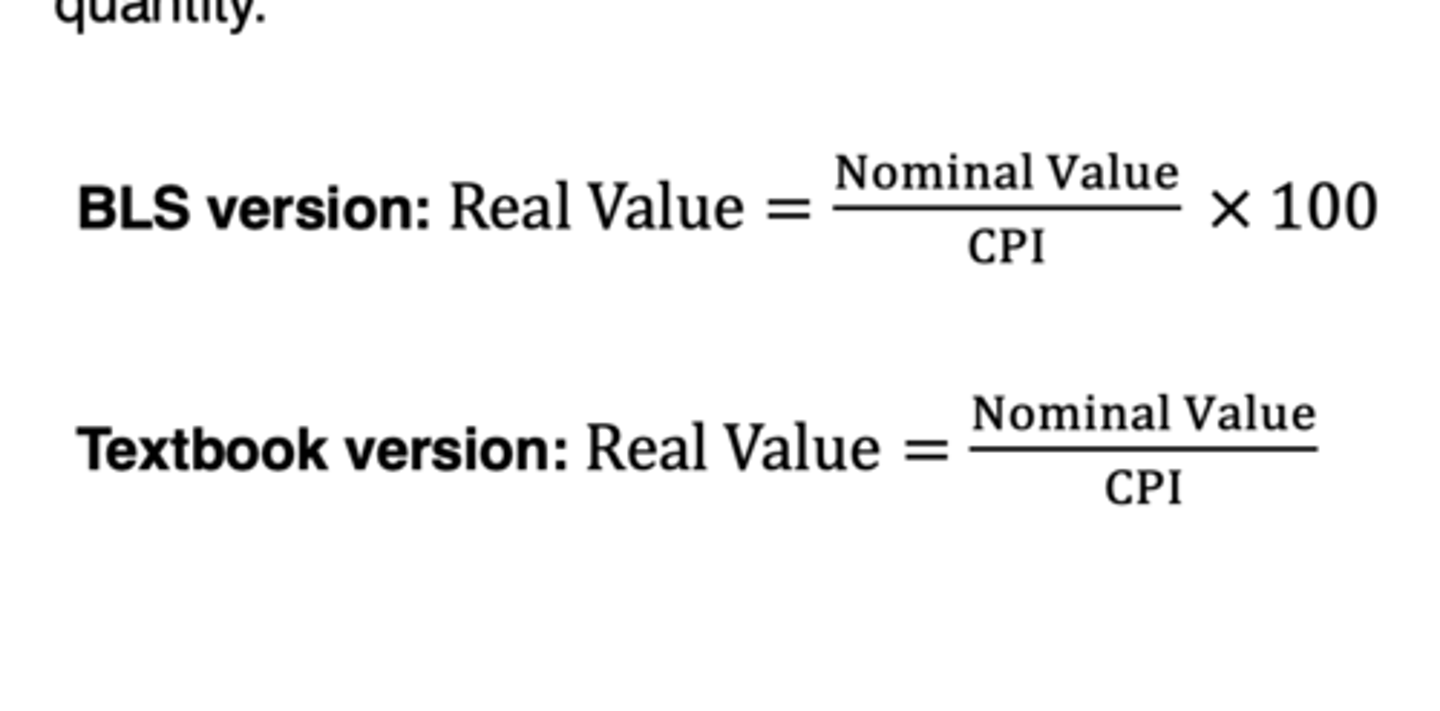
Real Value
Equation that describes how to deflate a nominal value using a price index
Shortcomings associated with the CPI
Substitution bias and introduction of new goods are both...
Unanticipated Inflation
Term describing that, when inflation is higher than expected the purchasing power of the given amount of money to be received in the future is lower than expected.
Equation for Nominal GDP
(PL * Y) where PL is price level and Y is Income
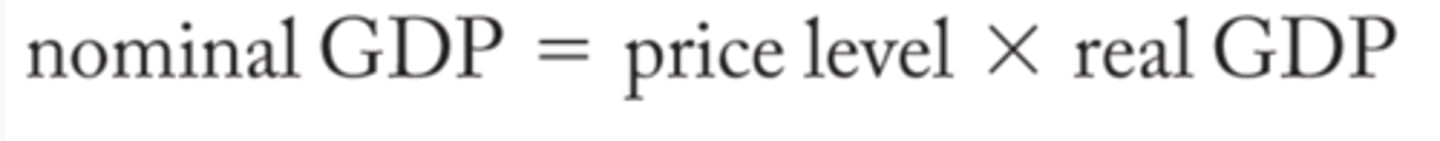
GDP Deflator
Term describing price index that measures the changes in prices for all goods and services produced in the economy in a given period, which tells us the aggregate price level
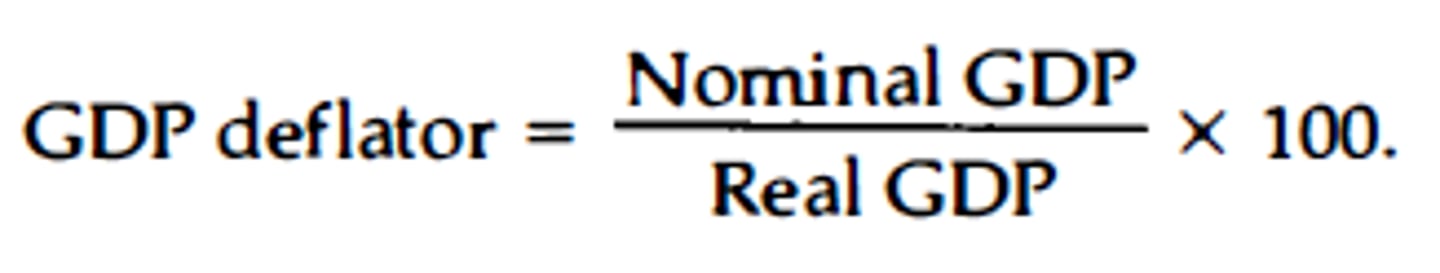
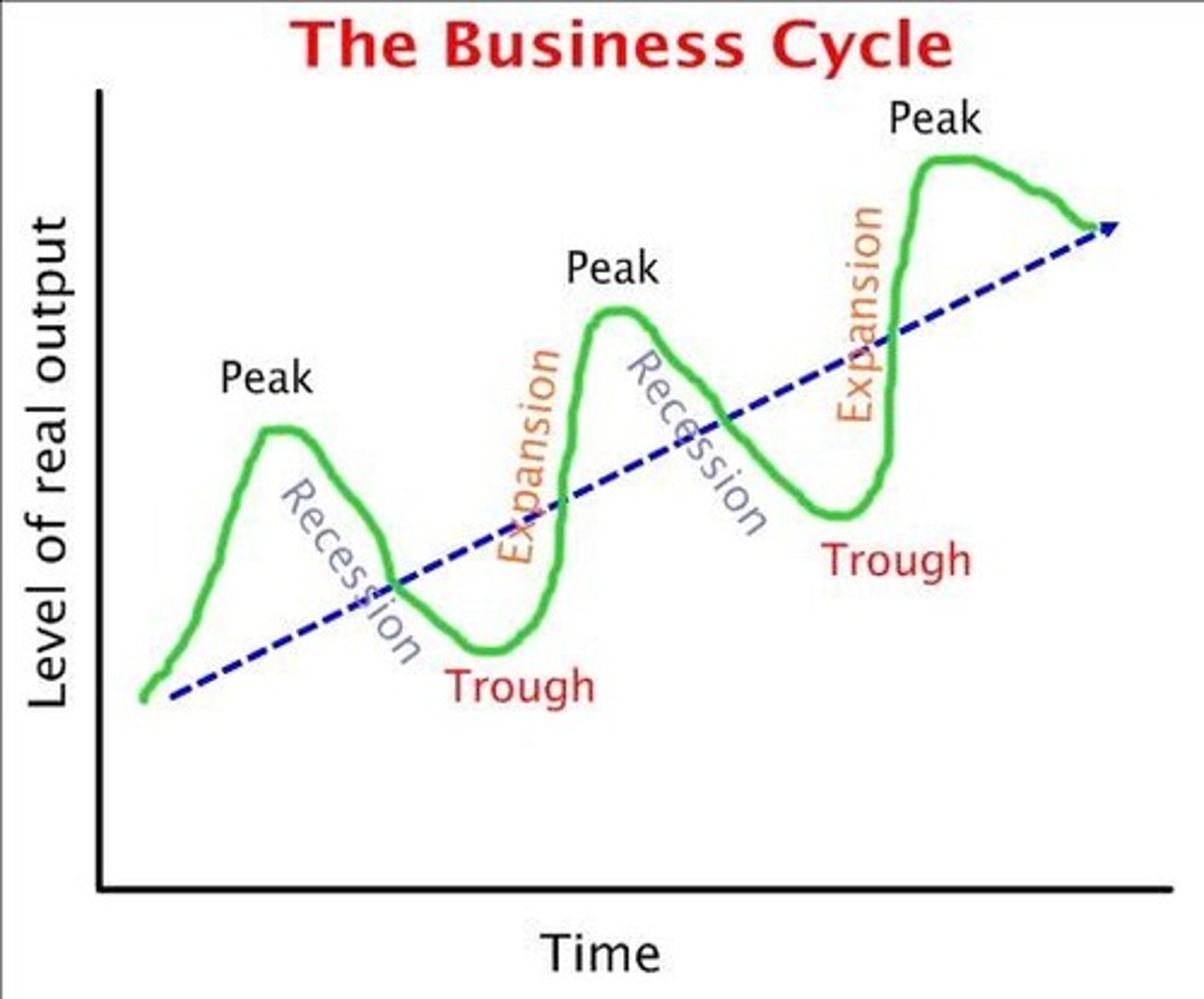
Business Cycle
Graph that shows the cycle the economy takes, where time is usually expressed in quarters
Aggregate
Term describing something added all together
The AD/AS Model
The basic model used to understand fluctuations in aggregate output and the aggregate price level. It uses the aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve together to analyze the behavior of the economy in response to shocks or government policy.
