Vision 1 & 2
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
sensation
transformation of physical chars of the world —> elec signals in the NS
transduction
transmission of visual signals down the optic nerve
perception
becoming aware of smth thru the senses
y can perception be inaccurate
brain can misinterpret stim (illusions
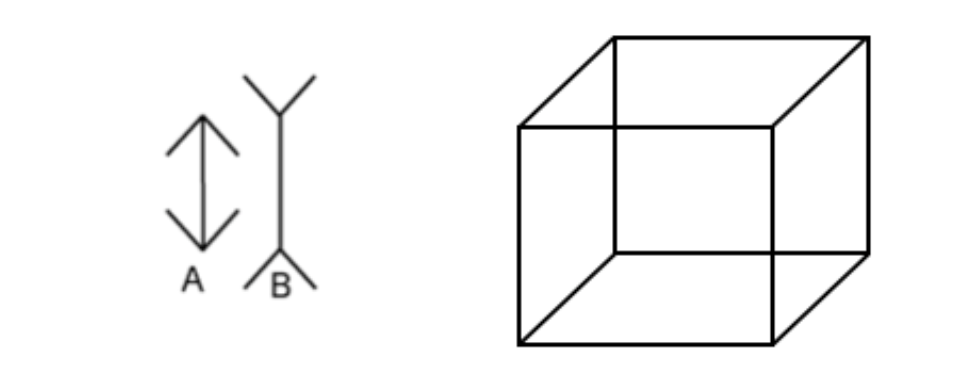
2 visual illusions that demonstrate misinterpretation
muller-lyer
necker cube
3 properties of light
wavelength
amplitude
purity
what does wavelength deter
colour (visible spectrum)
what wavelengths correspond to red & violet light
red = 750nm = longer
violet = 360nm = shorter
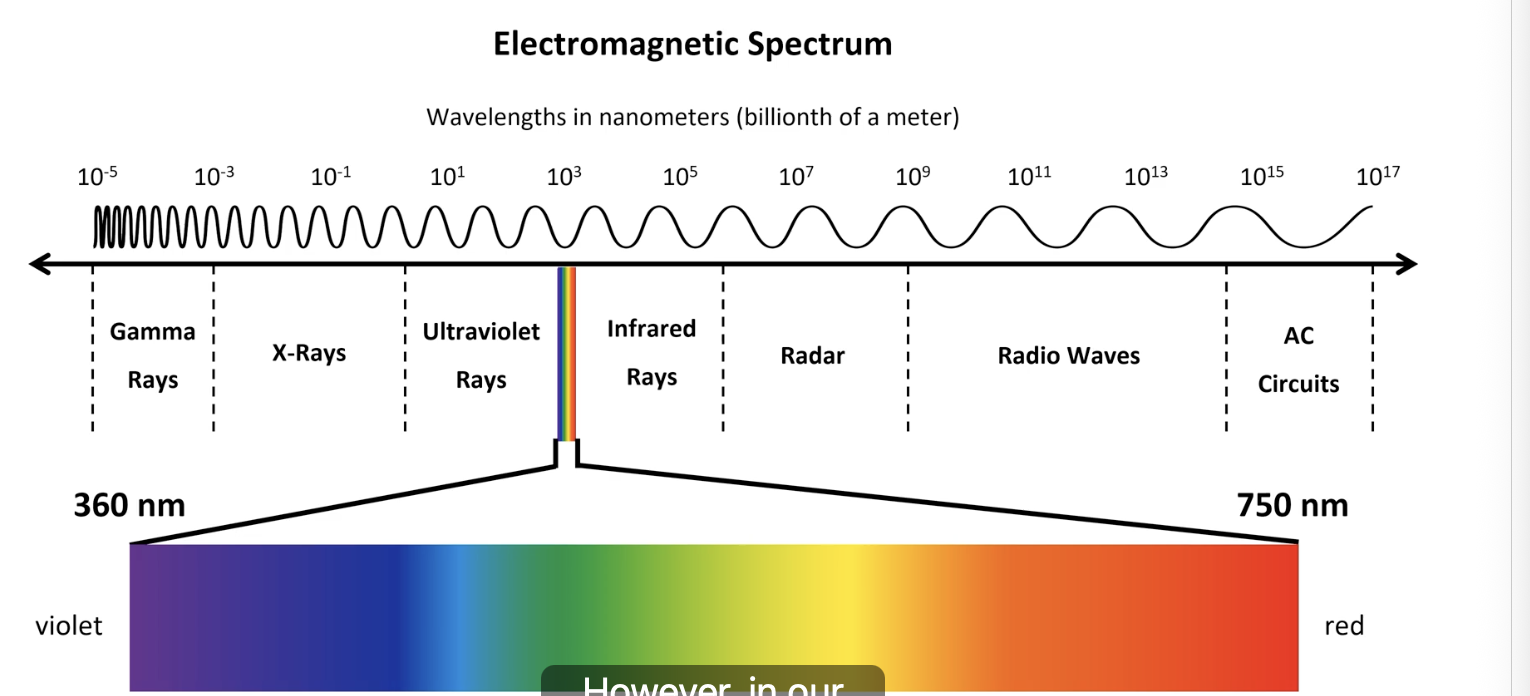
what does amplitude effect
perceived brightness
what does purity effect
saturation (richness of colour)
how many cone types do humans have
3
why did colour vision evolve in primates
to distinguish food
enhance contrast btwn objects & bg
colour blindness
partial or complete loss of func of 1(+) cone types
monochromacy
black & white vision
protanopia
loss/dysfunction of long wavelength(red) cones
