Unit 3: Populations (copy)
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Where do generalists exist? and specialists exist?
generalists exist under a broad range of conditions while specialists exist under a narrow range.
Specialists persist under
specialists persist quite well when environmental conditions remain relatively constant. they are very vulnerable to reductions in number.
Generalists fare better under
Generalists fare better under changing food or environmental conditions as they have a number of alternate food sources available to them.
When an environmental scientist refers to the success of a species, they are speaking about?
the population size of that species
Population size most commonly increases through? What is it defined as?
Population size most commonly increases through reproduction. Its defined as population growth rate and intrinsic growth rate.
Species have different reproductive strategies
The number of offspring an individual can produce in a given time period minus the deaths of the individual or its offspring during that same period.
Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources available..
every population has a particular maximum potential for growth called the biotic potential
What are K-Selected species?
generalists exist under a broad range of conditions while specialists exist under a narrow range.
What is the carrying capacity?
The carrying capacity is the limit to the number of individuals that can be supported by an existing habitat or ecosystem and is denoted as K.
Generalists fare better under
Generalists fare better under changing food or environmental conditions as they have a number of alternate food sources available to them.
Are population fluctuations usually big or small?
small
A K-Selected population has these traits in common:
large organisms that reach reproductive maturity relatively late, and produce few, large offspring per reproductive event
The slow growth of K-selected species means that
The slow growth of K-selected species means that an endangered species means that an endangered species cannot respond quickly to save it from extinction.
K-Selected Species
low population growth
long life spans
large organisms
lives in stable environments
remains close to carrying capacity
vulnerable to invasive species
few large offspring per reproductive event
reach reproductive maturity relatively late
What are R-Selected species?
Has a high intrisitic growth rate and their populations increase rapidly
R-Selected Species
reproduce often
produces large amounts of offspring
rapidly surpasses their carrying capacity
reaches reproductive maturity early
produce many small offspring with the potential for high growth rates
What is overshoot and die back?
An increase in the population so it passes carrying capacity and then a rapid decline in population due to death.
Once overshoot happens
There are more individuals than the system can support and so a major die back is unavoidable
Environmental Scientists use growth models to
predict how systems like populations might change in the future.
Density-dependent factors influence an
individual's probability of survival and reproduction in a manner that depends on the size of the population.
Density independent factors-
Are those that have the same effect on an individual's probability of survival and reproduction at any population size.
What are R-Selected species?
Has a high intrisitic growth rate and their populations increase rapidly
A high number of births and a low number of deaths produce
A high population growth rate
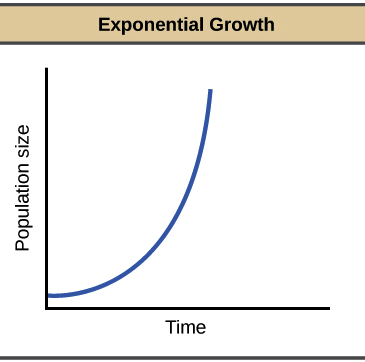
Exponential Growth Model is
A model that estimates a population’s future size after a given period of time based on the biotic potential and the number of reproducing individuals currently in the population
When populations are not limited by resources
Growth can be very rapid because more births occur with each unit of time
When we graph an exponential growth model, it produces
A J-Shaped Curve
What does a J-shaped curve represent?
The change in a growing population over time.
No population can experience
exponential growth forever as it will approach the carrying capacity at which point its growth will slow and level off
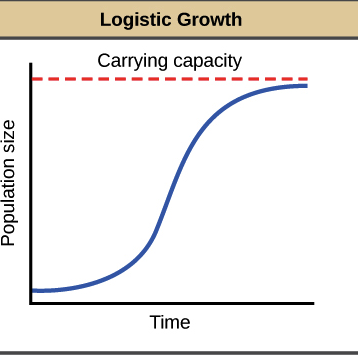
What does a Logistic Growth model describe?
a population that is limited by the carrying capacity. The growth is initially exponential but slows as the population approaches the carrying capacity of the environment.
Organisms that are r-selected species include
small fish, insect species, pests, and certain plant species
What is the carrying capacity?
The carrying capacity is the limit to the number of individuals that can be supported by an existing habitat or ecosystem and is denoted as K.
The population size of a K-Selected species is largely determined by
the carrying capacity
Are population fluctuations usually big or small?
small
A K-Selected population has these traits in common:
large organisms that reach reproductive maturity relatively late, and produce few, large offspring per reproductive event
The slow growth of K-selected species means that
The slow growth of K-selected species means that an endangered species means that an endangered species cannot respond quickly to save it from extinction.
K-Selected Species
low population growth
long life spans
large organisms
lives in stable environments
remains close to carrying capacity
vulnerable to invasive species
few large offspring per reproductive event
reach reproductive maturity relatively late
When the population nears one half of the carrying capacity,
the population growth hits an inflection point and growth starts to slow, when graphed it forms an s-shaped curve
Animal populations and human populations can so severely transform an ecosystem causing a resource to become
so depleted that the carrying capacity declines.
In some cases, like with the reindeer the
loss of population can easily be reversible as the vegetation can regrow and be managed by officers
Every 5 days, the human population increases and decreases roughly by
1.3 million people. 2 million infants are born, and 750,000 people die.
