Orgo midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/288
Earn XP
Last updated 5:44 PM on 3/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
289 Terms
1
New cards

What is the ground-state electronic configuration of a carbon atom?
B) 1s2,2s2,2p2
2
New cards

What is the ground-state electronic configuration of a fluorine atom?
D) 1s2, 2s2, 2p5
3
New cards

What is the ground-state electronic configuration of a magnesium cation (Mg2+)?
A) 1s2, 2s2, 2p6
4
New cards

What is the ground-state electronic configuration of a chlorine anion (Cl—)?
B) 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2,3p6
5
New cards
Which of the following statements about valence electrons is true?
A) They are the most tightly held electrons.
B) They do not participate in chemical reactions.
C) They are the outermost electrons.
D) They reveal the period number of a second-row element.
A) They are the most tightly held electrons.
B) They do not participate in chemical reactions.
C) They are the outermost electrons.
D) They reveal the period number of a second-row element.
C) They are the outermost electrons.
6
New cards
Which of the following statements about bonding is true?
\
A) Covalent bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one element to another.
B) Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal.
C) Ionic bonds result from the sharing of electrons between two nonmetals.
D) Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between two metals.
\
A) Covalent bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one element to another.
B) Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal.
C) Ionic bonds result from the sharing of electrons between two nonmetals.
D) Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between two metals.
B) Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal.
7
New cards
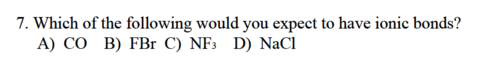
Which of the following would you expect to have ionic bonds?
\
A) CO
B) FBr
C) NF3
D) NaCl
\
A) CO
B) FBr
C) NF3
D) NaCl
D) NaCl
8
New cards
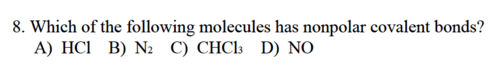
Which of the following molecules has nonpolar covalent bonds?
\
A) HCl
B) N2
C) CHCl3
D) NO
\
A) HCl
B) N2
C) CHCl3
D) NO
B) N2
9
New cards
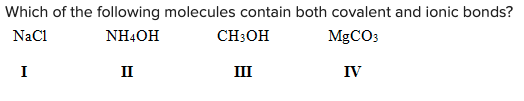
Which of the following molecules contain both covalent and ionic bonds?
\
A) I, II
B) I, IV
C) II, III
D) II, IV
\
A) I, II
B) I, IV
C) II, III
D) II, IV
D) II, IV
10
New cards
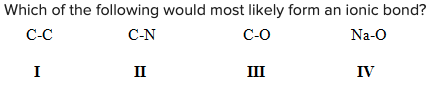
Which of the following would most likely form an ionic bond?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D) IV
11
New cards
Which of the following statements correctly describes the typical number of bonds for carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen in most neutral organic molecules?
\
A) Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds, nitrogen forms 2 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 3 covalent bonds.
B) Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds, nitrogen forms 3 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 2 covalent bonds.
C) Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds, nitrogen forms 5 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 2 covalent bonds.
D) Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds, nitrogen forms 5 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 4 covalent bonds.
\
A) Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds, nitrogen forms 2 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 3 covalent bonds.
B) Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds, nitrogen forms 3 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 2 covalent bonds.
C) Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds, nitrogen forms 5 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 2 covalent bonds.
D) Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds, nitrogen forms 5 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 4 covalent bonds.
B) Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds, nitrogen forms 3 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 2 covalent bonds.
12
New cards
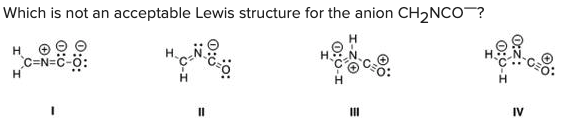
Which is not an acceptable Lewis structure for the anion CH2NCO—?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
C) III
13
New cards
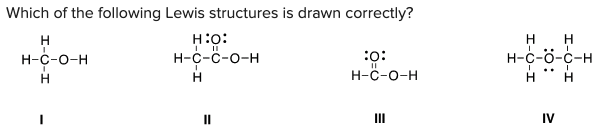
Which of the following Lewis structures is drawn correctly?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D) IV
14
New cards
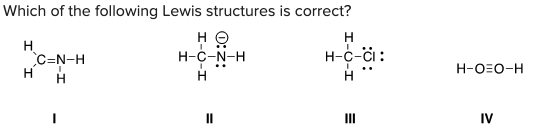
Which of the following Lewis structures is correct?
\
A) I, II
B) I, III
C) II, III
D) III, IV
\
A) I, II
B) I, III
C) II, III
D) III, IV
C) II, III
15
New cards
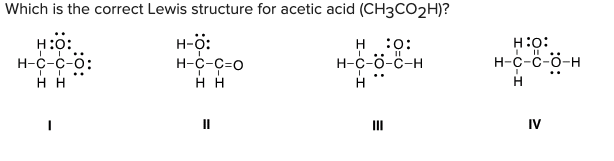
Which is the correct Lewis structure for acetic acid (CH3CO2H)?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D) IV
16
New cards
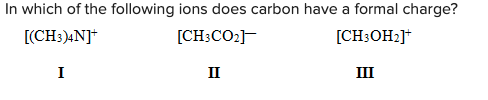
In which of the following ions does carbon have a formal charge?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) None of the above
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) None of the above
D) None of the above
17
New cards
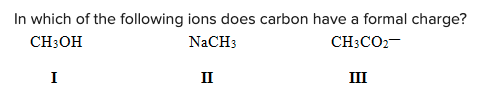
In which of the following ions does carbon have a formal charge?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) None of the above
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) None of the above
B) II
18
New cards
What is the formal charge of carbon in carbon monoxide (CO) when drawn with a triple bond?
\
A) 0
B) -2
C) -1
D) +1
\
A) 0
B) -2
C) -1
D) +1
C) -1
19
New cards
Which of the following statements about constitutional isomers is true?
A) Constitutional isomers are different molecules having different molecular formula.
B) Constitutional isomers are different molecules having same molecular formula.
C) Constitutional isomers are same molecules having different molecular formula.
D) Constitutional isomers are same molecules having the same molecular formula.
A) Constitutional isomers are different molecules having different molecular formula.
B) Constitutional isomers are different molecules having same molecular formula.
C) Constitutional isomers are same molecules having different molecular formula.
D) Constitutional isomers are same molecules having the same molecular formula.
B) Constitutional isomers are different molecules having same molecular formula.
20
New cards
How many constitutional isomers are there for a molecule having the molecular formula C2H6O?
\
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
\
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
B) 2
21
New cards
How many constitutional isomers are there for a molecule having the molecular formula C3H8O?
\
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
\
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
C) 3
22
New cards
How many constitutional isomers are there for a molecule having the molecular formula C3H6?
\
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
\
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
B) 2
23
New cards
How many constitutional isomers are there for a molecule having the molecular formula C2H4Cl2?
\
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
\
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
B) 2
24
New cards
How many different consitutional isomers are there for a compound having the molecular formula C3H6O?
\
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
\
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
D) 7
25
New cards