deuteranopia
loss/dysfunction of medium-wavelength(green) cones
tritanopia
loss/dysfunction of short-wavelength(blue) cones
trichromat
normal-sighted person w all 3 cones types
dichromat
person w only 2 functioning cone types
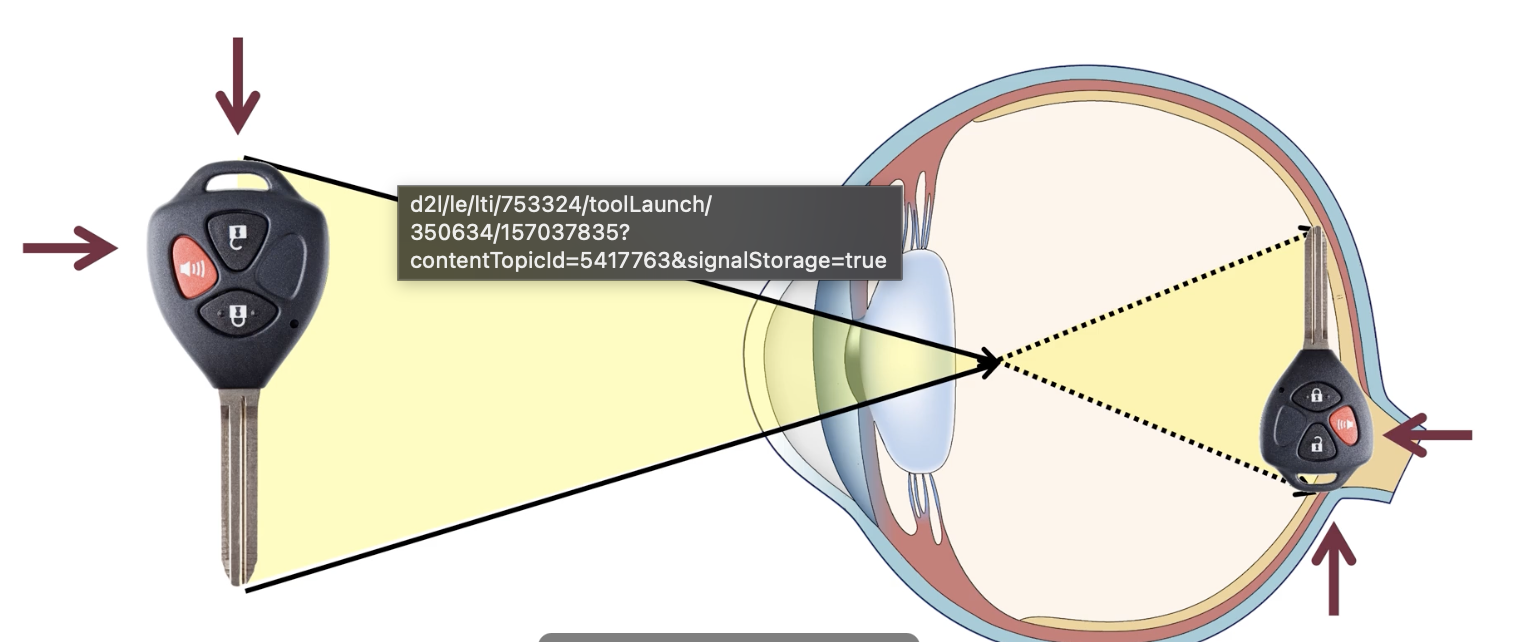
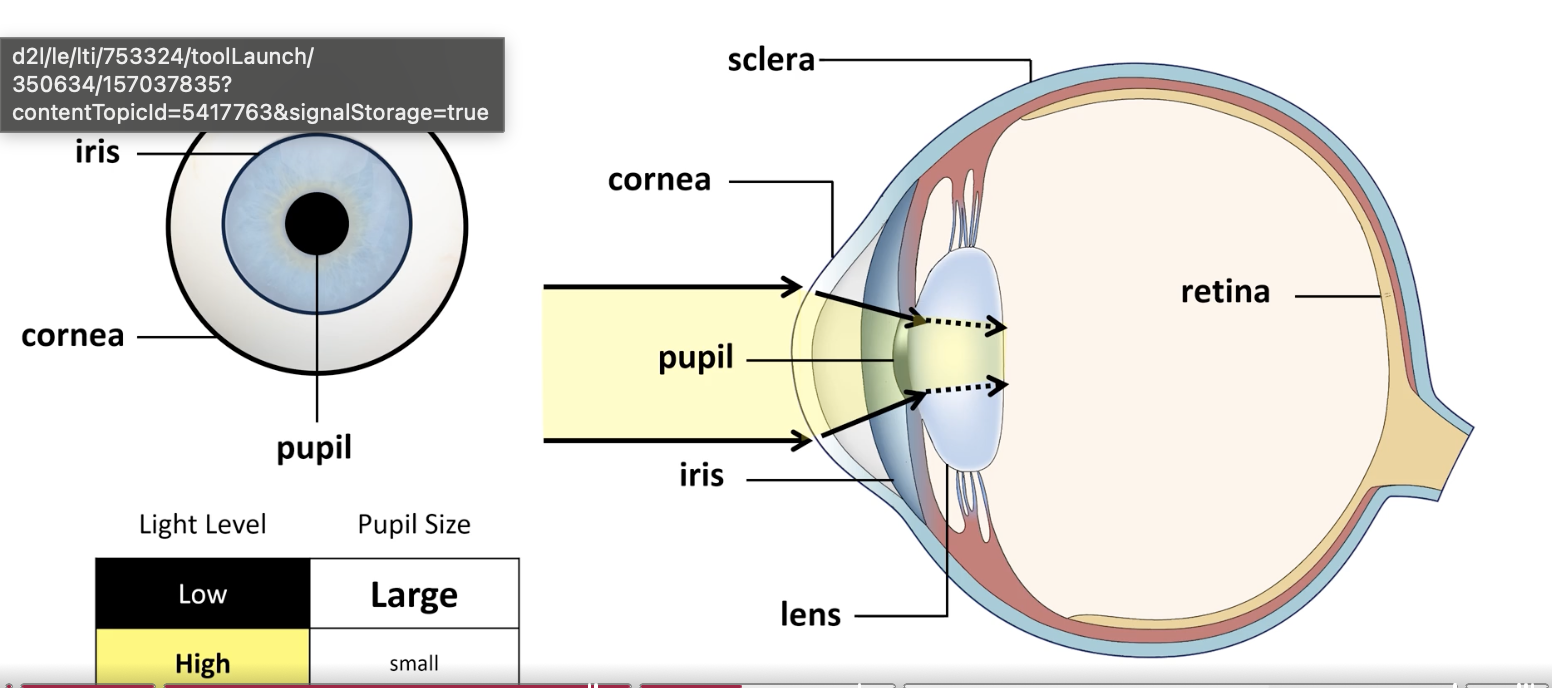
cornea
begins focusing light
~80% of focusing
sclera
tough white outer covering of eye
iris
muscle band controls pupil size
when do pupils dilate (larger opening)
low light i.e. not enough light reaches retina
when do pupils constrict (tiny opening)
bright light i.e. too much light reaches retina
lens
final focusing of light onto retina
~20% of focusing
curvature flips & reverses image
accommodation
lens shape change to focus objects at diff distances
how does lens change to focus objects at near/close distances
gets rounder to produce clear image
how does lens change to focus objects at far distances
gets elongated to focus image on back of eye
hyperopia/farsightedness
see things far, objects close blurry
shorter eye length
less curved lens
imaged focused behind retina
