Module 4 Early Christian
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Catacombs of Domitilla
- named after Flavia Domitilla, member of an Imperial family
Edict of Milan
- religious toleration was granted throughout the empire
Basilicas
- the creation of basilicas signified the establishment of Christ as an authority figure
Christian house in Dura-Europos, Syria
Catacomb of Priscilla
- built for Priscilla's family then eventually used by Christian community
- earliest depictions of Biblical scenes in fresco (fresh); themes of salvation
- earliest representation of the Madonna and child
- earliest inventions of Christian iconography
- 13km long, 3 stories deep
- housed the remains of some Christian martyrs
Christians preferred ___ rather than ______?
Burial rather than cremation
Fractio Panis
- similar to the Last Supper as there is the communal ritual of breaking the bread
Christ's portrayal
Good shepherd - as he takes care of his people just like a shepherd and flock
What kind of pose is seem in Christ's portrayal as the Good Shepherd?
Contrapposto
Sarcophagus of Junius Bassus
- depictions of Biblical scenes
- Redemption through Christ - salvation of Junius Bassus as a convert
- carved on three sides, meant to be installed next to a wall
Junius Bassus
- prefect (high official) of Rome
- baptized right before his death
The sarcophagus of Junius Bassus shows what type of redemption?
- redemption through Christ, salvation as a convert
Sacrifice of Isaac
- part of Sarcophagus of Junius Bassus
Where was Basilicas used?
- formal meeting place and for law courts
Christ's giving of the law
- traditio legis - Christ is seen as a young man in that Roman tradition
- giving of the law - done by the emperor
Pontius Pilate, Peter, and Paul
all were executed under Roman rule
What architecture is seen in Old Saint Peter's Basilica?
- adapted Roman elements such as columns
- Axially planned
- Apse
- Nave
Axially planned
- longitudinal axis unlike centrally planned Pantheon
Apse
- semi circular recess where the altar is usually located
Nave
- central corridor where the clergy would be; processional space
Architecture of Old Saint Peter's Basilica
Axially planned
Apse
Nave
Apse
- altar
Nave
- central corridor where the clergy would be
Narthex
- entrance
- vestibule
Atrium
- courtyard
Santa Maria Antiqua
- Sistine Chapel of the Medieval Age
- layers of imagery on top of each other showing different styles
Palimpsest
- illustrations painted on top of each other
- omissions to text still leave a trace
- writings not fully erased, people keep adding
- use and reuse of walls
Maria Regina
- image of Maria Regina as Byzantine empress
BYZANTINE EMPIRE
Byzantine Empire
Constantinople
- modern name is Istanbul, Turkey
- Byzantine capital from 330 CE
Basilica San Vitale, Ravenna
- famous for mosaic lining on the walls
- not located in the Byzantine empire?!, but a famous declaration of emperor Justinian's power to build outside of their territory
- centrally planned
Centrally planned
- circular symettry unlike axial
Columns of the Basilica San Vitale, Ravenna
Apse mosaic
- Christ sitting on a throne handing a throne to Saint Vitalis
Theodora mosaic
- installed in front of Justinian mosaic to show the equality of the two
- depicted with halo and jewels
Justinian Mosaic
- depicted with a halo and an imperial crown
What are the two ambitions of Justinian's rule?
- restore territorial boundaries of the empire
- establish religious uniformity
Apse of the Basilica San Vitale, Italy
Christ, Justinian, Theodora
Hagia Sophia, Constantinople
- Church translated Holy Wisdom (Hagia: holy, Sophia: wisdom)
Golden dome
- suspended from heaven
- turned into a mosque in 1453
How to put a dome on flat walls?
- pendentive: triangular segment of a spherical surface
Medallion with Christ from an Icon Frame
- Byzantine art that depicts Jesus, Mary, and saints
Iconoclasm
- iconoclast criticized icons as sacrilegious
- image breaking
Exodus 20:2-5
I am the Lord your God, who brought you out of Egypt, out of slavery.
Exodus 23:24
Do not bow down before their gods or worship them or follow their practices. You must demolish them and break their sacred stones to pieces.
