Physics: Topic 5 - forces
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What is a vector quantity?
Had a magnitude and a direction
E.g. forces, velocity, acceleration
What is a scaler quantity?
Has a magnitude (size) but no direction
E.g. energy, speed, mass, temp
What is a force?
A push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object (particles, humans, earth etc)
How do forces affect motion?
change speed
Change direction
Change shape
Contact forces
normal reaction force
Tension
Air resistance
Friction
Non-contact forces
electrostatic
Magnetic
Gravitational
What is normal contact force?
Acts on any object while in contact with a surface
What is mass?
amount of matter an object has
Stays the same
Kg
What is weight?
force or object due to gravity
Changes based on what gravitational field it’s in
Newtons
What is gravity?
A force caused by a larger object, causes/changes weight of a smaller object in its field
Weight equation?
weight = mass x gravitational field strength (depends on distance between objects)
N= kg x N/kg
What is Newton’s first law?
An object at rest will remain at rest, or a moving object will continue moving, unless there is a resultant force acting on the object
What is a resultant force?
Affect of all the forces acting on us
At least 2 forces acting on you at all time
weight + normal reaction force
When are forces balanced ?
the forces are opposite each other
The resultant force acting= 0N
When are forces unbalance?
not equals to one another and/or not opposite
If resultant force doesn’t equal 0N, we have a change in motion
When does an object accelerate?
If the resultant force is acting with motion
When does an object decelerate?
When resultant force is acting against motion
In what direction does the resultant force act?
Always acts in the direction of the bigger force
What does equilibrium mean?
When all forces are balanced, object not:
accelerating
Changing direction
Going up or down
Resolving + resultant forces in 2d?
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Elastic deformation?
When we stretch an object, remove the force, and it returns to its original shape (happens up to the objects elastic limit)
Inelastic (permanent) deformation?
Past the elastic limit, no longer returns to original shape after the forces are removed from the stretched shape
Hooke’s Law?
The extension of a spring (x) is directly proportional to the force applied to it (f)
Only applies up to elastic limit
Hookes law equation
Force = spring constant x extension
F = k x x
Hooke’s law graph
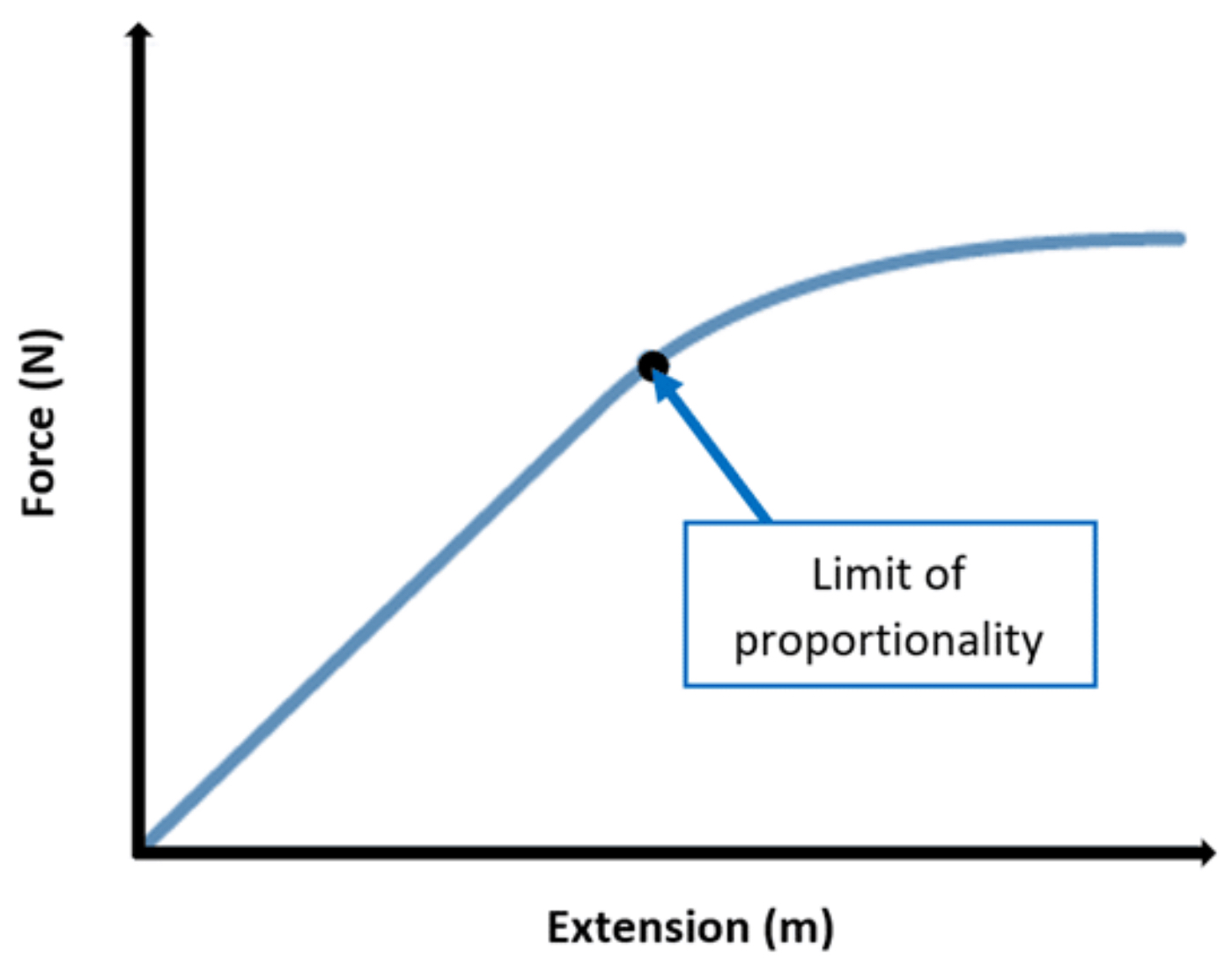
Hooke’s law practical?