myopia/nearsightedness
see thing close, object far blurry
longer eye length
more curved lens
image focused in front of retina
vitreous humour
clear jelly filling main chamber of eye
diagram eye
retina
neural paper thin tissue that lines back of the eye
y is the retina ‘inside-out’
photoreceptors receive nutrients from the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
what are the 3 layers of the retina
photoreceptor
bipolar cells
ganglion cells
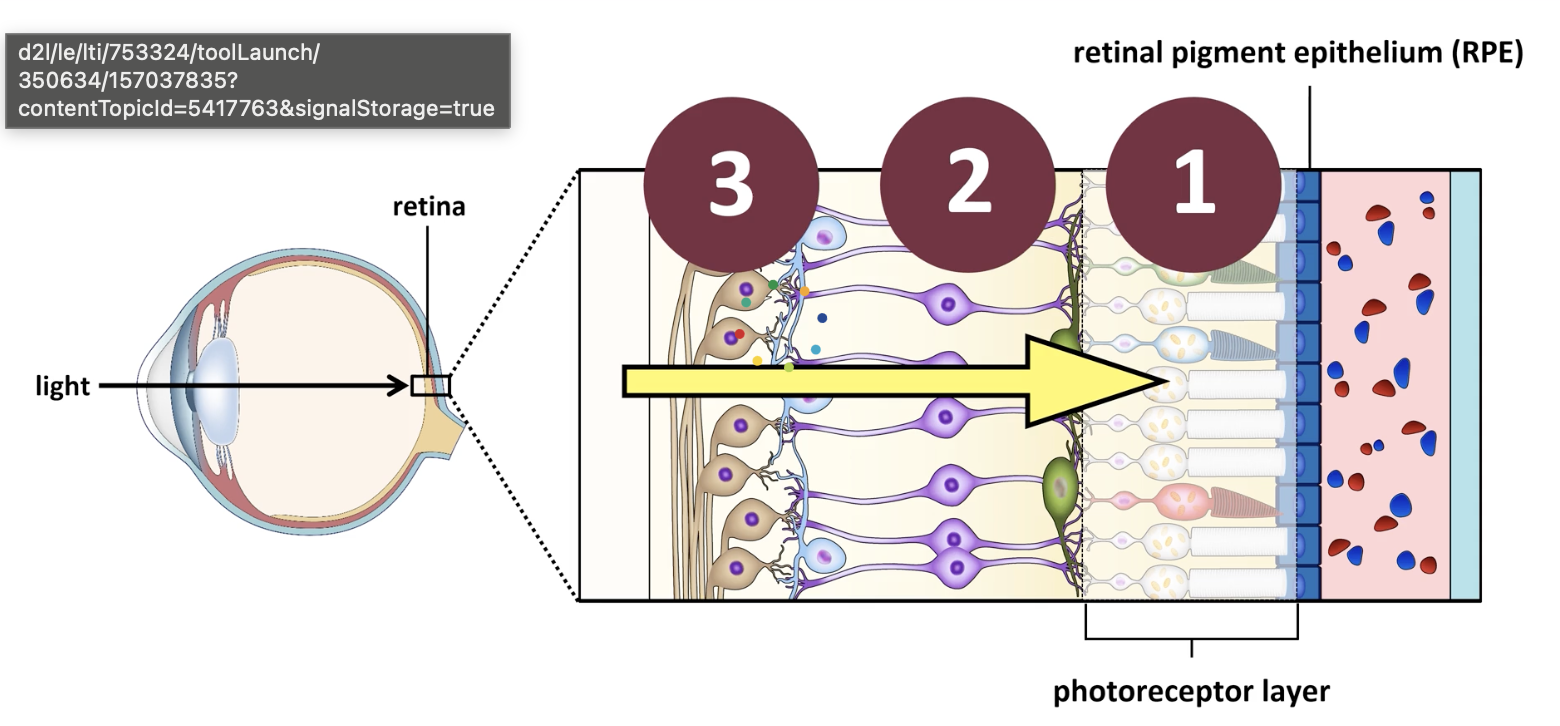
retina: photoreceptor layer
cells that translate physical stimulus of light —> neural signal that’s relayed to the brain
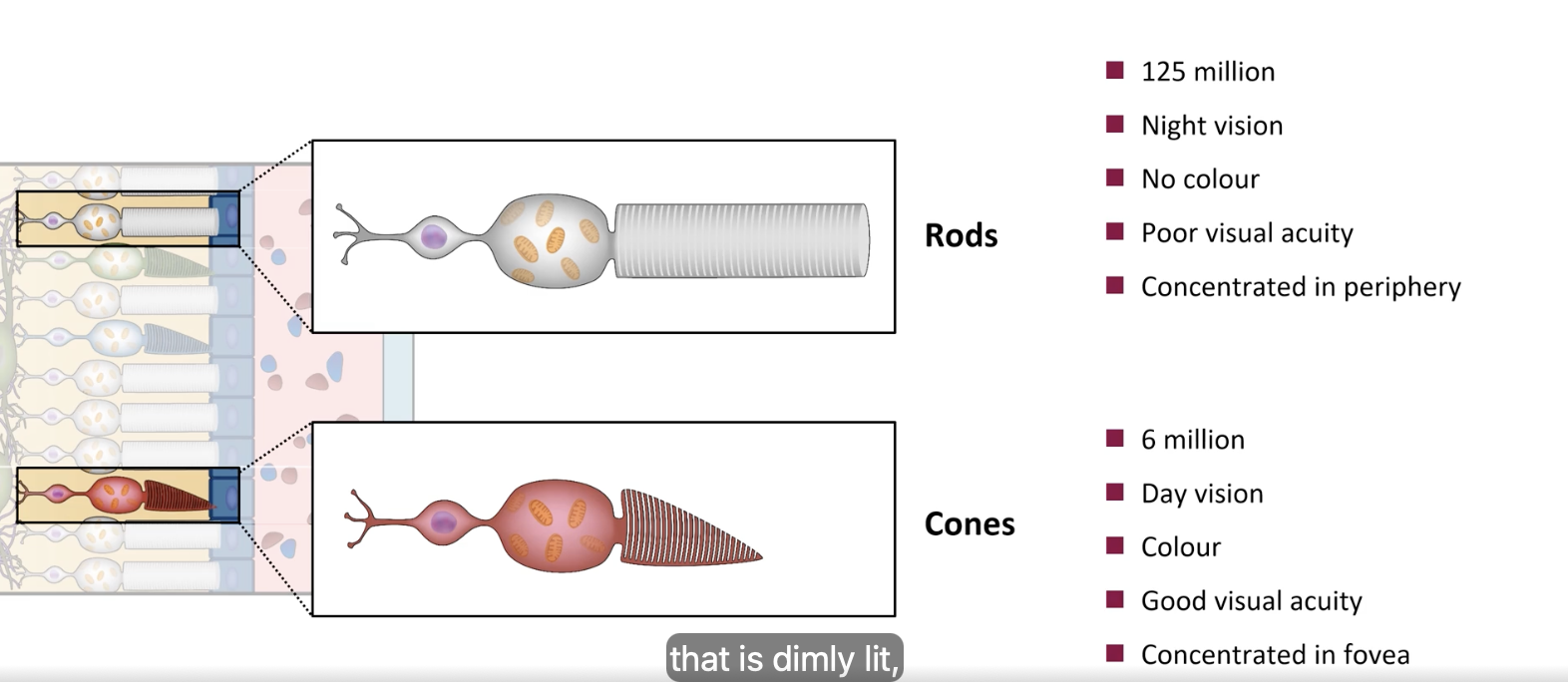
retina: photoreceptor layer: rods
night vision
low light
no colour
poor visual acuity
concentrated in periphery
retina: photoreceptor layer: rods: what pigment do they contain
rhodosphin
make highly sensitive to light
retina: photoreceptor layer: cones
day vision
colour
good visual acuity
concentrated in fovea
retina: photoreceptor layer: cones: what pigment do they contain
iodopsin
makes less sensitive to light
retina: bipolar cells
