Unit 2: Digestion
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
mouth
entry of food
chemical digestion via salivary amylase
mechanical digestion via chewing
salivary glands
release enzymes eg salivary amylase
amylase = starch → glucose
oesophagus
carries food to stomach
bolus (ball of food) passes via peristalsis
wave like muscle movements that push bolus one way using circular and longitudinal muscles
liver
produces basic bile that neutralises stomach’s acidic chine
gall bladder
stores bile that neutralises stomach’s acidic chine
stomach
mechanically churns food
protein digestion occurs here
acidic chine emulsifies lipids
pepsin, protease, trypsin = proteins/polypeptides → amino acids
pancreas
releases digestive enzymes into small intestine
lipase = triglycerides → fatty acids and glycerol
duodenum
sucrase = sucrose → fructose + glucose
Small intestine
most digestion happens here
villi (small hair like structures composed of capillaries, lymph vessel, mucosa, submucosa, circular muscles, longitudinal muscles, serosa)
some enzymes released
maltase = maltese → glucose
lactase = lactose → glucose + galactose
lipase = triglycerides → fatty acids + glycerol
protease, trypsin, pepsin → proteins, polypeptides, → amino acids
phospholipase = phospholipids → fatty acids + phosphate + glycerol
dipeptase = dipeptides → amino acids
protase = peptide → amino acids
DNase, RNase = DNA, RNA → nucleotides
Large intestine
reabsorption of water
vitamins/minerals absorbed
processes undigested food, faeces
extra carb digestion with bacteria
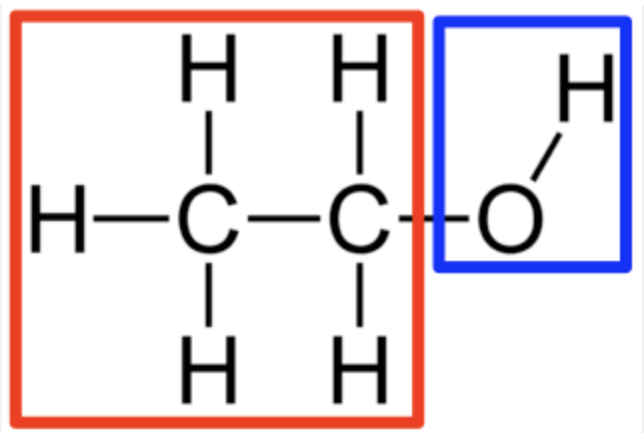
Hydroxyl group
-OH
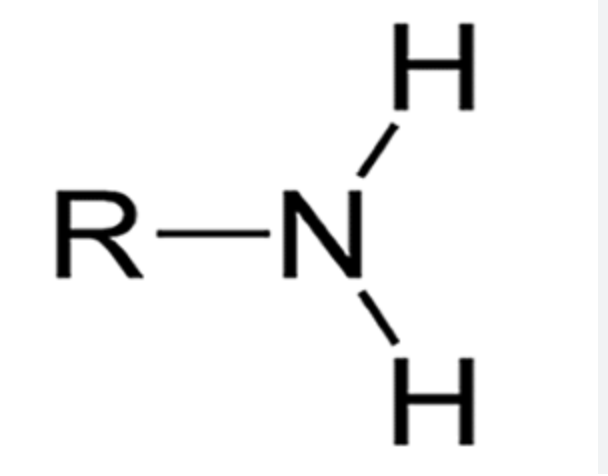
Amine group
-NH2
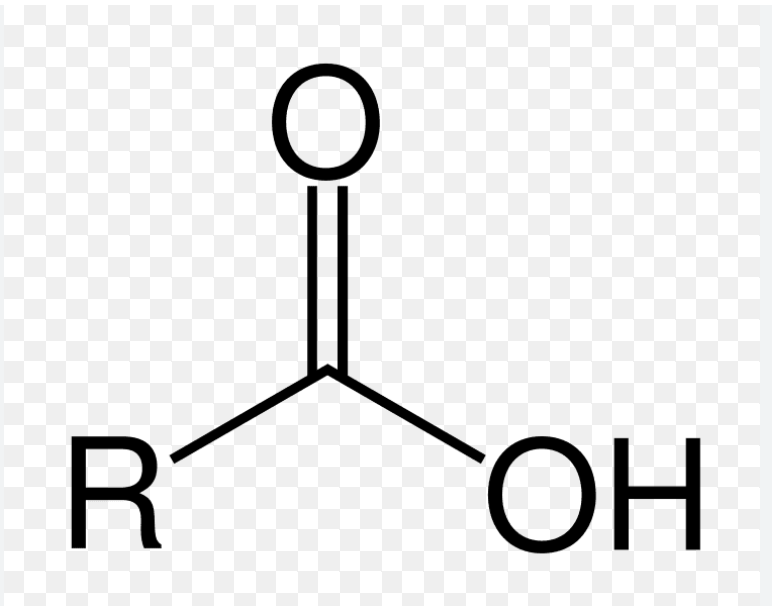
Carboxyl group
-COOH
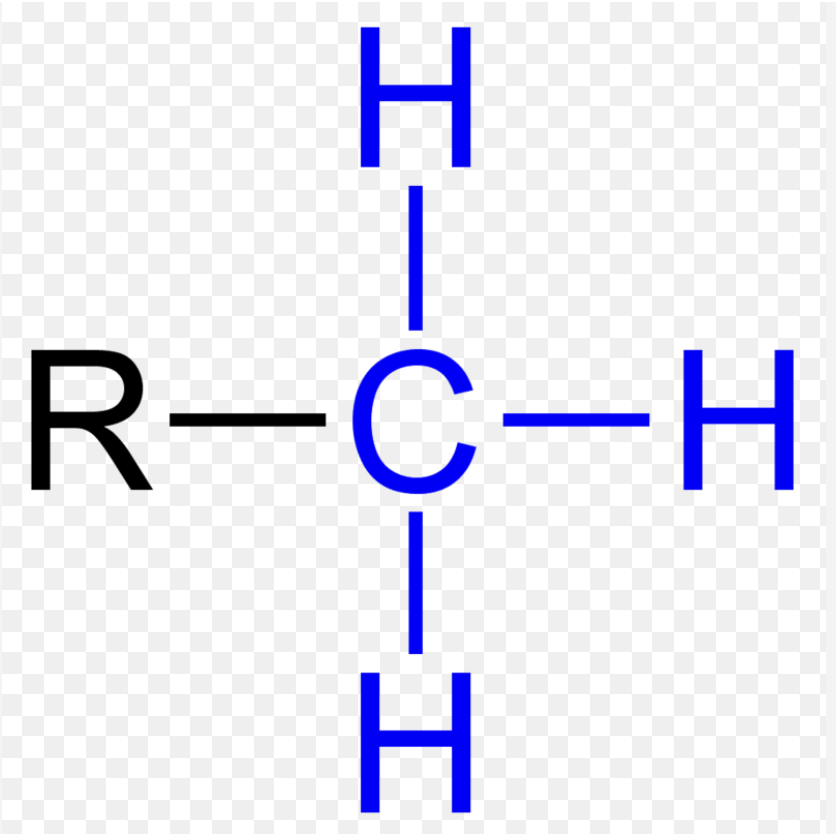
Methyl group
-CH3