How did human population growth change from the past 400 years?
agricultural output increased and the separation and treatment of human waste began to improve. food and sanitation also increased causing birth rates to increase.
what is oscillation?
the regular ups and downs seasonally of a population
Why will specialist species be more affected when there is a changing environment?
They will be more affected when there is a changing environment because they only rely on very specific things like a type of food, habitat, etc.
When the population nears one half of the carrying capacity,
the population growth hits an inflection point and growth starts to slow, when graphed it forms an s-shaped curve
Animal populations and human populations can so severely transform an ecosystem causing a resource to become
so depleted that the carrying capacity declines.
The biotic potential of a population depends on
the limiting resources of the population
Which of the following is not common in K-Selected Species?
Little Parental Care
In a graph, it shows the population going up and down seasonally, this is known as
oscillation
Why would an exponential growth population be more affected by seasonal drought than a population with logistic growth?
Seasonal growth affects the availability of resources and the scarce resources can lead to a decline and greatly impact the population.
Every 5 days, the human population increases and decreases roughly by
1.3 million people. 2 million infants are born, and 750,000 people die.
Some scientists believe that we have already
outgrown or will outgrow the resources that we humans rely on
Once overshoot happens
There are more individuals than the system can support and so a major die back is unavoidable
Why will specialist species be more affected when there is a changing environment?
They will be more affected when there is a changing environment because they only rely on very specific things like a type of food, habitat, etc.
Density-dependent factors influence an
individual's probability of survival and reproduction in a manner that depends on the size of the population.
Density independent factors-
Are those that have the same effect on an individual's probability of survival and reproduction at any population size.
When the population nears one half of the carrying capacity,
the population growth hits an inflection point and growth starts to slow, when graphed it forms an s-shaped curve
What is survivorship?
Different patterns that explain how populations change over time in response to a variety of factors.
Some scientists believe that we have already
outgrown or will outgrow the resources that we humans rely on
Exponential Growth stops or slows when
an environmental limit is reached
Some scientists believe that we have already
outgrown or will outgrow the resources that we humans rely on
Once overshoot happens
There are more individuals than the system can support and so a major die back is unavoidable
Environmental Scientists use growth models to
predict how systems like populations might change in the future.
Infant mortality rate is defined as
the number of deaths of children under 1 year of age per 1,000 live births
What is survivorship?
Different patterns that explain how populations change over time in response to a variety of factors.
Where are the survival patterns plotted?
On a graph as a function of age which are called the survivorship curves
What are age structure diagrams?
It describes how populations are distributed across age ranges, and insights into future population changes
What are the three ranges of age structure diagrams?
Pre reproductive age (0-14), Reproductive years (15-44), post reproductive age (45+)
Once overshoot happens
There are more individuals than the system can support and so a major die back is unavoidable
Some scientists believe that we have already
There are more individuals than the system can support and so a major die back is unavoidable
Environmental Scientists use growth models to
predict how systems like populations might change in the future.
Infant mortality rate is defined as
the number of deaths of children under 1 year of age per 1,000 live births
What is TFR?
Total fertility rate, an estimate of the average number of children that each woman in a population will bear throughout her childbearing years.
child mortality rate is defined as
the number of deaths of children under 5 years of age per 1,000 live births
Exponential Growth stops or slows when
an environmental limit is reached
What are the three ranges of age structure diagrams?
Pre reproductive age (0-14), Reproductive years (15-44), post reproductive age (45+)
Type II Curve-
A pattern of survival over time where there is a relatively constant decline in survivorship throughout the lifespan.
Type III Survivorship Curve-
Has low survivorship early in life with a few individuals reaching adulthood.
Species have different reproductive strategies
The number of offspring an individual can produce in a given time period minus the deaths of the individual or its offspring during that same period.
High fecundity-
When food is abundant, individuals have a tremendous ability to reproduce
Where do generalists exist? and specialists exist?
Specialists persist under
The study of human populations and populations trends are called and what is the scientist?
demography and demographer
inputs include
births and immigration
Why would an r-selected species usually follow type III survivorship?
They are born in large numbers as many die quickly.
when inputs are greater than outputs..
the population growth rate is positive
Infant mortality rate is defined as
the number of deaths of children under 1 year of age per 1,000 live births
what is CDR
crude death rate, number of deaths per 1000 individuals every year
how is global population growth calculated?
CBR - CDR / 10 × 100
What is net migration rate?
difference between immigration and emigration in a given year per 1000 people
How do you calculate the growth rate for a single nation?
(CBR + immigration) - (CDR - emigration) / 10 × 100
What is the calculation for net migration rate?
number of immigrants / yr over number of people in the population
what is doubling time?
used for assuming that the growth rate is constant and seeing the number of years it takes for it to double
What is the formula for doubling time?
70/growth rate %
Theory of demographic transition states that
a country moves from high to low birth and death rates as development occurs and the country moves from preindustrial to an industrialized economic system
what are the four stages of demographic transition?
slow population growth - steady state - cbr = cdr
rapid population growth - births outnumbers deaths
stable population growth - cbr and cdr decrease
declining population growth - cbr below cdr
what is the ipat equation?
impact = population x affluence x technology
what does affluent mean
wealthy / rich
what is affluence?
created by economic opportunity and does not have a simple a relationship as population.
the more affluent a society or individual has
the higher the environmental impact they have
what does technology do?
degrade our environment and minimize our impact