Capacitance
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Capacitance
The charge stored per unit pd in a capacitor
Capacitor
An electrical component that stores charge made of two parallel conducting plates with an insulator between them (dielectric)
Dielectric
An insulating material placed between the two plates of a capacitor in order to increase the amount of charge it can store
Permittivity of free space ε0
A measure of the ability of a vacuum to allow an electric field to pass through it
Relative Permittivity/dielectric constant
The ratio of a charge stored in a capacitor with the dielectric to charge stored without the dielectric
Permittivity ε
A measure of the ability to store an electric field in the material
Polar molecules
Molecules with a positive and negative end (therefore has their own electric field)
If no electric field: arranged in random direction
If electric field: move and align themselves within the field (follow field lines)
What does the strength of a polar molecule’s electric field depend on
The strength of the dielectric’s permittivity, which opposes the capacitor’s field thus reducing the capacitor’s field strength.
Therefore potential difference required to charge capacitor decreases
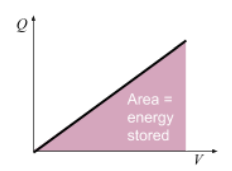
Area under charge against potential difference graph
Energy stored by a capacitor
Grad 1/C so C constant
E = ½QV
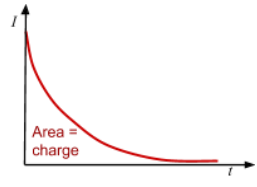
Shape of current against time for charging a capacitor
Area = Charge
Shape of p.d/charge against time for charging a capacitor
Gradient of Q against t = current
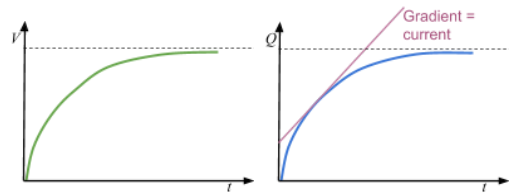
Explain why the charging graphs have their shape
Once the capacitor is connected to a power supply, current starts to flow and negative charge builds up on the plate connected to the negative terminal
On the opposite plate, electrons are repelled by the negative charge building up on the initial plate, therefore these electrons move to the positive terminal and an equal but opposite charge is formed on each plate, creating a potential difference
As the charge across the plates increases, the potential difference
increases but the electron flow decreases due to the force of electrostatic repulsion also increasing, therefore current decreases and eventually reaches zero
Shape of current/p.d/charge against time for discharging a capacitor
I against t: Area = charge
Q against t: Gradient = current
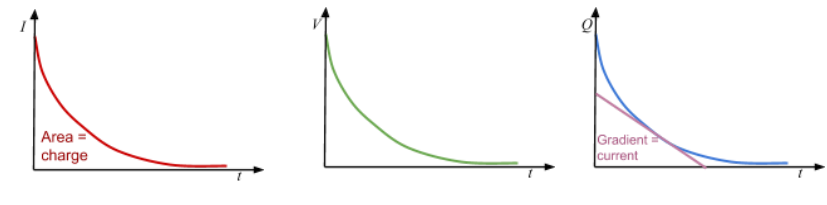
Explain why the discharging graphs have their shape
When the capacitor is discharging the current flows in the opposite direction, and the current, charge and potential difference across the capacitor will all fall exponentially, meaning it will take the same amount of time for the values to halve
Charging and discharging equations
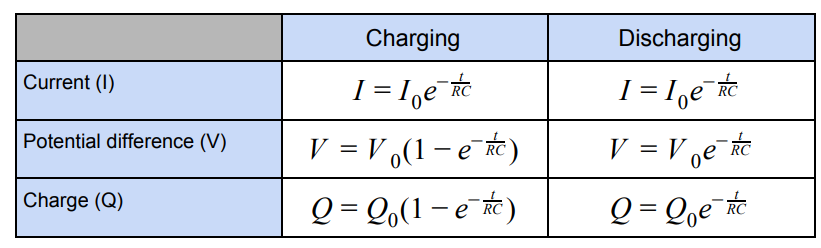
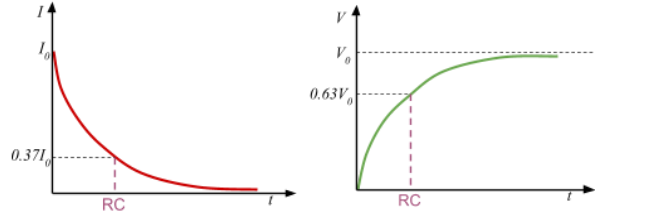
Time constant
t = RC
Value of time taken to:
Discharge a capacitor to 1/e ≈ 37% initial value (of Q,I or V)
Charge a capacitor to (1-1/e) ≈ 63% of its initial value (of Q or V)
How to find time constant from a graph of Q/I/V against time
Find the time where the values are either 0.37 of the initial value if discharging or 0.63 of the maximum value if charging