Which of the following molecules are constitutional isomers?
\
A) I, II, IV
B) II, III, IV
C) I, III, IV
D) I, II, III
\
A) I, II, IV
B) II, III, IV
C) I, III, IV
D) I, II, III
D) I, II, III
26
New cards
Which of the following compounds has an atom with an unfilled valence shell of electrons?
\
A) H2O
B) BCl3
C) CH4
D) CO2
\
A) H2O
B) BCl3
C) CH4
D) CO2
B) BCl3
27
New cards
Which of the following statements about resonance structures is true?
\
A) Resonance structures have the same placement of electrons but different arrangement of atoms.
B) Resonance structures have the same placement of atoms but different arrangement \\n of electrons.
C) Resonance structures have the same placement of atoms and the same arrangement of electrons.
D) Resonance structures have different placement of atoms and different arrangement of electrons.
\
A) Resonance structures have the same placement of electrons but different arrangement of atoms.
B) Resonance structures have the same placement of atoms but different arrangement \\n of electrons.
C) Resonance structures have the same placement of atoms and the same arrangement of electrons.
D) Resonance structures have different placement of atoms and different arrangement of electrons.
B) Resonance structures have the same placement of atoms but different arrangement of electrons.
28
New cards
Which of the following statements about resonance structures is not true?
A) There is no movement of electrons from one form to another.
B) Resonance structures are not isomers.
C) Resonance structures differ only in the arrangement of electrons.
D) Resonance structures are in equilibrium with each other.
A) There is no movement of electrons from one form to another.
B) Resonance structures are not isomers.
C) Resonance structures differ only in the arrangement of electrons.
D) Resonance structures are in equilibrium with each other.
A) There is no movement of electrons from one form to another.
29
New cards
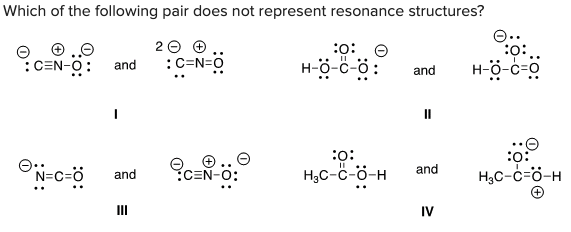
Which of the following pair does not represent resonance structures?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
C) III
30
New cards
What 2 things will change between two resonance structures?
\
A) The position of multiple bonds and non-bonded electrons.
B) The position of multiple bonds and single bonds.
C) The placement of atoms and single bonds.
D) The placement of atoms and non-bonded electrons.
\
A) The position of multiple bonds and non-bonded electrons.
B) The position of multiple bonds and single bonds.
C) The placement of atoms and single bonds.
D) The placement of atoms and non-bonded electrons.
A) The position of multiple bonds and non-bonded electrons.
31
New cards
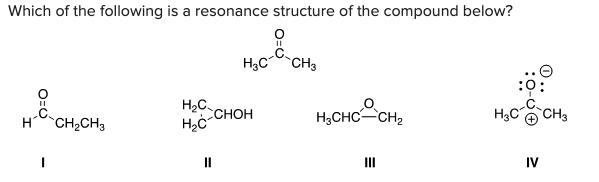
Which of the following is a resonance structure of the compound below?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D) IV
32
New cards
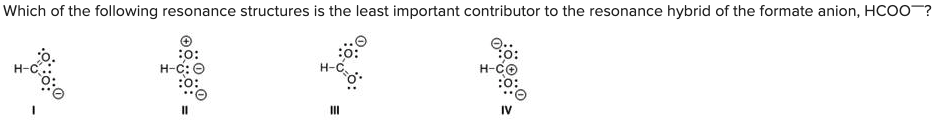
Which of the following resonance structures is the least important contributor to the resonance hybrid of the formate anion, HCOO—?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B) II
33
New cards
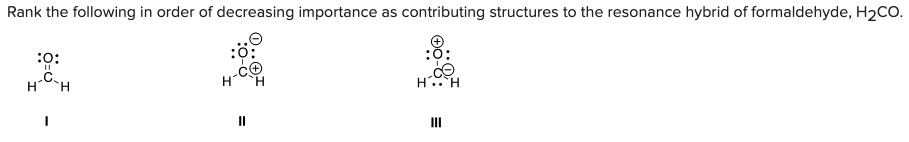
Rank the following in order of decreasing importance as contributing structures to the resonance hybrid of formaldehyde, H2CO.
\
A) I > II > III
B) I > III > II
C) II > I > III