relay signals from photoreceptors to ganglion cells
retina: bipolar cells: horizontal & amacrine cells
combine & process info w/in retina
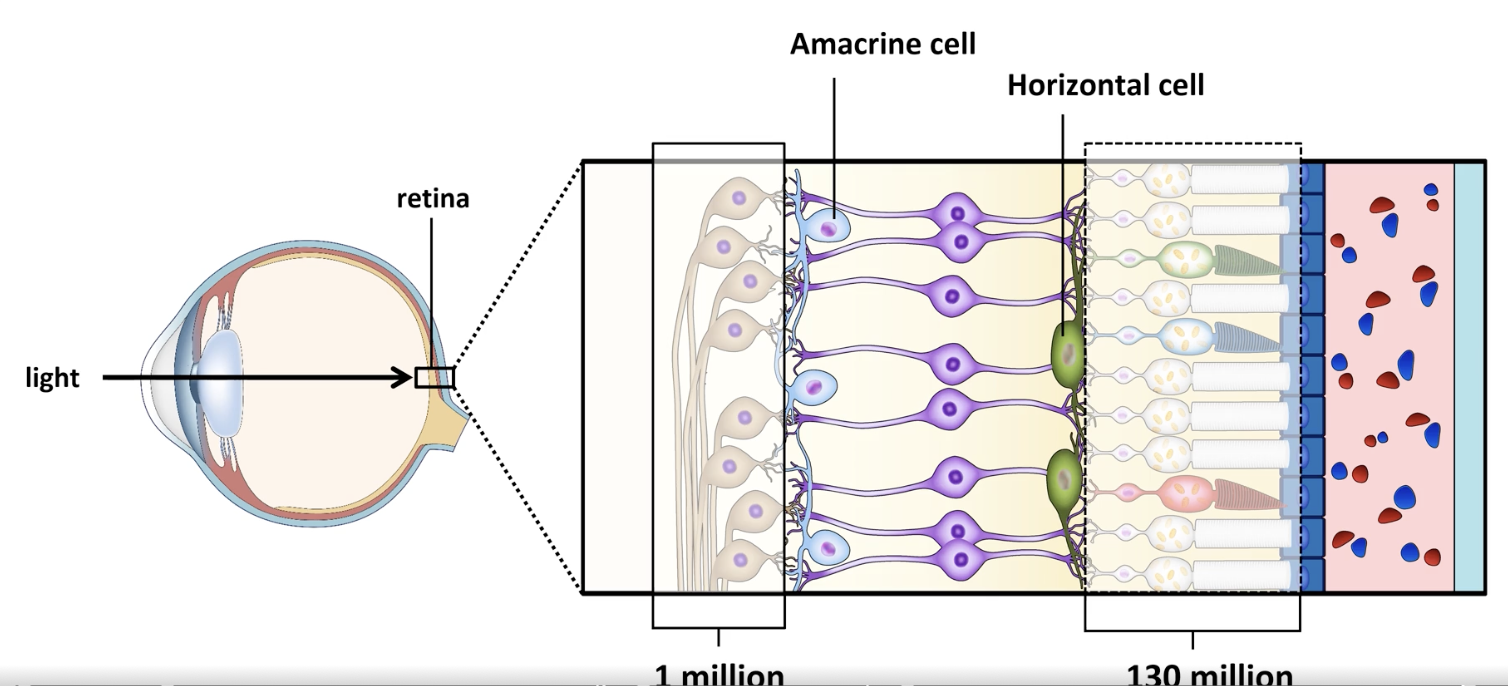
retina: ganglion cells
send visual signals to the brain via the optic nerve
retina: ganglion cells: what causes the blind spot
optic disc has no photoreceptors
receptive field
area of retina where stimulation affects a ganglion cell’s firing
receptive field: centre-surround organization
center stimulation = incs firing rate
surround stimulation = no change firing rate
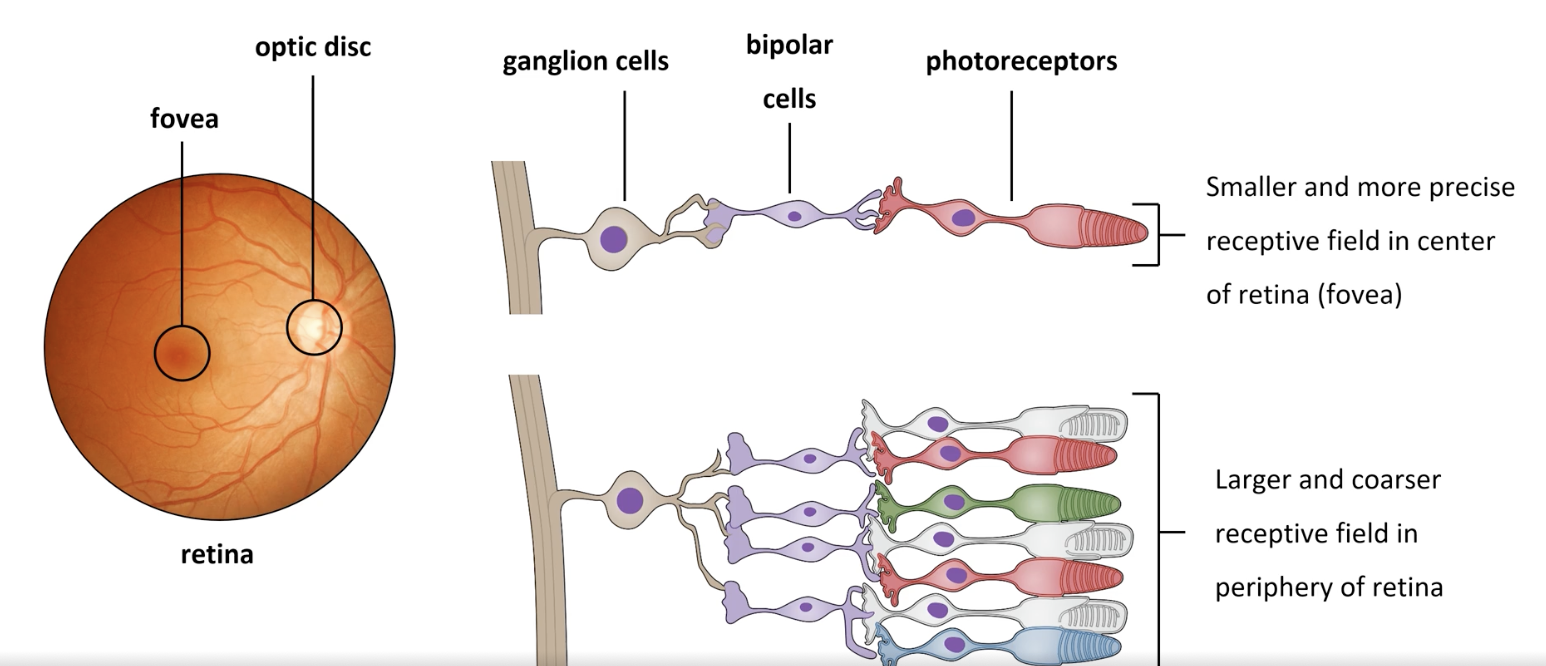
y is visual acuity highest in the fovea
1 cone often connects to 1 ganglion cell
y is peripheral vision less precise
many photoreceptors converge onto 1 ganglion cell
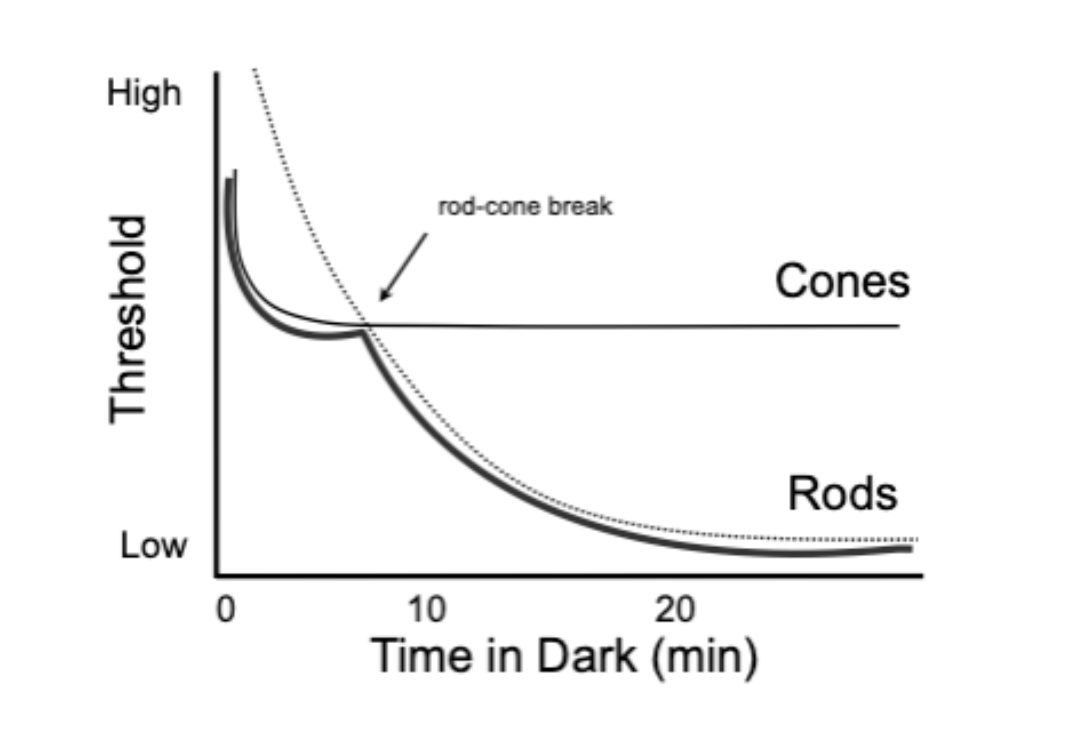
what happens in the 1st few mins of darkness
cones rapidly inc sensitivity
rod-cone break
after 5-10min in darkness, rods become more sensitive than cones
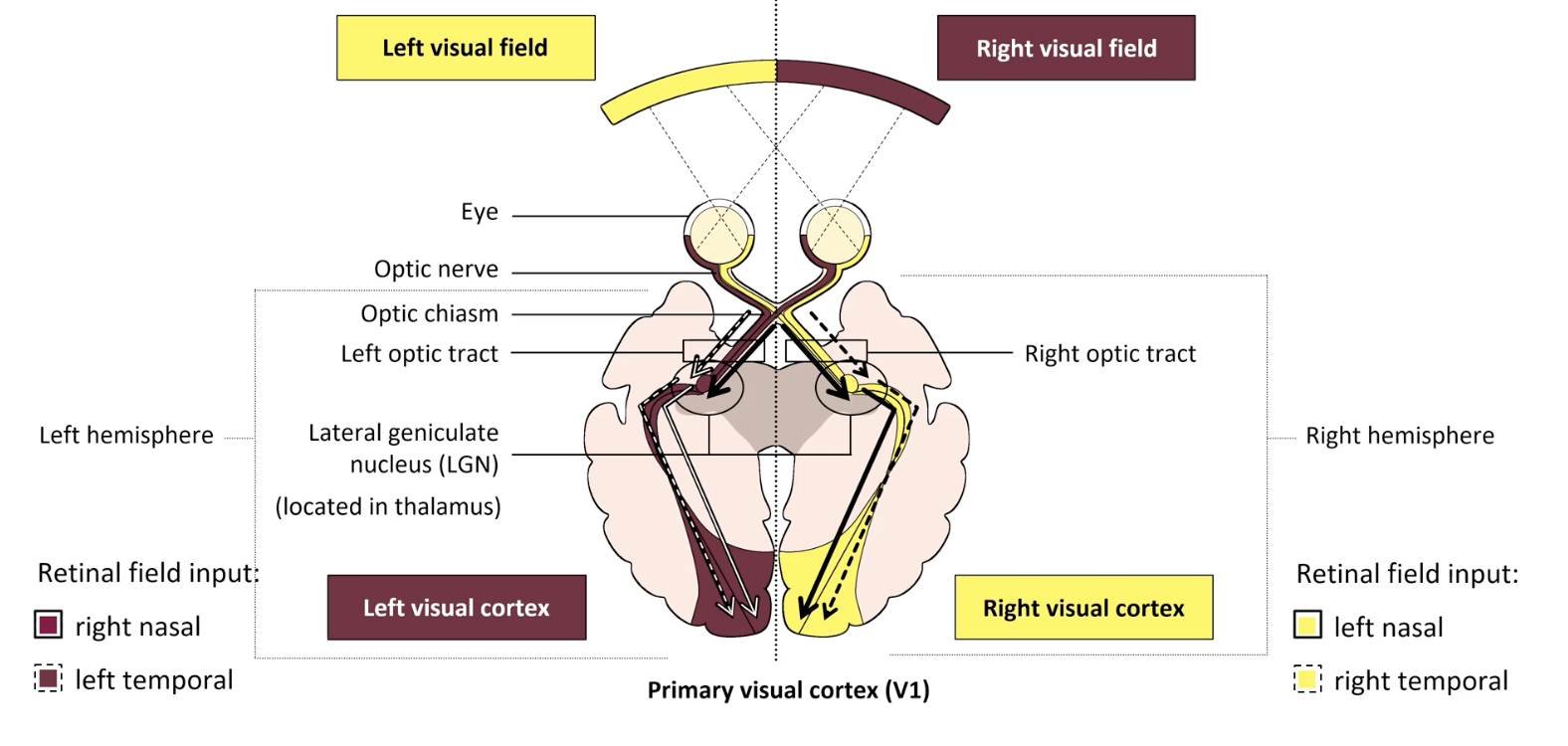
which hemisphere processes the left visual field
right hemisphere
optic chiasm
