Introduction to the Nervous System
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
T/F: Cranial nerves are a critical part of the CNS.
F, cranial nerves are a part of the PNS.
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
An acquired inflammatory disorder causing demyelination of CNS axons, leading to sclerotic plaques and disrupted neural conduction.
What are some common dentally relevant signs/symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis?
Trigeminal neuropathy
Dysphagia
Dysphonia/Dysarthria
What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
An acquired inflammatory disorder causing demyelination of PNS and autonomic axons, leading to progressive paralysis.
What is Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease?
A non-inflammatory hereditary protein mutation that effects the myelin and axon structure of PNS axons, leading to limb muscle weakness.
What are some common dentally relevant signs/symptoms of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease?
Cranial nerve dysfunction
Bruxism
Respiratory dysfunction
What are bipolar neurons?
Special sensory neurons with one axon and one dendrite.
What are pseudounipolar neurons?
Sensory neurons with a single axon that branches into both the CNS and PNS.
What are multipolar neurons?
Motor neurons commonly found in the CNS with one axon and many dendrites.
What are neuroglia?
Supporting cells of the nervous system.
What is an astrocyte?
A neuroglial cell that helps support, nourish, and maintain the CNS, and regulates the blood-brain barrier.
What is a microglia?
A specialized macrophage that activates an immune defense of the CNS.
What is an oligodendrocyte?
A neuroglial cell that produces myelin for up to 50 axons in the CNS.
What is an ependymal cell?
A neuroglial cell that produces CSF in the choroid plexus (found in the ventricles of the brain).
What is a schwann cell?
A neuroglial cell that produces myelin for a single axon in the PNS.
What is a satellite cell?
A neuroglial cell that helps support, nourish, and maintain the PNS.
What is the neurolemma?
The outer cytoplasmic layer of a schwann cell that provides axon protection and regeneration.
Cell bodies in the CNS are called ____ while cell bodies in the PNS are called ____.
Nuclei
Ganglia
Axons in the CNS are called ____ while axons in the PNS are called ____.
Tracts
Nerves
What does the endoneurium cover?
A single axon and its myelin sheath.
What is a fascicle in relation to the nervous system?
A bundle of axons wrapped together by the perineurium.
What does the epineurium cover?
An entire nerve, or bundle of fascicles.
What arteries supply the meninges?
The meningeal arteries.
What nerve innervates the anterior and middle cranial fossae?
CN V
What nerves innervate the posterior cranial fossa?
CN IX, X, C1-3
What are the meningeal layers from most superficial to deep?
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
What meningeal layers wrap around the brain and continue around the spinal cord?
All of them.
What meningeal layer is continuous with the epineurium around nerves?
The dura mater.
Where are dural sinuses located?
Within the dura mater.
What are arachnoid granulations?
Small projections in the arachnoid mater that protrude into the dural sinuses and allow CSF to enter the dural sinus and return to the veins.
What are the characteristics and functions of CSF?
It is not rich in protein
It cushions the CNS
Provides immunological support for CNS
Regulates blood flow
What is the flow of CSF from the lateral ventricles to the spinal cord or subarachnoid space?
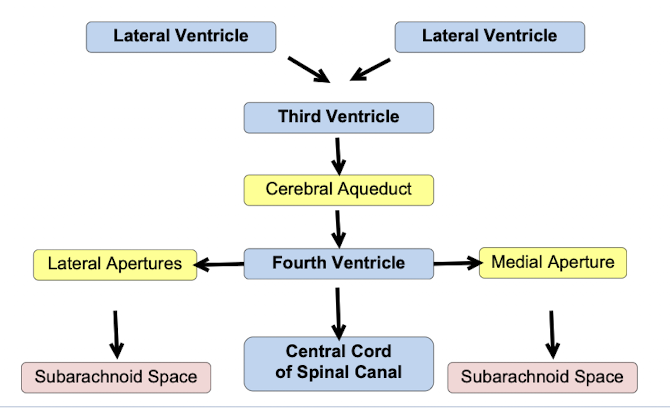
What is non-communicating hydrocephalus?
Obstructive hydrocephalus
When CSF accumulates in the ventricles.
What is communicating hydrocephalus?
Non-obstructive hydrocephalus
When CSF is not reabsorbed into the veins, causing a build-up in the subarachnoid space.
What is the circle of willis?
An arterial anastomosis which provides blood circulation to the brain.
What main arteries supply the circle of willis?
Vertebral arteries
Internal carotid arteries
Which arteries are the most common site for an ischemic stroke?
Middle cerebral arteries
What are the symptoms of a stroke?
Face drooping
Arm weakness
Slurred speech, dizziness, and impaired vision
Time to call 911
What is the purpose of the blood-brain barrier?
It selectively separates circulating blood from the CNS
What is the glymphatic system?
A pathway that clears waste products from the brain by moving CSF through brain tissue.
What system runs along the dural sinuses of the skull?
The glymphatic system
Through what sinuses does CSF enter the blood and exit the skull?
Sigmoid sinus
Vertebral veins
Cavernous sinus/Pterygoid veins
What vein corresponds with the sigmoid sinus?
Internal jugular vein
What vein corresponds with the cavernous sinus/pterygoid veins?
Maxillary vein