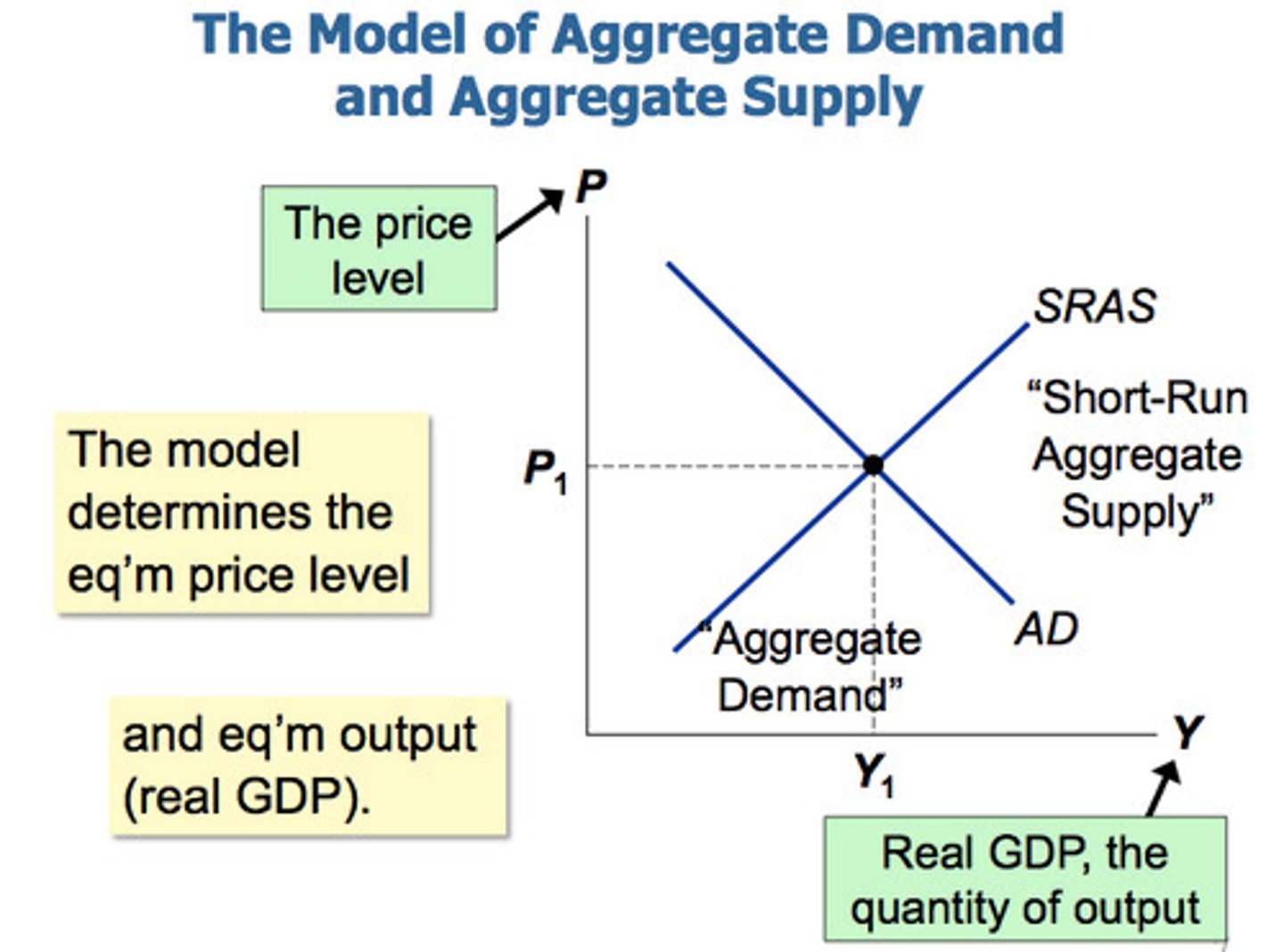
Aggregate Demand (AD) Curve
Graph describing the demand for all goods and services produced in product markets, for example using the expenditure model of GDP
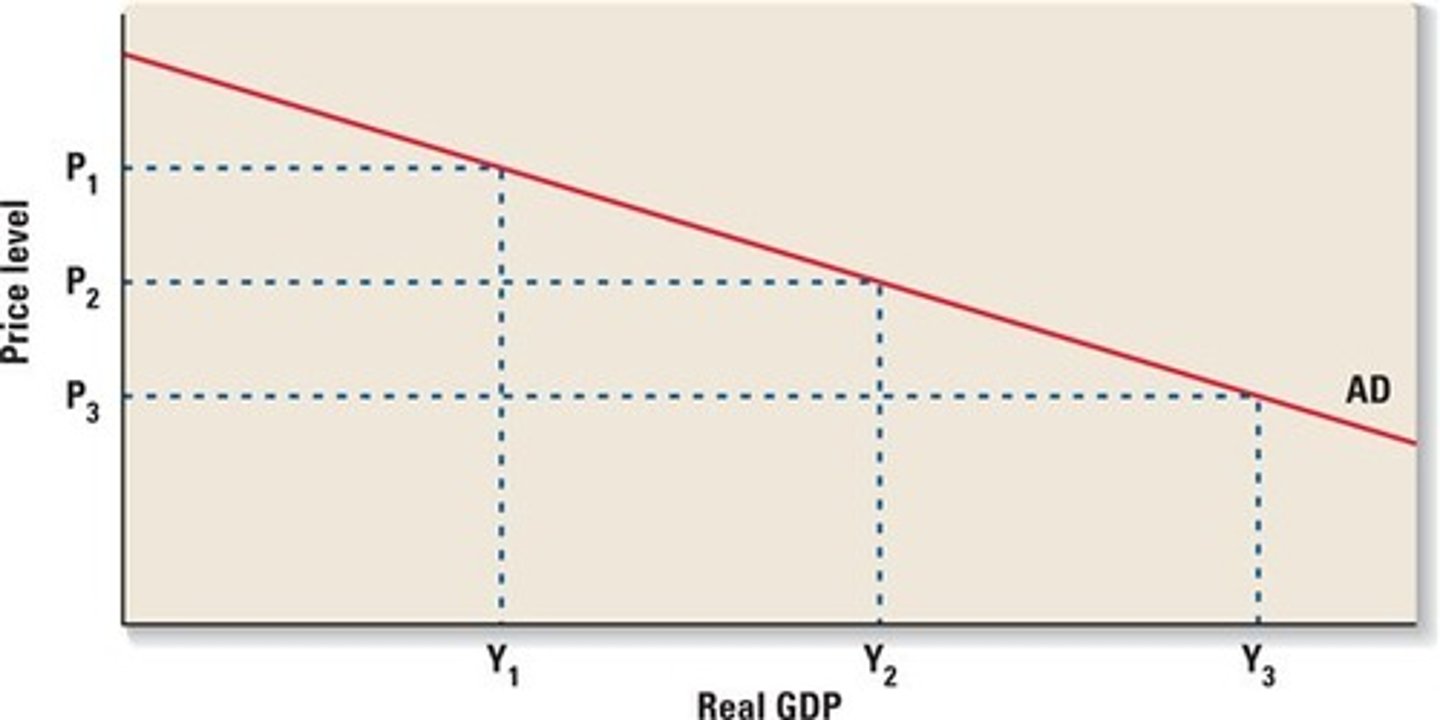
ΔQD (Change in Quantity Demanded)
Term describing that a change in quantity demanded is a movement along a given demand curve and is ONLY caused by a change in price
ΔD (Change in Demand)
Term describing that a change in demand shifts the demand curve and is caused by a change in a non-price determinant of demand. Essentially saying that a change in demand is to change in quantity demanded at every price
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
Term describing the tendency to take some of the money you are paid and spend it
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
Term describing the tendency to take some of the money you are paid and spend it
MPC = 0.65
MPS = 0.35
If you get $100, spend $65 and save $35, what would your MPC and MPS mean?