D) III > II > I
\
A) I > II > III
B) I > III > II
C) II > I > III
D) III > II > I
A) I > II > III
34
New cards
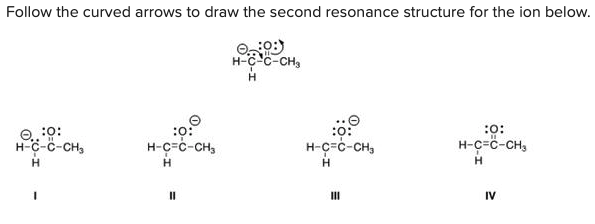
Follow the curved arrows to draw the second resonance structure for the ion below.
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
C) III
35
New cards
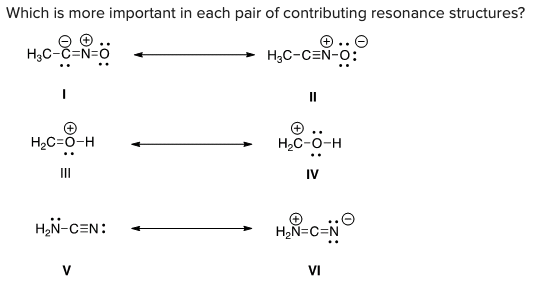
Which is more important in each pair of contributing resonance structures?
\
A) II, IV, V
B) II, III, V
C) II, III, VI
D) I, IV, V
\
A) II, IV, V
B) II, III, V
C) II, III, VI
D) I, IV, V
B) II, III, V
36
New cards
What is the approximate value of the H-C-H bond angle in methane, CH4?
\
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
\
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
B) 109.5°
37
New cards
What is the approximate C-C-C bond angle in propene, CH3CH = CH2?
\
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
\
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
C) 120°
38
New cards
What is the approximate H-C-O bond angle in formaldehyde, H2CO?
\
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
\
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
C) 120°
39
New cards
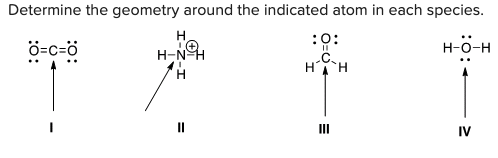
Determine the geometry around the indicated atom in each species.
\
A) I = Linear; II = tetrahedral; III = trigonal planar; IV = tetrahedral
B) I = Linear; II = tetrahedral; III = trigonal planar; IV = linear
C) I = Trigonal planar; II = linear; III = tetrahedral; IV = trigonal planar
D) I = Tetrahedral; II = trigonal planar; III = linear; IV = tetrahedral
\
A) I = Linear; II = tetrahedral; III = trigonal planar; IV = tetrahedral
B) I = Linear; II = tetrahedral; III = trigonal planar; IV = linear
C) I = Trigonal planar; II = linear; III = tetrahedral; IV = trigonal planar
D) I = Tetrahedral; II = trigonal planar; III = linear; IV = tetrahedral
A) I = Linear; II = tetrahedral; III = trigonal planar; IV = tetrahedral
40
New cards
What is the approximate bond angle for the C-C-N bond in acetonitrile, CH3CN?
\
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
\
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
D) 180°
41
New cards
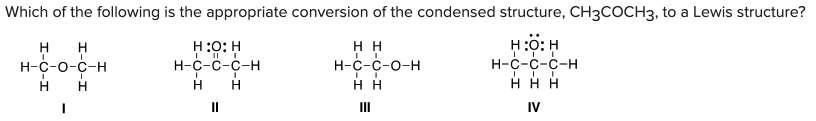
Which of the following is the appropriate conversion of the condensed structure, CH3COCH3, to a Lewis structure?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B) II
42
New cards
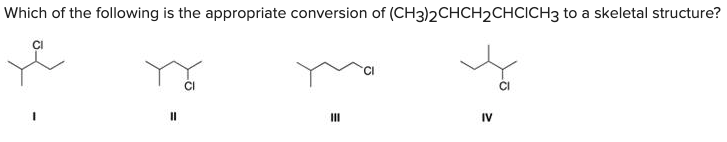
Which of the following is the appropriate conversion of (CH3)2CHCH2CHClCH3 to a skeletal structure?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B) II
43
New cards
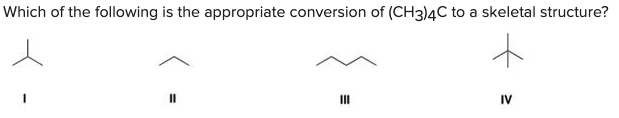
Which of the following is the appropriate conversion of (CH3)4C to a skeletal structure?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D) IV
44
New cards
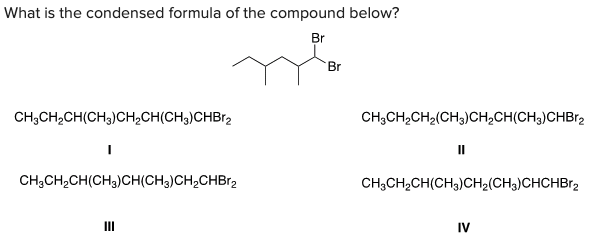
What is the condensed formula of the compound below?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
A) I
45
New cards
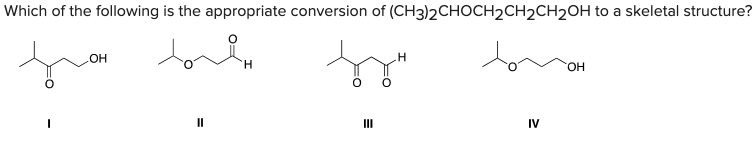
Which of the following is the appropriate conversion of (CH3)2CHOCH2CH2CH2OH to a skeletal structure?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D) IV
46
New cards
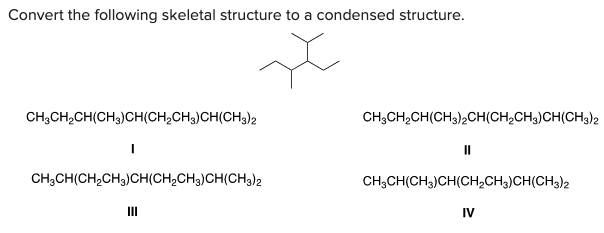
Convert the following skeletal structure to a condensed structure.
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
A) I
47
New cards