Hagia Eirene, Constantinople
- some emperors were iconoclasts so some churches did not have icons or decorative walls
- Theophilos (iconoclast), Methodios I (iconophile)
Theotokos Mosaic
- located in the apse of Hagia Sophia
Prince Vladimir I of Kyiv
- emperor of Kyivan Rus, became an ally of Byzantinian emperor Basil II
Virgin of Vladimir
- one of the most beloved artworks in Russia, but not Russian in origin as it was likely a diplomatic gift
- actually by Saint Luke
- attributed to several miracles
Battle of Novgorod and Suzdal
- depicts the power or the icon of the Virgin and Christ
- the icon allegedly saved Novgorod when an enemy arrow hit the image
Crusades
- a series of holy wars
- began with the Holy Roman Empire to capture the Holy Land (Jerusalem) from the Muslim rule
- passed through Asia Minor through the help of the Byzantine Empire
Fourth Crusade
- recapturing of Jerusalem but ended up sacking Constantinople
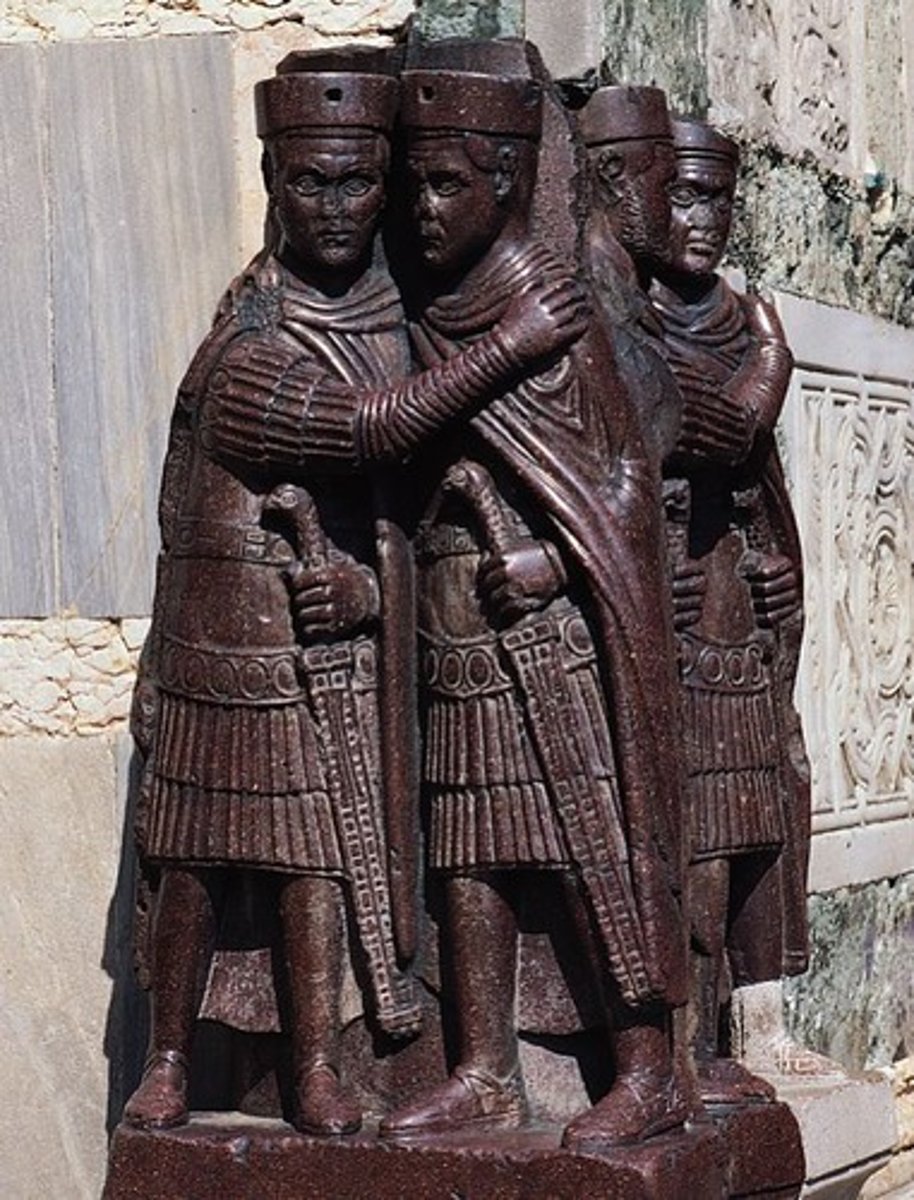
