Root of Neck and Cervical Viscera
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
The root of the neck is a junctional region between the ___
neck and thorax
-and between the neck and upper limb (axilla)
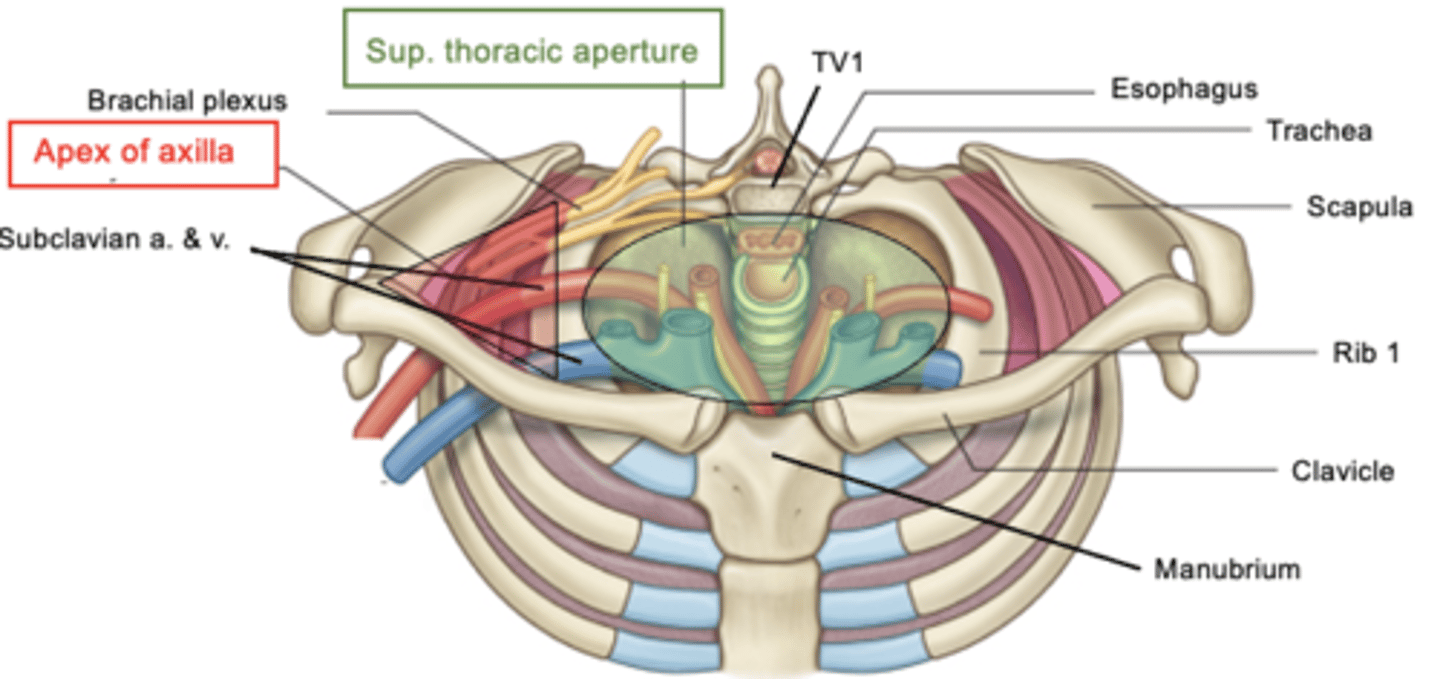
What is the superior thoracic aperture bounded by?
T1, 1st rib, and superior border of manubrium
(bounded posteriorly by thoracic vertebrae)
The Apex of Axilla is a ___
triangular opening btw the clavicle, 1st rib, and superior border of scapula
-main structure passing thru is branchial plexus and subclavian artery/vein
What do the Apex of the lung and Capula of the pleura project through?
superior thoracic aperture into root of neck
-penetrating wounds involving apex of lung can allow air to escape into pleural cavity --> collapsed lung
___ keeps the diaphragm alive
C3, C4, C5
Right and Left Subclavian Veins:
formed by subclavian vein + internal jugular vein
-in the chest, 2 brachiocephalic veins unite to form superior vena cava
-right is shorter than left
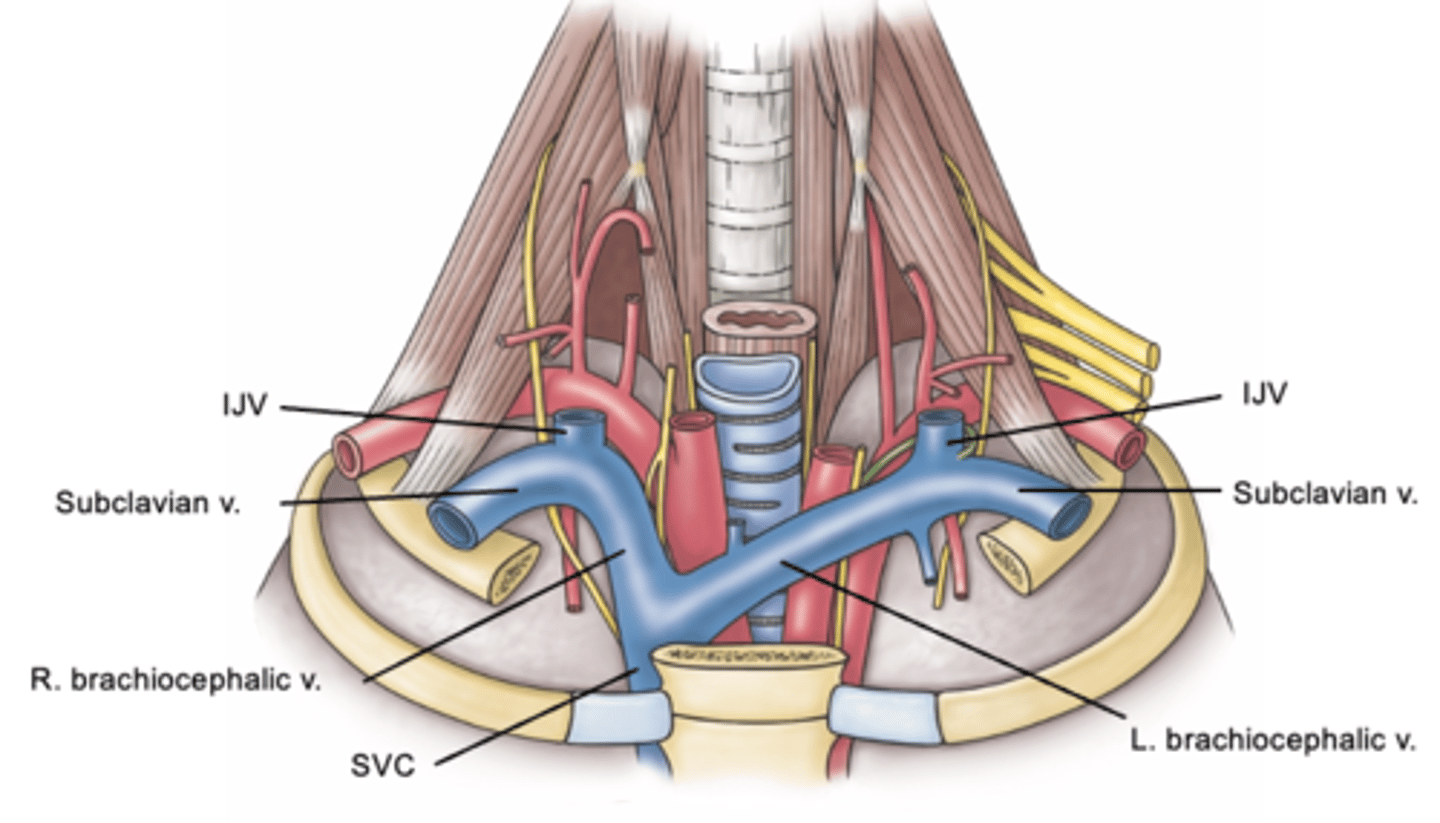
Where does the Superior Vena Cava (SVC) carry blood to?