Avobenzone is an active ingredient in some common sunscreens. Which of the following is the correct molecular formula for avobenzone?
\
A) C22O22O3
B) C20H22O3
C) C21H23O3
D) C20H24O3
\
A) C22O22O3
B) C20H22O3
C) C21H23O3
D) C20H24O3
B) C20H22O3
48
New cards
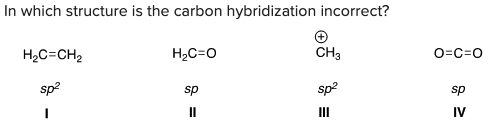
In which structure is the carbon hybridization incorrect?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B) II
49
New cards

What is the hybridization for each of the indicated atoms in the following compound?
\
A) I = sp2; II = sp2; III = sp2.
B) I = sp2; II = sp3; III = sp3.
C) I = sp; II = sp2; III = sp3.
D) I = sp2; II = sp2; III = sp3.
\
A) I = sp2; II = sp2; III = sp2.
B) I = sp2; II = sp3; III = sp3.
C) I = sp; II = sp2; III = sp3.
D) I = sp2; II = sp2; III = sp3.
D) I = sp2; II = sp2; III = sp3.
50
New cards
What is the hybridization of the carbon atom in the methyl cation, (CH3+)?
A) sp3
B) sp2
C) sp
D) p
A) sp3
B) sp2
C) sp
D) p
B) sp2
51
New cards
What is the hybridization of the nitrogen atom in the ammonium cation, NH4+?
\
A) sp3
B) sp2
C) sp
D) p
\
A) sp3
B) sp2
C) sp
D) p
A) sp3
52
New cards
Which atomic orbitals overlap to form the C-H σ bonding molecular orbitals of ethane, CH3CH3?
\
A) Csp2 + H1s
B) Csp3 + H1s
C) C2p + H1s
D) Csp + H1s
\
A) Csp2 + H1s
B) Csp3 + H1s
C) C2p + H1s
D) Csp + H1s
B) Csp3 + H1s
53
New cards
Which atomic orbitals overlap to form the C-H σ bonding molecular orbitals of ethylene, H2C=CH2?
\
A) C2p + H1s
B) Csp + H1s
C) Csp3 + H1s
D) Csp2 + H1s
\
A) C2p + H1s
B) Csp + H1s
C) Csp3 + H1s
D) Csp2 + H1s
D) Csp2 + H1s
54
New cards
Which atomic orbitals overlap to form the carbon-carbon σ and π bonding molecular orbitals of ethylene, H2C=CH2?
\
A) Csp3 + Csp3, and C2p + C2p
B) Csp3 + Csp3, and Csp2 + Csp2
C) Csp2 + Csp2, and C2p + C2p
D) Csp2 + Csp2, and Csp2 + Csp2
\
A) Csp3 + Csp3, and C2p + C2p
B) Csp3 + Csp3, and Csp2 + Csp2
C) Csp2 + Csp2, and C2p + C2p
D) Csp2 + Csp2, and Csp2 + Csp2
C) Csp2 + Csp2, and C2p + C2p
55
New cards
Which atomic orbitals overlap to form the C-H σ bonding molecular orbitals of acetylene, C2H2?
\
A) Csp + H1s
B) C2p +H1s
C) Csp3 + H1s
D) Csp2 + H1s
\
A) Csp + H1s
B) C2p +H1s
C) Csp3 + H1s
D) Csp2 + H1s
A) Csp + H1s
56
New cards
Which atomic orbitals overlap to form the carbon-carbon σ (sigma bonding) molecular orbital of acetylene, C2H2?
A) Csp2 + Csp2
B) Csp + Csp
C) Csp3 + Csp3
D) C2p + C2p
A) Csp2 + Csp2
B) Csp + Csp
C) Csp3 + Csp3
D) C2p + C2p
B) Csp + Csp
57
New cards