Simple Spending Multiplier
Equation that describes how money that you spend is multiplied in the economy
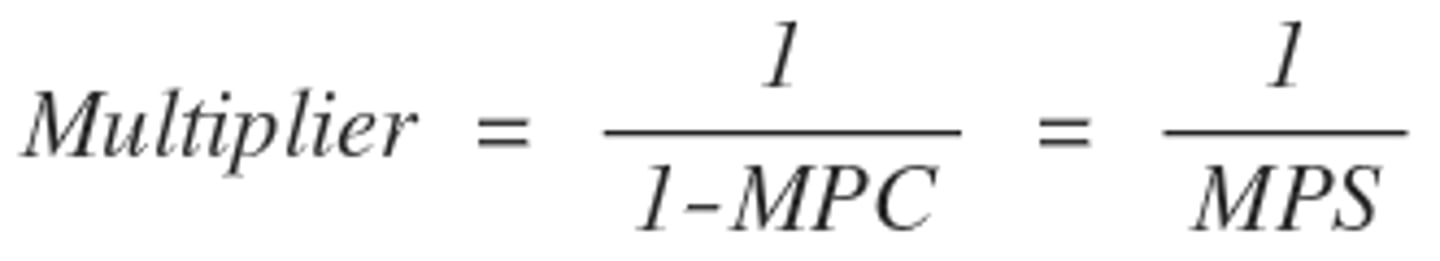
Tax Multiplier
MPC/MPS - Always 1 less than the spending multiplier
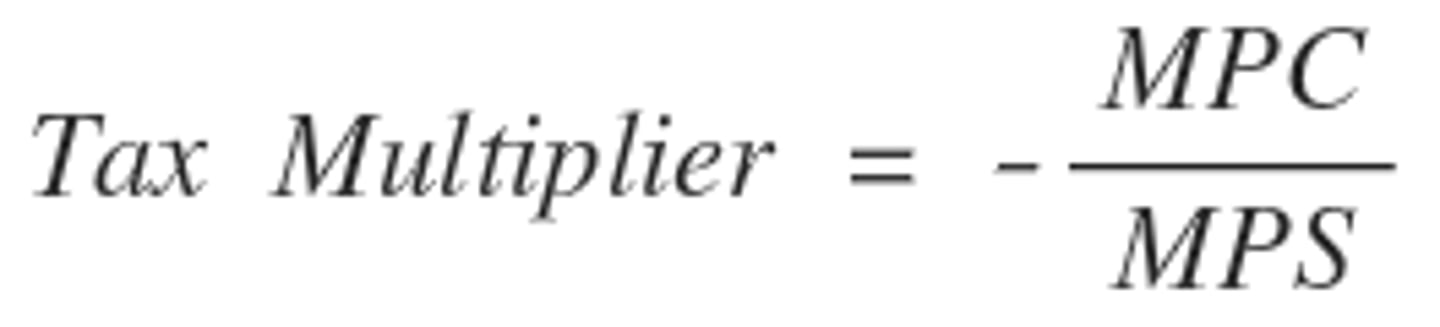
Money Multiplier
Equation that describes how modifications by the Fed change the money supply
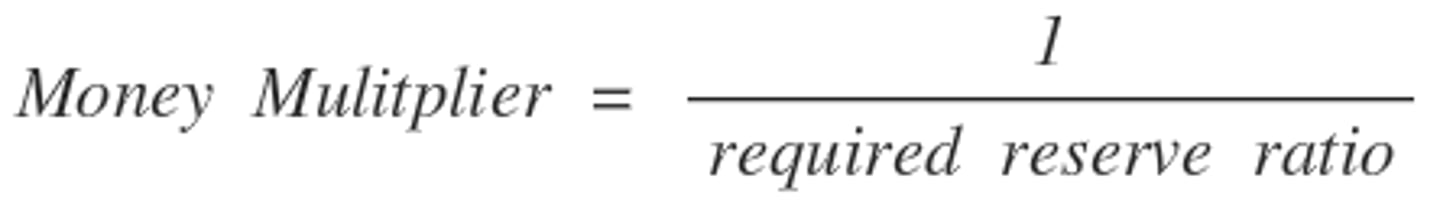
Short Run
Term that refers to the time period in which at least one input price is fixed
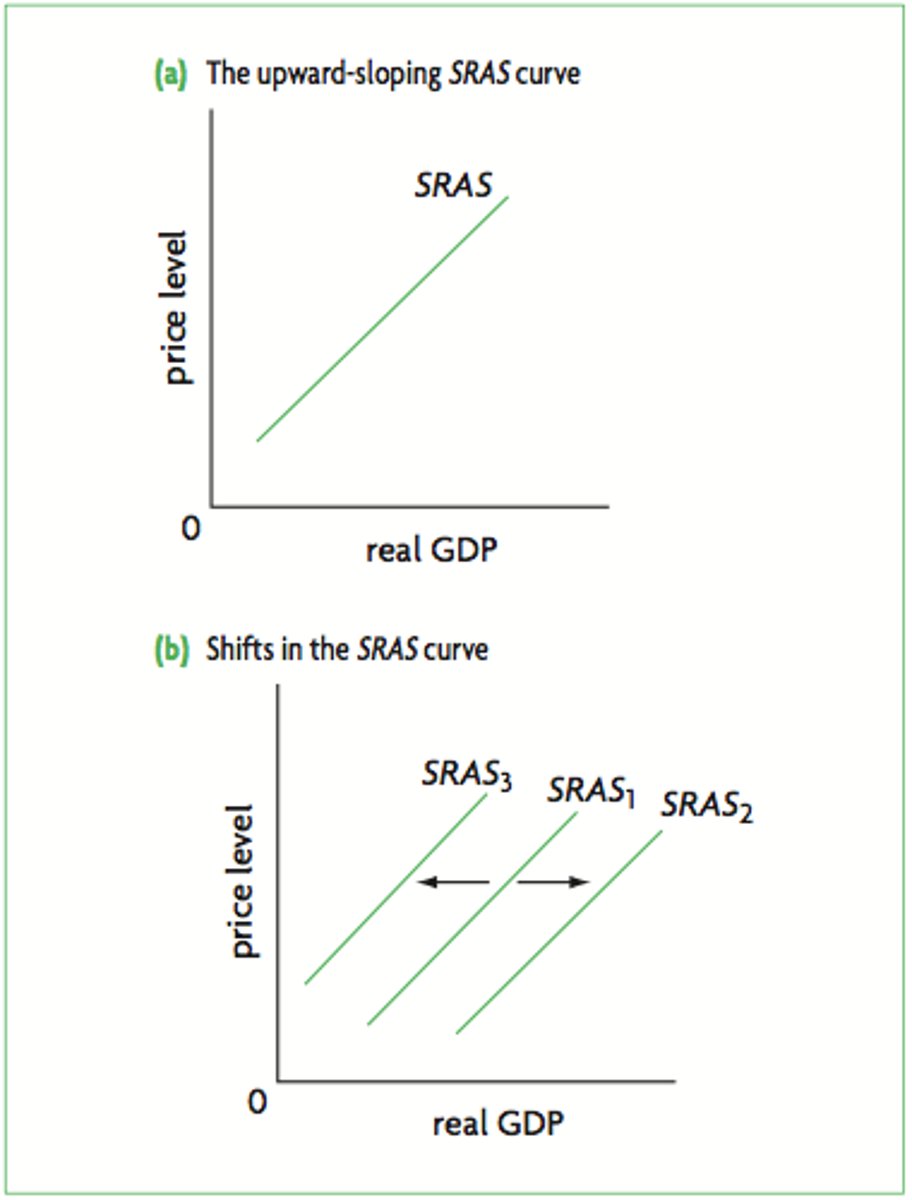
Short Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS) Curve
Graph describing the ship between the price level and the quantity of aggregate output supplied in the short run
Total Profit Equation
Aggregate Price Level - Input Costs
Capital Stock
Term describing the accumulation of physical capital, like factories, tools, and equipment, used to produce goods and services