Portraits of the Four Tetrarchs
- Constantinople was looted
- four people leading the empire
- Most of the objects ended up in Venice as it was the provider of ships
- symbolizes unified power

Venetian Mosaic
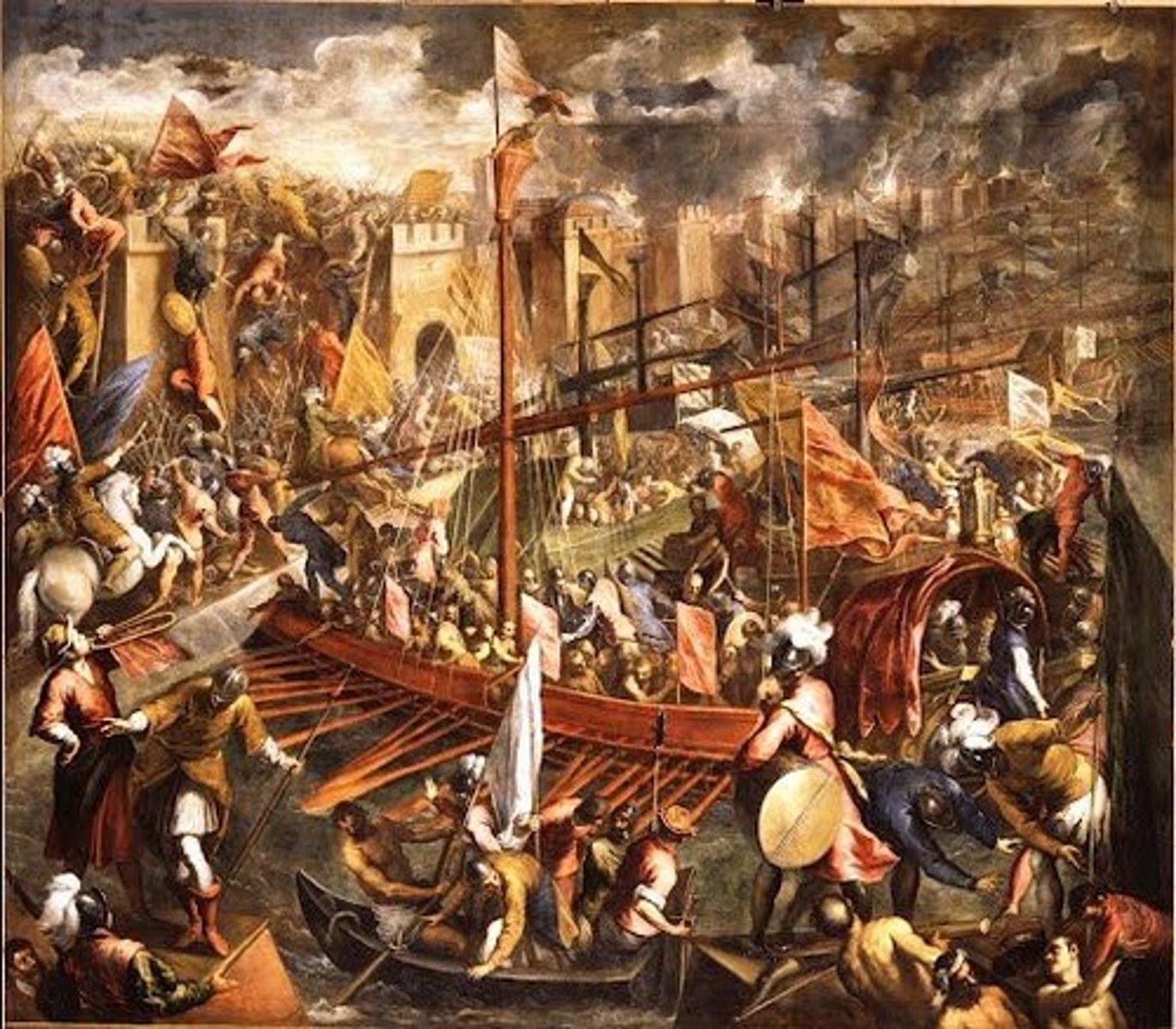
- depicted the fall of Constantinople

Siege of Constantinople
- Byzantine Empire could not fully recover from the Fourth Crusade
- Black Death (bubonic plague) came around 14th century and wiped half of its population
- Constantinople was then attacked by the Ottomans with heavy artillery

EARLY MEDIEVAL ART
Middle Ages
- Medium Aevum
- called medieval (retroactive term) because it's in between the Roman and Renaissance eras
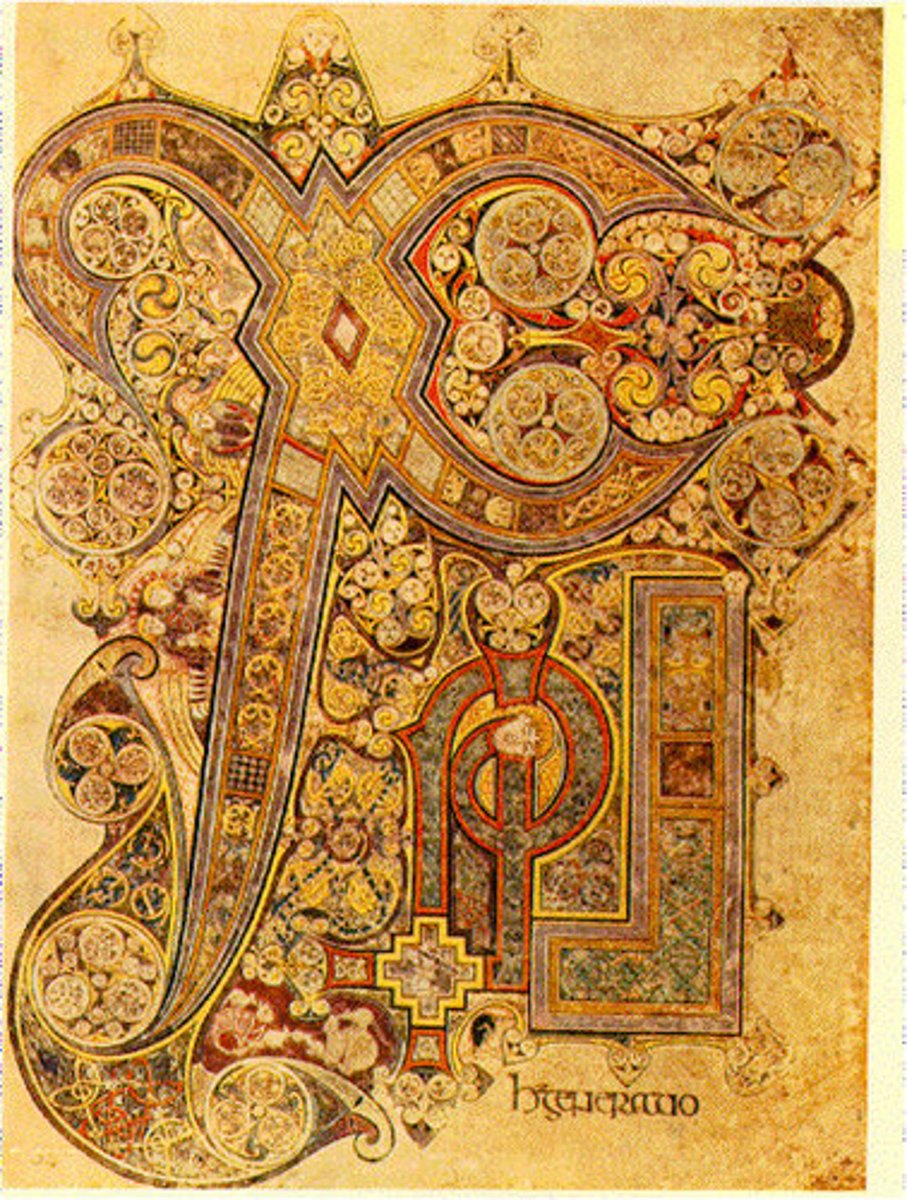
Book of Kells
- manuscript containing the four Gospels of the New Testament: Matthew, Mark, Luke, John

Dark Ages
- at this time, Roman culture art and culture were considered old
- reflects more of our knowledge at the time rather than the state of society