When forming molecular orbitals from atomic orbitals, what is the order of increasing C-H bond strength for the following set?
\
A) II < I < III
B) III < I < II
C) III < II < I
D) I < II < III
\
A) II < I < III
B) III < I < II
C) III < II < I
D) I < II < III
D) I < II < III
58
New cards

What is the order of decreasing bond length for a C-C bond composed of the following molecular orbitals?
\
A) I > III > II
B) I > II > III
C) III > II > I
D) II > III > I
\
A) I > III > II
B) I > II > III
C) III > II > I
D) II > III > I
B) I > II > III
59
New cards
Which of the following statements about electronegativity and the periodic table is true?
\
A) Electronegativity decreases across a row of the periodic table. B) Electronegativity increases down a column of the periodic table.
C) Electronegativity increases across a row of the periodic table.
D) Electronegativity does not change down a column of the periodic table.
\
A) Electronegativity decreases across a row of the periodic table. B) Electronegativity increases down a column of the periodic table.
C) Electronegativity increases across a row of the periodic table.
D) Electronegativity does not change down a column of the periodic table.
C) Electronegativity increases across a row of the periodic table.
60
New cards

Rank the following atoms in order of increasing electronegativity, putting the least electronegative first.
\
A) I < II < III < IV
B) I < IV < II < III
C) III < II < IV < I
D) I < II < IV < III
\
A) I < II < III < IV
B) I < IV < II < III
C) III < II < IV < I
D) I < II < IV < III
B) I < IV < II < III
61
New cards

Rank the following atoms in order of decreasing electronegativity, putting the most electronegative first.
\
A) I > IV > II > III
B) II > III > IV > I
C) III > IV > II > I
D) III > II > IV > I
\
A) I > IV > II > III
B) II > III > IV > I
C) III > IV > II > I
D) III > II > IV > I
D) III > II > IV > I
62
New cards
Which molecule has the greatest difference in electronegativity (DE) between the two different elements?
\
A) CO2
B) H2S
C) NH3
D) H2O
\
A) CO2
B) H2S
C) NH3
D) H2O
D) H2O
63
New cards
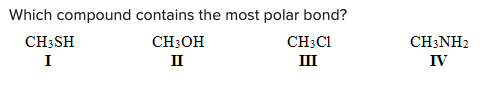
Which compound contains the most polar bond?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B) II
64
New cards