Negative Supply Shock
An unexpected decrease in the availability of a key resource that temporarily decreases productivity
Positive Supply Shock
An unexpected increase in the availability of a key resource that temporarily increases productivity
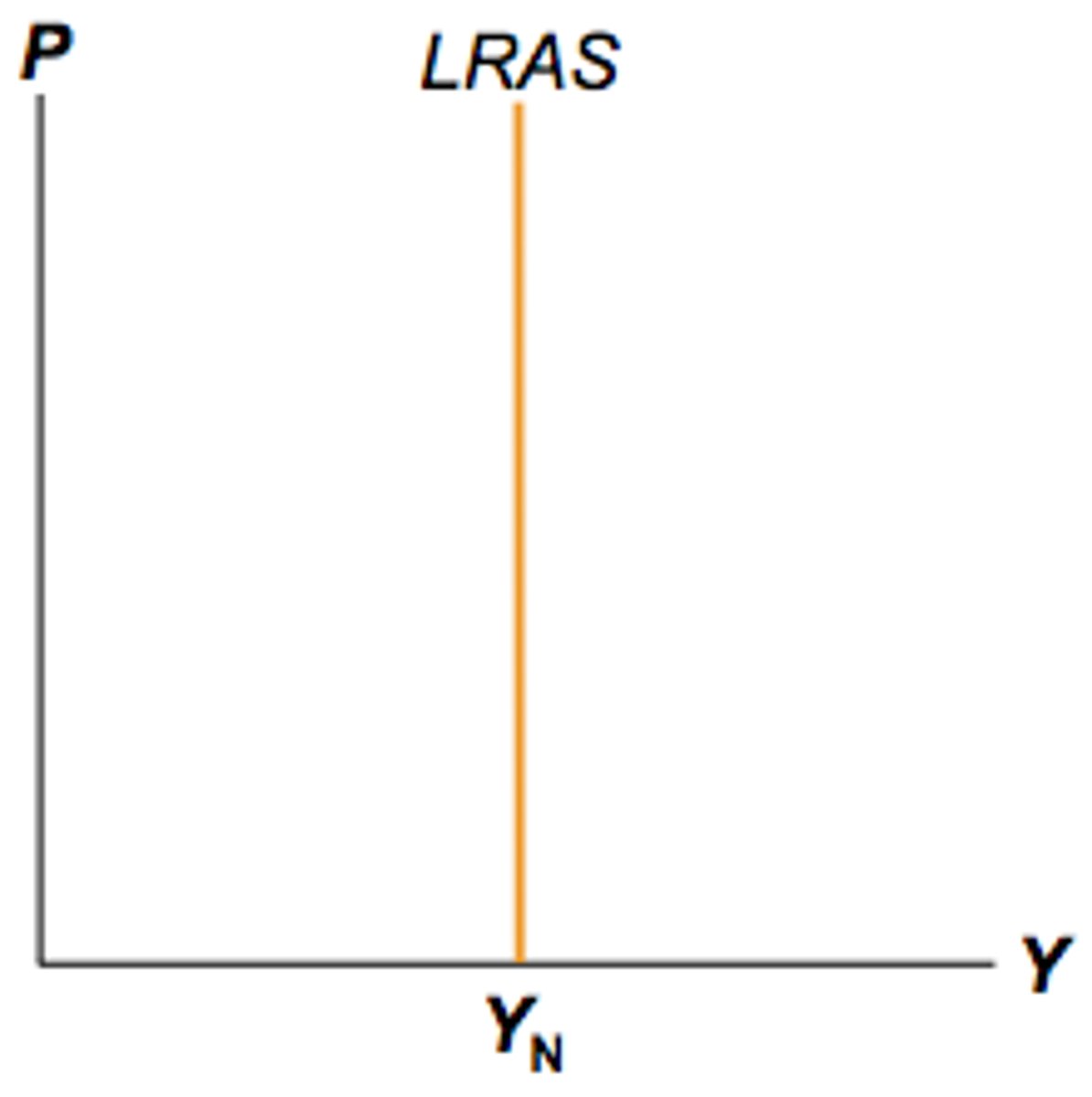
Long-Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS) Curve
Graph describing the normal level of aggregate demand and supply in the long run
Planned investment
Term describing the amount of business firms collectively intend to invest at each level of GDP
Stagflation
Term describing a scenario where higher prices at the same time as a slowdown in the economy happen, which is the worst possible scenario
Hyperinflation
A very rapid rise in the price level; an extremely high rate of inflation.