- groups such as Vandals destroyed the remains of Roman civilization
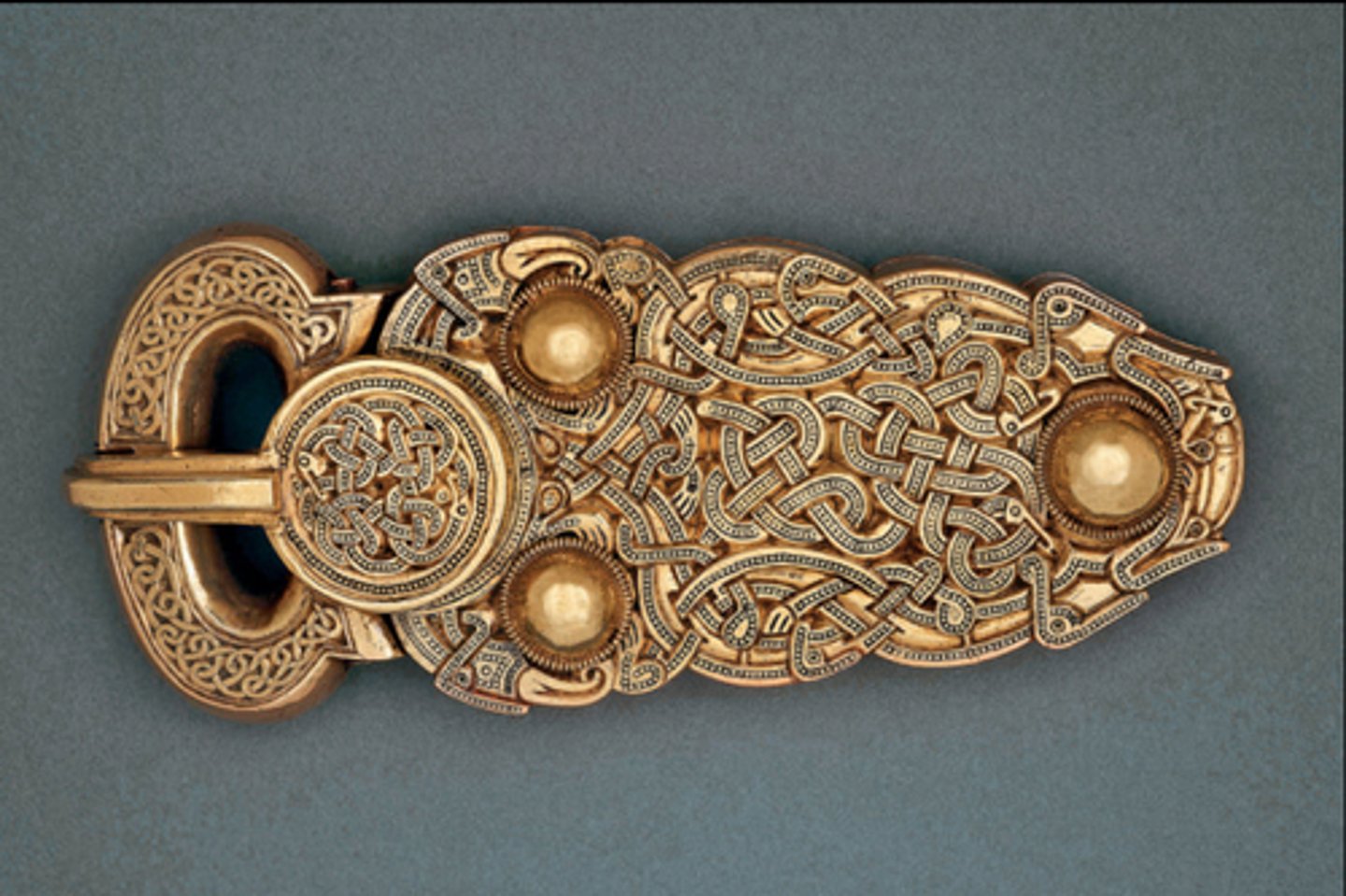
Sutton Hoo Burial Ship
- found by amateur archaeologist, Basil Brown
- burial was for an important person who died early 7th century as effort and manpower were needed to bury a whole ship
- contained military equipment, textiles, and treasure
- ship burials were rare in Anglo-Saxon society
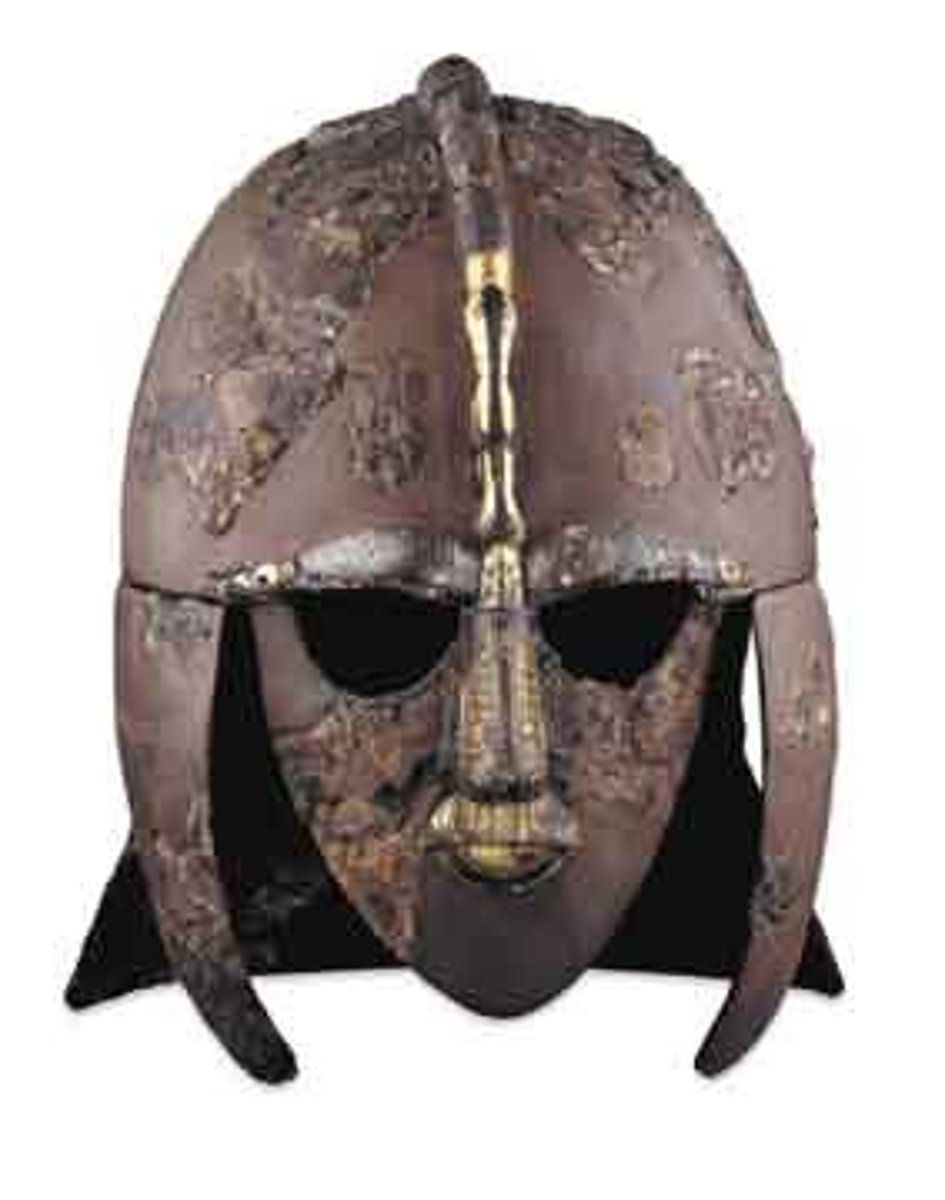
Sutton Hoo Helmet
- reconstructed from 500 fragments
- comprised of an iron cap, neck guard, cheek pieces, and face mask
- was embossed with decorative animal panels called Style II

Sutton Hoo purse lid and shoulder clasp
- known for their intricate design
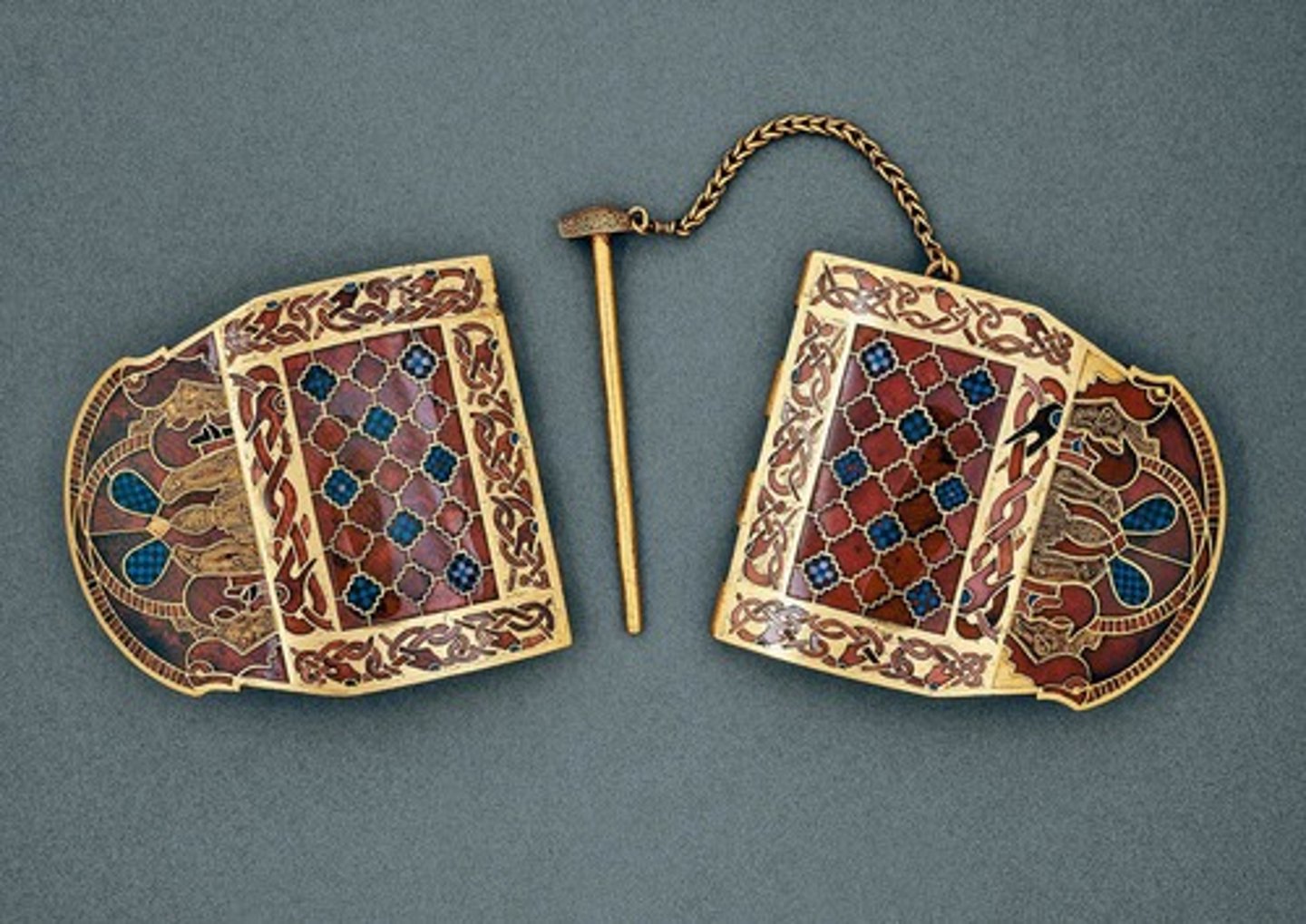

Cloissone technique
- French (partitioned)
- used in the Sutton Hoo purse lid
- technique where formed wires in close shapes are affixed onto a base
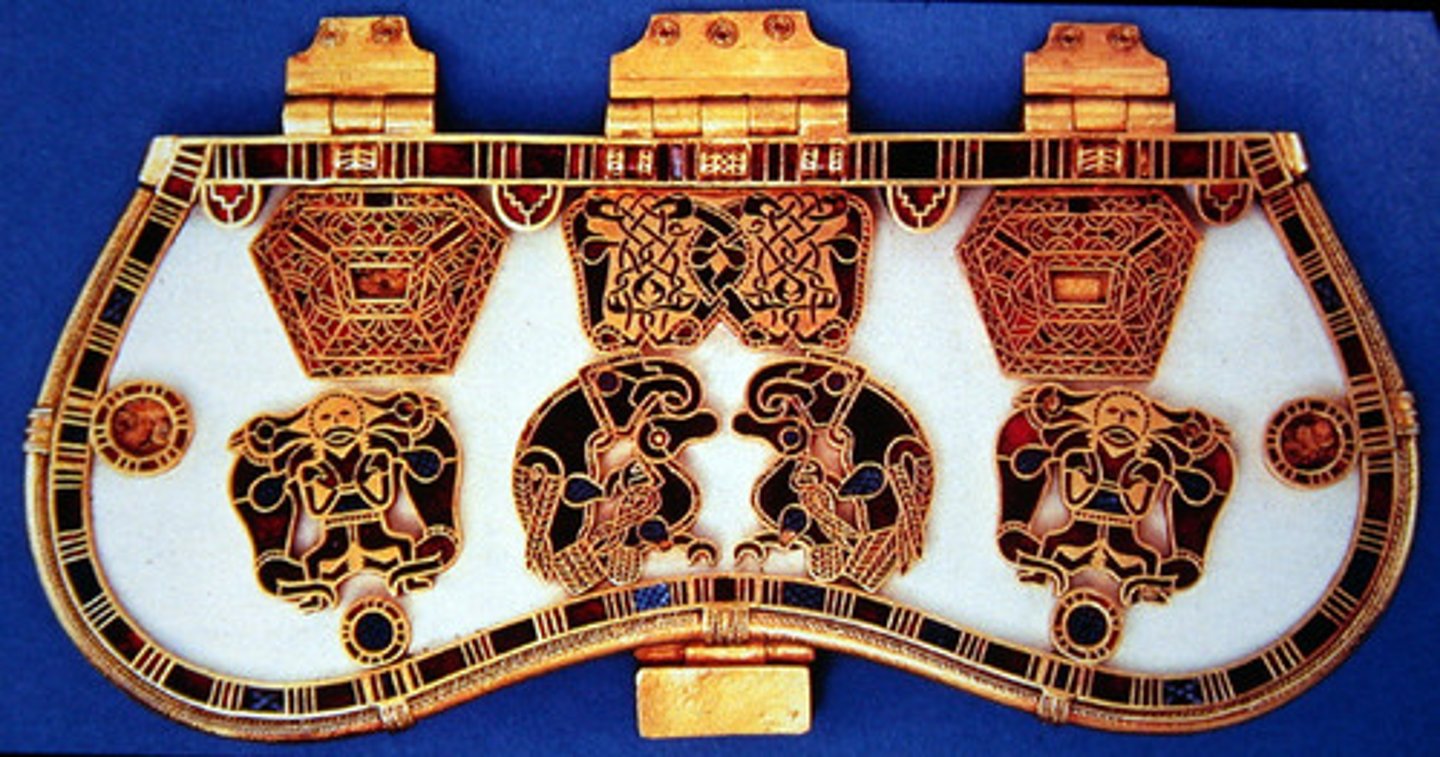

Horror vacui
- used in Sutton Hoo belt buckle