where optic nerve axons cross
lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
end of optic tract
axons synapse here
in thalamus: relay to cortex
P-cells
small retinal ganglion cells
detailed info of colour, pattern, form, texture, depth
layers 3-6 of LGN receive input
M-cells
large retinal ganglion cells
convey info abt movement
layers 1-2 of LGN receive input
primary visual/straite cortex diagram (V1)
3 cells of V1
simple cells
complex cells
hypercomplex cells
3 cells of V1: simple cells
sensitive to orientation of bars of light
3 cells of V1: complex cells
sensitive to orientation of bars of light & direction of its movement
3 cells of V1: hyper complex cells
sensitive to orientation of bars of light, direction of its movement, & length of it
ocular dominance columns
neurons that respond preferentially to input from either L or R eye
orientation columns
neurons that respond preferentially to stimuli of specific angles
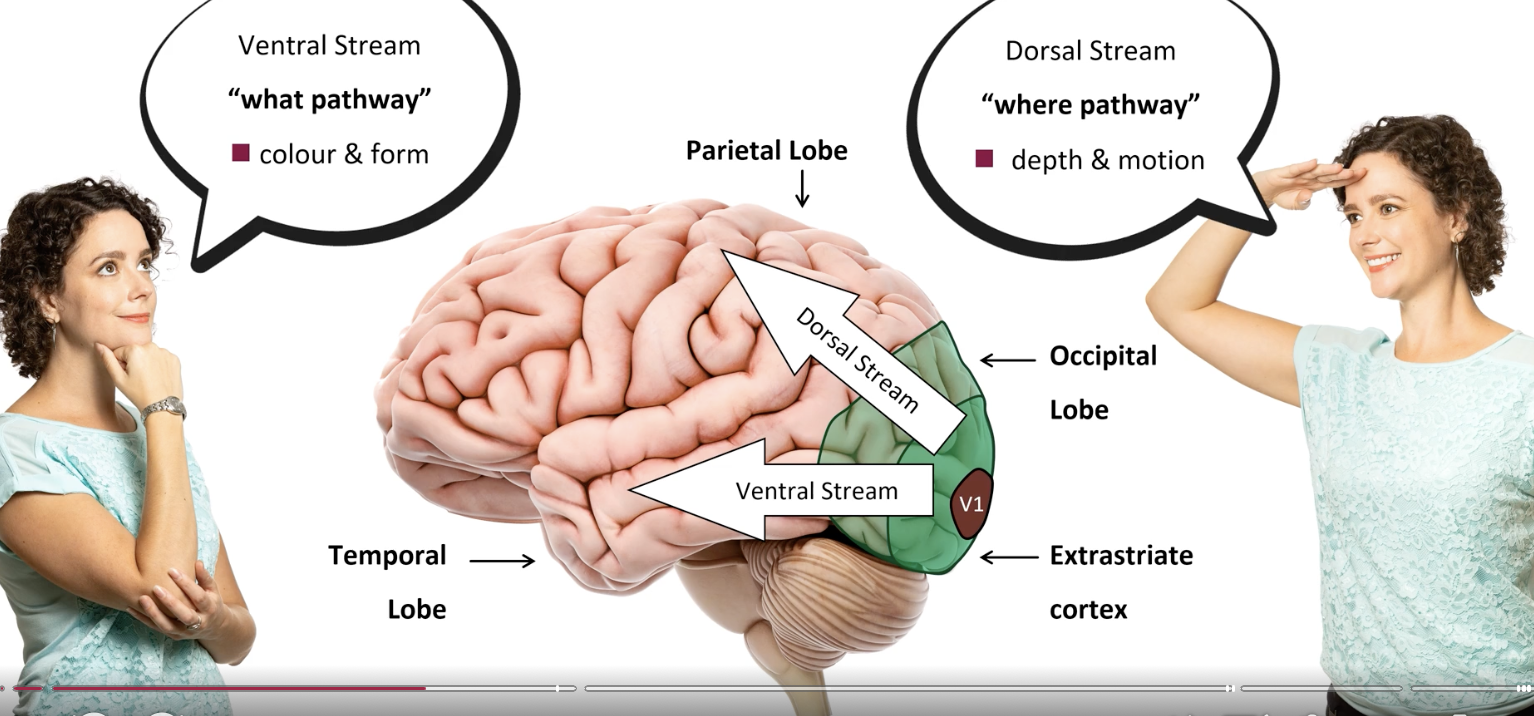
extrastraite cortex
V2-5 & IT
colour
motion
object recognition
dorsal stream
‘where’ pathway - where objects are