Which of the following compounds are non-polar?
\
A) I, IV
B) I, II
C) II, III
D) II, IV
\
A) I, IV
B) I, II
C) II, III
D) II, IV
A) I, IV
65
New cards
Which of the following molecules has non-polar covalent bonds?
\
A) CO2
B) N2
C) CCl4
D) HF
\
A) CO2
B) N2
C) CCl4
D) HF
B) N2
66
New cards
Which of the following molecules has polar covalent bonds?
\
A) MgO
B) NH3
C) Cl2
D) NaBr
\
A) MgO
B) NH3
C) Cl2
D) NaBr
B) NH3
67
New cards
Which of the following covalent bonds has the largest dipole moment?
\
A) C-H
B) C-C
C) C-O
D) H-F
\
A) C-H
B) C-C
C) C-O
D) H-F
D) H-F
68
New cards
Which of the following molecules has the smallest dipole moment?
\
A) CO2
B) HCl
C) H2O
D) NH3
\
A) CO2
B) HCl
C) H2O
D) NH3
A) CO2
69
New cards
Which of the following molecules does *not* have a net dipole moment of zero?
\
A) CCl4
B) BF3
C) CO2
D) NH3
\
A) CCl4
B) BF3
C) CO2
D) NH3
D) NH3
70
New cards
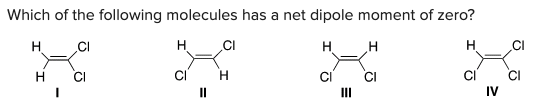
Which of the following molecules has a net dipole moment of zero?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B) II
71
New cards
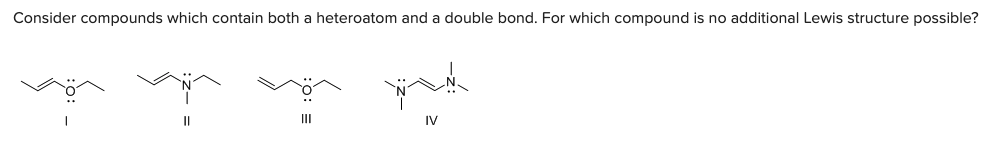
Consider compounds which contain both a heteroatom and a double bond. For which compound is no additional Lewis structure possible?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
C) III
72
New cards
Which of the following statements about Lewis acids is true?
\
A) Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors.
B) Lewis acids are proton donors.
C) Lewis acids are electron pair donors.
D) Lewis acids are proton acceptors.
\
A) Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors.
B) Lewis acids are proton donors.
C) Lewis acids are electron pair donors.
D) Lewis acids are proton acceptors.
A) Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors.
73
New cards
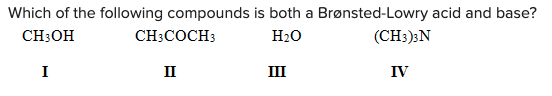
Which of the following compounds is both a Brønsted-Lowry acid and base?
A) I, II
B) I, III
C) II, IV
D) I, IV
A) I, II
B) I, III
C) II, IV
D) I, IV
B) I, III
74
New cards
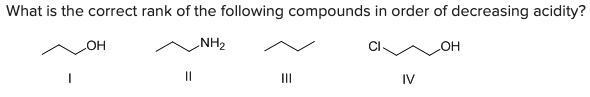
What is the correct rank of the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity?
\
A) IV < III < II < I
B) II < IV < I < III
C) III < II < I < IV
D) I < II < III < IV
\
A) IV < III < II < I
B) II < IV < I < III
C) III < II < I < IV
D) I < II < III < IV
C) III < II < I < IV
75
New cards
Which of the following statements about Lewis bases is true?
\
A) Lewis bases are proton donors.
B) Lewis bases are proton acceptors.
C) Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
D) Lewis bases are electron pair acceptors.
\
A) Lewis bases are proton donors.
B) Lewis bases are proton acceptors.
C) Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
D) Lewis bases are electron pair acceptors.
C) Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
76
New cards
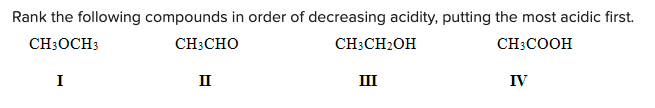
Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity, putting the most acidic first.
\
A) IV > II > III > I
B) III > IV > II > I
C) III > IV > I > II
D) IV > III > II > I
\
A) IV > II > III > I
B) III > IV > II > I
C) III > IV > I > II
D) IV > III > II > I
D) IV > III > II > I
77
New cards
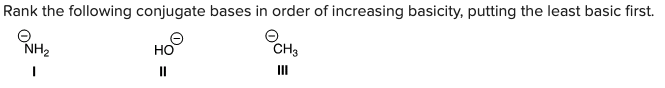
Rank the following conjugate bases in order of increasing basicity, putting the least basic first.
\
A) I < II < III
B) II < I < III
C) I < III < II
D) II < III < I
\
A) I < II < III
B) II < I < III
C) I < III < II
D) II < III < I
B) II < I < III
78
New cards
Which of the following species cannot act as both a Brønsted-Lowry acid and base?
\
A) HSO4-
B) HCO3-
C) HO-
D) H2PO4-
\
A) HSO4-
B) HCO3-
C) HO-
D) H2PO4-
C) HO-
79
New cards
Which of the following species is the strongest base?
\
A) HO-
B) CH3COO-
C) Cl-
D) H2N-
\
A) HO-
B) CH3COO-
C) Cl-
D) H2N-
D) H2N-
80
New cards
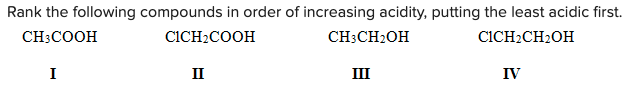
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing acidity, putting the least acidic first.
\
A) III < I < IV < II
B) II < I < IV < III
C) III < IV < I < II
D) III < I < II < IV
\
A) III < I < IV < II
B) II < I < IV < III
C) III < IV < I < II
D) III < I < II < IV
C) III < IV < I < II
81
New cards