- fear of empty spaces which is why the whole object is decorated

Lindisfarne Gospels
- created and illustrated by Eadfrith, bishop of Lindisfarne
-Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John
- written in Latin and translated to Old English
- earliest surviving translation of Gospels in any English languages
Codex
- ancient manuscript in book form
- made either of antelope or calf hide (vellum) or sheep or goat hide (parchment)
- heavily designed
Franks
- one of the most powerful barbarian tribes that took advantage of declining Western Roman empire
Clovis I
- first unifier of the Franks and converted to Christianity in 508
Charlemagne (Charles the Great)
- Franks were ruled by him in 768 - 814
- eventually because the first emperor of the Holy Roman Empire
- father of Europe, one of the king of Franks, first Holy Roman emperor
Aachen
- center of the Holy Roman Empire; present day Germany
Carolingian art
- art at the time of Charlemagne
- first revival of Classical art
Charlemagne coin
- expanding empire: Charlemagne rebuilt structures lost due to the fall of Western Roman empire
- his Christian faith binded distant lands
- literacy was also part of his empire as he taught priests and religious leaders to spread Christian teachings
- consolidated Christianity
- was given a crown by Pope Leo III
Palatine Chapel
- in Aachen (New Rome)
- centrally planned
- superficial resemblance to San Vitale - imported Ravenna capitals and columns
- Charlemagne's throne is in the gallery
Scriptorium
- center for copying and illustrating manuscripts
Carolingian Miniscule
- the empire produced a new script which is more legible and easier to read
- with this, one skilled scribe can copy 7 pages (25 lines a day)
- this increased legibility and clarity which were important to Charlemagne to increase literacy
The Ebbo Gospels
- stylistic variation made during Carolingian Empire
- portaits of evangelists are rendered painterly
- spatial perspective, 3d object in space
Charlemagne depicted leading an army
- this shows how despite the rise in education, there were still massacres and mass executions
- Carolingian empire eventually split into three kingdoms
Otto I
- Christian Saxon king began his rise in power and then crowned Holy Roman emperor
Otto II
son of Otto I, married princess Theophano of the Byzantine empire
Otto III
- seen as bigger than the other figures
- territories Otto ruled:
Territories Otto III ruled?
Sclavinia, Germania, Gallia, and Rome
Gospels of Otto III
- there was a development in style, exact likeness of the figure was not necessary, but needed clarity on whom was depicted
- gold paint
- trypophobia
Bernward Doors
- commissioned by Bishop Bernward, a member of Ottonian court
Left and Right Door
Left: Fall of Man
Right: Redemption of Man
Rottgen Pieta
- Mary cradling the dead body of Jesus
ROMANESQUE ART
Great Schism
- separation of east Catholic and west Orthodox
What happened in 1096?
