COGSCI 1 Lecture 15 - Cognitive Development
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Piagettian Stages of Cognitive Development
Theory of how humans acquire, construct, and use knowledge
Piaget observed that children of different ages made different kinds of mistakes when solving problems → belief that children think and speak differently than adults
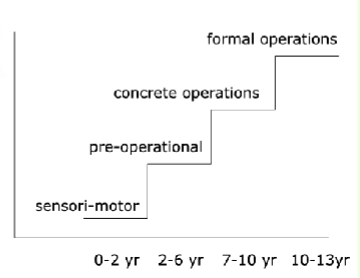
Sensorimotor Stage
(Birth - 2 years)
Children act on objects (e.g., grasping, sucking, stepping), coordinate sensory experiences (e.g., vision and hearing) from these interactions, and form schemas (internal mental representations) about objects
They learn to think about aspects of the environment outside of the reach of their senses
Object Permanence
Understanding that objects continue to exist even though they cannot see it
Pre-Operational Stage
(Ages 2 - 7)
Child develops ability to symbolize objects and events that are absent
Engages in pretend play
However, the child still has trouble seeing things from different points of view: thinking is egocentric
Understanding at this stage is based on appearances rather than principles
Concrete Operations Stage
(7-11 years)
Child develops higher order schemas called operations — understands the reversible consequences of actions
Formal Operations Stage
(Over age 11)
Child develops ability to engage in hypothetical and deductive reasoning and to think about abstract concepts
Strengths of Piaget’s Theory
Provides good overview of children’s thinking at different points
Fascinating Observations
Weaknesses of Piaget’s Theory
depicts children’s thinking as being more consistent than it actually is
Later research had found that children are more cognitively competent than Piaget recognized
Understates contribution of the social world
Does not explain underlying mechanisms
Folk Physics
Innate understanding of basic principles governing the behavior of physical objects
Infant Folk Physics
more weight on spatiotemporal continuity than on featural continuity
Adult Folk Physics
Featural consistency is more important
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)
Designed to deal with time series and sequence data
Can be used to model object permanence
Applications of RNNs
Speech Recognition
Speech Synthesis
Machine Translation
Music Composition
Time Series Prediction
Robot Control
Mind Reading
The ability to understand other people’s mental state
Allows us to make sense of other people
Allows us to coordinate our behavior with theirs
Pretend Play
Typically emerges around 14 months, is considered a major milestone in cognitive and social development
Metarepresenation
Use of a representation to represent another representation, rather than referring directly to the world
False Belief (Displacement) Task
One of the best-known tests for mindreading ability
Tests whether children are able to abstract away from their own knowledge to understand that someone else can have different (and mistaken) beliefs about the world
Container Test
Child is shown a familiar kind of container that contains an unexpected object
Asked to predict what other person will think is inside
Theory of Mind Mechanism (TOMM)
Ability to identify and reason about other people’s complex mental states, such as beliefs, desires, hopes and fears;
understanding other people