Consider the following molecule with protons labeled, I-III. Rank these protons in order of decreasing acidity, putting the most acidic first.
\
A) I > II > III
B) III > II > I
C) I > III > II
D) III > I > II
\
A) I > II > III
B) III > II > I
C) I > III > II
D) III > I > II
B) III > II > I
82
New cards
Which of the following lists contains common heteroatoms found in organic molecules?
\
A) N, O, S, P, Cl
B) Na, O, S, P, Cl
C) Na, Mg, S, N, Cl
D) Na, Mg, O, N, Cl
\
A) N, O, S, P, Cl
B) Na, O, S, P, Cl
C) Na, Mg, S, N, Cl
D) Na, Mg, O, N, Cl
A) N, O, S, P, Cl
83
New cards
Why do heteroatoms confer reactivity on a particular molecule?
\
A) Because they have lone pairs and create electron-rich sites on carbon.
B) Because they have lone pairs and create electron-deficient sites on carbon.
C) Because they are electronegative and act as electrophiles.
D) Because they are electropositive and act as nucleophiles.
\
A) Because they have lone pairs and create electron-rich sites on carbon.
B) Because they have lone pairs and create electron-deficient sites on carbon.
C) Because they are electronegative and act as electrophiles.
D) Because they are electropositive and act as nucleophiles.
B) Because they have lone pairs and create electron-deficient sites on carbon.
84
New cards
Why do π bonds confer reactivity on a particular molecule?
\
A) Because π bonds are difficult to break in chemical reactions.
B) Because π bonds make a molecule an acid.
C) Because π bonds are easily broken in chemical reactions.
D) Because π bonds make a molecule an electrophile.
\
A) Because π bonds are difficult to break in chemical reactions.
B) Because π bonds make a molecule an acid.
C) Because π bonds are easily broken in chemical reactions.
D) Because π bonds make a molecule an electrophile.
C) Because π bonds are easily broken in chemical reactions.
85
New cards

Which of the following molecules contain the same functional groups?
\
A) I, II, III
B) I, II, IV
C) II, III, IV
D) I, III, IV
\
A) I, II, III
B) I, II, IV
C) II, III, IV
D) I, III, IV
D) I, III, IV
86
New cards
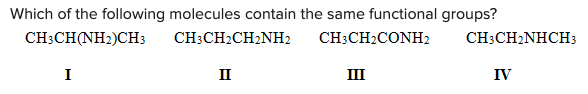
Which of the following molecules contain the same functional groups?
\
A) I, II, IV
B) I, II, III
C) II, III, IV
D) I, III, IV
\
A) I, II, IV
B) I, II, III
C) II, III, IV
D) I, III, IV
A) I, II, IV
87
New cards
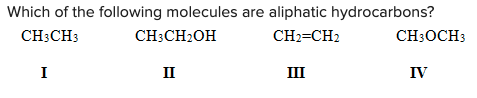
Which of the following molecules are aliphatic hydrocarbons?
A) I, II, III
B) I and III
C) II, III, IV
D) II and IV
A) I, II, III
B) I and III
C) II, III, IV
D) II and IV
B) I and III
88
New cards
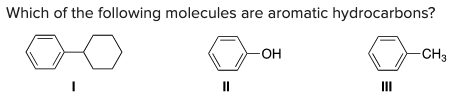
Which of the following molecules are aromatic hydrocarbons?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I and III
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I and III
D) I and III
89
New cards
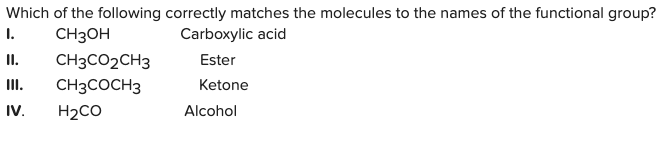
Which of the following correctly matches the molecules to the names of the functional group?
\
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) II and III
D) II and IV
\
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) II and III
D) II and IV
C) II and III
90
New cards

