1. The Living World
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What is Biodiversity?
It is the degree of variability among living organisms.
What does Biodiversity encompass?
___
___ diversity
___ diversity
___ diversity
[NOT IN NCERT]
It encompasses all ecological complexes.
Ecosystem
Community diversity
Species diversity
Genetic diversity
What is Systematics?
It is the study of biodiversity. It attempts to classify the diversity of organisms on the basis of identification, classification, and nomenclature.
Systematics takes into account evolutionary relationships between organisms.
What is the process of Identification under Systematics?
It aims to identify the correct name and position of an organism in the already established classification system. It is done with the help of keys.
What is the process of Classification under Systematics?
It involves the scientific grouping of identified organisms into convenient categories or taxa based on some easily observable and fundamental characters.
It involves hierarchy of steps in which each step represents a rank or category.
It is an arrangement of living organisms according to their common characteristics and placing the group within taxonomic hierarchy.
What is the hierarchial arrangement of the various categories under Classification?
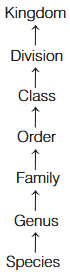
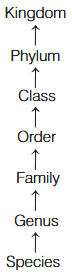
Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
What is the mnemonic for remembering the hierarchial arrangement of various categories under Classification?
Do Koalas Prefer Cake Or Frosting, Generally Speaking?
(D is for Domain btw)
or you could do “Dear Kevin, Please Come Over For Gay S*x”
What is Nomenclature, under Systematics?
After classification, organisms are subjected to a format of two-word naming system called binomial nomenclature. It consists of two components, i.e., generic name and specific epithet.
In Mangifera indica, what does Mangifera and indica mean?
Mangifera is the generic name (genus) and indica is the specific epithet (particular species) of mango.
Who was the Binomial Nomenclature system proposed by?
This system was proposed by C Linnaeus (a Swedish Botanist) in 1753 in his book Species Plantarum.
What is the Polynomial system of Nomenclature?
It is a type of naming system containing two or more words.
What is the Trinomial system of Nomenclature? What do the words represent?
It is a component of polynomial system and contains three words. Third word represents the sub-species and first two-words remain the same as in binomial system.
What are the Codes of Binomial Nomenclature?
There are five codes of nomenclature which help to avoid errors, duplication and ambiguity in scientific names.
These codes are as follows:
ICBN: International Code of Botanical Nomenclature
ICZN: International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
ICVN: International Code of Viral Nomenclature
ICNB: International Code for Nomenclature of Bacteria
ICNCP: International Code for Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants
What is the full form of ICBN?
International Code of Botanical Nomenclature
What is the full form of ICZN?
International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
What is the full form of ICVN?
International Code of Viral Nomenclature
What is the full form of ICNB?
International Code for Nomenclature of Bacteria
What is the full form of ICNCP?
International Code for Nomenclature of Cultivated Plants
What is Taxonomy?
It deals with the principles and procedures of:
characterisation - observing the features of an organism
identification - relating the observed features to a class of organisms that exist
classification - classifying the organism like it’s phylus genus order etc
nomenclature - naming that thang
It reflects the natural and phylogenetic relationships among organisms. It also provides the details of external and internal structures, cellular structure and ecological information of organisms.
What is Classical Taxonomy?
It is also known as old taxonomy. In classical taxonomy, species is the basic unit and it can be described on the basis of one or few preserved specimens. Organisms are classified on the basis of some limited features.
What is Modern Taxonomy/New Systematics?
According to it, species are dynamic and ever-changing entity. Studies of organisms are done on a huge number of variations. It includes cytotaxonomy, numerical taxonomy, chemotaxonomy, etc.
Who was the concept of Modern Taxonomy given by?
Julian Huxley (1940).
What are the four universal rules of Nomenclature?
Biological names are generally in Latin and written in italics. They are Latinised or derived from Latin irrespective of their origin.
The first word in a biological name represents the genus while the second component denotes the specific epithet.
Both the words in a biological name, when handwritten, are separately underlined, or printed in italics to indicate their Latin origin.
The first word denoting the genus starts with a capital letter while the specific epithet starts with a small letter.
What is the scientific term for categories?
Taxa.
What are obligate categories?
The taxonomic categories, which are always used in hierarchical classification of organisms.
What are intermediate categories?
The sub-categories like sub-species, sub-class, sub-family, etc., which facilitate more sound and scientific placement of various taxa.
What is Taxonomic Hierarchy?
Arrangement of taxonomic categories in a descending order during the classification of an organism.
