Clinical Approach to Oncology (Objectives Only)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Define CR.
- Complete remission/response: Complete disappearance of tumor(s) and symptoms of disease
Define PR.
- Partial remission/response: At least 30% reduction in the sum of diameters of target lesions.
Define SD.
- Stable Disease: Less than 30% reduction or 20% increase in the sum of diameters of target lesions
Define PD.
- Progressive disease: Either the appearance of one or more new lesions at at least a 20% increase in the sum of diameters of target lesions
Define PFI.
- Progression free interval/survival: The amount of time elapsed without evidence of progressive tumor growth or death
Define DFI.
- Disease free interval: The amount of time that elapses without disease recurrence
What is ORR?
- Overall response rate = CR and PR
What is BRR?
- Biological respnose rate = CR + PR + SD
Define adverse events.
- Any unfavorable and unintended clinical sign or disease temporally associated with the use of a medical treatment that may or may not be considered related to the medical treatment
Define adjuvant treatment.
- Treatment with chemotherapeutic agent after achieving control of the primary tumor with surgical resection or radiation therapy
Define neoadjuvant treatment.
- Chemotherapy used prior to treatment with other modalities for local tumor control, with the intent of decreasing the tumor size
Define induction therapy.
- Chemotherapy treatment with the intent of a cure. Initial chemotherapy protocol
Define rescue therapy.
- Use of chemotherapy after a tumor fails to respond to a previous therapy or after tumor recurrence
Define MTD.
- Maximum tolerated dose: Highest dose of a given drug that can be administered in the absence of unacceptable or irreversible side effects (used in most chemotherapy protocols)
Define BED.
- Biologically effective dose: Targeted therapy (Palladia): esponse at a putative target that is related to the mechanism of action of the agent
Define metronomic drug dosing:
- Low-dose chemotherapy given on daily to every-otherday schedule. Aimed to slow progression of tumor through multiple mechanisms (angiogenesis, tumor immunology)
What are normal cells in the body that are always replicating?
- Bone marrow
- GI cells
- Hair follicles (more so in people)
What is the half-life of neutrophils, platelets and RBCs?
- Neutrophils: Hours to 1 day (shortest - why we monitor them closely)
- Platelets: 7-10 days
- RBCs: 100-120 days (dogs); 70-80 days (cats)
1:10:100 rule
What is the timeline for the nadir of most chemotherapeutic agents?
- 5 to 7 days post-dose
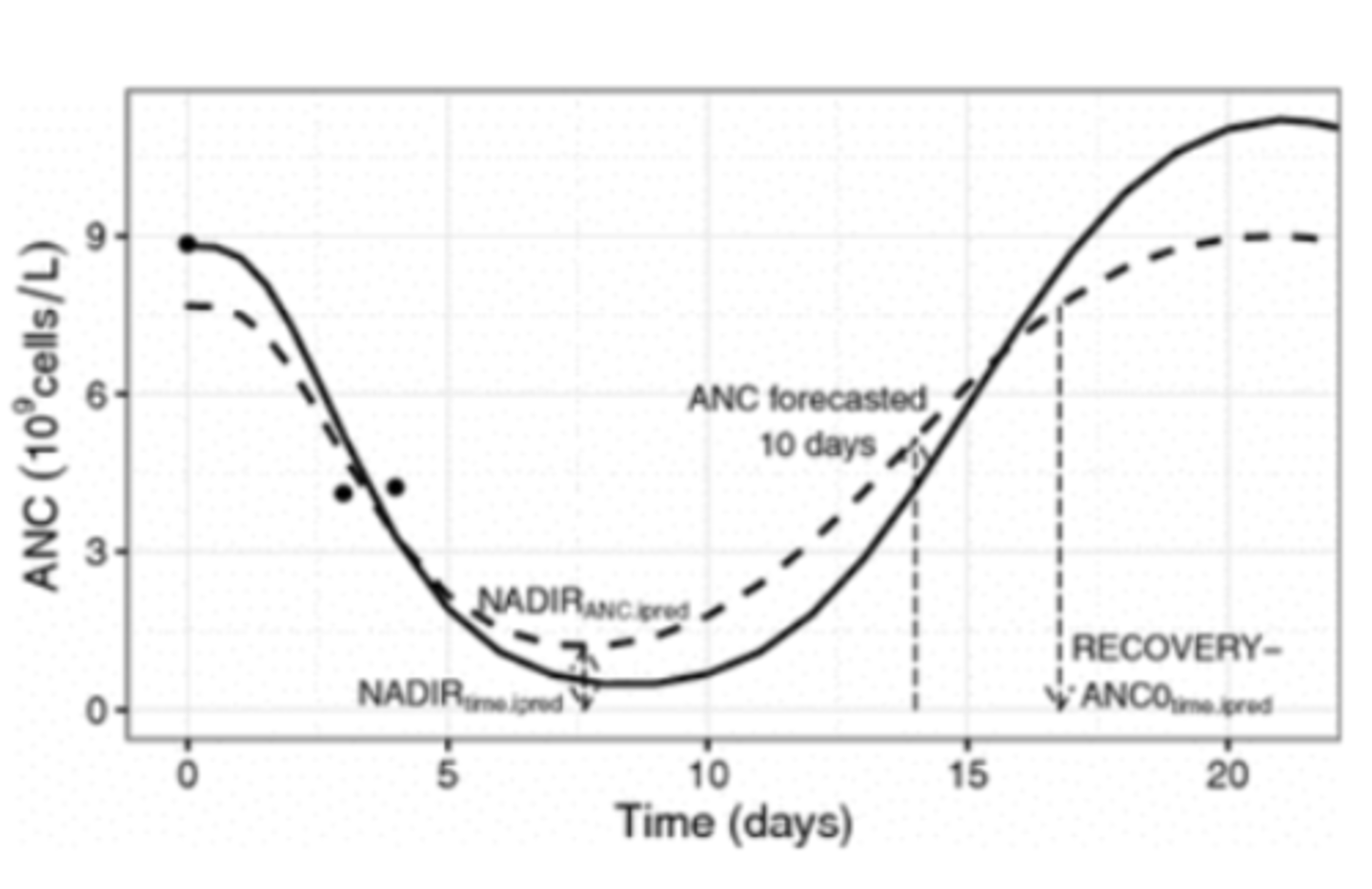
Be able to assess blood work of a patient receiving chemotherapy and know when antibiotics/hospitalization may be indicated.
- Grade 2/Mild toxicity -> 1000 neutrophils/microliter -> No ABX
- Grade 3/Moderate toxicity -> 500-999 neutrophils/microliter -> Oral broad-spectrum ABX, repeat CBC in 2-3 days; Do not hospitalize; No parenteral fluids (SQ or IV) or supportive care unless pt is febrile