depth & motion
extrastriate cortex —> parietal lobe
V2, V4, IT
ventral stream
‘what’ pathway - what object is
colour & form
extrastriate cortex —> temporal lobe
V3, V5
monocular depth cues
only need to captured by 1 eye
monocular depth cues: 2 motion based
motion parallax
optic flow
monocular depth cues: 2 motion based: motion parallax
based on relative speeds of near & far objects while in motion
monocular depth cues: 2 motion based: optic flow
perceived motion of visual field that results from ones own movement thru the enviro
monocular depth cue: 4 pictorial based
interposition
linear perspective
aerial perspective
shading
monocular depth cue: 4 pictorial based: interposition
1 object overlaps & tf occludes another object
monocular depth cue: 4 pictorial based: linear perspective
parallel lines observer appear to converge on a single vanishing pt on the horizon
monocular depth cue: 4 pictorial based: aerial perspective
visual effect of light when passing thru the atmosphere that causes distant objects to appear hazy/blurry
monocular depth cue: 4 pictorial based: shading
helps us infer direction of light
binocular depth cue
need to be captured by both eyes
binocular depth cue: stereopsis
perception of depth via binocular disparity
binocular depth cue: convergence
as object moves closer to face the gazes of our eyes converge
adjustable lens
humans
allows accommodation
cumulative selection
evolutionary process where new adaptations are layered onto older adaptations
factors affects eye architecture across species
light avail
food position (above or below)
movement, shape, colour of prey
simple eyes
vertebrates
single lens
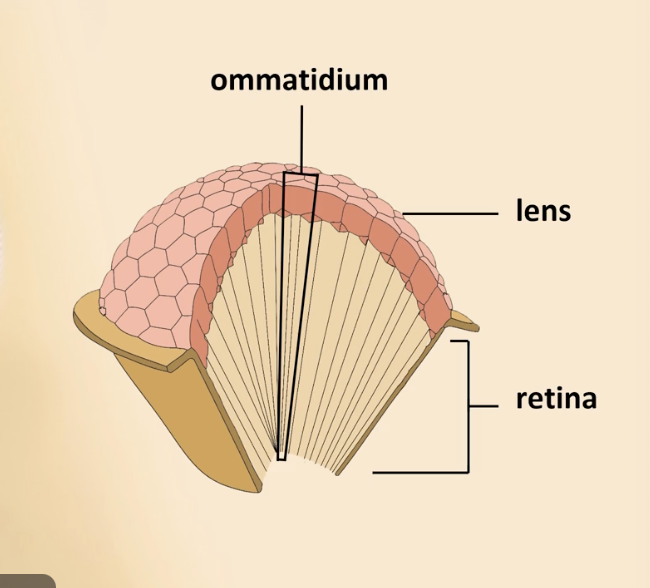
compound eyes
arthropods
made of many ommatidia: tiny light-capturing ind arrangements of tubule units
good 4 detecting movement at close dis
2 funcs of eye
resolution (acuity/discern fine detail)
sensitivity (ability to detect light, faint or vivid)
effect of eye size on vision
larger = better resolution & sensitivity = useful for hunting & foraging
small = species that spend time underground
trade-off btwn acuity & night vision
can’t max both due to high metabolic cost
round lens adv