Why is Taxonomic Hierarchy also known as Linnaean Hierarchy?
It was first introduced by Linnaeus (1751).
What are the Taxonomic categories showing hierarchical arrangement in ascending order for Plants?
What are the Taxonomic categories showing hierarchical arrangement in ascending order for Animals?
What is a taxon?
Taxon refers to a group of similar, genetically related individuals having certain characters distinct from those of other groups.
When was the term “Taxon” introduced and by whom?
The term ‘Taxon’ was first introduced by ICBN during 1956.
What is a Kingdom?
It is the highest category in taxonomy. A kingdom includes all the organisms which share a set of distinguished characters.
What is a Phylum or Division?
It is a taxonomic category higher than class and lower in rank to kingdom. The term ‘Phylum’ is used for animals, while ‘Division’ is commonly employed for plants. It consists of more than one classes having some similar correlated characters.
What is a Class?
It is a major category, which includes related orders.
What is an Order?
It is a group of one or more related families that possess some similar correlated characters, which are lesser in number as compared to a family or genera.
What is a Family?
It is a group of related genera with less number of similarities as compared to genus and species.
What is a Genus?
It comprises a group of related species, which has more characters common in comparison to species of other genera. In other words, genera are the aggregates of closely related species.
What is a Species?
Taxonomic studies consider a group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities as a species (John Ray). It is the lowest or basic taxonomic category, which consists of one or more individuals of a population.
Give 6 examples of Taxonomical aids.
Herbarium
Museums
Keys
Manuals and Catalogues
Monographs
Botanical and Zoological parks
What are Taxonomical Aids?
They include techniques, procedures and stored information that are useful in identification and classification of organisms.
What is a Herbarium?
Storehouse of collected plant specimens that are dried, pressed and preserved on sheets.
What is a Museum?
Place for the collection of preserved plants and animal specimens.
What is a Key?
Used for identification of plants and animals based on their similarities and dissimilarities.
What are Manuals and Catalogues?
Provide information for identification of names of species found in an area.
What are Monographs?
Contain information on any one taxon.
What are Botanical and Zoological parks?
Contain the living collection of plants and animals in the conditions similar to their natural habitat.
What is the importance of Taxonomical Aids?


Do you remember this?
Yes.
What is the scientific name for Lion?
Panthera leo.
What is the scientific name for potato?
Solanum tuberosum.
What is the scientific name for humans?
Homo sapiens.
Mangifera indica is the scientific name of ___.
Mango
Solanum tuberosum is the scientific name of ___.
Potato
Panthera leo is the scientific name of ___.
Lion
Homo sapiens is the scientific name of ___.
Human
What is the scientific name of leopard?
Panthera pardus
What is the scientific name of tiger?
Panthera tigris
Panthera pardus is the scientific name of ___.
leopard
Panthera tigris is the scientific name of ___.
Tiger
Solanum, Petunia and Datura are part of which family?
Solanaceae
Panthera and Felis are part of which family?
Felidae
What is the scientific name of the house fly?
Musca domestica
Musca domestica is the scientific name of what?
housefly
Triticum aestivum is the scientific name of what?
wheat
What is the scientific name of wheat?
Triticum aestivum
What is the family that humans belong to?
Hominidae
What is the family that house flies belong to?
MUSKIDI
(Muscidae)
What is the family that mangoes belong to?
Anacardiaceae
What is the family that wheat belongs to?
Poaceae
What is the order that humans belong to?
Primata
What is the order that house flies belong to?
Diptera
What is the order that mangoes belong to?
Sapindales
What is the order that wheat belongs to?
Poales
What is the class that humans belong to?
Mammalia
What is the class that house flies belong to?
Insecta
What is the class that mangoes belong to?
Dicotyledonae
What is the class that wheat belongs to?
Monocotyledonae
What is the Phylum that humans belong to?
Chordata
What is the Phylum that house flies belong to?
Arthopoda
What is the Phylum that mangoes belong to?
Angiospermae
What is the Phylum that wheat belongs to?
Angiospermae
Who was the Darwin of the 20th century?
Ernst Mayr
Who earned the triple crown of biology?
Ernst Mayr
Who pioneered the biological concept of species?
Ernst Mayr
What is metabolism?
It is all the reactions that occur within a cell. Combination of catabolism and anabolism.
What were the earliest classification system based on?
uses of various organisms
What are monotypic genera?
genera which only have 1 species within
What are polytypic genera?
genera which have multiple species within