- Grade 4/Severe toxicity -> >500 neutrophils/microliter +/- fever -> Oral broad spectrum ABX, IV if fever, recheck CBC in 24 hours, hospitalize if febrile
What are some pain management options for cancer in a palliative setting?
- Medications: NSAIDs, Gabapentin, Opioids, amantadine (good for chronic bone pain)
- Bisphosphonates (Clinically apparent analgesic benefit is often in excess of one month; Controversial if true pain relief)
- Acupuncture
- Radiation
In what contexts should NSAIDs vs. steroids be used for palliative management of cancer pain?
- NSAIDs -> Carcinomas (high COX-2 expression)
- Steroids -> Round cell tumors (cause apoptosis of neoplastic round cells at immunosuppressive doses)
What are some options for encouraging anorectic animals to eat?
- Different flavors, formulations, toppers, broths
- Paper plates: Dogs and cats have way better sensory olfactory - smell things in tupperware
- Feeding tubes
True or false: Just because a patient is eating does not mean they are eating enough
- True
True or false: Anorexia/cachexia is an extremely common paraneoplastic condition in veterinary medicine.
- False; Can occur but is less common in vet med, many patients are overweight
What are some medical management options available for nutritional support of cancer patients in a palliative setting?
- Anti-nausea: Maropitant, Ondansetron, Metoclopramide
- Gastroprotectants: Sucralfate, Omeprazole, Famotidine
- Anti-diarrheal: Metronidazole, Tylosin, Loperamide Immodium, Crofelemer Canalevia (FDA approved specifically for chemotherapy-induced diarrhea)
Define caregiver burden.
- Response of distress to difficulties encountered while providing care for an individual with an illness. Includes time and physical demands, as well as perceptions and emotional responses.
Define QOL.
- Quality of life = sense of life's 'goodness'. Client's subjective evaluation of positive and negative aspects of own life
Define grief.
- Bereavement reaction. Feelings of sadness and despair owing to a loss or anticipated loss
What are some management practices to support clients in a palliative cancer management setting?
- Treat every client as an individual
- Avoid minimizing the feelings of burden
Share the power of knowledge (www.petcaregiverburden.com)
- Collaborative care plan
- Help client problem solve
- Offer words of encouragement
- Elicit owners understanding of pet's illness and current state of health
- Ask how much the owner wants to know about the pet's situation
- Give the pertinent information according to what was discovered in point number two
- Respond empathetically to the owner's emotional response and include our own reaction to the information
- Summarize strategies and review decisions that are made concerning goal and care decisions
Tumors grow in a _________ fashion.
- Sigmoidal
What is the limit of detection for neoplasia? Limit of symptoms?
- 10^9 cells
- 10 ^11 cells