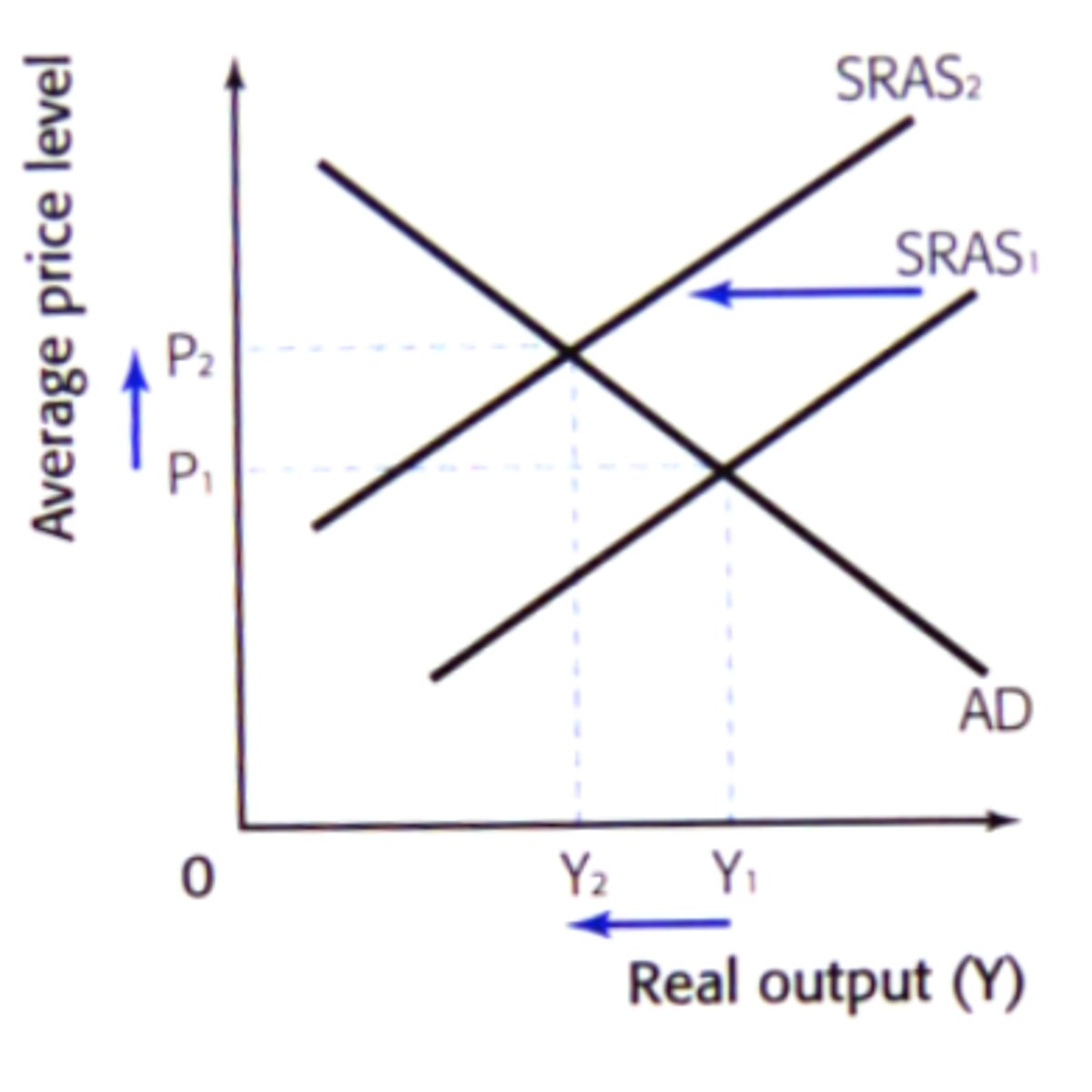
Cost-push inflation
When prices rise due to an increase in the cost of production
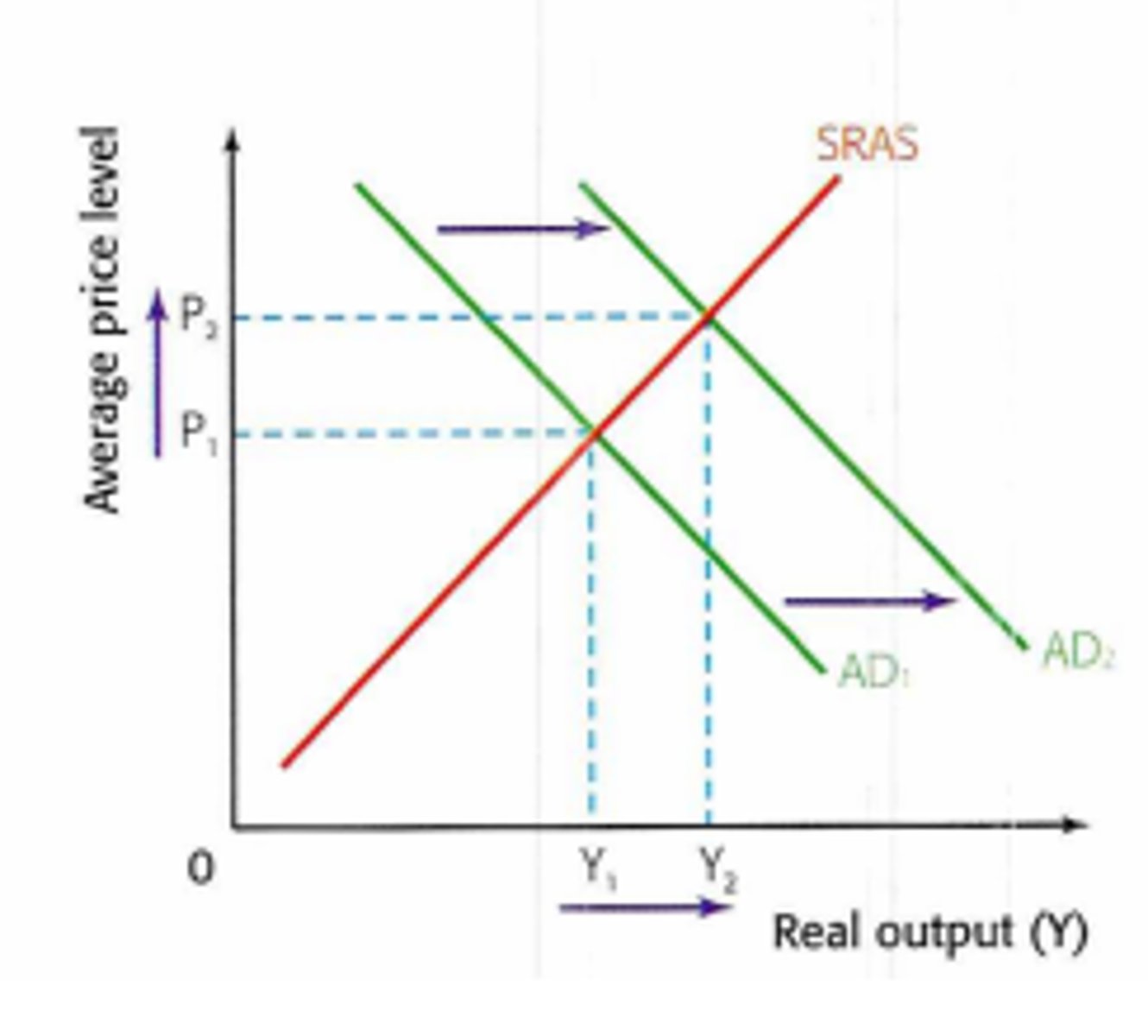
Demand-pull inflation
Inflation that is caused by an increase in aggregate demand
Open Market Operation
The purchase and sale of U.S. government bonds
Fiscal Policy
The use of government spending and tax collection to influence the economy
Monetary Policy
Managing the economy by altering the supply of money and interest rates
Automatic Stabilizers
Term describing policies that are already in place in an economy due to previously passed legislation, such as income and corporate taxes
Money
Term describing anything that can be used to purchase goods and services
Liquidity
Term describing how easily something can be converted into cash
