Chapter 4 - Economic Efficiency, Surplus, and Market Failures
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Laissez-faire
Refers to the concept of freely functioning markets without government intervention.
Market Failure
Occurs when a free market does not produce a socially desirable price or quantity. Caused by:
Lack of Competition
Asymmetric Information
Externalities
Existence of Public Goods (nonrivalry and nonexclusivity)
Lack of Competition
When a market lacks competition, inefficient production and higher prices are more likely.
Externalities
External benefits or external costs generated by the actions of others. They can lead to a market equilibrium that is not socially optimal.
Asymmetric information
Occurs when one party in a transaction has more information about a product than the other. This can lead to prices being set too high or too low.
Nonrivalry
Means that one person's consumption of a good does not reduce the amount available for others to consume.
Nonexclusivity
Means that once a good is provided, it is impossible to prevent others from enjoying it.
Public Goods
Goods that one person can consume without diminishing what is left for others. They exhibit nonrivalry and nonexclusivity. Private markets do not provide them in sufficient quantities.
Willingness to Pay (WTP)
Is the maximum amount a consumer is willing and able to pay for a good or service, representing the highest value they believe it is worth.
Consumer Surplus
Is the net benefit a consumer receives from purchasing a good or service, calculated as the difference between their willingness-to-pay (WTP) and the actual price. It represents a form of savings for consumers.
Willingness to Sell (WTS)
Is the minimum amount a producer is willing and able to sell a good or product, representing the lowest value they believe it is worth.
Producer Surplus
Is the net benefit a producer receives from selling a good or service, measured as the difference between the price they receive and their willingness-to-sell (WTS). It represents a form of earnings for producers.
Total Surplus
Is the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus, representing the total net benefit to society from market transactions. It is maximized when the market is in equilibrium.
Consumer Surplus on a Graph
Represented below the demand curve and above the price. (In green)
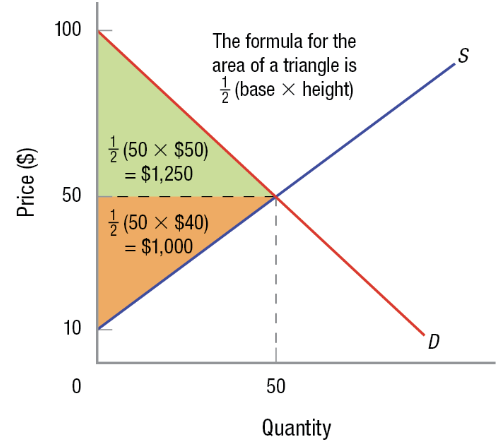
Producer Surplus on a Graph
Represented above the supply curve and below the price. (In orange)
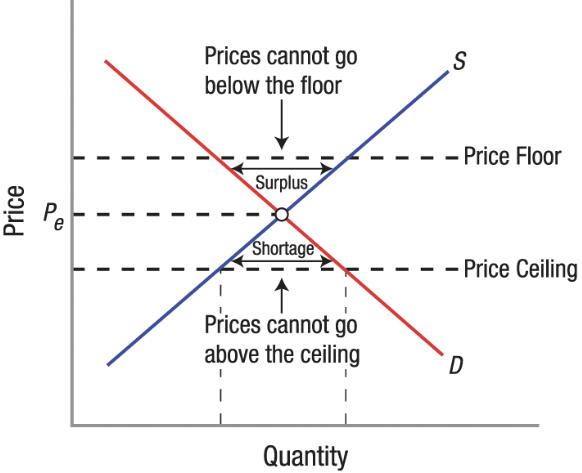
Price Floor
Price Ceiling
A government-mandated maximum price that can be charged for a good or service.
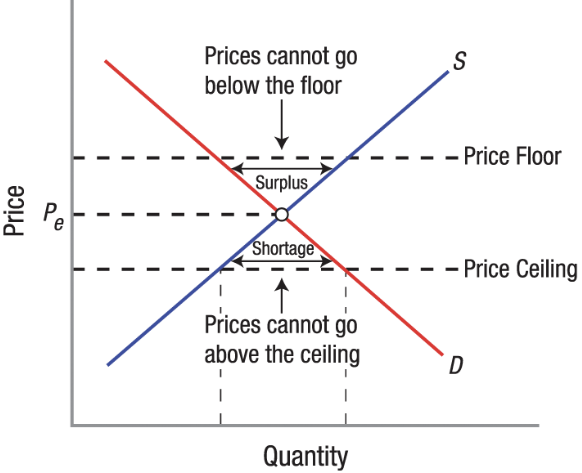
Binding Price Ceiling
Price ceilings set below the equilibrium price.