Which of the following correctly matches the molecules to the names of the functional group?
\
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) III and IV
D) I and III
\
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) III and IV
D) I and III
D) I and III
91
New cards

Which of the following correctly matches the molecules to the names of the functional group? \n
A) I and II
B) II and IV
C) III and IV
D) II and III
A) I and II
B) II and IV
C) III and IV
D) II and III
B) II and IV
92
New cards

Consider the molecule *donepezil* (used to treat Alzheimer's disease). Which of the following lists the correct functional groups present in *donepezil*?
\
A) Amide, aromatic, ether, ketone. B) Amide, aromatic, ester, ketone. C) Amine, aromatic, ester, ketone. D) Amine, aromatic, ether, ketone.
\
A) Amide, aromatic, ether, ketone. B) Amide, aromatic, ester, ketone. C) Amine, aromatic, ester, ketone. D) Amine, aromatic, ether, ketone.
D) Amine, aromatic, ether, ketone.
93
New cards

Consider the molecule *atenolol* (a β blocker used to treat hypertension). Which of the following lists the correct functional groups present in *atenolol*?
\
A) Primary alcohol, amide, primary amine, aromatic, ether.
B) Secondary alcohol, amide, secondary amine, aromatic, ether. C) Secondary alcohol, amide, primary amine, aromatic, ether.
D) Secondary alcohol, amide, secondary amine, aromatic, ester.
\
A) Primary alcohol, amide, primary amine, aromatic, ether.
B) Secondary alcohol, amide, secondary amine, aromatic, ether. C) Secondary alcohol, amide, primary amine, aromatic, ether.
D) Secondary alcohol, amide, secondary amine, aromatic, ester.
B) Secondary alcohol, amide, secondary amine, aromatic, ether.
94
New cards
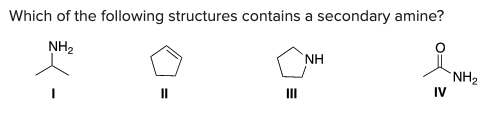
Which of the following structures contains a secondary amine?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
C) III
95
New cards
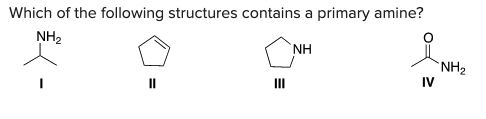
Which of the following structures contains a primary amine?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
A) I
96
New cards
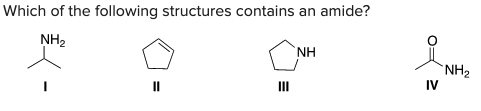
Which of the following structures contains an amide?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D) IV
97
New cards
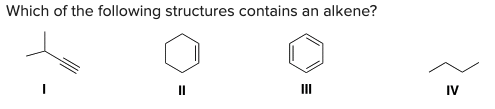
Which of the following structures contains an alkene?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B) II
98
New cards
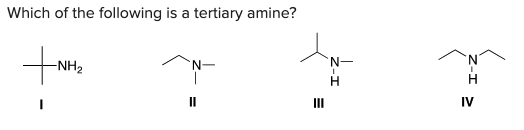
Which of the following is a tertiary amine?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B) II
99
New cards
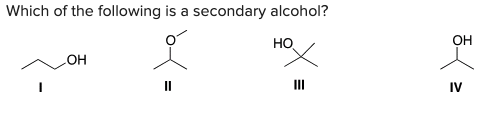
Which of the following is a secondary alcohol?
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
\
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D) IV
100
New cards
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between the surface area of a molecule and the strength of the intermolecular forces?
\
A) The larger the surface area, the weaker the intermolecular force.
B) The larger the surface area, the stronger the intermolecular forces. C) The smaller the surface area, the stronger the intermolecular forces. D) There is no relationship between surface area and intermolecular forces
\
A) The larger the surface area, the weaker the intermolecular force.
B) The larger the surface area, the stronger the intermolecular forces. C) The smaller the surface area, the stronger the intermolecular forces. D) There is no relationship between surface area and intermolecular forces
B) The larger the surface area, the stronger the intermolecular forces.