Real interest rate equation
Real interest rate = nominal interest rate - inflation rate

Unit of account
Term describing that people commonly accept money as a way to set prices
Store of value
Term describing that money holds purchasing power over time
Medium of exchange
Term describing that money is used to exchange goods and services
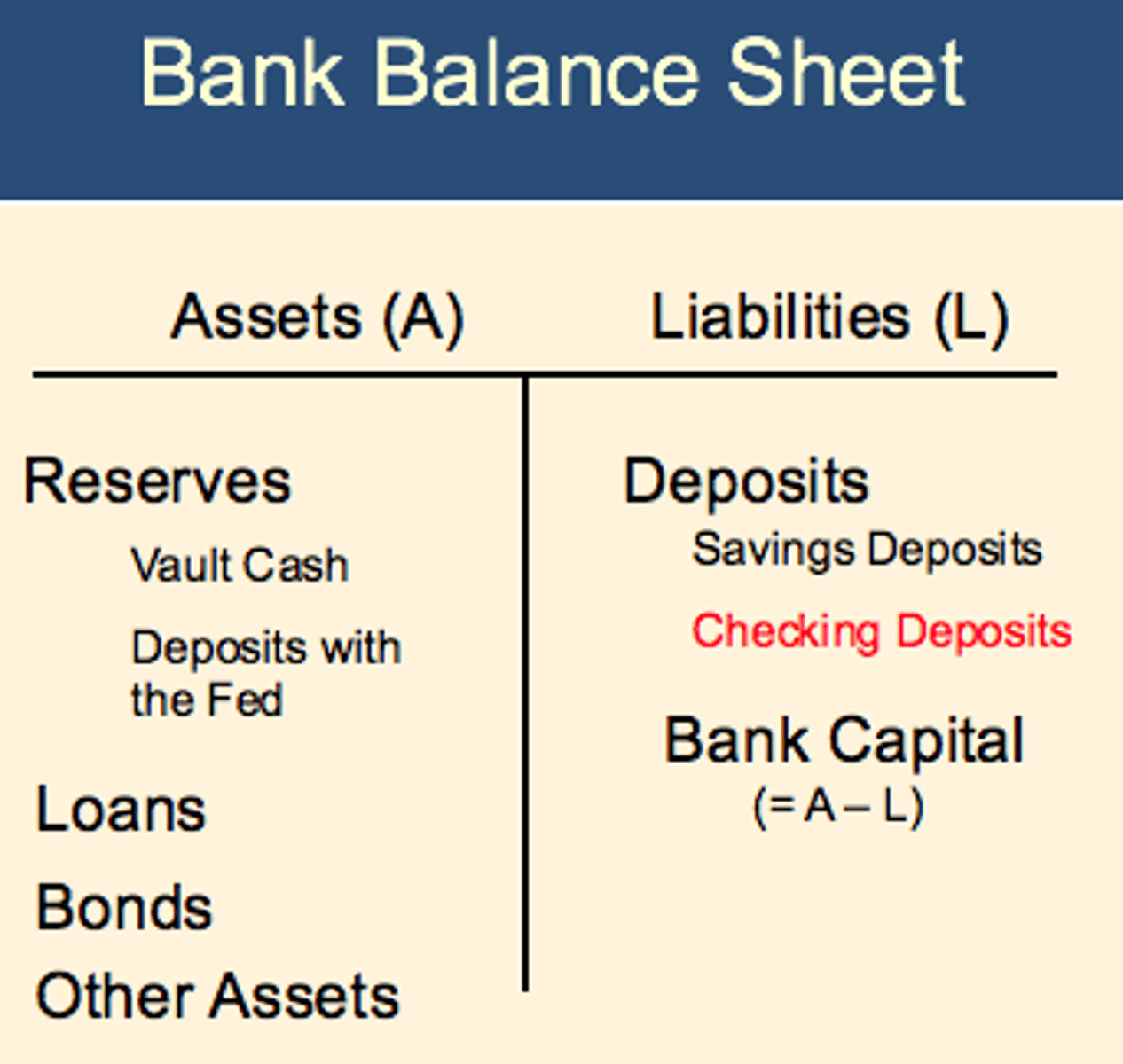
Bank balance sheet
Shows the amount of bank assets and bank liabilities each individual bank has, and both sides are equal to each other
M1 Money
The nearest definition of money which includes cash, traveler's checks, and checkable bank deposits and, as of 2020, savings accounts
Monetary base
Money held in reserves or in circulation, NOT deposits or savings
Shifters of money demand
