Wk 6 - Gait, Gait Deviations, Causes and Solutions for those Deviations
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What position/orientation should you place the socket and foot for a patient with:
Knee ROM: 0-128
Adduction angle: 4o
Socket: 5 degrees flexion (sagittal) due to having full extension, 4 degrees aDduction (coronal), PTB anterior (Transverse)
Foot: proximal bisection/weight line at the posterior 1/3 point of foot (sagittal), posterior bisection of heel (coronal) if there is no bisection line then have the foot “inset”/medial up to 1 cm (if they have a longer limb closer to 1 cm but if it is shorter then under 1 cm) making a varus moment due to the GRF, 5 degrees of toe out (transverse)

Describe the socket angle of this prosthesis and the position of the foot relative to the socket
Right prosthesis with Neutral socket with foot more anterior


Describe the socket angle of this prosthesis and the position of the foot relative to the socket
Right prosthesis with Flexed socket with a neutral foot


Describe the socket angle and the foot position
Right prosthesis with a proximal bisection line, aBducted socket with outset foot


Describe the socket angle and foot position
Right prosthesis, neutral socket, and outset foot

When patient dons socket, the socket angle now what?
Matches the patient’s bony alignment
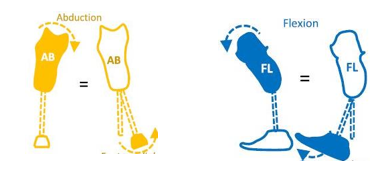
When socket is put into too much abduction, what happens to the foot?
Causes the foot while on the patient to rest on the lateral edge, making foot more medial
What are the 3 phases of alignment?
Bench → Static → Dynamic
What does alignment influence? How?
Alignment influences the magnitude and distribution of forces throughout gait due to GRF being transmitted to the socket/limb
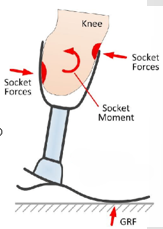
What can malalignment lead to?
Socket pressures/limb issues
Increased energy expenditure
What should we take into consideration when alignment is concerned?
Consider relationship between socket and limb.
Residual limb is essentially a stationary object
Socket is mobile and influenced by GRF
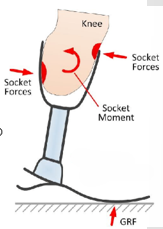
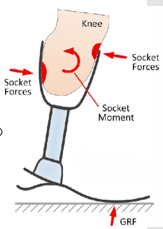
What moment is being exhibited in the knee? Why if this happening? What pressures are being felt?
Due to too much plantarflexion, there is a knee extension moment happening and results in anterior medial and posterior distal pressures being felt.
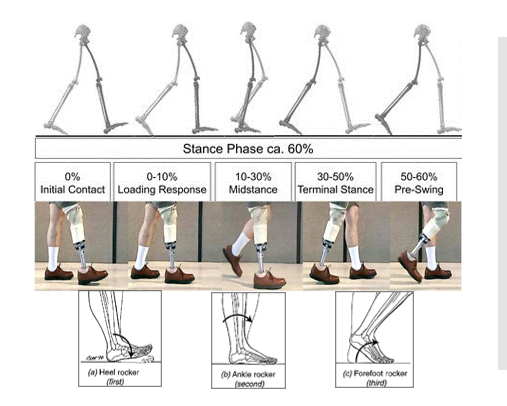
What phase of gait are we most concerned with in Trans-Tibial?
Stance Phase
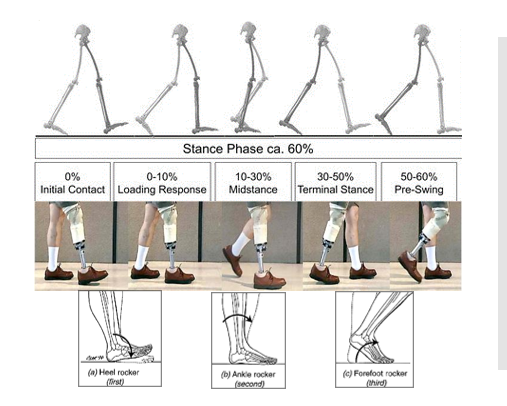
Mid-stance is single or double limb support?
SINGLE limb support
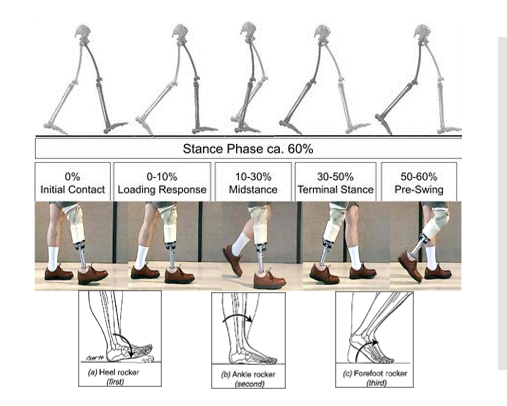
Terminal stance is single or double limb support?
Double-limb support
What are the goals of creating gait as “normal” as possible?
Smooth
Symmetric
Comfortable
How do we accomplish observing gait deviations and address them?
“Deviation” is what we observe and “cause” is the patient/prosthetic gait problem - we accomplish this by observational gait analysis
What do we focus on, in order, for static alignment?
Focus on socket fit - that socket is comfortable (if not, they won’t load the socket), limb position in socket is correct (consider PTB location and bony prominences)
Ensure 50:50 weight distribution (is my height correct? Is the foot flat on the ground? Is the pylon vertical? Does toe out match contralateral side?)
How do we begin dynamic alignment?
Begin with static alignment to ensure the patient is stable and don’t forget to wrap socket with fiberglass before dynamic alignment
What is the goal behind dynamic alignment?
Goal is to minimize a patient’s gait via incremental changes.
What do we observed as the patient walks?
Whole body vs. limb segments
Sagittal plane vs. coronal plane
Stance phase vs. swing phase
What can be likely general causes of dynamic alignment deviations?
Patient - weakness or contracture
Prosthesis - socket fit, suspension, components
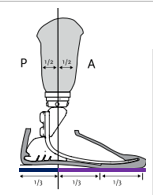
In the sagittal plane, what are stance phase deviations generally caused by?
Heel/toe lever ALMOST ALWAYS
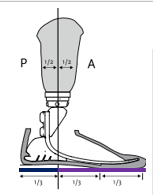
Which “lever” are we interested in first for the gait cycle?
Heel lever because it is first in time for initial contact
What effect does heel/toe lever have on the knee? If heel/toe lever is too long, what happens to the knee in what phase(s) of gait?
GRF would be more posterior to the knee, causing a greater knee flexion moment. More heel at initial contact means that the weight line will be more anterior
Longer toe off at the end of stance phase makes a larger knee extension moment due to greater GRF anterior to the knee.
Dorsiflexing the foot does what to the socket?
Flexes the socket!
How do we increase the heel lever?
Translation - foot posterior/socket anterior
Angular - flex socket or dorsiflex foot
Other - firmer heel/bumper, higher heel height
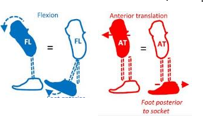
Why would a firmer heel/bumper or a higher heel height increase the heel lever?
Firmer heel makes less shock absorption, cannot squish so force goes up to the knee, generating a higher knee flexion moment
For higher heel height, the higher heel lever creates a greater knee flexion moment
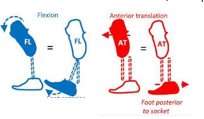
How do we decrease the heel lever?
Translation - foot anterior or socket posterior
Angular - extend socket, plantarflex foot
Other - softer heel/bumper, lower heel height
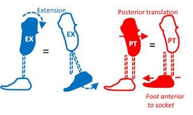
Why would a softer heel/bumper or lower heel height decrease the heel lever?
Almost no knee flexion moment, making the GRF more anterior
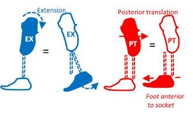
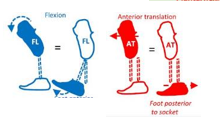
How do we increase the toe lever?
Translation - foot anterior
Angular - extend socket, plantarflex foot
Other - stiffen/lengthen keel to create an extension moment
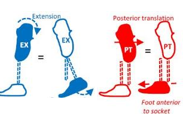
How do we decrease the toe lever?
Translation - Foot posterior
Angular - Flex socket, dorsiflex foot
Other - Soften/shorten keel
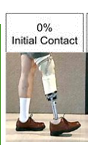
At Initial contact of gait - what are our goals?
Knee in 5-10 degrees of flexion
Even step length
During loading response, what are our goals?
Smooth knee flexion to 20 degrees and appropriate heel compression with some amount of deflection. Shock absorbing!

At Midstance, what are our goals?
Vertical pylon
½ inch varus thrust
2-4” wide base of support
Limited lateral trunk lean
Minimal knee movement in the coronal plane
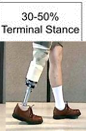
At terminal stance, what are our goals?
Smooth heel off
Knee begins to flex
At Pre-Swing, what are our goals?
Smooth transfer of body weight
Adequate suspension
During swing, what are our goals?
Heel travels along line of progression
Adequate toe clearance
Name the different stance phase deviations
Insufficient knee flexion
Excessive/abrupt knee flexion
Pylon lean
Excessive varus/valgus moment
Lateral trunk bending
Drop off
Delayed progression
Excessive toe out
When would insufficient knee flexion occur? In what plane?
Initial contact - sagittal plane
What is insufficient knee flexion? Why does it happen?
Knee remains extended and patient “rides” the heel due to lack of knee flexion moment
Causes (prosthetic) include insufficient heel lever
Why could insufficient knee flexion occur?
An insufficient heel lever (too short) is the cause, reasons why include:
Foot too anterior
Socket too extended/foot too plantarflexed
Heel too soft or shoe heel too low
When would excessive/abrupt knee flexion occur? In what plane?
Initial contact - sagittal plane
What is excessive/abrupt knee flexion? Why does it happen?
Knee quickly flexes during weight acceptance. Causes from the patient could be from weak quadriceps or a knee flexion contracture. Causes from the prosthetic could be excessive heel lever
Why would excessive heel lever cause excessive/abrupt knee flexion?
Foot is too posterior, socket too flexed/foot too dorsiflexed, heel too firm or shoe heel too high
Where would the patient feel pressure if they had excessive/abrupt knee flexion? How would they describe it (subjective)?
Pressure would be felt anterior distal and proximal posterior; “knee feels like it wants to buckle…..bring thrown forward”
What part of gait is pylon lean concerning? What plane does it concern?
Loading response → Midstance → Terminal stance - coronal plane
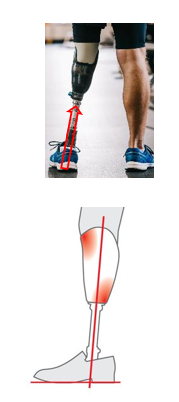
Name of pylon lean is based on what? What are the different leans?
Direction from distal to proximal AND towards the socket
In the coronal plane….they are named Medial or Lateral lean
In the sagittal plane…..they are named Anterior or Posterior lean
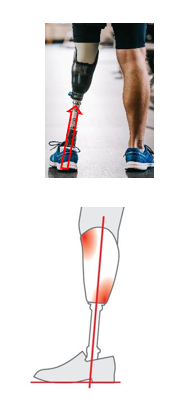
A vertical pylon translates to….
No lean!
What are the different prosthetic causes for medial and lateral lean?
Medial lean = too much socket aDduction
Lateral lean = too much socket aBduction
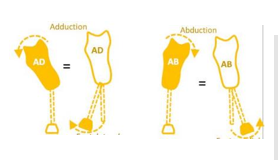
What part of gait is excessive varus/valgus moment concerning? What plane?
Loading response → Midstance → Terminal stance - coronal plane
What prosthetic causes result in excessive varus moment?
Foot too inset (narrow base)
Socket M-L too large (moves socket further to hit the limb)
Too much socket aBduction (lateral lean)
Inset is varus or valgus?
VARUS
Outset is varus or valgus?
VALGUS
What prosthetic causes result in excessive valgus moment?
Foot too outset (wide base)
Too much socket aDduction (medial lean)
Where are the pressures felt for excessive valgus?
Pressure would be felt proximal lateral and distal medial
Which shift do we hate the most? Medial or lateral?
MEDIAL
Where are socket pressures felt for excessive varus?
Distal lateral and proximal medial
What phase of gait concerns lateral trunk bending?
Loading response → Midstance → Terminal stance - coronal plane
What is lateral trunk bending? What are prosthetic causes for it happening?
Generally bending towards prosthesis in stance
Causes include prosthesis is too short (putting more weight on the prosthesis side versus the sound side), residual limb pain, foot too outset (creating a valgus moment - patient tries to make it more varus by leaning over)