good close-up focus
circular pupil adv
better for night vision
slit-shaped pupil adv’s
enhances visual acuity
reduces chromatic aberration: tendency for wavelength light to enter at periphery = blur retinal image
horizontal pupil adv’s
grazing animals
enhances panoramic vision
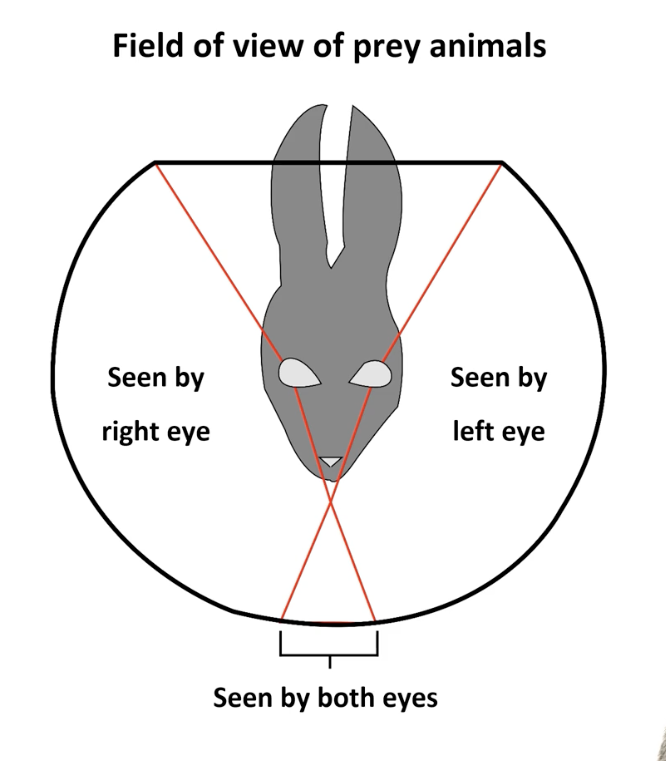
laterally-directed eyes
wide total field view
2 sep visual fields
poor depth perception
prey animals
front-facing eyes
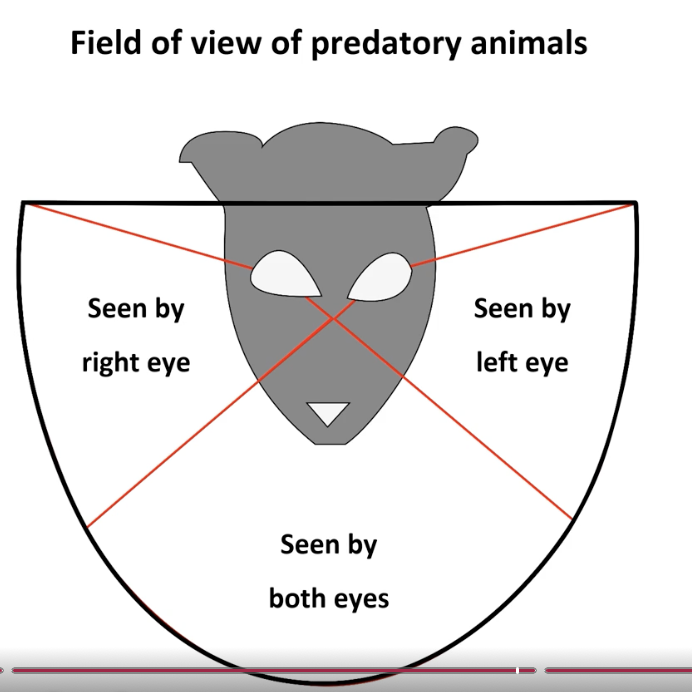
narrow total field of view
single overlapping field
excellent depth perception
predatory animals
preferential looking paradigm
method used to deter infant visual acuity
visual acuity at birth
least developed sensory sys at birth
when does visual development begin
prenatally
2nd prenatal month
eyes r formed
6th prenatal month
fetus reacts to light
retinal cells fire randomly
visual development relies on
heavy visual input from enviro
newborn visual limitations
weak lens muscle
inconsistent pupil rxns
vision @ 3 mons
almost adult-like focusing
retinal ganglion cell development
conts until early childhood