to the right atrium of heart
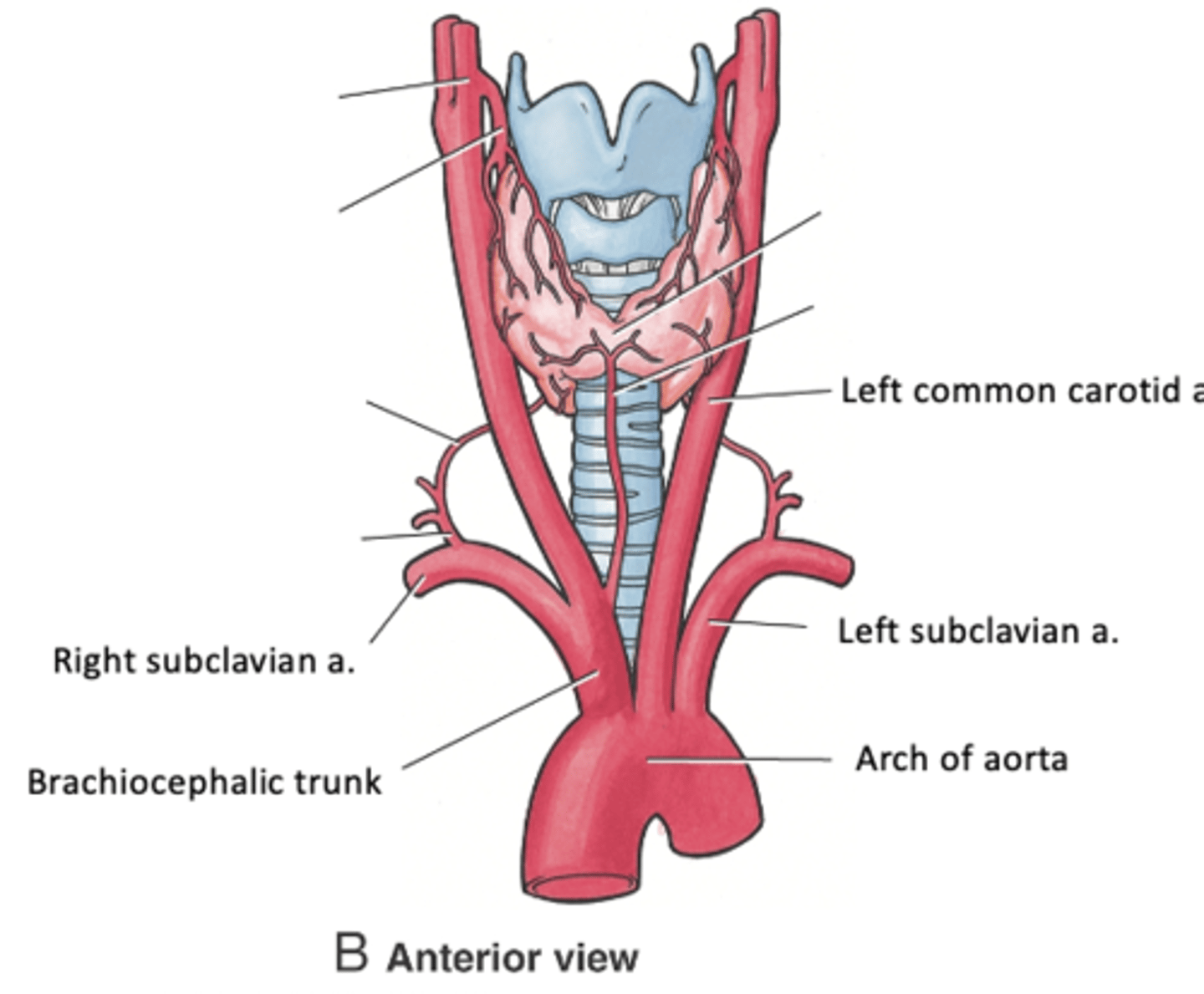
Traveling right to left, what are the 3 Parts of the Subclavian Artery?
1. Brachiocephalic trunk
2. Left common carotid artery
3. Left subclavian artery
The subclavian artery is divided into 3 parts based on its relationship to the ___
anterior scalene muscle
Anterior scalene inserts on the ___
Posterior scalene inserts on the ___
1st rib; 2nd rib
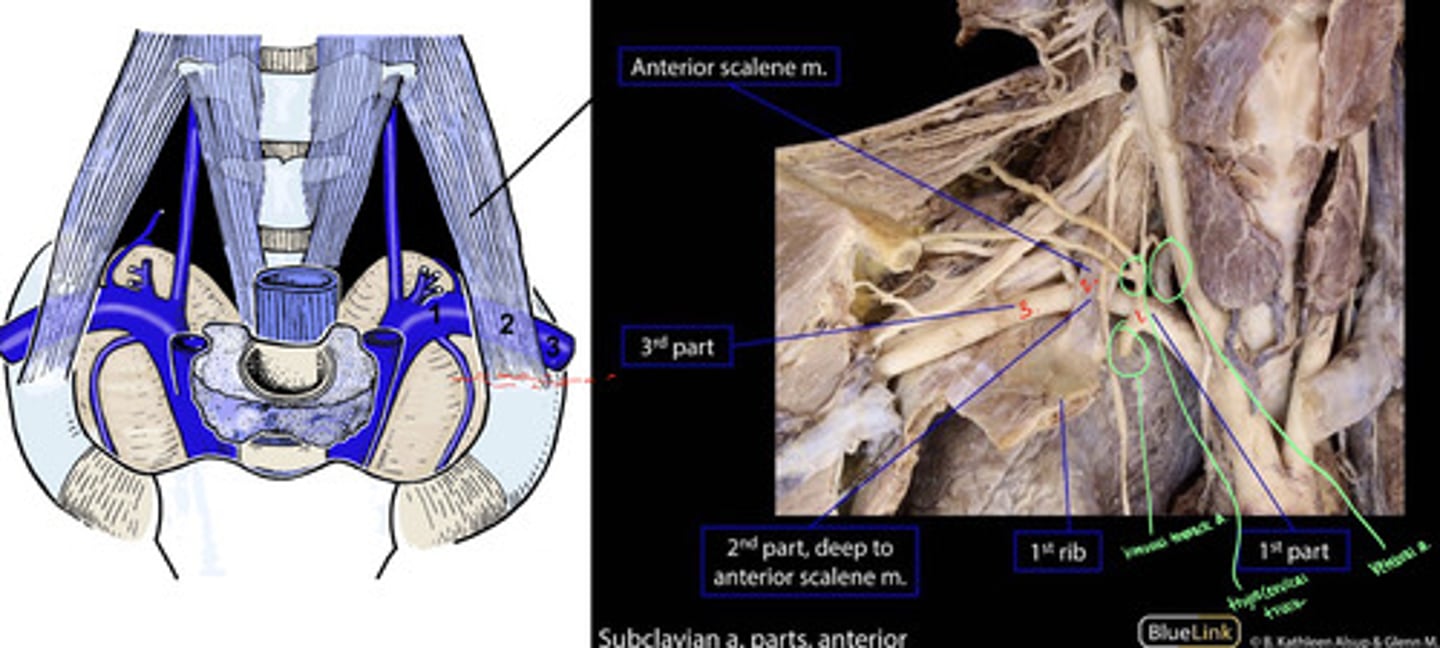
Branches of the 1st part of subclavian artery:
-vertebral artery (to brain)
-internal thoracic a. (to anterior chest wall)
-thyrocervical trunk
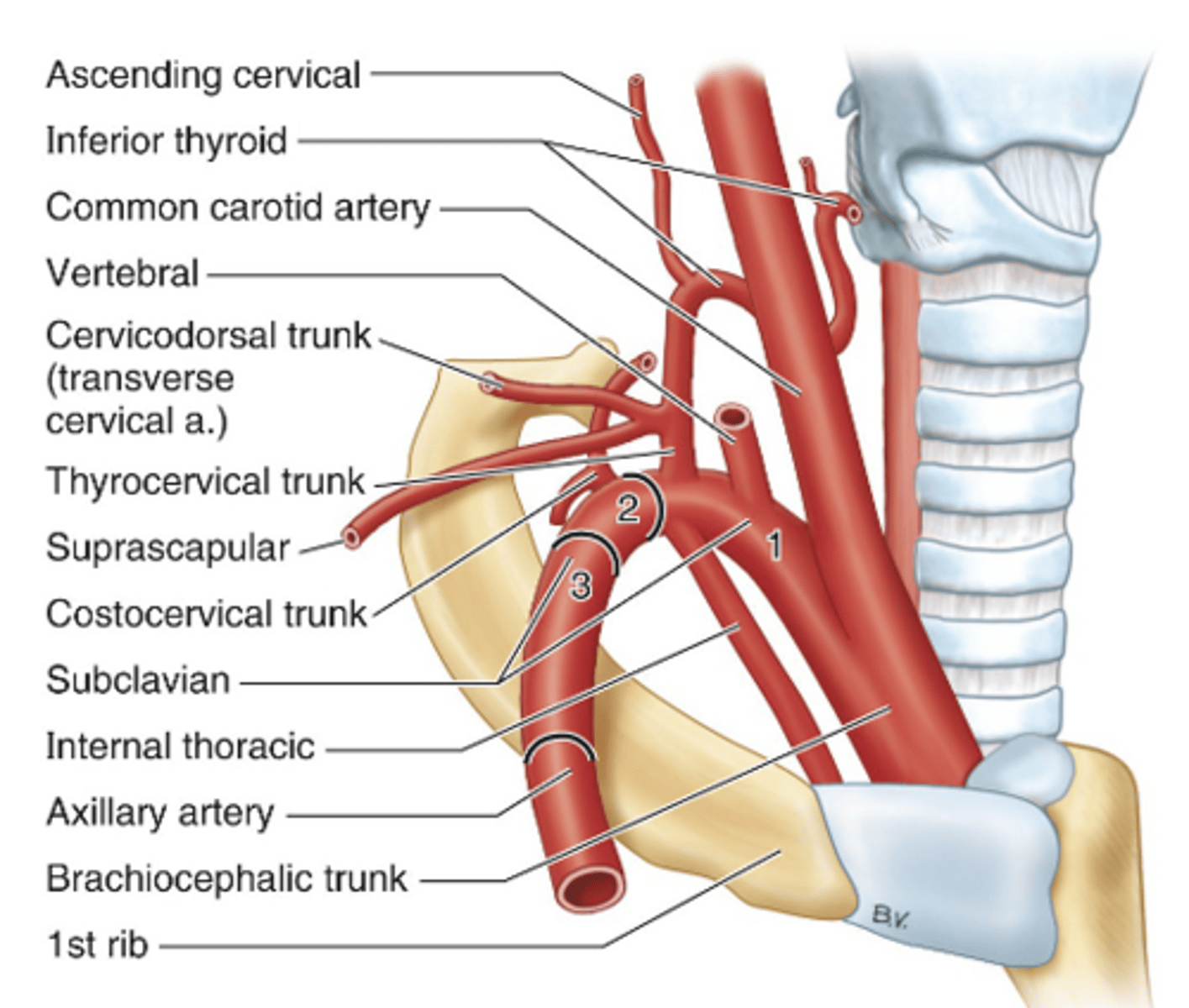
Which artery is the ONLY one to descend/go down into ribs?
internal thoracic artery
Thyrocervical trunk:
2 lateral branches
-supracapsular a. (supply muscles on posterior scapula)
-cervicodorsal trunk --> dorsal scapular and superficial cervical arteries (supply muscles in lateral cervical region)
What are the muscles in the lateral cervical region?
trapezius and medial scapular muscles
What are the terminal branches of thyrocervical trunk?
inferior thyroid artery and ascending cervical artery
2nd part of subclavian artery:
costocervical trunk
-divides into superior intercostal and deep cervical arteries
-supply first 2 intercostal spaces and posterior deep cervical muscles
The dorsal scapular artery is often arising from the ___ part of subclavian artery
3rd part
-but can arise from cervicodorsal trunk
-supplies levator scapulae and rhomboid muscles
The ___ is the first and largest branch of subclavian artery
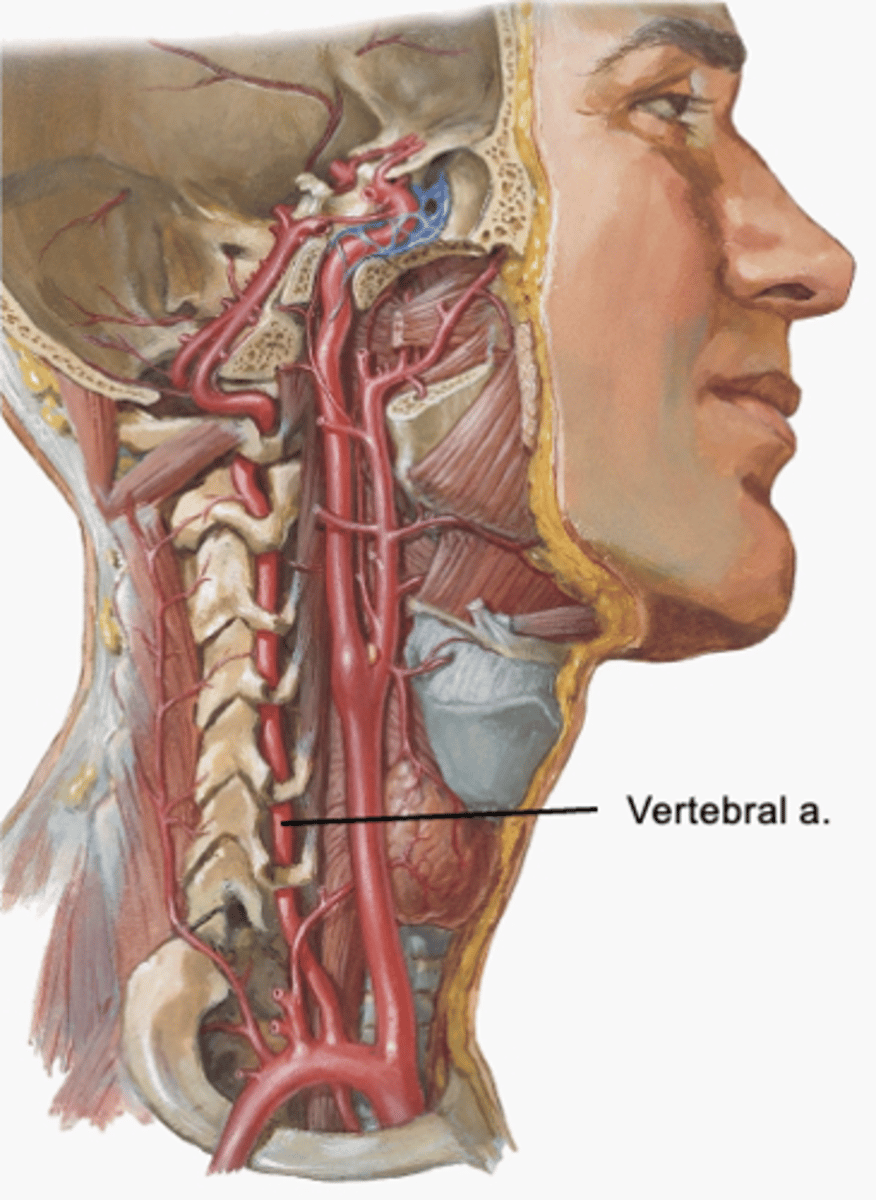
vertebral artery
-enters the transverse foramen of CV6 and continues into cranial cavity to supply the brain
The ___ is the largest lymph vessel in the body
thoracic duct
-thin walled, beaded appearance
-injury to duct can result in CYCLOTHORAX (leakage of lymph into pleural cavity) and ATELECTASIS (collapsed lung)
Where does thoracic duct begin?
at cisterna chyli in abdomen
-passes thru aortic hiatus to enter thorax
-ascends along thoracic vertebral bodies posterior to esophagus
-receives lymph from left bronchomediastinal, subclavian, and jugular lymphatic trunks
-terminates into left venous angle
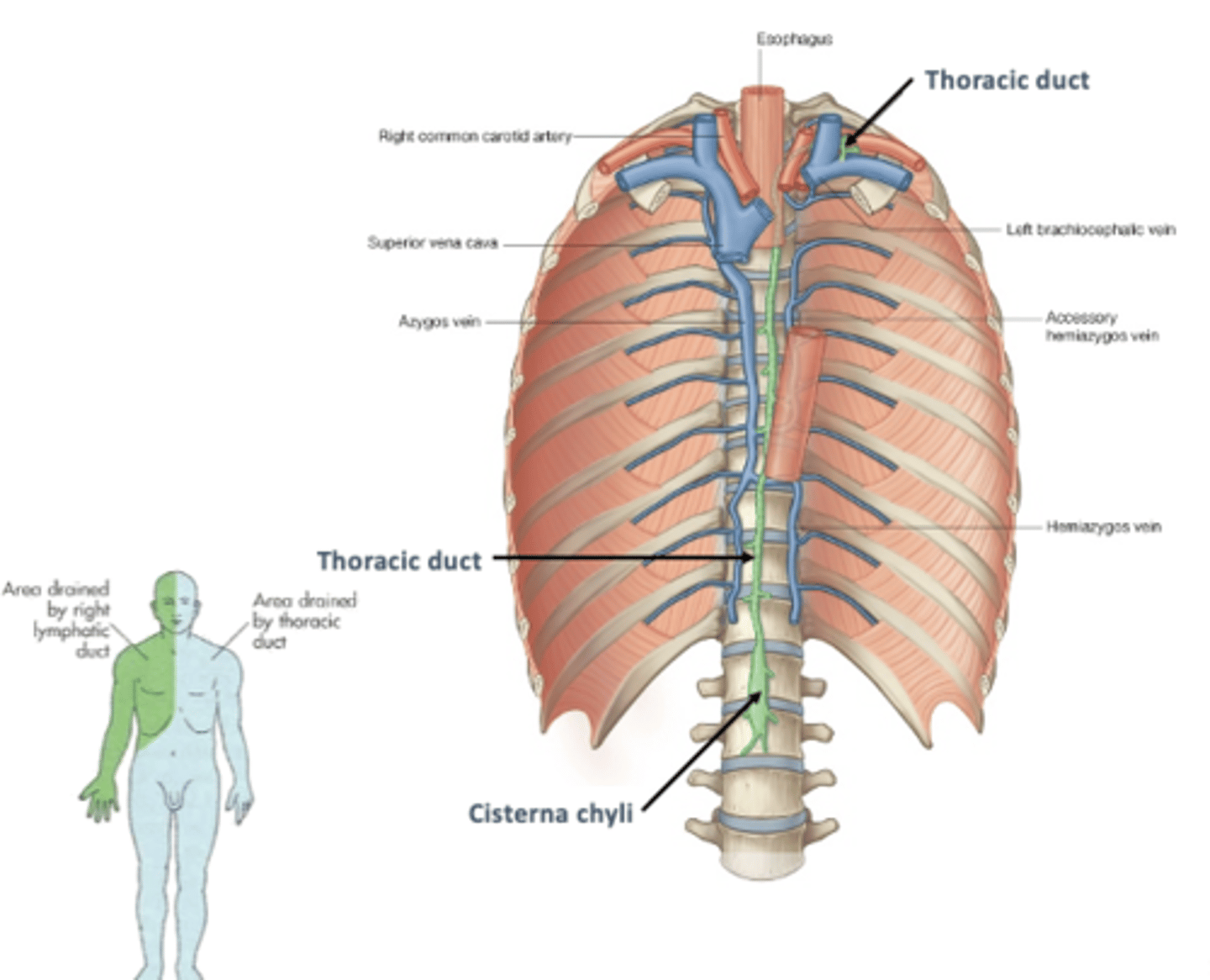
Where is the termination of the thoracic duct?
into left venous angle and right lymphatic duct into right venous angle
Roots and trunks of brachial plexus are ___
supraclavicular (lie in root of neck)
What is the brachial plexus?
nerve network that innervates entire upper limb with both motor and sensory fibers
-anesthesia of upper limb: anesthetic agent injected superior to midpoint of clavicle

What are the roots of the brachial plexus?
C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1
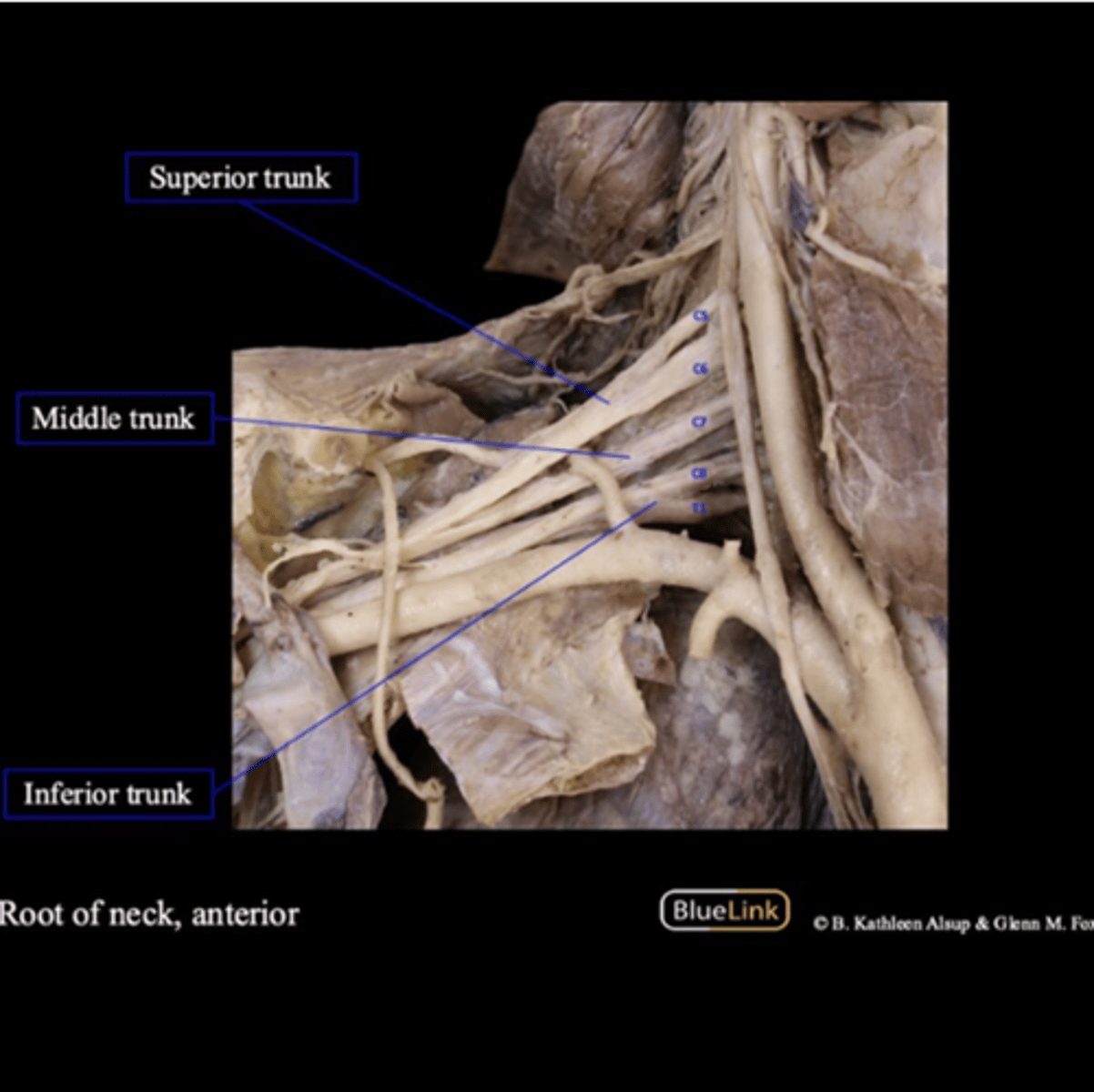
Which roots make up the superior trunk?
C5 and C6
Which roots make up the middle trunk?
C7
Which roots make up the inferior trunk?
C8 and T1
The Right vagus nerve passes ___ to the right subclavian artery and ___ to the right brachiocephalic vein to enter thorax
anterior; posterior
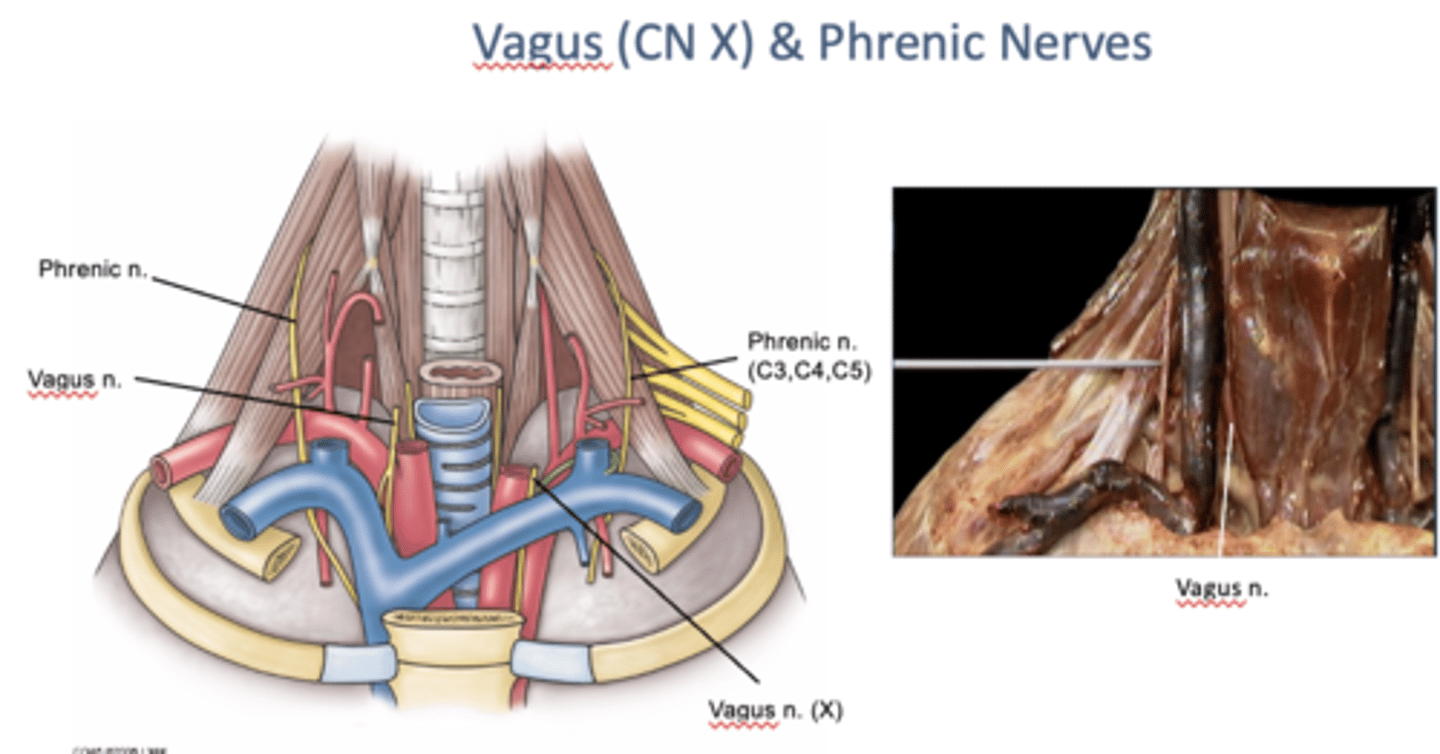
The Left vagus nerve descends between the ___ and ___
left common carotid and left subclavian arteries
-and posterior to left brachiocephalic vein to enter thorax
The Right recurrent laryngeal nerve loops around the ___
1st part of right subclavian artery
-Left recurrent laryngeal nerve arises in the thorax and loops around the arch of the aorta
-Both recurrent laryngeal nn then ascend in the tracheoesophageal groove, supplying both the trachea and esophagus
Where are the phrenic nerves formed?
at lateral borders of anterior scalene muscles (by union of fibers from C3, 4, and 5)
-descend anterior to the anterior scalene mm
-proceed between the subclavian artery and subclavian vein on each side to enter the thorax. They supply the diaphragm
The interscalene triangle is bounded by ___
anterior and middle scalene muscles, and rib 1
-contains branchial plexus and subclavian artery (but NOT vein)
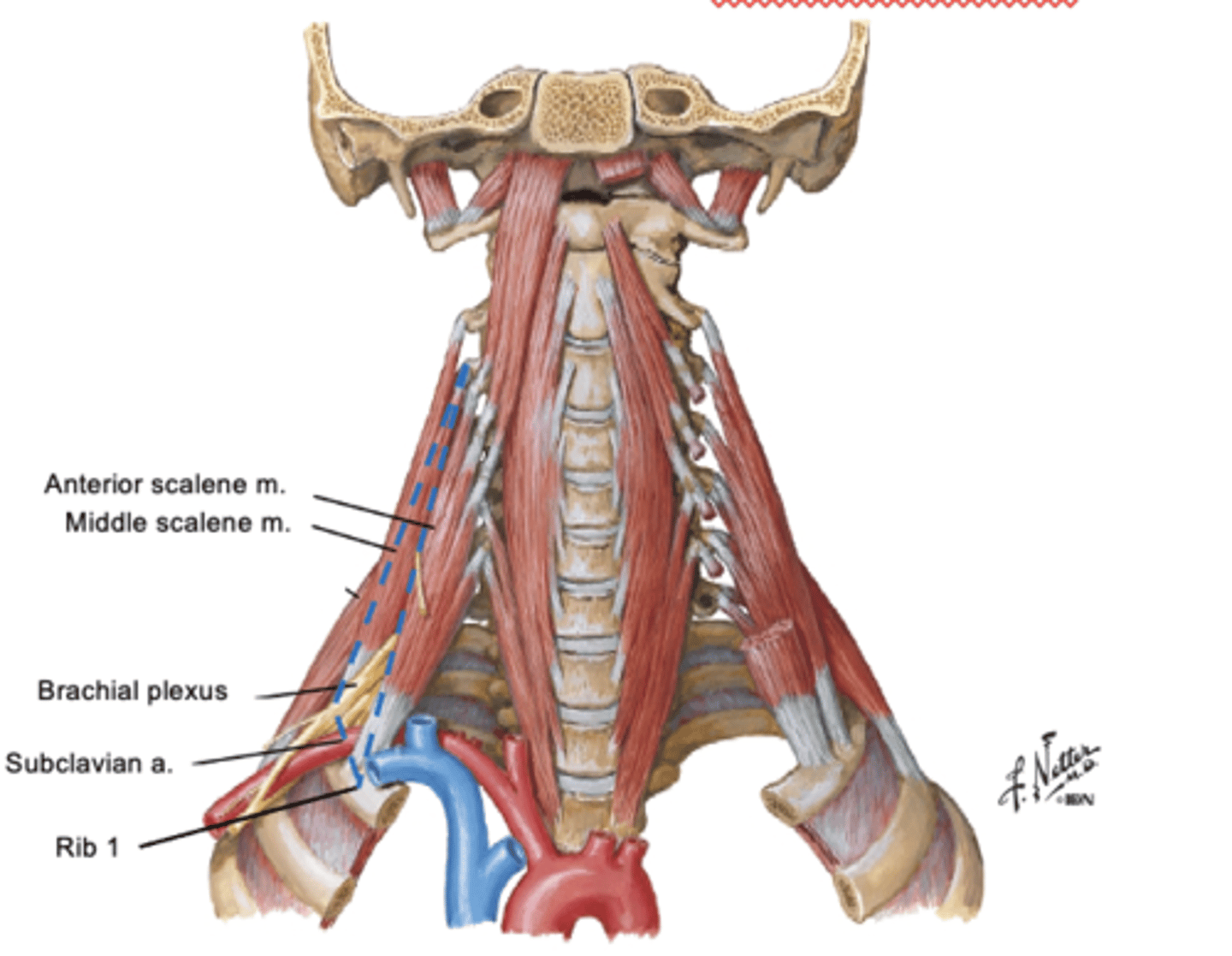
The anterior and middle scalene muscles both attach to ___
1st rib
The interscalene triangle may become too narrow due to the presence of a ___
cervical rib
-can compress subclavian artery leading to ischemia (reduced blood supply) to upper limb
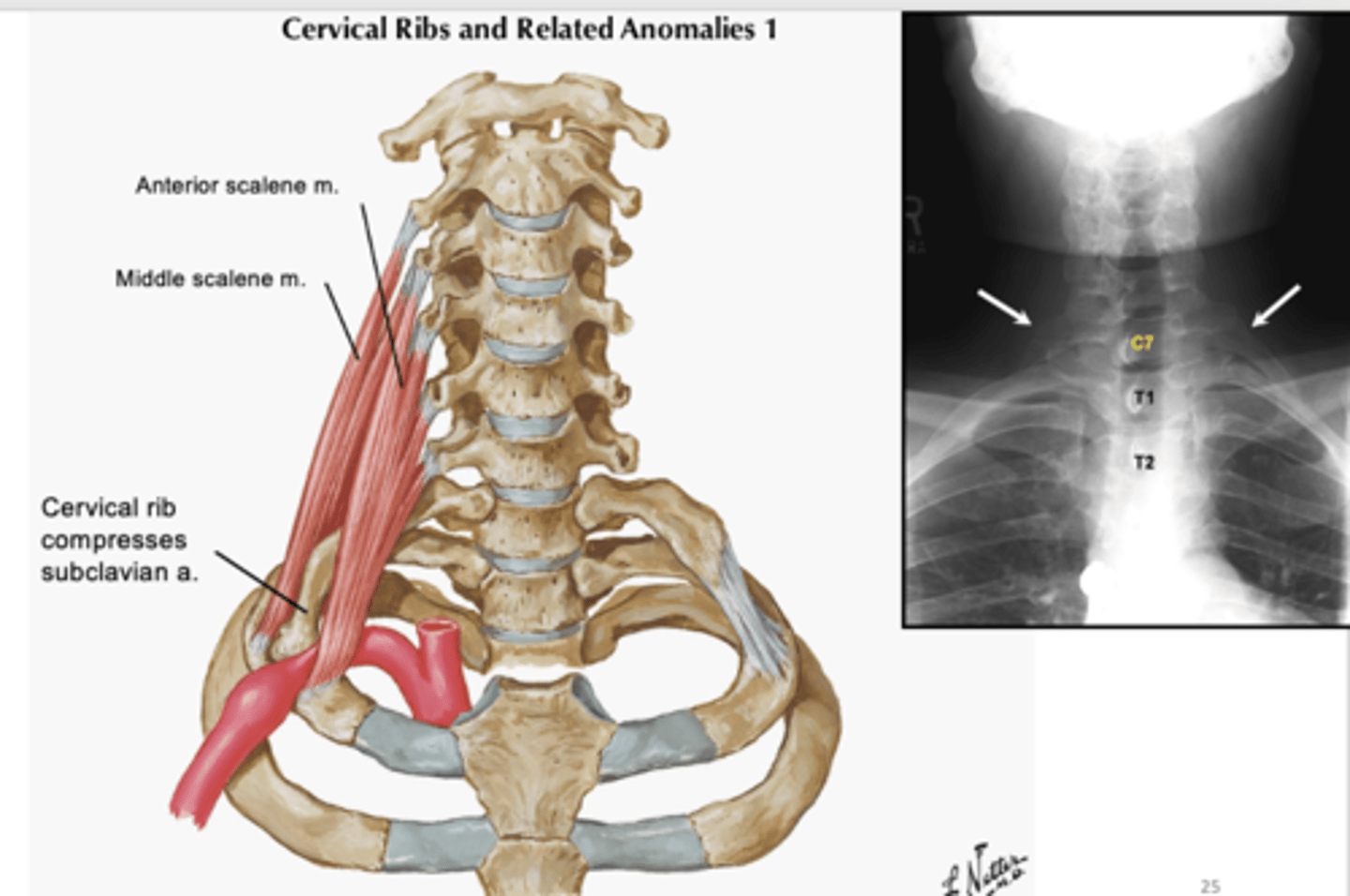
A cervical rib can also compress the ___
brachial plexus
-lower trunk of plexus is elevated with compression of nerve fibers leading to pain, paresthesia, and muscle weakness
Compression of subclavian artery/branchial plexus is termed ___
Anterior Scalene Syndrome or Thoracic Outlet Syndrome

The ___ gland is the largest endocrine gland
thyroid gland
-secretes thyroxin
-2 lateral lobes united by isthmus
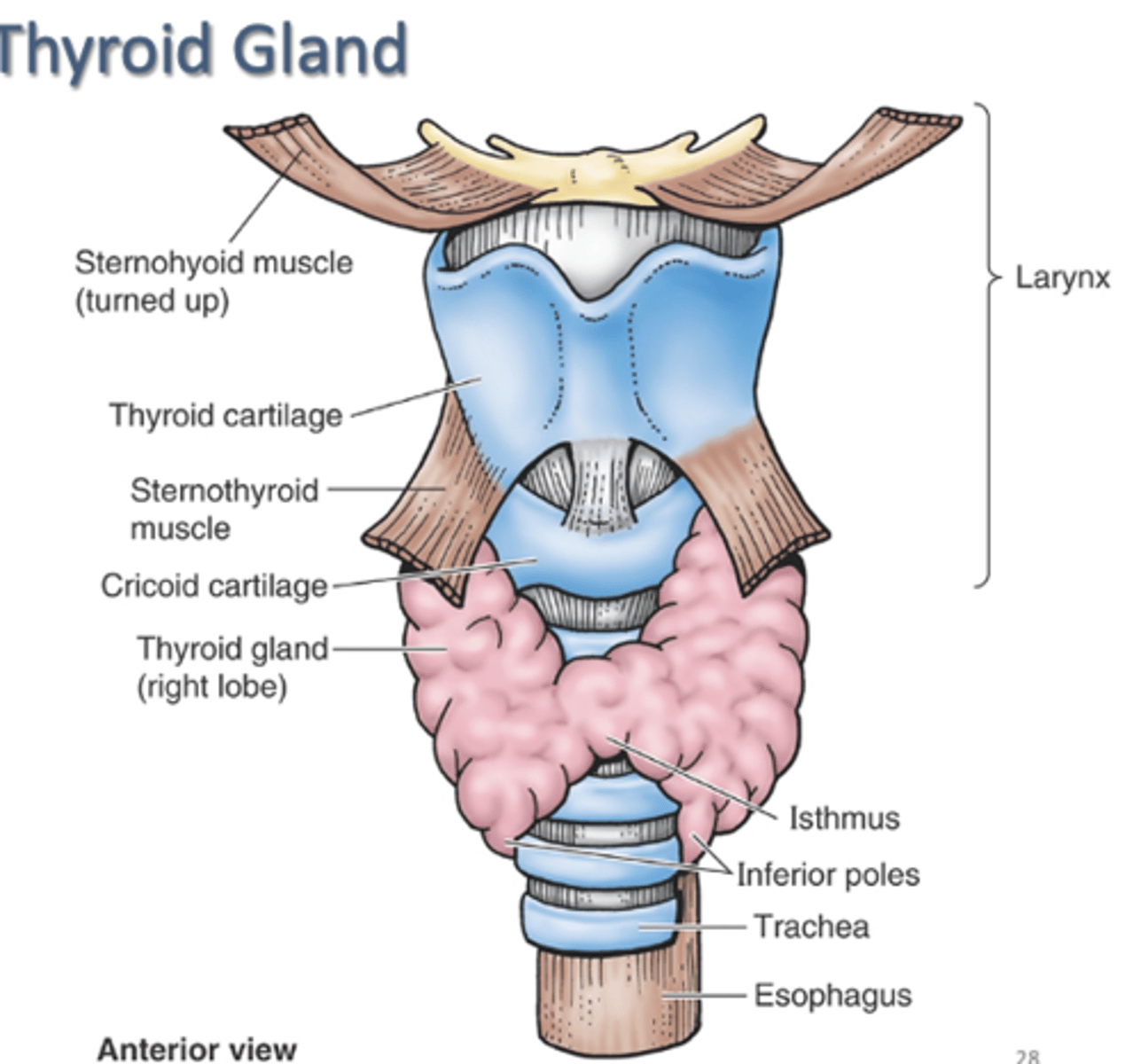
Trachea:
fibrocartilagenous tube, supported by incomplete tracheal cartilages
-extends from inferior end of larynx at C6 level
-ends at level of sternal angle or T4-T5 IV disc
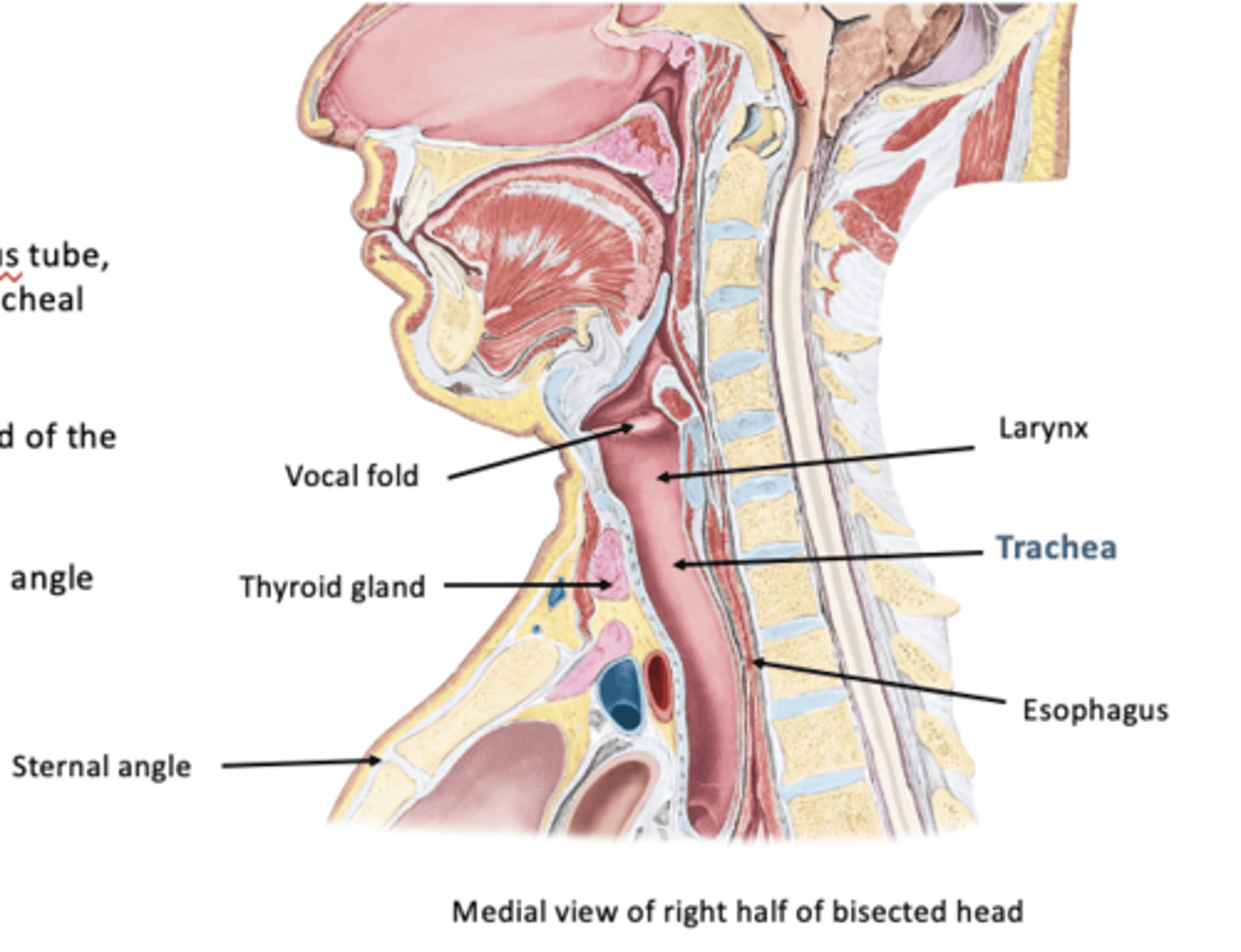
In adults, the trachea is about ___ in diameter
2.5 cm
-infants has diameter of a pencil
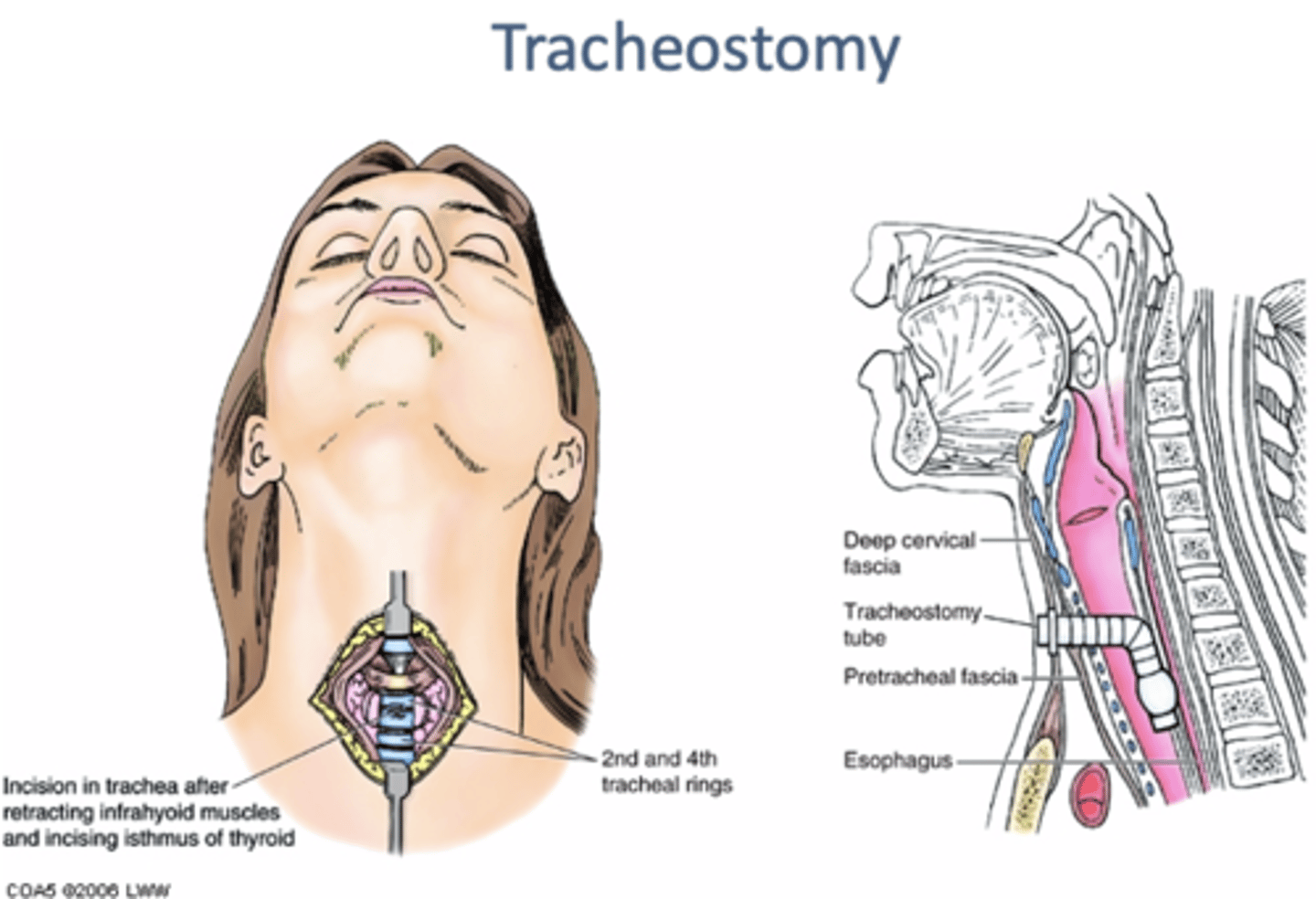
Tracheostomy:
making an opening of anterior wall of trachea
-airway in patients with upper airway obstruction
-incision can be made above, thru, or below isthmus of thyroid gland
Esophagus:
has cervical, thoracic, and abdominal parts
-cervical: begins at CV 6, continuous with cricopharyngeus m of pharynx
-esophagus passes thru diaphragm at TV 10
-after a short abdominal course ends in stomach
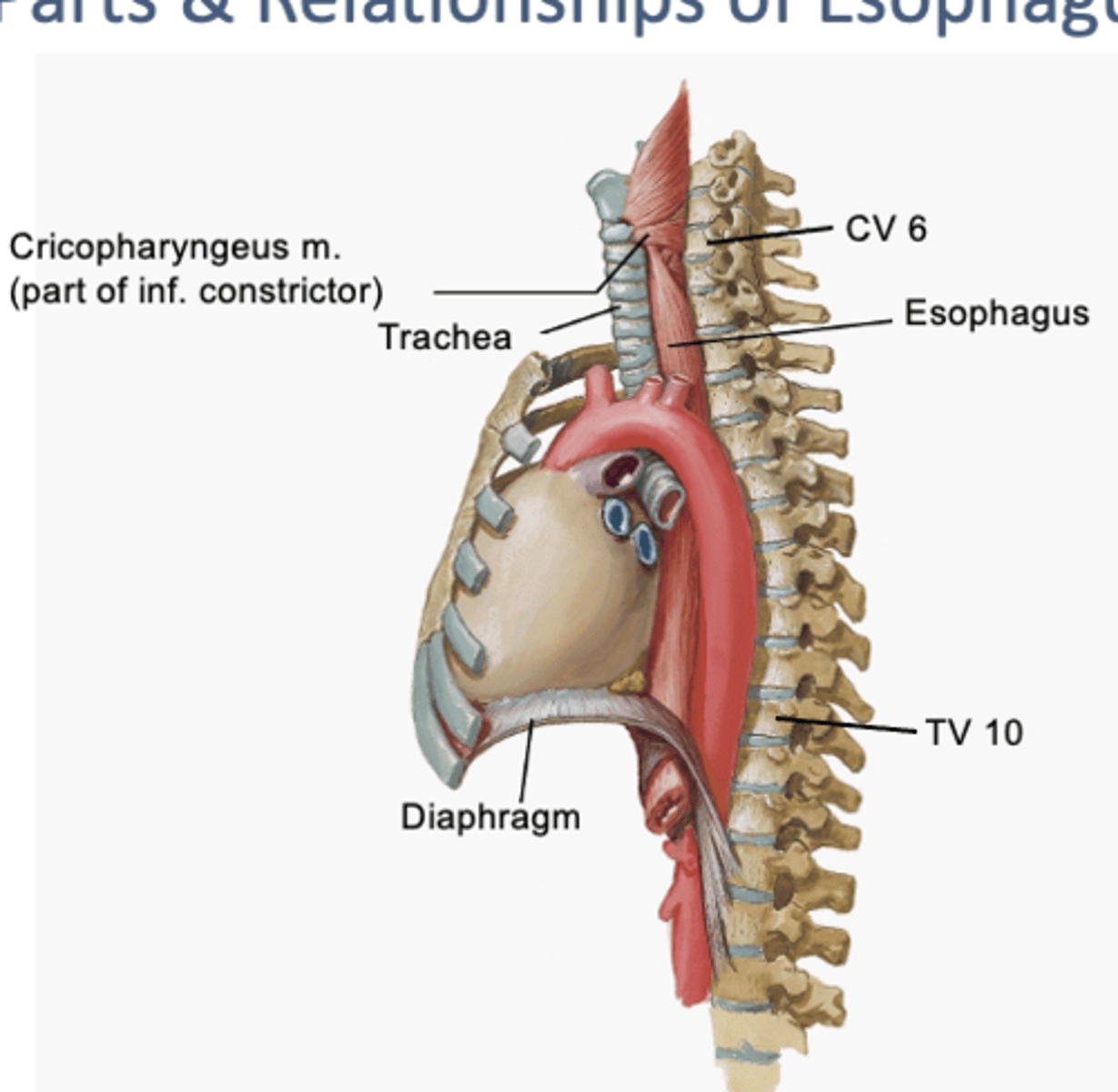
The cervical esophagus lies directly ___
behind the trachea
-and in front of vertebral column
What are the 4 constrictions of the esophagus?
1. Pharyngoesophageal constriction (inferior constrictor m of pharynx and esophagus)
2. Aortic constriction (arch of aorta compresses esophagus)
3. L main bronchus constriction
4. Diaphragm constriction (esophagus passes thru diaphragm)
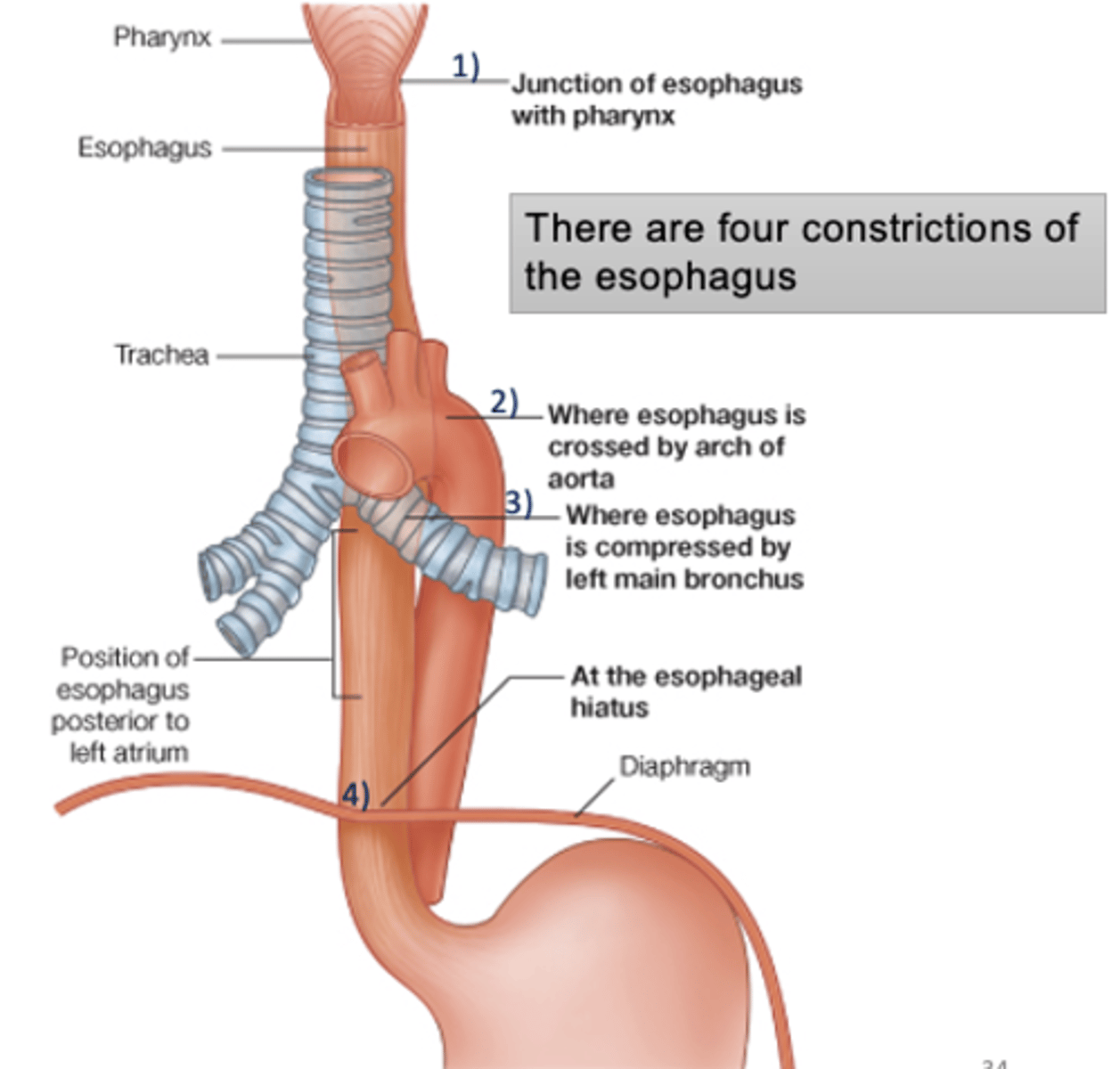
Where is the narrowest part of the alimentary tract?
pharyngoesophageal
-junction of esophagus with pharynx
___ has a tendency to develop at the sites of esophagus constrictions
cancer of the esophagus
-pt with a tumor may experience DYSPNEA (diff breathing) due to compressed trachea, HEMOPTYSIS (coughing up blood) due to erosion of small vessels supplying walls of esophagus and trachea, HOARSENESS (invasion of L recurrent laryngeal nerve), and FATAL HEMORRHAGE
The thoracic part of GI tract lacks a ___
serosal coat that acts as a temporary barrier to cancerous invasion of adjacent structures
Esophagus descends into thorax between the ___
trachea and vertebral column
-located posteriorly to left atrium of heart
-upper 1/3 is skeletal muscle replaced by smooth muscle
-supplied by branches of aorta
-innervated by esophageal plexus arises from vagus nerves
-passes thru esophageal hiatus at T 10 vertebral level