Blood vessels
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What are the 3 main blood vessels
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
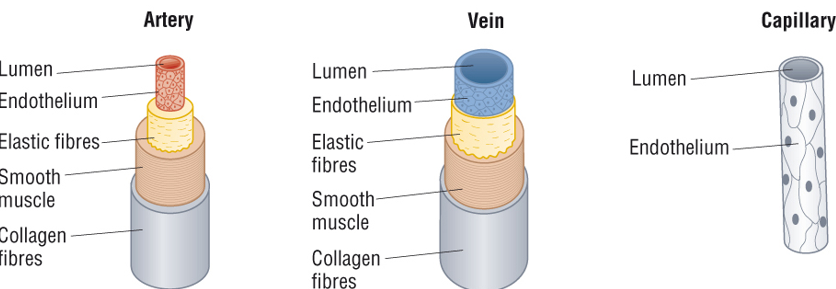
Describe the arteries
Maintains high pressure by elastic tissue which stretches/recoils.
It has a small lumen and smooth muscle which contracts and relaxes to widen or constrict lumen.
Has thick walls which contain collagen
Endothelium is folded, unfolds when artery stretches
Describes the veins
Blood flows at low pressure to heart due to thinner layers of collagen, smooth muscle and elastic tissue
Has a large lumen
Have valves to prevent backflow
Found in skeletal muscle contraction of muscle moves blood along
Describe the capillaries
Very narrow lumen 7 micrometres wide which is the diameter of one RBC
Narrow lumen increases time for exchange by diffusion
Leaky walls to allow plasma and dissolved substances to leave blood
Walls are one cell thick
What are the tissues found in blood vessels
Elastic fibres
Collagen
Smooth muscle
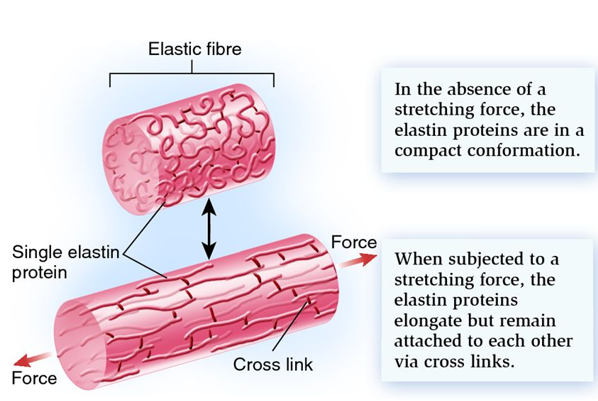
Describe role and structure of elastic fibres
Made of elastin and gives stretch and flexibility to blood vessels
Can stretch when force applied and recoil when force removed
Describe role and structure of collagen
It is a strong structural protein, made up of strong fibres
Give support to maintain the shape and volume of blood vessels
Found in tendons, cartilage, ligaments and skin
Describes the role and structure of smooth muscle
Contracts and relaxes to change lumen size
What are arterioles
Link arteries and capillaries
Have more smooth muscle in their walls than arteries this means that:
They can constrict/ dilate to divert blood to individual organs. Vasoconstriction prevents blood flowing into a capillary bed. Vasodilation regulates blood flow to capillaries
Less elastin as pulse is weak
Note:
Blood pressure lowers from arteries to arterioles to prevent rupture of capillaries. Achieved as they have more smooth muscle and a smaller lumen so increases resistance
What is the capillary beds
Network of capillaries running through tissue
Contain precapillary sphincters which help regulate flow of blood to tissues ( A bit like valves open and close to regulate blood flow)
What are venules
Link capillaries to veins
Combine to form veins
Collect blood from capillary bed and carry towards veins
Thin walls, small amount of smooth muscle, elastin and collagen
Describe how valves in veins work
Prevent backflow of blood as blood moves forward when muscles nearby contract, when muscles relax pressure drops so valves close.
How are arteries and arterioles suited for their functions
Arteries:
Have small lumen but smooth muscle can constrict or relax to change its shape. Thick walls contain lots of elastic tissue and smooth muscle. Allows them to withstand high pressure of blood from heart, and elastic recoil helps maintain blood pressure
Arterioles:
Have a narrower lumen and more smooth muscle within their walls, which increases resistance and causes blood pressure to fall before it reaches capillaries, preventing damage. Smooth muscle allows vasoconstriction and vasodilation controlling amount of blood to capillary beds