The reserve requirement, the discount rate, and open market operations are all...
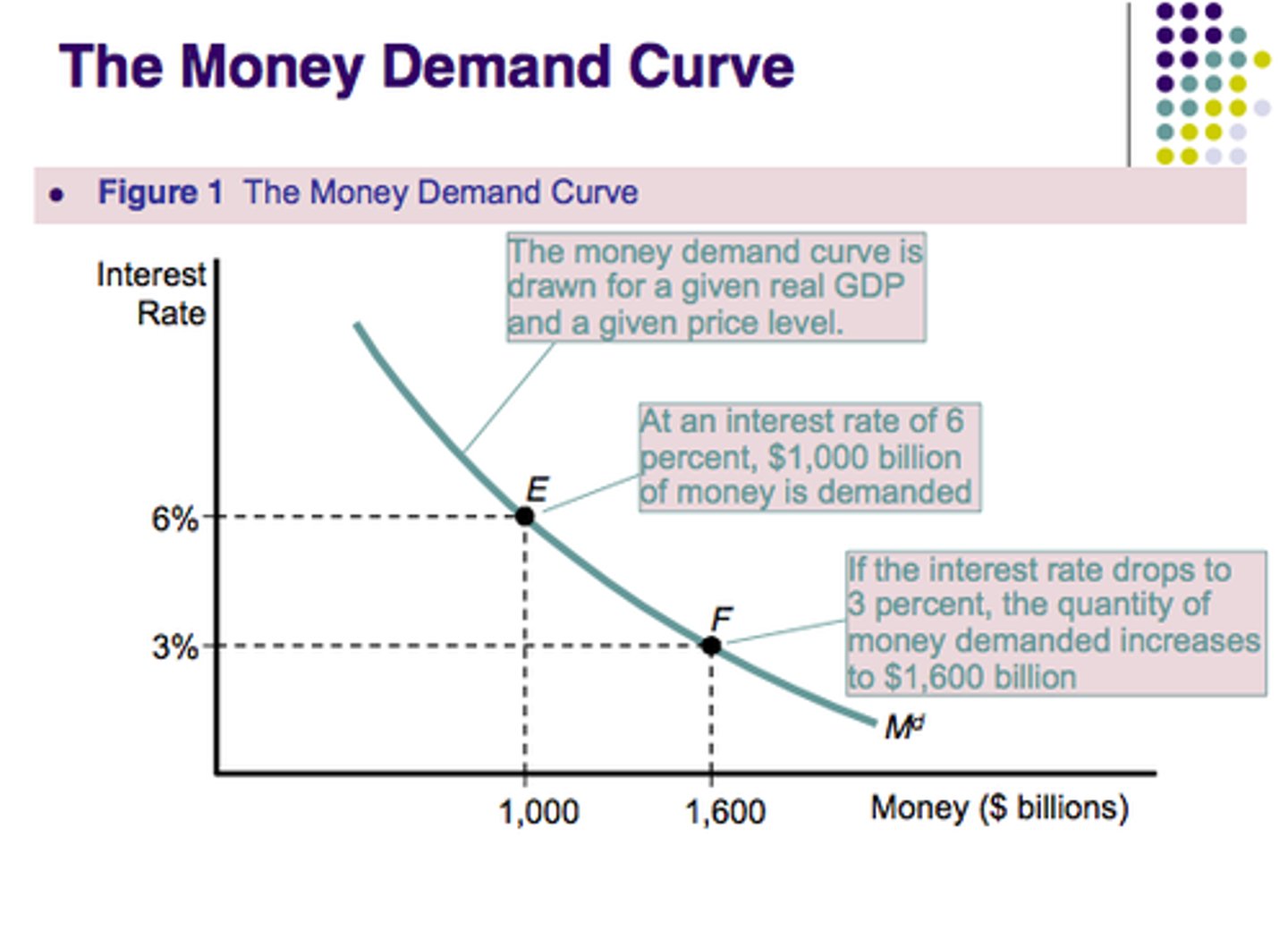
Money Demand Curve
Shows the relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the interest rate
Monetary Policy
Term describing a central bank's policies of influencing nominal interest rates to help achieve macroeconomic objectives
Policy Rate
Term describing the overnight interbank lending rate, also called the federal funds rate in the United States
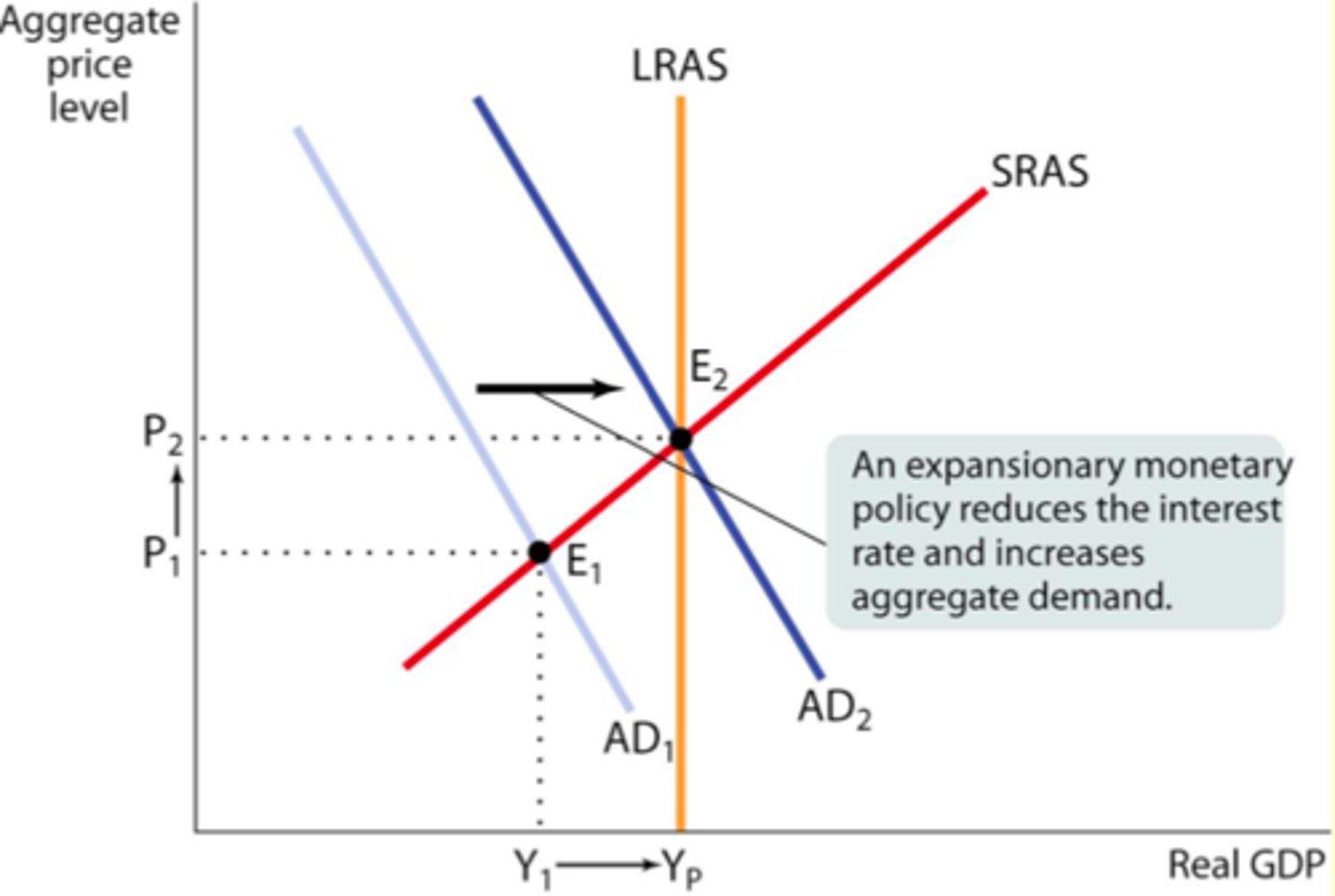
Expansionary Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve's policy of decreasing interest rates to increase real GDP
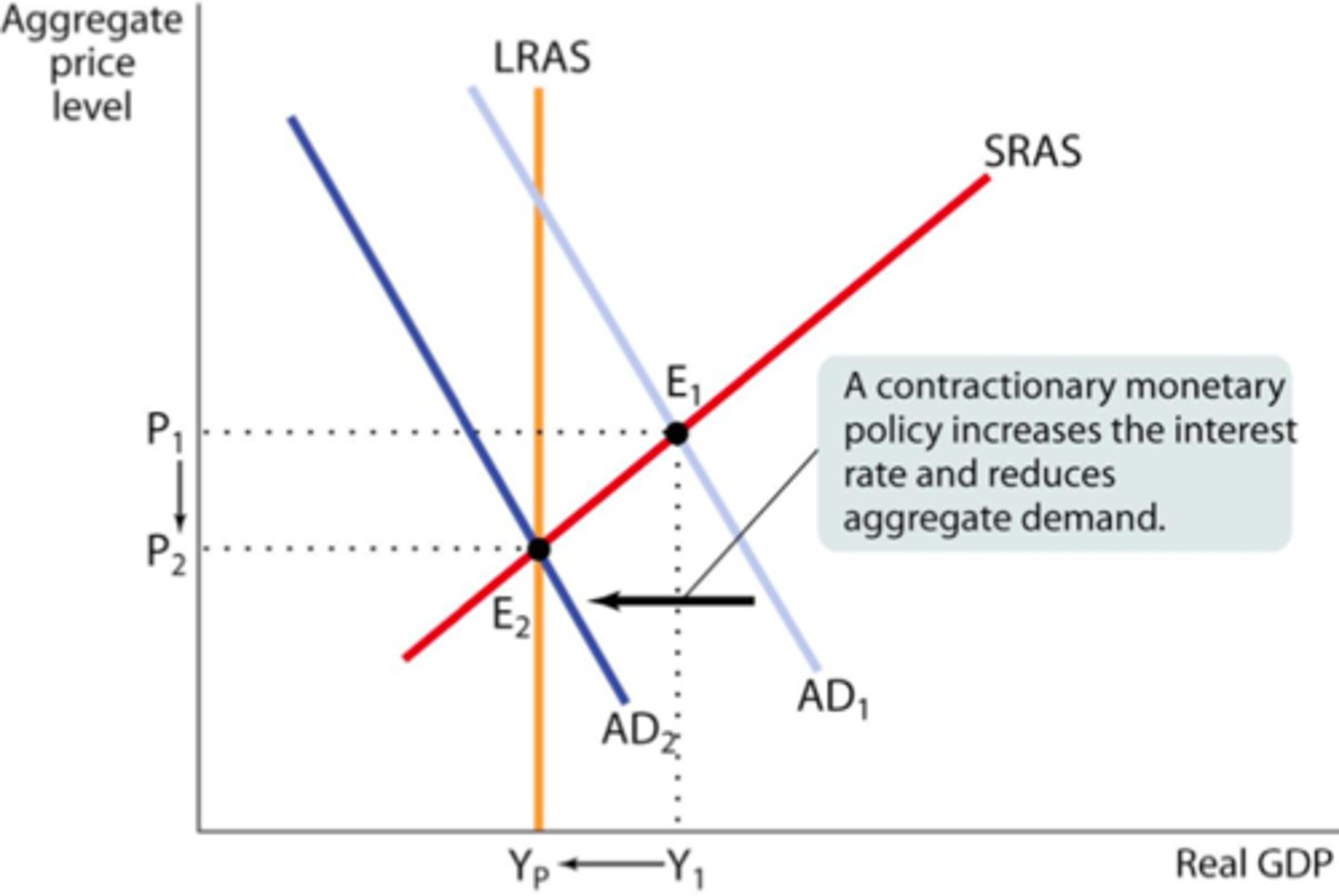
Contractionary Monetary Policy
A monetary policy that reduces the supply of money and loans to reduce inflation
