breathing and gas exchange
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Respiratory surface
The surface in organisms where gas exchange occurs, such as the lungs in mammals or gills in fish.
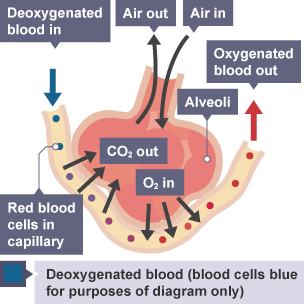
Alveoli
Small air sacs at the end of the lungs where gas exchange takes place, surrounded by capillaries.
Ventilation
The process of inhaling and exhaling air to facilitate gas exchange in the lungs.
Goblet cells
Cells in the respiratory system that produce mucus to trap dust, debris, and pathogens.
Epithelial cells
Cells that move mucus in the respiratory system, aiding in the removal of trapped particles.
Pleural cavity
The space between the lungs and ribs filled with fluid to reduce friction during breathing.
Respiration
The breakdown of glucose to produce energy in living organisms.
Emphysema
A condition where the alveoli become damaged, usually due to repeated infections
Respiratory Surface must have
large surface area, thin permeable membrane, moist exchange surface
Large surface area
the larger the SA the quicker the diffusion
Thin permeable surface
the shorter the distances, the better
moist exchange surface
gases usually dissolve in water in order to pass through a membrane
Inspiration 1
intercostal muscles contract, raising the ribcage upwards and outwards
Inspiration 2
The diaphragm contracts and pushes down on the organs in the abdomen
Inspiration 3
both these movement increase the internal volume and decrease the internal pressure
inspiration 4
air enters and inflates the lungs
expiration 1
intercostal muscles relax, lowering the ribcage
expiration 2
the diaphragm relaxes and is pushed upwards by the organs
expiration 3
both these movements result in a decrease in internal volume and an increase in the internal pressure
expiration 4
air is forced out the lungs
Gas exchange in the alveolus
Process where oxygen enters the blood from the alveoli and carbon dioxide is removed for exhalation.