measure length of spring with meter ruler
Add 100g to end of spring
Measure new length
Repeat adding 100g until 700g
Repeat entire experiment 2x more
Calculate average extension and force (mass/ 1000)
Plot graph
Energy in springs?
Work is done when we extend or compress an object
Elastic potential energy equation
Epe: 0.5 x spring constant x extension (squared)
Spring constant : 2 x epe / extension (squared)
Extension: (square root) 2xepe / spring constant
What is a moment?
A turning motion/force on an object
Moment equation
Moment (N/M) = force (N) x perpendicular distance from pivot (m)
Principle of Moments
If an object is balanced the total clockwise moment about a pivot is equal to the total anti-clockwise moment about a pivot
What does a lever consist of?
pivot
Effort
Load
What is a lever?
A force multiplier
What are gears?
Toothed wheels used in machines to transfer the Turing affects of forces
What do gears do?
Transfer rotations and increase moments
What is the relationship between the size of gears and the moment?
the smaller the gear the smaller the moment as it has a smaller radius
Pressure in fluids?
fluids are liquids and gases
pressure increases with depth
Larger force is exerted over the water (weight)
Pressure (due to liquid) : depth x density x gravitational field strength
Pa: m x kg/m3 x N/kg
Gas pressure?
The force per unit area exerted by moving gas particles
What is the atmospheric pressure?
101,000 Pascals / 101 Kap
How to increasegas pressure
increase temp
Increase concentration
What is atmospheric pressure?
The pressure that acts on us because of the atmosphere above us
What is displacement?
The total distance moved from the starting point, vector quantity
Typical speed to know?
walking = 1.5 m/s
Running. 3 m/s
cycyking = 6 m/s
What is instantaneous speed.
The speed of a particular instant can change
What is velocity?
The speed of an object in a particular direction (vectors)
Velocity equation?
Displacement / time
Average speed and average velocity equation?
average speed = total distance/ total time
Average velocity = total displacement/ total time
Instantaneous velocity in a circular path?
constantly changing as the direction of movement is changing
What does the gradient show on a displacement time graph ?
velocity
What does a curved line of a displacement graph represent?
changing velocity
What is acceleration?
the acceleration of an object is the rate of change of velocity
What effects acceleration ?
the speed (increasing or decreasing)
The direction
What type of quntaity is acceleration ?
vector
Acceleration equation ?
Accelortaion = final velocity- initial velocity/ time
Unit for acceleration?
M/s2
What does the gradient represent on a velocity time graph?
the instantaneous acceleration
How do you find the distance travelled on a velocity time graph?
the area under the graph
What is Newton’s second law?
the accelortaion of a body is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on inversely proportional to the mass of the body
What is inertia?
the tendency of an object to resist acceleration
Inertial mass is the same as the mass
Why does drag increase on falling objects?
object is travelling faster so collides with more air per second
Why is weight constant for a falling object?
because the mass and gravitational field strength don’t change
Relationship between resultant force of a falling object and its speed?
when one increases the other decreases
If no resultant form then the object stops accelerating
What is thinking distance ?
the distance travelled during during the reaction time
During reaction time the car is travelling at a constant speed
Thinking distance = speed x reaction time
Directly proportional to the speed of the car and to the reaction time of the driver
What affects thinking distance ?
stimulants (drug alcohol)
Using device
Weather (poor visibility)
Age and tiredness
Speed
What is breaking distance ?
distance traveled under breaking force
Depends on size of develoration
Greater force means shorter breaking distance e
Greater mass means larger breaking distance
Doubling the speed increase the breaking distance by a factor of 4
What effects breaking distance?
speed
Mass
Road conditions (ice)
Tire grip and brake conditions
What does the momentum of an object depend on?
proportional to its mass
Proportional to its velocity
Units for momentum?
Kgm/s
What type of quantity is momentum?
vector quantity; has magnitude and direction
Principal of conservation of momentum?
the total momentum before a collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision