NMR
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
what species can be observed with NMR?
nuclei with a non zero spin
depends on the number of protons and neutrons
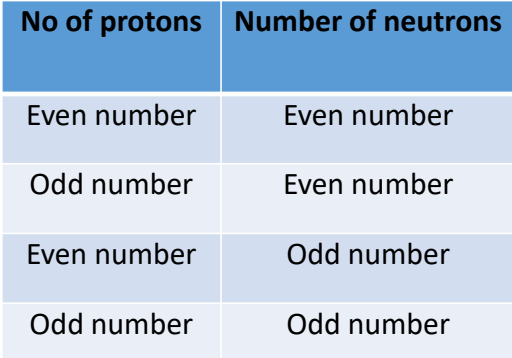
what are each nuclear spin?
what is the most useful nucleus for NMR?
spin of ½ = sharp peak
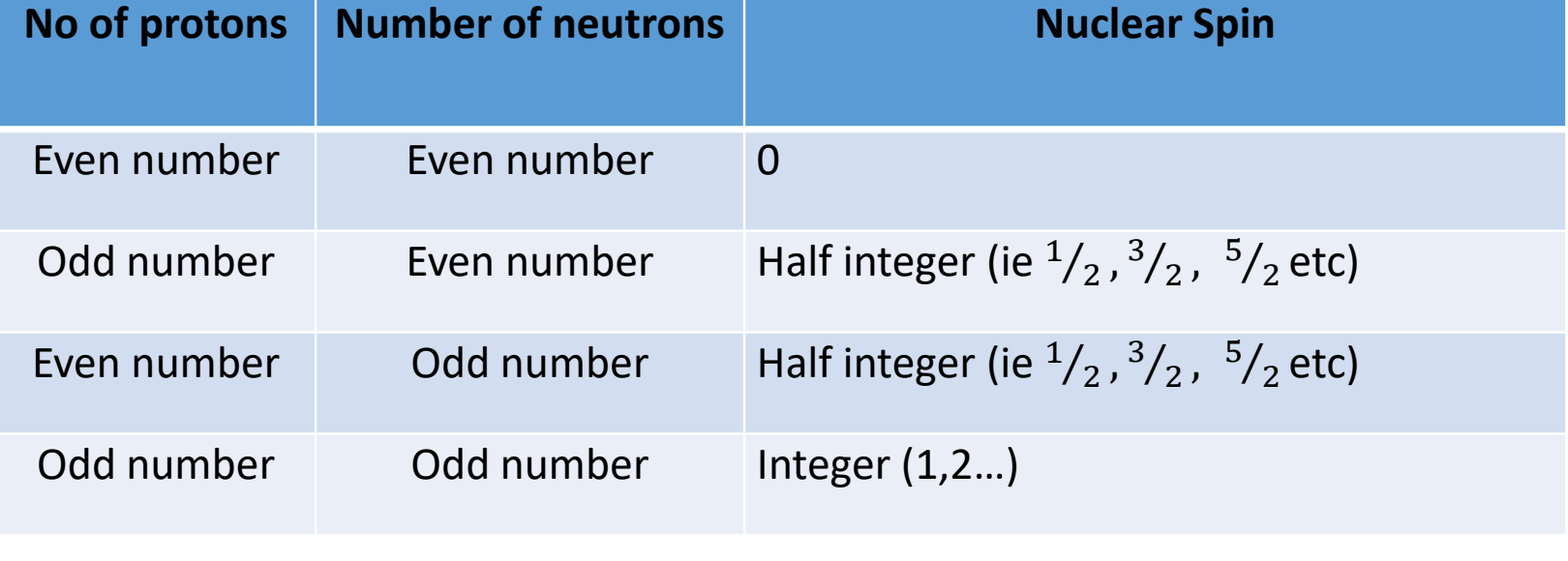
what happens when nucleus is placed in magnetic field?
nucleus of spin ½ is placed in magnetic field
spin can have m = +1/2 or m= -1/2 (aligned or opposed to magnetic field)
show spin splitting in energy as magnetic field (B) increases on graph
how does energy changes as B increases? what are the spin states like at zero field?
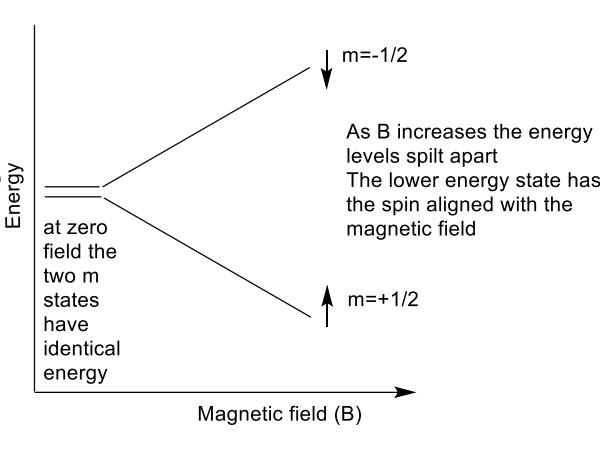
what does energy difference between spin states depend on?2
magnetic field strength
property of nucleus called gyromagnetic ratio
what is frequency equation? units?
gives freq in MHz
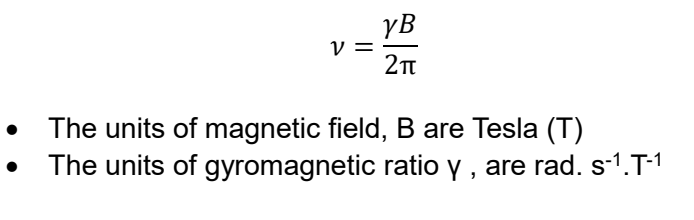
what does magnetic field experienced at nucleus depend on?
chemical environment
electron density
anisotropy - pi systems
how does electron density affect magnetic field and thus chemical shift? how does this affect energy difference between spin states?
electrons shield the nucleus from external magnetic field
smaller frequency as effective field is lower
smaller chemical shift
lower energy difference
how does pi system affect magnetic field and therefore chemical shift?
double bonds and aromatic rings create local fields which boost/decrease the field felt by the nucleus = increases chemical shift
show local magnetic fields made from benzene ring with external field acting up
how does this affect H on ring?
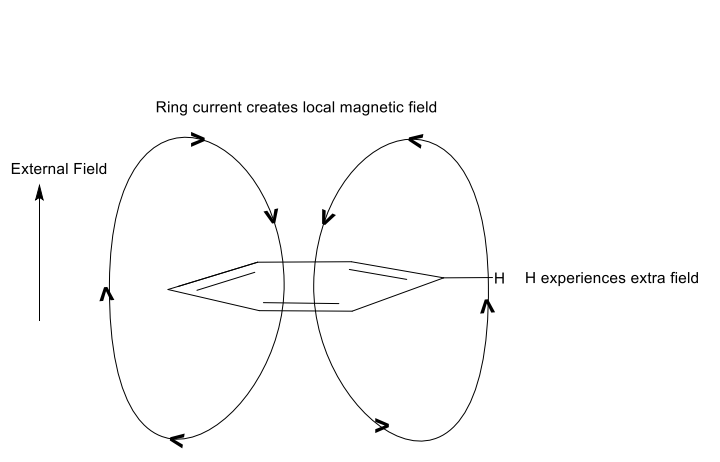
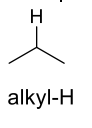
what are the approx chemical shifts of alkyl-H
1-2ppm
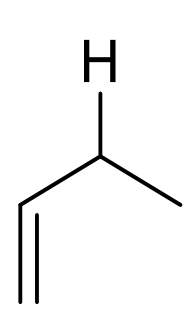
what are the approx chemical shifts of H next to alkene?
2-3ppm
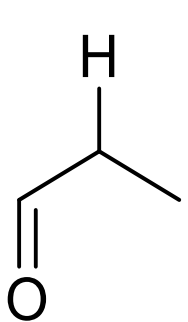
what is approx chemical shift of H next to carbonyl?
2-3ppm
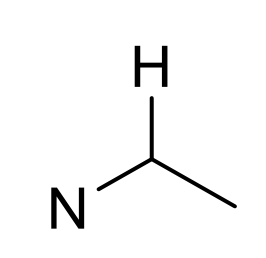
what is approx chemical shift of H next to N?
2.5-3.5ppm
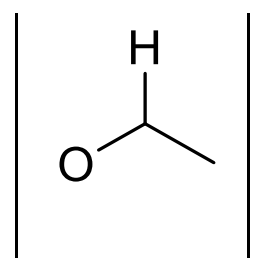
what is approx chemical shift of H next to O?
3.5-4.5ppm
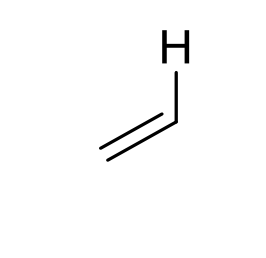
what is approx chemical shift of H on alkene?
4.5-7ppm
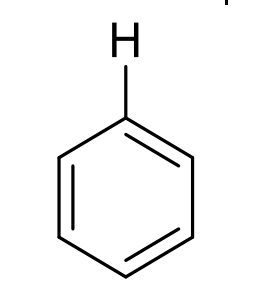
what is approx chemical shift of H on benzene?
7-8.5ppm
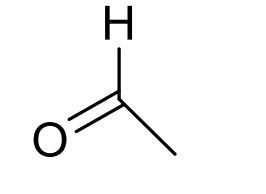
what is approx chemical shift of aldehyde H?
9-10ppm
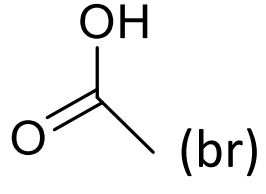
what is approx chemical shift of H on carboxylic acid?
10+ppm
how does a methyl group affect chemical shift?
electron donating group and is ortho para directing
shields ortho and para (decreases chem shift)
how does an acetyl group affect chemical shift?
electron withdrawing group and is meta directing
deshields ortho and para to itself
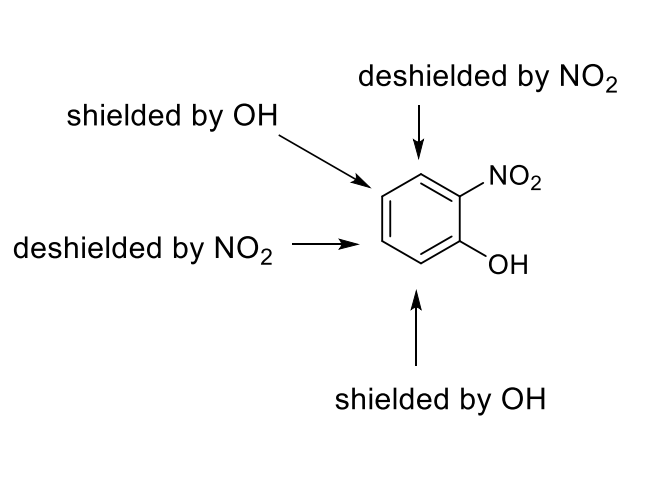
how is each position affected? (ie is it shielded or deshielded?)
how does this affect each chemical shift
deshielded increases chemical shift
shielded increases chemical shift
OH is ortho para directing and EDG
NO2 is meta directing and EWG
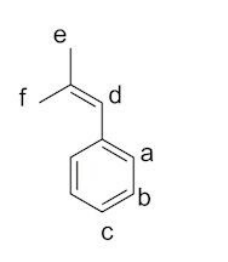
why is e and f separate environments?
f is always cis to the phenyl group when bond rotates
e is alway trans to phenyl group when bond rotates

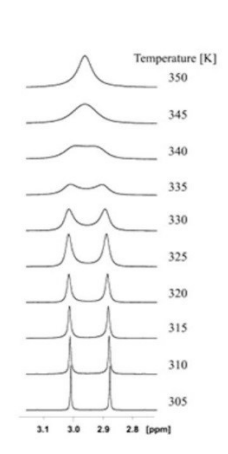
why does a and b have two separate peaks? does this change at higher temp?
slow rotation around amide bond
if sample heated, start spinning faster so peaks overlap
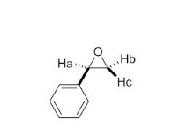
why is Hb and Hc different environments?
groups cannot interconvert so they are not the same environment
Hc is locked onto same face of ring as aromatic so is cis
Hb is always trans to aromatic ring
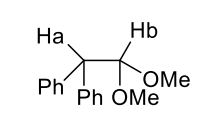
how does chiral centre affect H’s on CH2?
different environment - diastereotopic hydrogens
show how different spin state combinations leads to doublet?
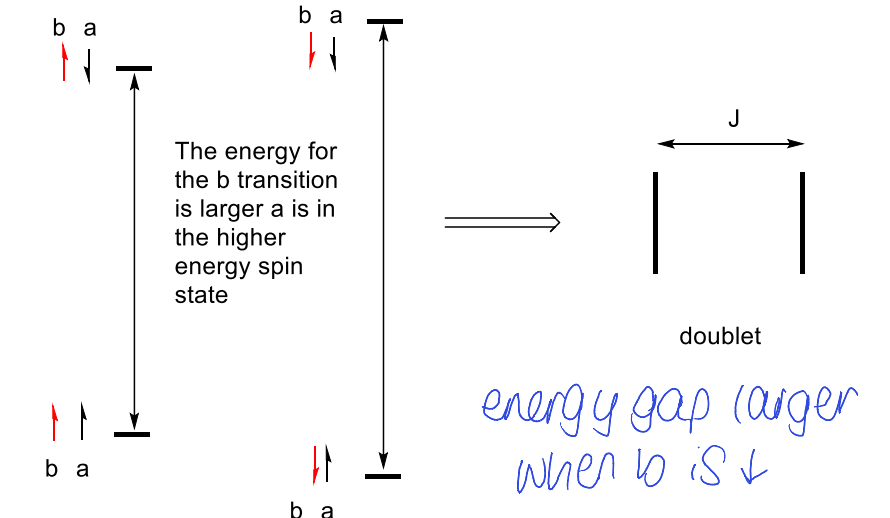
how does difference in transitions depend on spin states? show how this makes triplet

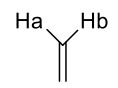
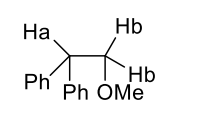
what is J value of geminal alkene coupling?
0-3Hz
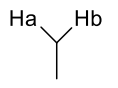
what is J value of geminal alkane coupling? (diastereotopic)
12-20Hz
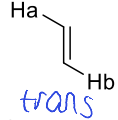
what is trans J value?
around 17Hz
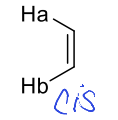
what is cis J value?
around 10 Hz
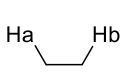
what is J value?
around 7Hz
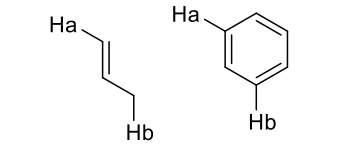
what is J value for 4 bond coupling?
0-2 Hz
what is roofing?
the outside line in a peak makes a roof over the inside line
taller lines point inwards towards each other
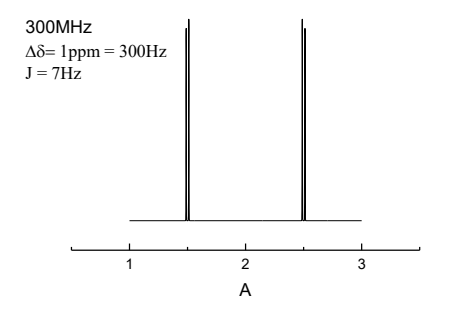
when do second order effects arise? what does it do to spectra?
when the chemical shift separation of two signals (in Hz) becomes similar to the
coupling constant
peaks may not be symmetrical around the centre, roofing, distortion to look like multiplet
how to limit second order effects?
stronger magnetic field
identical chem shift and coupling constant
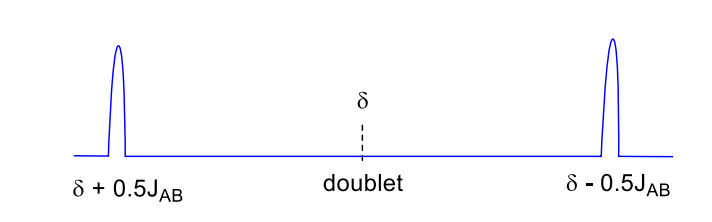
draw splitting tree with J values of doublet
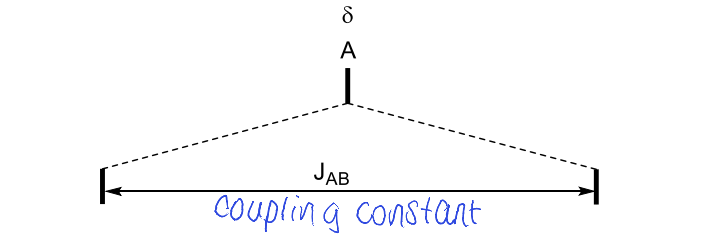
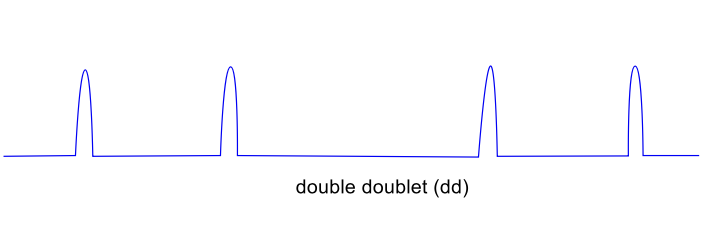
draw splitting tree with J values of doublet doublet

how are intensities split for splitting tree?
show intensity of 4 splitting twice and show JAB and JAC
intensity at the top is divided equally for every split
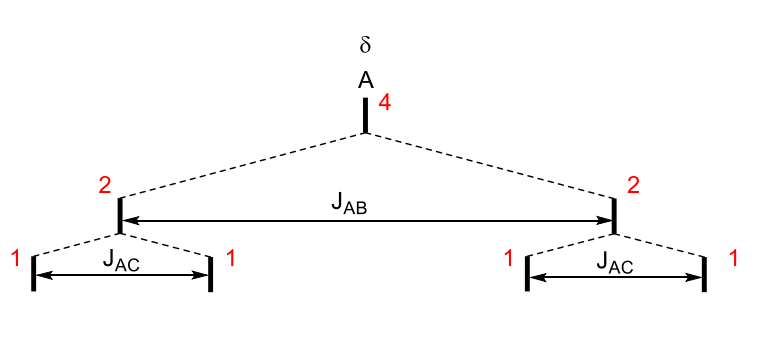
how does a dd turn into a triplet?
what happens as JAC gets bigger? when JAC = JAB?
coupling constants start getting similar - central peaks overlap
JAC gets bigger, middle lines get closer
JAC = JAB two lines perfectly overlap
what would make JAC=JAB?2
two protons that are being coupled to are identical
coupling constants happen to be the sae
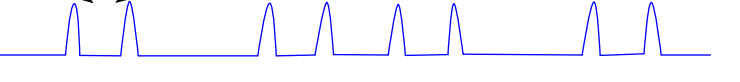
show splitting tree for ddd
which peaks is JAB between?
JAB is 1 to 4 rather than 1 to 3
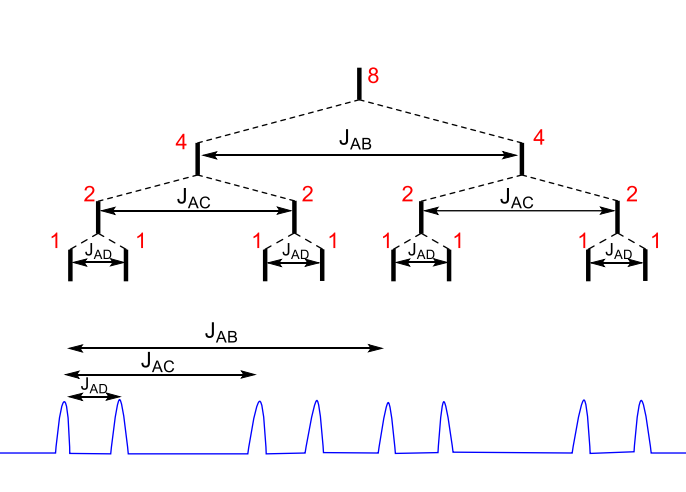
for ddd, what happens when JAB < JAC + JAD

for ddd, what happens when JAB = JAC + JAD
middle lines overlap
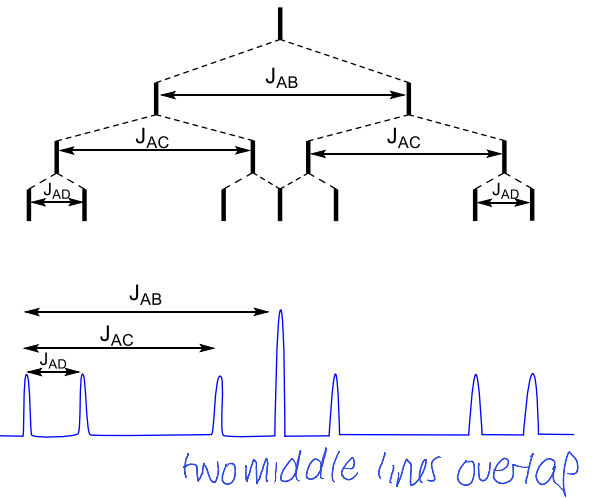
what happens when JAB = JAC > JAD?
ddd becomes dt
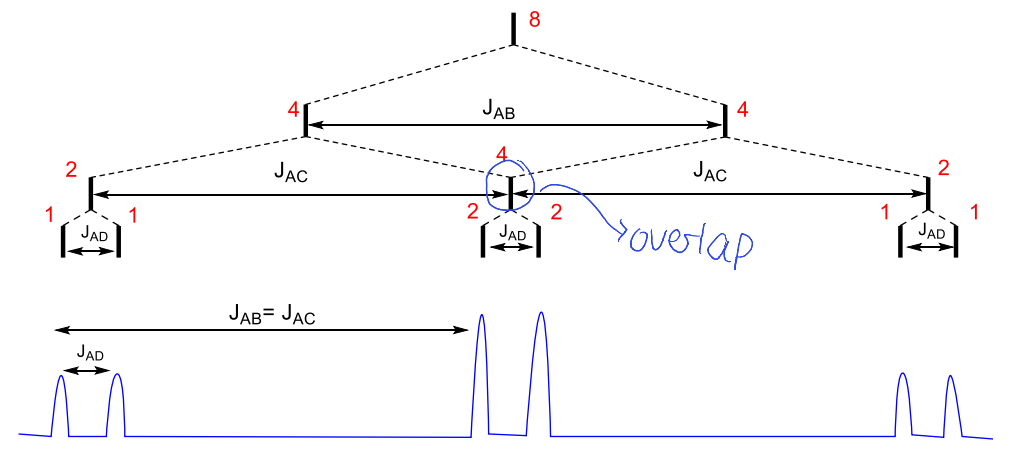
what happens when dt has JAB > JAC = JAD

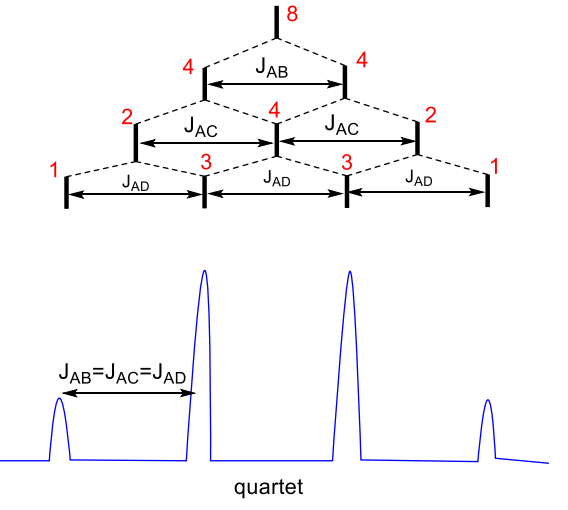
what happens when JAB = JAC = JAD?
quartet
how does a neighbouring C=O affect coupling constants?
makes coupling constants higher
why might a J value not match?
spectral lines have a width
overlaps can obscure small differences
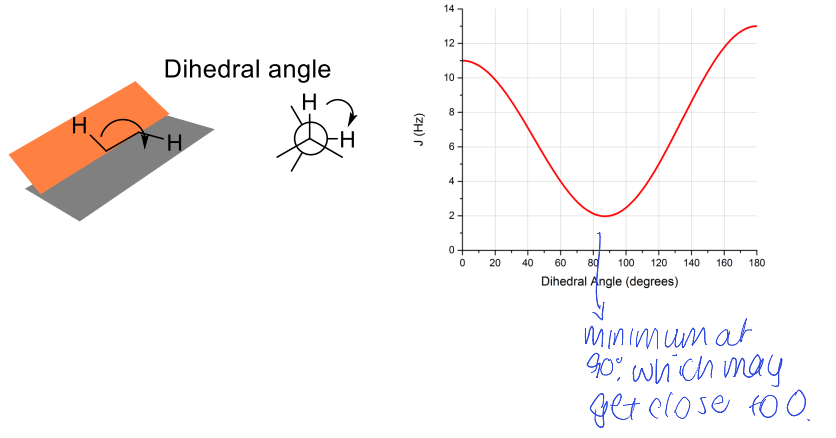
what is the Karplus relationship?
maxima at 0 and 180 (180 max is bigger than 0)
minima at 90
coupling constants depend on dihedral angle
why is 13C less sensitive than 1H NMR?
spin of ½ but abundance of 1%
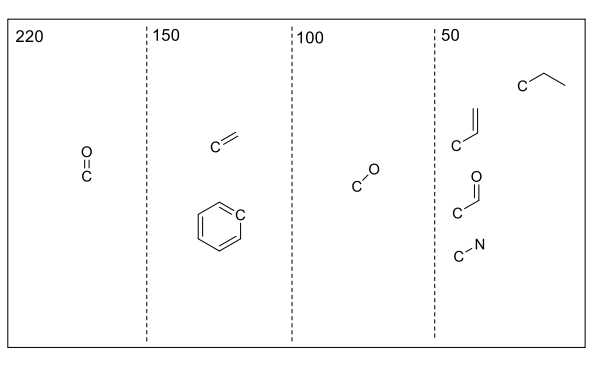
what are the approx regions for carbon-13 shifts?