- first Crusade
Feudal Society
- based on land ownership and military control
- slaves (property)
- serfs: peasants
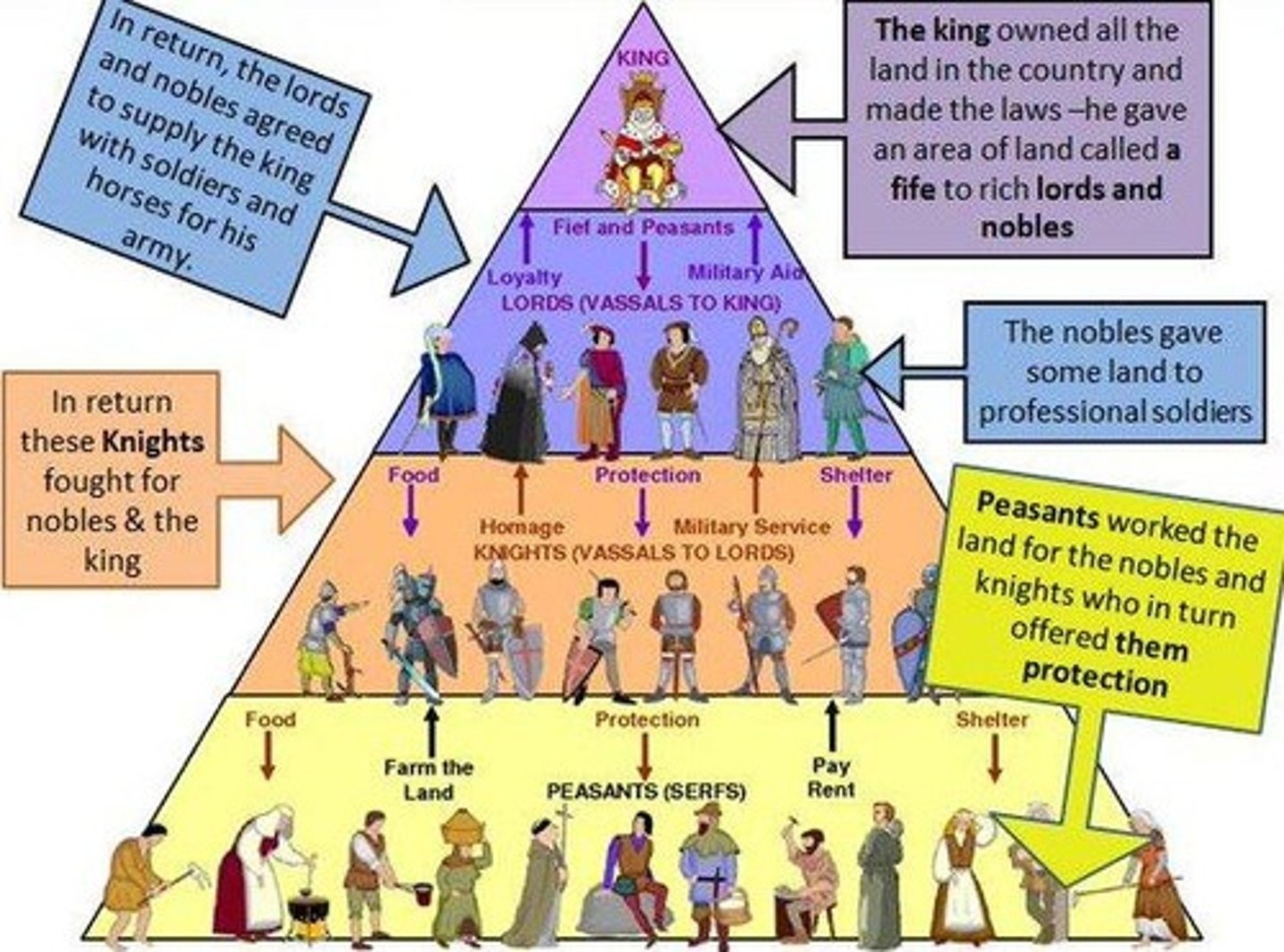
Arrangement of Feudal Society from highest to lowest
- kings, nobles, knights, and serfs
Religious Pilgrimages
- journey to a sacred place: act of piety/devotion
Camino de Santiago
- travel on foot across Europe to a holy shrine where bones, believed to belong to Saint James, were unearthed
Relics
- religious object connected to a saint or other holy person, stored in a reliquary
- could take the form of body parts (fingers), clothes, fragments of a cross
- often obtained from crusades
- huge sacred and economic value and every church wanted a relic to increase its popularity - black market boomed with fake and stolen goods
Apsidioles
- where relics would be placed
Romanesque
- revival of stone structures, interior was often very dark
Last Judgment Tympanum, Gislebertus
- one of the monumental scriptures to be made in the Medieval period
- Jesus Christ is the central figure
- left are the damned and the right are going to heaven
- people enter through the left and leave through the right
Gislebertus (last judgment detail)
May this terror terrify those whom earthly error binds, for the horror of these images here in this manner truly depicts what will be
Bayeux Tapestry
- actually not a tapestry, it is awork of embroidery
- designed by a man and executed by a woman
- conquest of England
- 75 scenes, with Latin inscriptions
Bishop Odo rallying William the Conqueror's troops at the Battle of Hastings
- likely commissioned by Bishop Odo, half-brother of William
- Norman point of view as they are depicted favorably
- not just a depiction of royalty, but of regular people