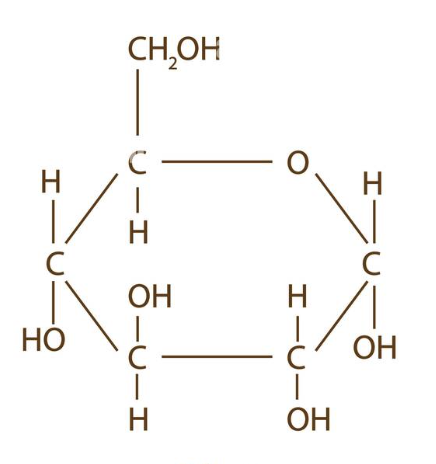
alpha - d - glucose
C6 H12 O6 (OH down)
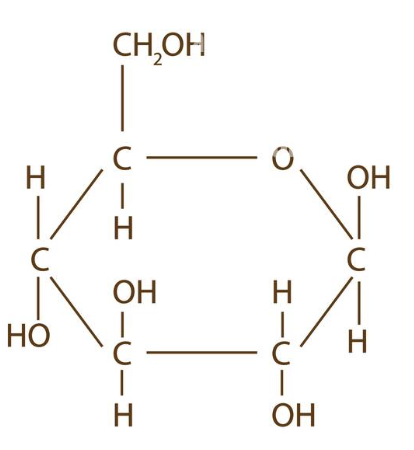
beta - d - glucose
C6 H12 O6 (OH up)
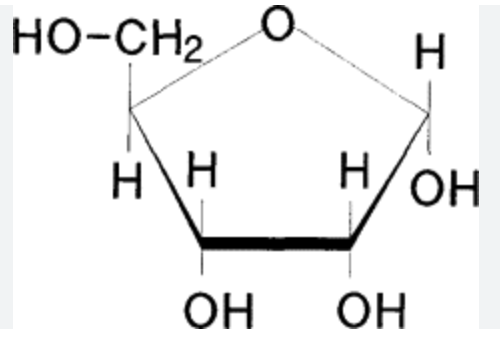
Ribose
C5 H10 O5
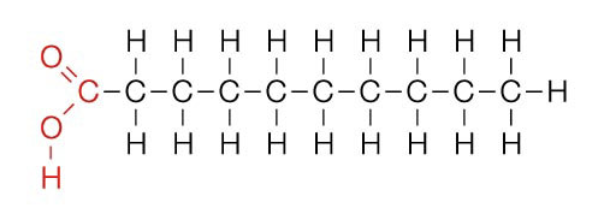
Saturated Fatty Acid
carboxyl + CH’s + methyl
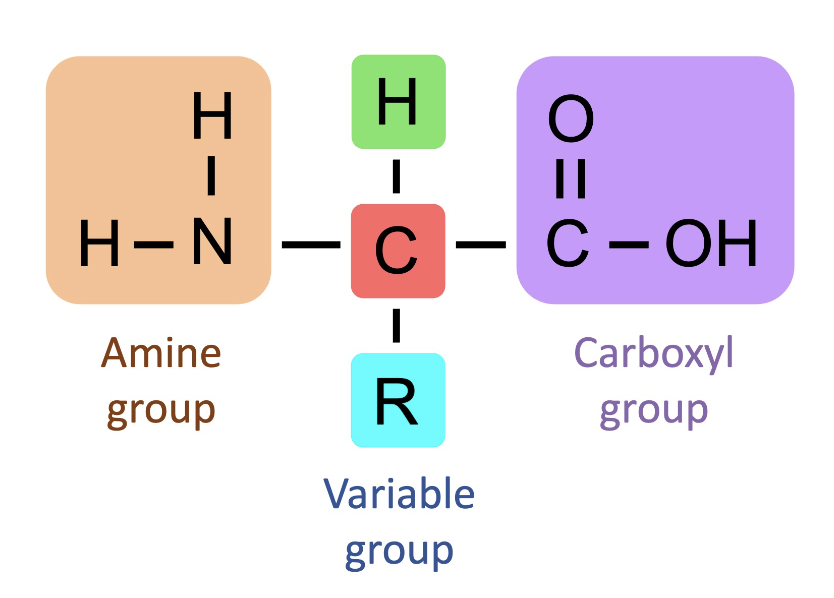
Generalised Amino Acid
carboxyl + H/C + R variable side chain + amine
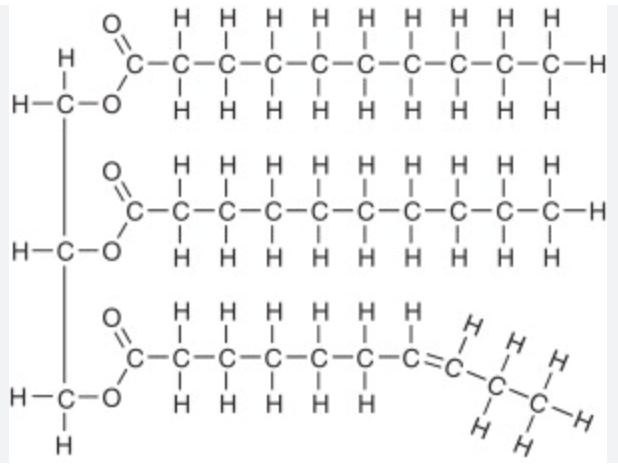
Triglycerides
glycerol + fatty acid
Fibrous proteins
Proteins made of amino acids, structural
collagen - structure against tears in teeth, bones, nails, hair, skin
rhodopsin - pigment rods in eyes
spider silk - strong sticky fluid
Globular proteins
Proteins made of amino acids, functional
rubisco - converts inorganic carbon to organic carbon
immunoglobin - antibodies
insulin - signal to absorb glucose out of the blood if blood sugar too high