Equine Intraocular Diseases (not done)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is iris hyoplasia?
Dark are of iris bulging forward usually dorsal due to a thinned iris stroma
What do need to rule out with iris hypoplasia?
Melanoma
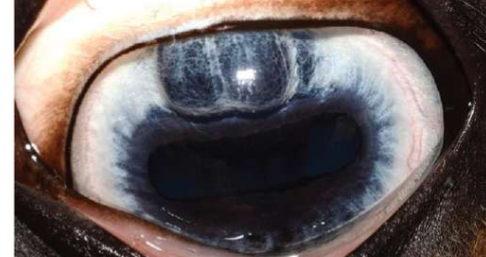
Iris hypoplasia
What are corpora nigra cysts?
May enlarge over time and should transilluminate
Rule out neoplasia
How do you treat corpora nigra cysts?
Benign neglect
If vision compromised refer for diode laser
Corpora nigra cyst
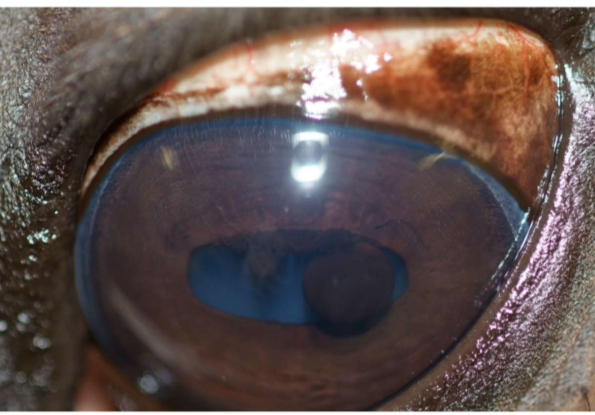
What is the most common iris neoplasia?
Melanoma (esp in gray horses)
Ho do you identify iris neoplasia?
Dark mass in anterior chamber
Need to use US to differentiate from cyst
How do you treat iris neoplasia?
Enucleation once secondary glaucoma develops

Iris neoplasia
What is the most common cause of equine blindness?
Equine recurrent uveitis
What are causes of uveitis?
Trauma: blunt of penetrating injury
Infectious: bacteria, viral, parasites
Misc: endotoxemia, septicemia, tooth root abscess, neoplasia, reflex uveitis
What are C/S of uveitis?
Blepharospasm, epiphora, conjunctival hyperemia, aqueous flare, miosis, a ton of other lol
How do you diagnose acute uveitis?
Rule out primary corneal disease with a fluorescein stain
What are other names of equine recurrent uveitis (ERU)?
Moon blindness or periodic ophthalmia
What is the prevalence of ERU (equine recurrent uveitis)?
8-25% of all horses
What do you need to tell owners if their horse gets ERU?
Not every case of uveitis leads to ERU but need to tell owner risk of recurrence or opposite eye risk
DO NOT LET THEM TREAT WITHOUT A VET EXAM
When can you classify ERU?
2 or more observed episodes of uveitis
T/F ERU can be uni or bilateral?
True
What is the pathogenesis of ERU?
Immune mediated, probably exposed to leptospirosis and the antibodies then recognize self-antigens and will attack the eye
Chronic uveitis (ERU) leads to brown pigment
What are end stage ERU lesions?
Blindness, phthisis bulbi, dyscoria/posterior synechia, cataract, lens luxation, retinal detachment
What causes glaucoma in horses?
Very uncommon, usually secondary to uveitis
How do you diagnose glaucoma?
Elevated IOP
PLR deficits or fixed and dilated pupil
Buphthalmos
Corneal changes (Haabs stria)
Optic nerve changes
How do you treat glaucoma?
Topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Topical beta-blockers
Uveitis treatment
Sx: laser treatment of ciliary body, end stage options for blind or painful eyes are enucleation or chemical ablation
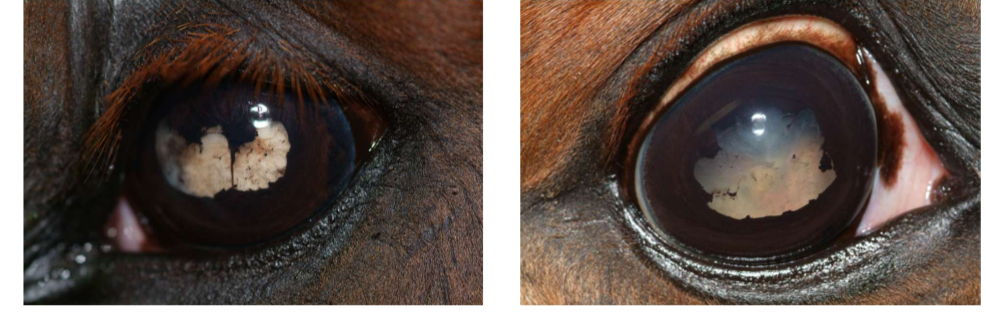
What breeds are predisposed to cataracts?
Belgian, thoroughbred, QH
Why do horses usually get cataracts?
Usually secondary to uveitis, can also be secondary to trauma, due to old age, or inherited
When should you do surgery on cataracts?
Young foals are preferred
NOT recommended for cataracts secondary to ERU