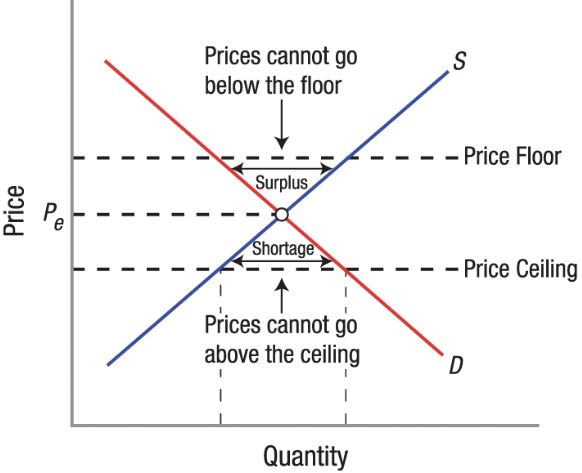
Effects of Price Ceilings
Creates Shortage
Increases consumer surplus and decreases producer surplus
Can lead to misallocation of resources, opportunity costs, and deterioration of quality.
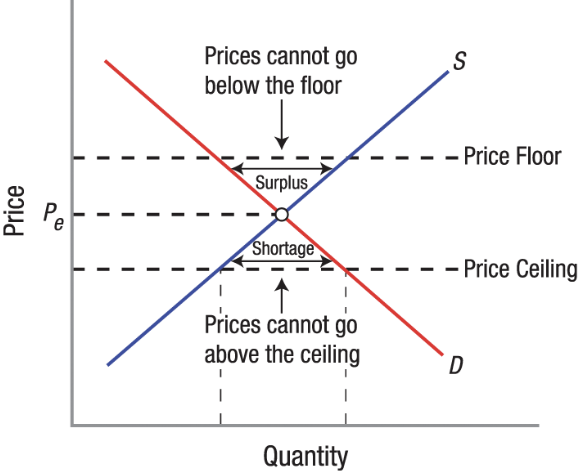
Price Floor
A government-mandated minimum price that sellers must charge for a good or service.
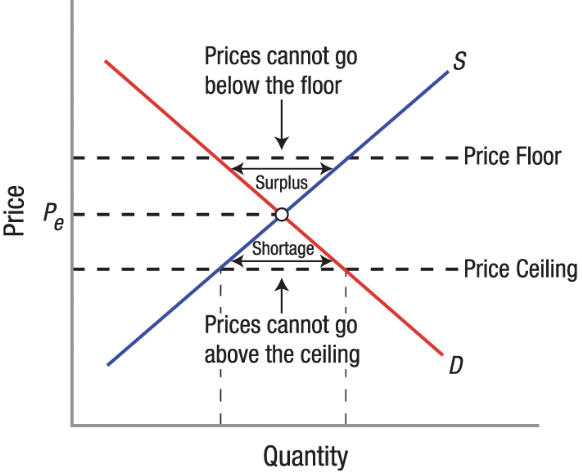
Binding Price Floor
Are price floors set above the equilibrium price, which cause surpluses.
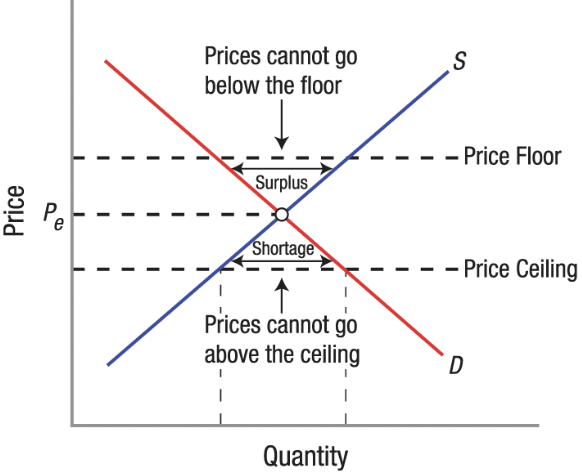
Effects of a Price Floor
Creates Surplus
Decreases consumer surplus and increases producer surplus
Reduces quantity sold
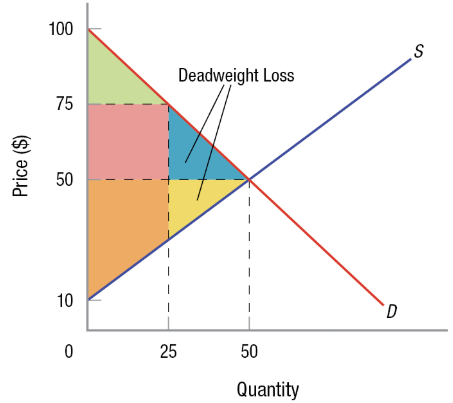
Deadweight Loss
The loss of total surplus that occurs when a market is not operating at equilibrium, representing potential gains from trade that are not realized. It is caused by inefficiencies in the market, such as prices deviating from equilibrium.