What phase of gait is Drop Off concerned with? What plane?
Terminal stance - sagittal plane
What is Drop Off? What are some causes and why?
Sensation of “stepping in a hole”
Causes from the prosthetic include insufficient toe lever (too short) - this can be caused by the foot being too posterior, socket too flexed/foot too dorsiflexed, keel too soft/short
What phase of gait is Delayed Progression concerned with? What plane?
Terminal stance - sagittal plane
What is Delayed progression? What are some causes of this and why?
Sensation of “walking uphill”
Knee hyperextension
Causes from the prosthetic include excessive toe lever - this can happen because of the foot being too anterior, socket too extended/foot too plantarflexed, or keel too stiff/long
Where would the patient feel pressure if they had delayed progression?
Patient would feel anterior proximal and posterior distal
Knee would want to “pop” back
What phase of gait is excessive toe out most concerned with? Which plane?
Terminal stance - coronal plane
What are the causes behind excessive toe out? How do we fix it?
Too much foot external rotation, shortens toe lever with toe rollover
Fix it by adjusting foot rotation
How does excessive toe out effect the knee?
Valgus moment during terminal stance
What are the two different swing phase deviations?
Medial/lateral whip
Insufficient toe clearance
Describe medial/lateral whip - what are some causes of it? What plane do we look in?
Foot moves in a medial or lateral arc - “whipping” medial and lateral movement
Causes from the prosthetic include socket donner with incorrect rotation, loose socket fit/suspension issue, or improper alignment of cuff suspension attachment (not super common anymore)
How can we check/tell if the socket was donned with incorrect rotation?
Check to see if it is lined up on the PTB! If not, that is probably the issue
Describe insufficient toe clearance, what plane we look at, and possible causes
Patient scuffs toe or trips
Causes by the patient are muscle weakness
Causes by the prosthetic include:
Loose socket fit/suspension issue (first thing you should check!)
Prosthesis too long
Foot too plantarflexed