why would b have a lower shift than c?
b is more shielded as MeO is ortho para directing
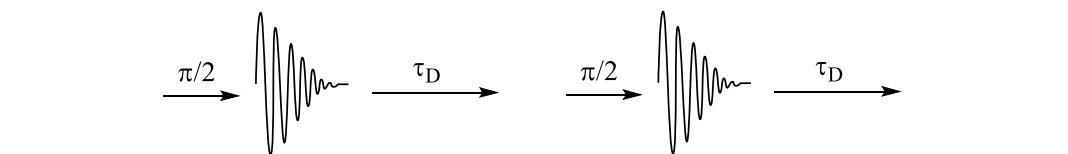
how are carbon-13 NMR signals affected by relaxation?
what happens in perfectly relaxing system? show starting state with 12 up and 6 down then acquisition
same signal for every scan
same number of electrons moves in order to give equal occupation
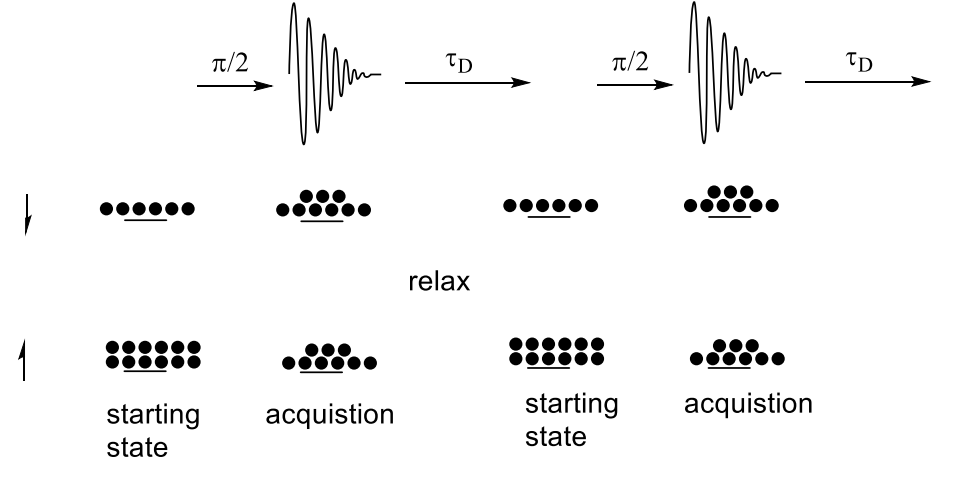

how does imperfect relaxation affect carbon-13 NMR?
show beginning with 12 up and 6 down
between scans, the electrons don’t fully return to equilibrium.
fewer move to give equal occupation
this means signals are lower

what is the main relaxation route for 13C?
why do C’s with no hydrogens have small signals?
oscillating dipoles from attached hydrogens
therefore if no attached hydrogens, relaxation is very inefficient giving a small signal
why is carbon-hydrogen coupling not seen in 13C?
spectrum is acquired with proton decoupling which means machine is irradiating H’s
how are protons removed from 13C spectra?
machine irradiates H’s
change spin states rapidly - C-H coupling removed from spectrum
see average of up and down of hydrogens which removes them
in dept135 experiments (shows CH/CH3/CH2), which way do each type of carbon point?
CH and CH3 is up
CH2 is down
C disappears
what can 19F and 31P be used for in NMR?
100% abundant with ½ spin
can run NMR directly or can see influence on other nuclei through heteronuclear coupling
what does it mean when an instrument has a certain frequency e.g. 400MHz for proton NMR?
magnetic field makes 1H resonate at 400MHz
how to find frequency for one nuclei compared to another?
why would the frequencies be different?
they have different gyromagnetic ratios
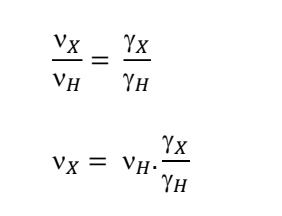
how does J change when measured between different spectra?
J is the same between spectra
does 13C NMR show carbon-carbon coupling?
no because natural abundance of 13C is very low so chances of 13C neighbouring is very low