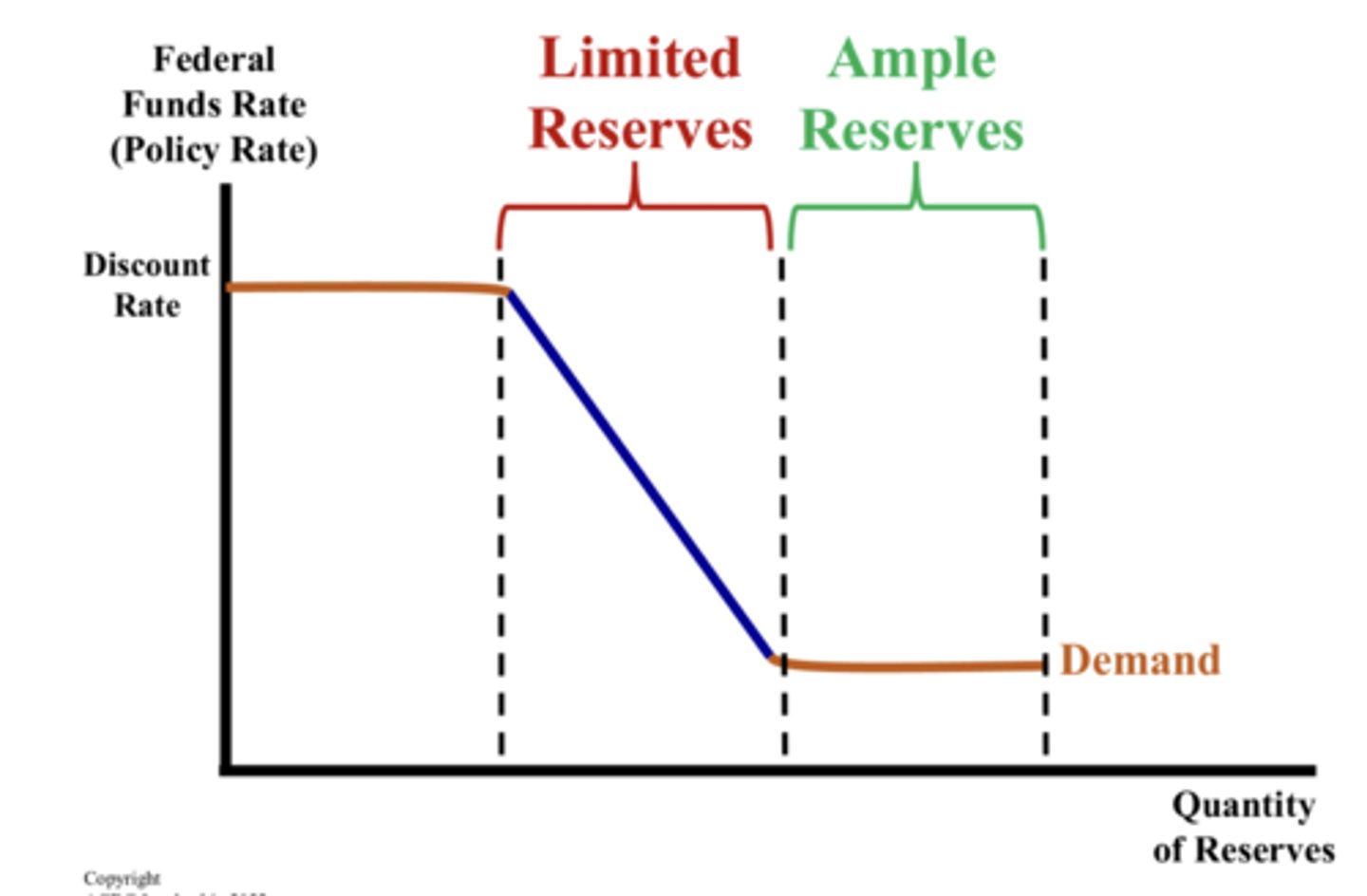
Limited Reserves
Term describing a banking system in which reserves are not overly abundant, there is a non-zero reserve requirement, and commercial banks hold required reserves and possibly also some excess reserves
Ample Reserves
Term describing a banking system in which reserves are abundant, the required reserve ratio is zero, and changing the money supply does not change the nominal interest rate
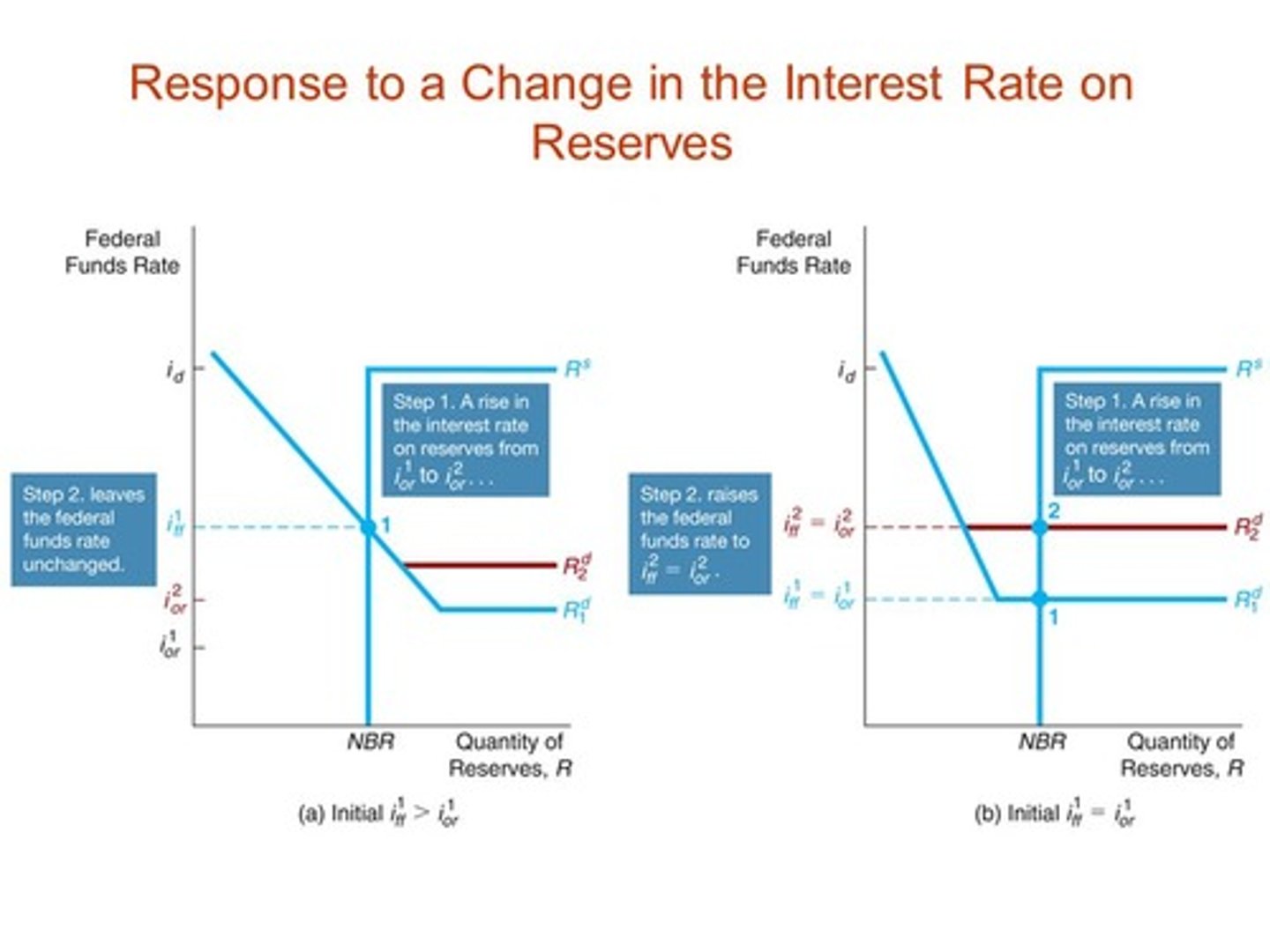
Reserve Market Model Graph
Graph describing the market for bank reserves
Interest on Reserves
Term describing a monetary policy tool for an ample reserves system that describes the interest rate commercial banks earn on their funds and their reserve balance accounts with the Fed